Phase conjugation lasers based on stimulated Brillouin scattering with high-power and high-energy
-
摘要:
受激布里渊散射是一种三阶非线性光学过程,具有完全背向散射的相位共轭特性,利用这种特性,可以补偿高能高功率激光系统中强泵浦而引起的相位畸变,从而实现高光束质量激光输出。过去几十年开展了大量理论和实验研究以提升受激布里渊散射相位共轭镜(SBS-PCM)的作用效果,一部分研究集中在研究适合高功率激光系统应用的液体介质和介质纯化,一部分集中在SBS-PCM的结构优化(包括双池结构、结构参数优化、旋转楔板结构等)。回顾了影响SBS-PCM作用效果的主要因素,以及SBS-PCM在高功率激光系统中的应用,总结了近年来的一些应用成果,为SBS-PCM的实验研究提供了参考。
Abstract:Stimulated Brillouin scattering (SBS) is a third-order nonlinear process, which is phased conjugation reflected in the SBS phase conjugation mirror (SBS-PCM). Therefore, it is a very useful tool for the compensation of wavefront distortion induced by strongly thermally stressed active material, especially in high-power and high-energy lasers. To maximize the effectiveness of SBS-PCM, many research efforts have been poured in both theoretically and experimentally in the past decades. Several researchers have studied the liquid medium that is the best fit for SBS-PCM in high power laser systems; some have investigated the geometry (such as two-cell structure, choice of the optimum parameters, and the addition of a rotating wedge) of the system that will give the most appropriate desired characteristics; while some researched the impurities of the selected liquid. This work presents a review of the factors determining the performance of SBS-PCM, the applications of SBS-PCM in high power lasers, and recent scientific achievements in the SBS-PCM high power laser systems. This work is proposed as a reference and guiding manual for SBS-PCM-related experiments and research.
-
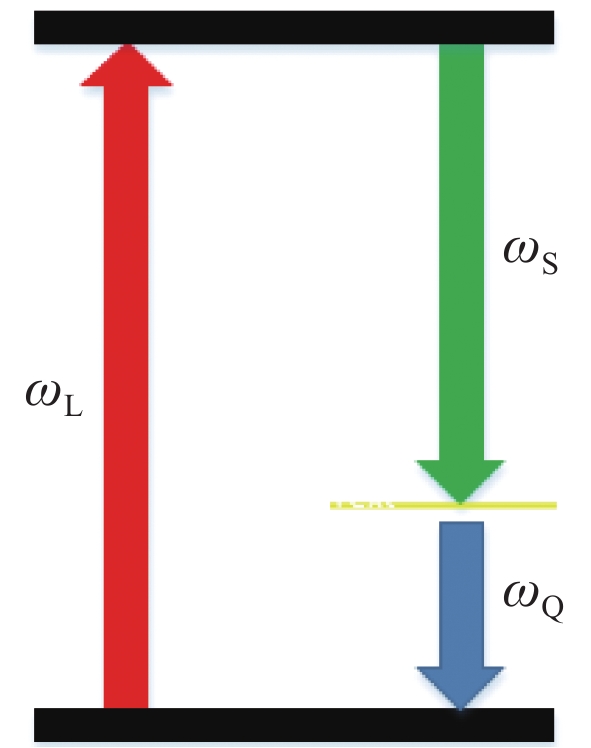
Figure 1. Nonlinear SBS energy level diagram; ωQ is the phonon frequency, ωS is the Stokes frequency, and ωL is the frequency of the incident electromagnetic wave[73]
Figure 2. Experimental set-up for measuring SBS medium properties (e.g., OBT)[48]
Figure 5. (a) Diagram of the unlocked case, (b) a concentric type produces weak density modulation and (c) backward focusing produces weak density modulation[82]
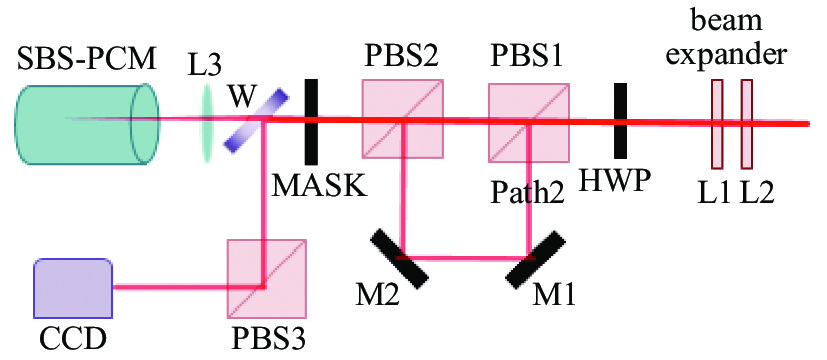
Figure 6. A sample experimental setup for a prepulse system. PBS: polarizing beam splitter; HWP: half-wave plate; L1: planoconcave lens; L2 and L3: planoconvex lens; M: mirrors; W: wedge; SBS-PCM (FC75, 30 cm long) [64]
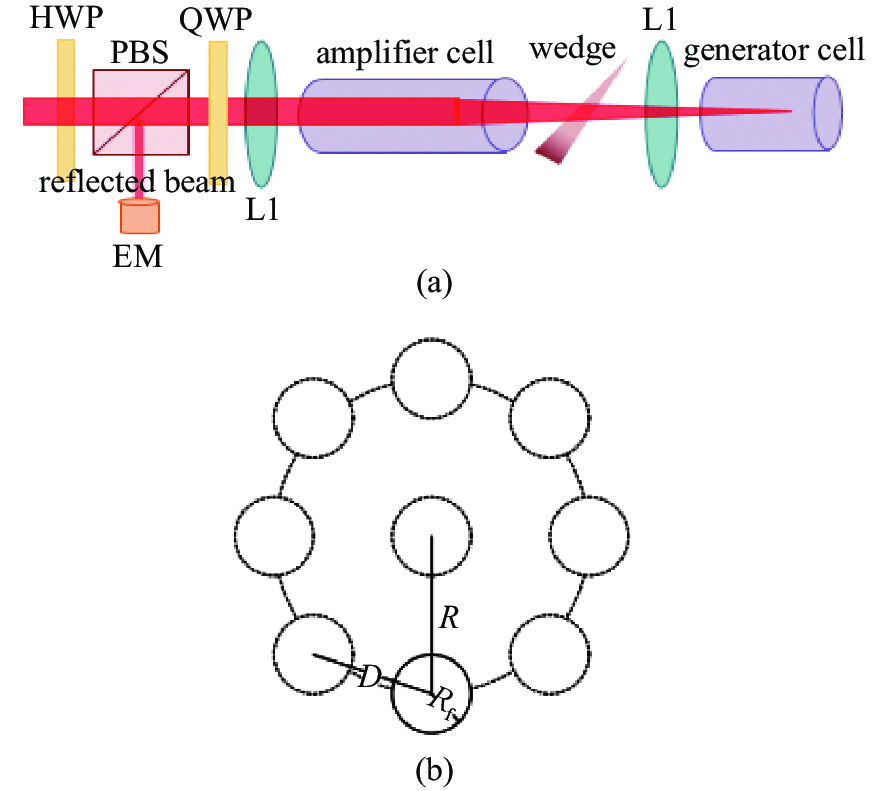
Figure 7. A typical experimental setup of a four-beam combination system using the RW-SSP. ISO: optical isolator; PZT: 45 degree mirror attached piezoelectric transducer; RW: rotating wedge device; QWP: quarter wave plate; EM: energy meter[40]
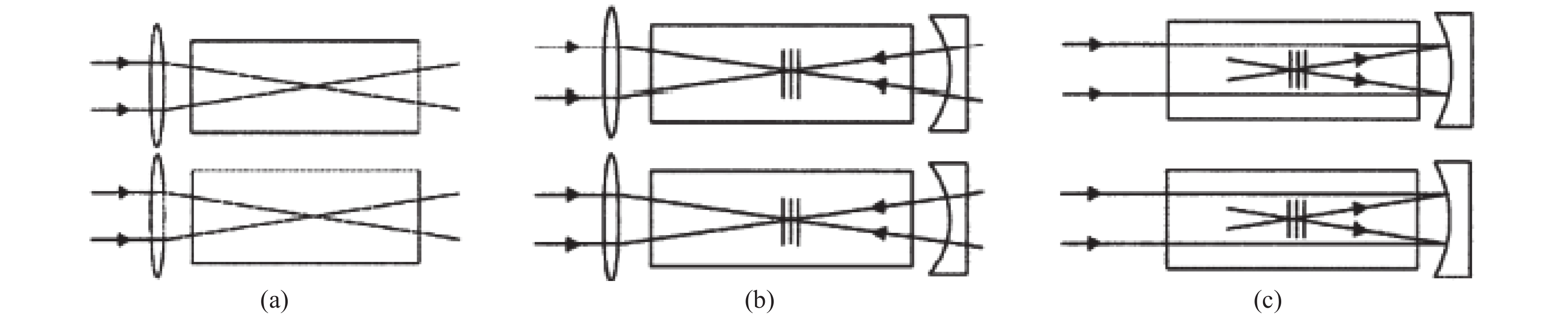
Figure 8. Experimental setup for the measurement of the leak beam patterns and the depolarization ratio for the four possible optical schemes in a double-pass Nd:YAG rod amplifier with an SBS-PCM. W: wedged window; AMP: Nd:YAG rod amplifier; FR: Faraday rotator [59]
Figure 9. Reflected energy with rotating off-centered lens and normal lens[25]
Figure 10. Closed-type SBS-PCM used to measure reflectivity at varying repetition rates. RT: quartz rotator; SF: spatial filter[26]
Figure 11. Fraction of the light pathway for testing SBS reflectivity[27]
Table 1. Some scientific achievements in SBS-PCM reflectivity
max. reflectivity (%) input energy/mJ frequency/Hz output Pulse width/ns medium year reference 98 800 200 38.8 FC-770 2017 [27] 95.2 900 170 20 FC-770 2017 [52] 94 160 200 10 FC-770 2018 [26] 93 600 200 9.3 FC-770 2020 [46] 92 10 500 14 HT-270 2019 [61] 92 120 500 10 FC-770 2018 [26] 88 220 10000 8.5 HT-70 2014 [86] 84.7 600 10 − FC-72 2010 [60] 81.2 50 1000 − HT-270 2019 [25] 78.4 300 10 − FC-72 2010 [51] 75 7.36 50 50 FC-75 2005 [63] 69 48 25000 8 FC-75 2011 [41] 60 130 1000 28 FC-75 2003 [87] 44 45 15000 − FC-75 2016 [38] -
[1] González M, Stehlé C, Audit E, et al. Astrophysical radiative shocks: from modeling to laboratory experiments[J]. Laser and Particle Beams, 2006, 24(4): 535-540. doi: 10.1017/S026303460606071X [2] Liu Jianxun, Ma Yanyun, Yang Xiaohu, et al. High-energy-density electron beam generation in ultra intense laser-plasma interaction[J]. Plasma Science and Technology, 2017, 19: 015001. doi: 10.1088/1009-0630/19/1/015001 [3] Yang Yue, Zhao Zongqing, Zheng Jianhua, et al. Production of bright high-energy X-rays based on interaction of laser and near-critical-density plasma[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2017, 29: 082003. doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201729.170138 [4] Santos J J, Bailly-Grandvaux M, Ehret M, et al. Laser-driven strong magnetostatic fields with applications to charged beam transport and magnetized high energy-density physics[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2018, 25: 056705. doi: 10.1063/1.5018735 [5] Li Hanzhen, Yu Tongpu, Hu Lixiang, et al. Ultra-bright γ-ray flashes and dense attosecond positron bunches from two counter-propagating laser pulses irradiating a micro-wire target[J]. Optics Express, 2017, 25(18): 21583-21593. doi: 10.1364/OE.25.021583 [6] Magnusson J, Gonoskov A, Marklund M. Energy partitioning and electron momentum distributions in intense laser-solid interactions[J]. The European Physical Journal D, 2017, 71: 231. doi: 10.1140/epjd/e2017-80228-1 [7] Kluge T, Rödel M, Metzkes-Ng J, et al. Observation of ultrafast solid-density plasma dynamics using femtosecond X-ray pulses from a free-electron laser[J]. Physical Review X, 2018, 8: 031068. [8] Li Yanfei, Shaisultanov R, Chen Yueyue, et al. Polarized ultrashort brilliant multi-GeV γ rays via single-shot laser-electron interaction[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2020, 124: 014801. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.124.014801 [9] Xue Kun, Dou Zhenke, Wan Feng, et al. Generation of highly-polarized high-energy brilliant γ-rays via laser-plasma interaction[J]. Matter and Radiation at Extremes, 2020, 5: 054402. doi: 10.1063/5.0007734 [10] Hoffmann D H H, Blazevic A, Ni P, et al. Present and future perspectives for high energy density physics with intense heavy ion and laser beams[J]. Laser and Particle Beams, 2005, 23(1): 47-53. [11] Hu Yanting, Zhao Jie, Zhang Hao, et al. Attosecond γ-ray vortex generation in near-critical-density plasma driven by twisted laser pulses[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2021, 118: 054101. doi: 10.1063/5.0028203 [12] Weichman K, Robinson A P L, Murakami M, et al. Strong surface magnetic field generation in relativistic short pulse laser–plasma interaction with an applied seed magnetic field[J]. New Journal of Physics, 2020, 22: 113009. doi: 10.1088/1367-2630/abc496 [13] Rosmej O N, Gyrdymov M, Günther M M, et al. High-current laser-driven beams of relativistic electrons for high energy density research[J]. Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 2020, 62: 115024. doi: 10.1088/1361-6587/abb24e [14] Domański J, Badziak J. Generation of ion beams from high-Z target irradiated by laser pulse of ultra-relativistic intensity[J]. Acta Physica Polonica A, 2020, 138(4): 586-592. doi: 10.12693/APhysPolA.138.586 [15] Liang Zhenfeng, Shen Baifei, Zhang Xiaomei, et al. High-repetition-rate few-attosecond high-quality electron beams generated from crystals driven by intense X-ray laser[J]. Matter and Radiation at Extremes, 2020, 5: 054401. doi: 10.1063/5.0004524 [16] Domański J, Badziak J. Properties of heavy ion beams produced by a PW sub-picosecond laser[J]. Journal of Instrumentation, 2020, 15: C05037. doi: 10.1088/1748-0221/15/05/C05037 [17] Frost M, Curry C B, Glenzer S H. Laser cutting apparatus for high energy density and diamond anvil cell science[J]. Journal of Instrumentation, 2020, 15: P05004. doi: 10.1088/1748-0221/15/05/P05004 [18] Kumar S, Park J, Nam S H, et al. Laser-induced plasma generated by a 532 nm pulsed laser in bulk water: unexpected line-intensity variation with water temperature and the possible underlying physics[J]. Plasma Science and Technology, 2020, 22: 074009. doi: 10.1088/2058-6272/ab812e [19] Savelyev M S, Agafonova N O, Vasilevsky P N, et al. Effects of pulsed and continuous-wave laser radiation on the fabrication of tissue-engineered composite structures[J]. Optical Engineering, 2020, 59: 061623. [20] Zhu Chenguang, Zhao Dongmei, Wang Kedian, et al. Direct laser writing of graphene films from a polyether ether ketone precursor[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2019, 54(5): 4192-4201. doi: 10.1007/s10853-018-3123-5 [21] Luo Dan, Liu Ying, Li Xiangyu, et al. Quantitative analysis of C, Si, Mn, Ni, Cr and Cu in low-alloy steel under ambient conditions via laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy[J]. Plasma Science and Technology, 2018, 20: 075504. doi: 10.1088/2058-6272/aabc5d [22] Bibeau C, Bayramian A, Beach R J, et al. Mercury and beyond: diode-pumped solid-state lasers for inertial fusion energy[J]. Comptes Rendus de l'Académie des Sciences-Series IV-Physics, 2000, 1(6): 745-749. [23] Kawashima T, Kanabe T, Matsui H, et al. Design and performance of a diode-pumped Nd: silica-phosphate glass Zig-Zag slab laser amplifier for inertial fusion energy[J]. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 2001, 40(11R): 6415-6425. [24] Zel’Dovich B Y, Popovichev V I, Ragulskii V V, et al. Connection between the wave fronts of the reflected and exciting light in stimulated Mandel’shtam–Brillouin scattering[J]. JETP Letters, 1972, 15: 109-112. [25] Wang Hongli, Cha S, Kong Hongjin, et al. Rotating off-centered lens in SBS phase conjugation mirror for high-repetition-rate operation[J]. Optics Express, 2019, 27(7): 9895-9905. doi: 10.1364/OE.27.009895 [26] Kang Zhijun, Fan Zhongwei, Huang Yutao, et al. High-repetition-rate, high-pulse-energy, and high-beam-quality laser system using an ultraclean closed-type SBS-PCM[J]. Optics Express, 2018, 26(6): 6560-6571. doi: 10.1364/OE.26.006560 [27] Tang Xiongxin, Qiu Jisi, Fan Zhongwei, et al. Experimental study on SBS-PCM at 200 Hz repetition rate pumped with joule-level energy[J]. Optical Materials, 2017, 67: 64-69. doi: 10.1016/j.optmat.2017.03.044 [28] Omatsu T, Kong H J, Park S, et al. The current trends in SBS and phase conjugation[J]. Laser and Particle Beams, 2012, 30(1): 117-174. doi: 10.1017/S0263034611000644 [29] Shin J S, Park S, Kong H J. Compensation of the thermally induced depolarization in a double-pass Nd: YAG rod amplifier with a stimulated Brillouin scattering phase conjugate mirror[J]. Optics Communications, 2010, 283(11): 2402-2405. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2010.02.013 [30] Zhang Ying, Ke Xizheng, Chen Mingsha. Simulation experiment of wavefront distortion correction in stimulated Brillouin scattering[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2018, 47: 1122001. doi: 10.3788/IRLA201847.1122001 [31] Raab V, Heuer A, Schultheiss J, et al. Transverse effects in phase conjugate laser mirrors based on stimulated Brillouin scattering[J]. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 1999, 10(4/5): 831-838. [32] Lamb R A, Damzen M J. Phase locking of multiple stimulated Brillouin scattering by a phase-conjugate laser resonator[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America B, 1996, 13(7): 1468-1472. doi: 10.1364/JOSAB.13.001468 [33] Chen Xudong, Chang Chengcheng, Pu Jixiong. Stimulated Brillouin scattering phase conjugation of light beams carrying orbit angular momentum (Invited Paper)[J]. Chinese Optics Letters, 2017, 15: 030006. doi: 10.3788/COL201715.030006 [34] Qiu Jisi, Tang Xiongxin, Fan Zhongwei, et al. High repetition rate and high beam quality joule level Nd: YAG nanosecond laser for Thomson scattering diagnosis[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2016, 65: 154204. doi: 10.7498/aps.65.154204 [35] Fan Zhongwei, Qiu Jisi, Tang Xiongxin, et al. A 100 Hz 3.31 J all-solid-state high beam quality Nd: YAG laser for space debris detecting[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2017, 66: 054205. doi: 10.7498/aps.66.054205 [36] Zhu Xuehua, Wu Daohua, Wang Guanling, et al. High efficiency laser spatial beam smoothing based on stimulated Brillouin scattering[J]. Laser Physics, 2019, 29: 065402. doi: 10.1088/1555-6611/ab16e0 [37] Kmetik V, Yoshida H, Fujita H, et al. Very high energy SBS phase conjugation and pulse compression in fluorocarbon liquids[C]. Proc. SPIE: Advanced High-Power Lasers, 2000, 3889: 818-826. [38] Tsubakimoto K, Yoshida H, Miyanaga N. High-average-power green laser using Nd: YAG amplifier with stimulated Brillouin scattering phase-conjugate pulse-cleaning mirror[J]. Optics Express, 2016, 24(12): 12557-12564. doi: 10.1364/OE.24.012557 [39] Qiu Jisi, Tang Xiongxin, Fan Zhongwei, et al. 200 Hz repetition frequency joule-level high beam quality Nd: YAG nanosecond laser[J]. Optics Communications, 2016, 368: 68-72. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2016.02.003 [40] Park S, Cha S, Oh J, et al. Coherent beam combination using self-phase locked stimulated Brillouin scattering phase conjugate mirrors with a rotating wedge for high power laser generation[J]. Optics Express, 2016, 24(8): 8641-8646. doi: 10.1364/OE.24.008641 [41] Yoshida H, Tsubakimoto K, Fujita H, et al. Stimulated-Brillouin-scattering via phase-conjugation-mirror for high-average-power Nd: YAG laser systems[C]//Proceedings of 2011 Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics Europe and 12th European Quantum Electronics Conference (CLEO EUROPE/EQEC). IEEE, 2011. [42] Yoshida H, Nakatsuka M, Hatae T, et al. YAG laser perfomance improved by stimulated Brillouin scattering phase conjugation mirror in Thomson scattering diagnostics at JT-60[J]. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 2003, 42(2R): 439-442. [43] Kornev A F, Makarov A M, Katsev Y V, et al. 2 Joule 10 Hz flashlamp-pumped 1047 nm Nd: YLF laser with near-diffraction-limited beam quality[C]//Proceedings of 2020 International Conference Laser Optics (ICLO). IEEE, 2020. [44] Wang Jianlei, Zhao Kaiqi, Feng Tao, et al. 1.5 J high-beam-quality Nd: LuAG ceramic active mirror laser amplifier[J]. Chinese Optics Letters, 2020, 18: 021401. doi: 10.3788/COL202018.021401 [45] Jaberi M, Farahbod A H, Soleimani H R. Effect of pump mode structure on reflectance of SBS mirrors[J]. Optical and Quantum Electronics, 2017, 49: 53. doi: 10.1007/s11082-017-0890-1 [46] Ding Jianyong, Yu Guangli, Fang Chunqi, et al. High beam quality of nanosecond Nd: YAG slab laser system with SBS-PCM[J]. Optics Communications, 2020, 475: 126273. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2020.126273 [47] Brignon A, Huignard J P. Phase conjugate laser optics[M]. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons, 2004. [48] Fisher R A. Optical phase conjugation[M]. New York: Academic Press, 1983. [49] Hasi W L J, Lu Z W, Gong S, et al. Investigation of stimulated Brillouin scattering media perfluoro-compound and perfluoropolyether with a low absorption coefficient and high power-load ability[J]. Applied Optics, 2008, 47(7): 1010-1014. doi: 10.1364/AO.47.001010 [50] Guo X Y, Hasi W L J, Zhong Z M, et al. Research on the SBS mediums used in high peak power laser system and their selection principle[J]. Laser and Particle Beams, 2012, 30(4): 525-530. doi: 10.1017/S0263034612000390 [51] Wang Y L, Lu Z W, Li Y, et al. Investigation on high-power load ability of stimulated Brillouin scattering phase conjugating mirror[J]. Applied Physics B, 2010, 98(2/3): 391-395. [52] Gao Yue, Wang Yanjie, Chan A, et al. High average power diode pumped solid state laser[J]. Laser Physics Letters, 2017, 14: 035803. doi: 10.1088/1612-202X/aa5c20 [53] Gyger F, Liu Junqiu, Yang Fan, et al. Observation of stimulated Brillouin scattering in silicon nitride integrated waveguides[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2020, 124: 013902. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.124.013902 [54] Garmire E. Perspectives on stimulated Brillouin scattering[J]. New Journal of Physics, 2017, 19: 011003. doi: 10.1088/1367-2630/aa5447 [55] Garmire E. Stimulated Brillouin review: invented 50 years ago and applied today[J]. International Journal of Optics, 2018, 2018: 2459501. [56] Neshev D, Velchev I, Majewski W A, et al. SBS pulse compression to 200 ps in a compact single-cell setup[J]. Applied Physics B, 1999, 68(4): 671-675. doi: 10.1007/s003400050684 [57] Dane C B, Neuman W A, Hackel L A. High-energy SBS pulse compression[J]. IEEE Journal of Quantum Electronics, 1994, 30(8): 1907-1915. doi: 10.1109/3.301654 [58] Park H, Lim C, Yoshida H, et al. Measurement of stimulated Brillouin scattering characteristics in heavy fluorocarbon liquids and perfluoropolyether liquids[J]. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 2006, 45(6A): 5073-5075. [59] Hasi Wuliji, Lü Zhiwei, He Weiming, et al. Study on Brillouin amplification in different liquid media[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2005, 54(2): 742-748. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3290.2005.02.042 [60] Wang Yulei, Lv Zhiwei, Guo Qi, et al. A new circulating two-cell structure for stimulated Brillouin scattering phase conjugation mirrors with 1-J load and 10-Hz repetition rate[J]. Chinese Optics Letters, 2010, 8(11): 1064-1066. doi: 10.3788/COL20100811.1064 [61] Wang Hongli. Research on pulsed compression technologies of kHz sub-nanosecond laser based on stimulated Brillouin scattering[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2019 [62] Li Yong. Investigation on compensate phase aberration of repetition laser by SBS-PCM[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2008 [63] Yoshida H, Nakatsuka M. High-power phase-conjugating mirror based on stimulated Brillouin scattering in liquid and solid materials[C]//Proceedings of 2005 Pacific Rim Conference on Lasers & Electro-Optics. IEEE, 2005: 1166-1167. [64] Beak D H, Yoon J W, Shin J S, et al. Restoration of high spatial frequency at the image formed by stimulated Brillouin scattering with a prepulse[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2008, 93: 231113. doi: 10.1063/1.3042101 [65] Kong Hongjin, Beak D H, Lee D W, et al. Waveform preservation of the backscattered stimulated Brillouin scattering wave by using a prepulse injection[J]. Optics Letters, 2005, 30(24): 3401-3403. doi: 10.1364/OL.30.003401 [66] Rockwell D A. A review of phase-conjugate solid-state lasers[J]. IEEE Journal of Quantum Electronics, 1988, 24(6): 1124-1140. doi: 10.1109/3.236 [67] Wang V, Giuliano C R. Correction of phase aberrations via stimulated Brillouin scattering[J]. Optics Letters, 1978, 2(1): 4-6. doi: 10.1364/OL.2.000004 [68] Kir'yanov Y F, Kochemasov G G, Maslov N V, et al. Influence of thermal defocusing on the quality of phase conjugation of Gaussian beams by stimulated Brillouin scattering[J]. Quantum Electronics, 1998, 28(1): 58-61. doi: 10.1070/QE1998v028n01ABEH001124 [69] Andreev N F, Khazanov E A, Pasmanik G A. Applications of Brillouin cells to high repetition rate solid-state lasers[J]. IEEE Journal of Quantum Electronics, 1992, 28(1): 330-341. doi: 10.1109/3.119532 [70] Andreev N, Kulagin O P, Palashov O V, et al. SBS of repetitively pulsed radiation and possibility of increasing the pump average power[C]//Proceedings of SPIE 2633, Solid State Lasers for Application to Inertial Confinement Fusion (ICF). 1995: 476-493. [71] Amnon Y. Phase conjugate optics and real-time holography[J]. IEEE Journal of Quantum Electronics., 1978, 14(9): 650-660. doi: 10.1109/JQE.1978.1069870 [72] Bai Zhenxu, Yuan Hang, Liu Zhaohong, et al. Stimulated Brillouin scattering materials, experimental design and applications: a review[J]. Optical Materials, 2018, 75: 626-645. doi: 10.1016/j.optmat.2017.10.035 [73] Damzen M J, Vlad V I, Babin V, et al. Stimulated Brillouin scattering: fundamentals and applications[M]. Bristol: IOP Publishing Ltd, 2003. [74] Boyd R W. Nonlinear optics[M]. San Diego, CA: Academic Press, 2020. [75] Hasi W L J, Lu Z W, Li Q et al. Research on the enhancement of power-load of two-cell SBS system by choosing different media or mixture medium[J]. Laser and Particle Beams, 2007, 25(2): 207-210. doi: 10.1017/S026303460700002X [76] Schiemann S, Ubachs W, Hogervorst W. Efficient temporal compression of coherent nanosecond pulses in a compact SBS generator-amplifier setup[J]. IEEE Journal of Quantum Electronics, 1997, 33(3): 358-366. doi: 10.1109/3.556004 [77] Yoshida H, Kmetik V, Fujita H, et al. Heavy fluorocarbon liquids for a phase-conjugated stimulated Brillouin scattering mirror[J]. Applied Optics, 1997, 36(16): 3739-3744. doi: 10.1364/AO.36.003739 [78] Lu Z W, Hasi W L J, Gong H P, et al. Generation of flat-top waveform by double optical limiting based on stimulated Brillouin scattering[J]. Optics Express, 2006, 14(12): 5497-5501. doi: 10.1364/OE.14.005497 [79] Boyd R W, Rza̧ewski K, Narum P. Noise initiation of stimulated Brillouin scattering[J]. Physical Review A, 1990, 42(9): 5514-5521. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.42.5514 [80] Wang Y L, Lu Z W, Li Y, et al. Investigation on high power phase compensation of strong aberrations via stimulated Brillouin scattering[J]. Applied Physics B, 2010, 99(1/2): 257-261. [81] Hon D T. Applications of wavefront reversal by stimulated Brillouin scattering[J]. Optical Engineering, 1982, 21: 212252. [82] Kong Hongjin, Lee S K, Lee D W, et al. Phase control of a stimulated Brillouin scattering phase conjugate mirror by a self-generated density modulation[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2005, 86: 051111. doi: 10.1063/1.1857088 [83] Wang Yulei, Lu Zhiwei, Lin Dianyang, et al. The performance of stimulated Brillouin scattering pulse improved by a prepulse seed[C]//Proceedings of 2010 Academic Symposium on Optoelectronics and Microelectronics Technology and 10th Chinese-Russian Symposium on Laser Physics and Laser Technology Optoelectronics Technology (ASOT). IEEE, 2010: 157-159. [84] Wang Y L, Lu Z W, He W M, et al. A new measurement of stimulated Brillouin scattering phase conjugation fidelity for high pump energies[J]. Laser and Particle Beams, 2009, 27(2): 297-302. doi: 10.1017/S026303460900038X [85] Jaberi M, Farahbod A H, Soleimani H R. Spectral behavior of amplified back-scattered Stokes pulse in two-cell phase conjugating mirror[J]. Optics Communications, 2015, 335: 7-15. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2014.08.066 [86] Kong Hongjin, Park S, Cha S, et al. Current status of the development of the Kumgang laser[J]. Optical Materials Express, 2014, 4(12): 2551-2558. doi: 10.1364/OME.4.002551 [87] Kiriyama H, Yamakawa K, Nagai T, et al. 360-W average power operation with a single-stage diode-pumped Nd: YAG amplifier at a 1-kHz repetition rate[J]. Optics Letters, 2003, 28(18): 1671-1673. doi: 10.1364/OL.28.001671 -




 下载:
下载: