Effect of target position on phase matching in high-order harmonic generation
-
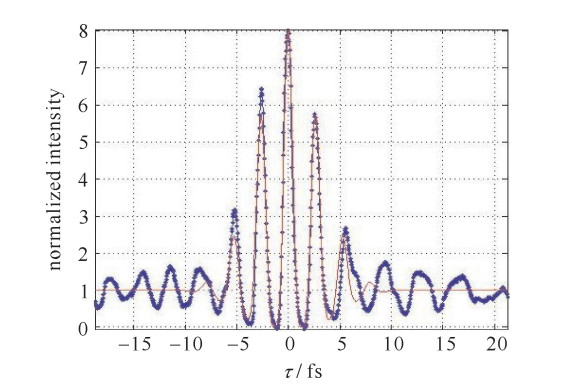
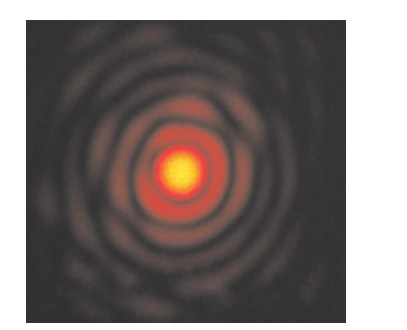
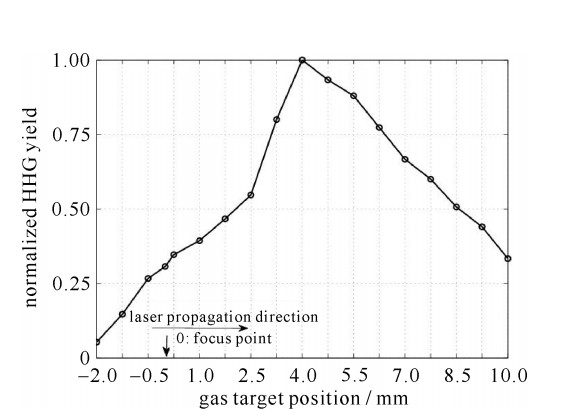
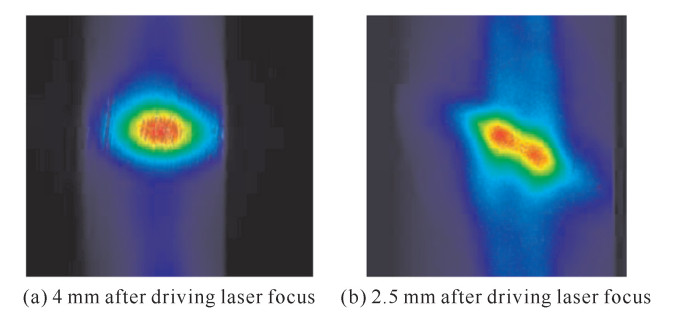
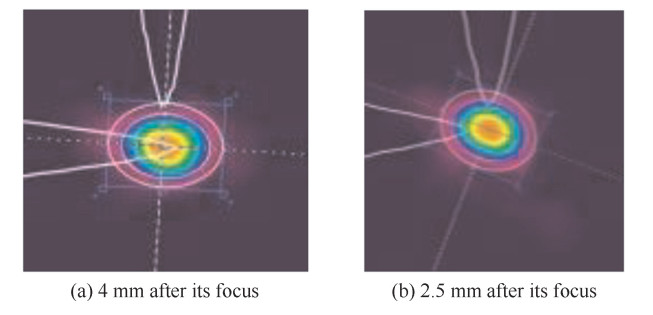
摘要: 为提高强激光场与惰性气体靶作用产生的孤立阿秒激光脉冲的能量,给出了一种实现高次谐波过程中最佳谐波相位匹配的定量实验方法。研究了气体靶源与高斯型驱动激光场聚焦点相对空间位置对谐波相位匹配及谐波产率的影响,得出了其最佳相位匹配位置始终位于驱动激光场聚焦点后3~5 mm,而在聚焦点之前的位置区域,严重的高次谐波相位失配导致谐波产率非常低。同时,在最佳相位匹配条件下,高次谐波场与驱动场具有相类似的空间强度分布特性,该结果印证了目前通常采用的高次谐波场为高斯光束的假设。Abstract: This paper presents an experimental method to realize the best high-order harmonic generation(HHG) phase matching in the interaction of strong optical field and gas target. By studying the effects of the relative location between gas target source and Gaussian-type driving field focus on the harmonic phase matching, conclusions are obtained that the optimum position of gas target for phase matching is always 3-5 mm behind the focal point of the driving field, with much lower HHG yield before the focus caused by serious harmonic phase mismatch. At the same time, in the optimum relative position, the driving field and the high-order harmonic field have similar spatial distribution characteristics, providing the experimental basis for the commonly used assumptions of Gaussian beam for high-order harmonic field.
-
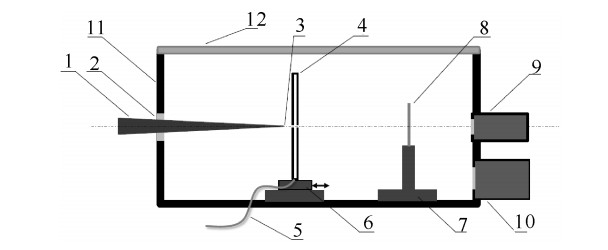
图 1 高次谐波实验真空腔示意图
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the HHG chamber
1-CEP stabilized few-cycle femtosecond laser centered at around 780 nm, 2-antireflective type quartz window, 3-focus of femtosecond laser pulse, 4- drilled hollow-core nickel tube, 5- inert gas pipeline, 6- 3D high precision stage, 7- filter holder, 8- metal film filter, 9- X-ray CCD detector, 10- turbo pump, 11-vacuum chamber, 12- acrylic chamber cover
-
[1] 周洪军, 钟鹏飞, 郑津津, 等. 不同厚度Al滤片对17~33 nm高次谐波抑制的定量研究[J]. 光学 精密工程, 2007, 15(7): 1016-1020. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXJM200707003.htmZhou Hongjun, Zhong Pengfei, Zheng Jinjin, et al. Quantitative research on higher order harmonic suppression in 17~33 nm with different thickness Al filters. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2007, 15(7): 1016-1020 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXJM200707003.htm [2] 卢发铭, 张盛, 夏元钦, 等. 双色飞秒强激光作用下的CO2分子高次谐波[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2014, 43(1): 77-80. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HWYJ201401013.htmLu Faming, Zhang Sheng, Xia Yuanqin, et al. High harmonic generation in CO2 using two-color femtosecond laser. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2014, 43(1): 77-80 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HWYJ201401013.htm [3] 秦沛, 任玉, 刘丽炜, 等. 金属纳米颗粒等离激元共振增强非线性介质谐波的发展现状[J]. 中国光学, 2016, 9(2): 213-225. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGA201602005.htmQin Pei, Ren Yu, Liu Liwei, et al. Development of plasmon-resonance of metal nanoparticles enhanced harmonic generation in nonlinear medium. Chinese Optics, 2016, 9(2): 213-225 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGA201602005.htm [4] 龚梓博, 陆星, 施可彬, 等. 光学频率梳非线性传输及其在相位噪声探测中的应用[J]. 中国光学, 2015, 8(1): 39-44 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGA201501005.htmGong Zibo, Lu Xing, Shi Kebin, et al. Nonlinear propagation of optical frequency comb and its application in phase noise detection. Chinese Optics, 2015, 8(1): 39-44 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGA201501005.htm [5] Krausz F, Ivanov M. Attosecond physics[J]. Review of Modern Physics, 2009, 81(1): 163-234. doi: 10.1103/RevModPhys.81.163 [6] Calegari F, Ayuso D, Trabattoni A, et al. Ultrafast electron dynamics in phenylalanine initiated by attosecond pulses[J]. Science, 2014, 346(6207): 336-339. doi: 10.1126/science.1254061 [7] Despre V, Marciniak A, Loriot V, et al. Attosecond hole migration in Benzene molecules surviving nuclear motion[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2015, 6: 426-431. doi: 10.1021/jz502493j [8] 李儒新, 程亚, 冷雨欣, 等. 超快光学与超强激光技术前沿研究[J]. 中国科学: 信息科学, 2016, 46(9): 1236-1254. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-PZKX201609003.htmLi Ruxin, Cheng Ya, Leng Yuxin, et al. Frontiers in ultrafast optics and ultra-intense laser technology. Scientia Sinica Informationis, 2016, 46(9): 1236-1254 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-PZKX201609003.htm [9] Goulielmakis E, Schultze M, Hofstetter M, et al. Single-cycle nonlinear optics[J]. Science, 2008, 320(5883): 1614-1617. doi: 10.1126/science.1157846 [10] Ferrari F, Calegari F, Lucchini M, et al. High-energy isolated attosecond pulses generated by above-saturation few-cycle fields[J]. Nature Photon, 2010, 4(12): 875-879 doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2010.250 [11] Sansone G, Benedetti E, Calegari F, et al. Isolated single-cycle attosecond pulses[J]. Science, 2006, 314 (5798): 443-446. doi: 10.1126/science.1132838 [12] Zhao K, Zhang Q, Chini M, et al. Tailoring a 67 attosecond pulse through advantageous phase-mismatch[J]. Optics Letters, 2012, 37(18): 3891-3893. doi: 10.1364/OL.37.003891 [13] Feng X, Gilbertson S, Mashiko H, et al. Generation of isolated attosecond pulses with 20 to 28 femtosecond lasers[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2009, 103: 183901. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.103.183901 [14] Vincenti H, Quere F. Attosecond lighthouses: how to use spatiotemporally coupled light fields to generate isolated attosecond pulses[J]. Physical Review Letters, 108(11): 113904. [15] Corkum P B. Plasma perspective on strong-field multiphoton ionization[J]. Physical Review Letters, 1993, 71(13): 1994-1997. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.71.1994 [16] Saleeres P, L'Huilier A, Lewenstein M. Coherence control of high-order harmonics[J]. Physical Review Letters, 1995, 74(19): 3776-3779. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.74.3776 [17] Gragossian A, Seletskiy D V, Sheik-Bahae M. Classical trajectories in polor-asymmetric laser fields: synchronous THz and XUV emission[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 34973. doi: 10.1038/srep34973 -




 下载:
下载: