Progress in research of dynamic properties and applications of spin-lasers
-
摘要:
在半导体激光器中引入自旋极化载流子是实现室温自旋电子应用的新途径,其超越了常规的磁阻效应。自旋极化载流子的注入导致自旋激光器具有丰富的动力学行为并展示出包括高频偏振振荡和偏振混沌动力学等特性,使其在保密光通信、量子计算、光信息处理和数据存储、可重构光互联以及生物医学传感等领域具有巨大的应用潜力。梳理了近年来自旋激光器的动力学特性及其应用研究进展。介绍了自旋激光器丰富的动力学行为及混沌演变机制;随后分析了自旋激光器的高频振荡特性;归纳了基于自旋激光器动力学特性的最新应用研究进展。在此基础上,展望了自旋激光器的发展趋势和面临的挑战,为相关领域的研究和工程应用提供参考。
Abstract:An alternative approach to realizing room temperature spintronic applications is introducing spin-polarized carriers in a semiconductor laser, which is beyond the usual magnetoresistive effects. Spin lasers have been widely applied in the fields of secure optical communication, quantum computing, optical information processing, and data storage, reconfigurable optical interconnection, and biomedical sensing because the injection of spin-polarized carriers results in the rich dynamic properties of spin lasers, including high-frequency polarization oscillations and polarization chaos regimes. In this paper, the research progress of the dynamic characteristics and applications of spin lasers in recent years is reviewed. Firstly, the dynamic behavior and chaotic evolution mechanism of spin lasers are introduced. Then the high-frequency polarization oscillation characteristics of spin lasers are analyzed. Furthermore, the latest research progress of applications based on the dynamic characteristics of spin lasers is summarized. Finally, the prospects and challenges of spin lasers are expected to enlighten fundamental researches and engineering applications in the relevant fields.
-
Key words:
- spintronic /
- spin laser /
- dynamic properties /
- polarization oscillation /
- polarization chaos
-
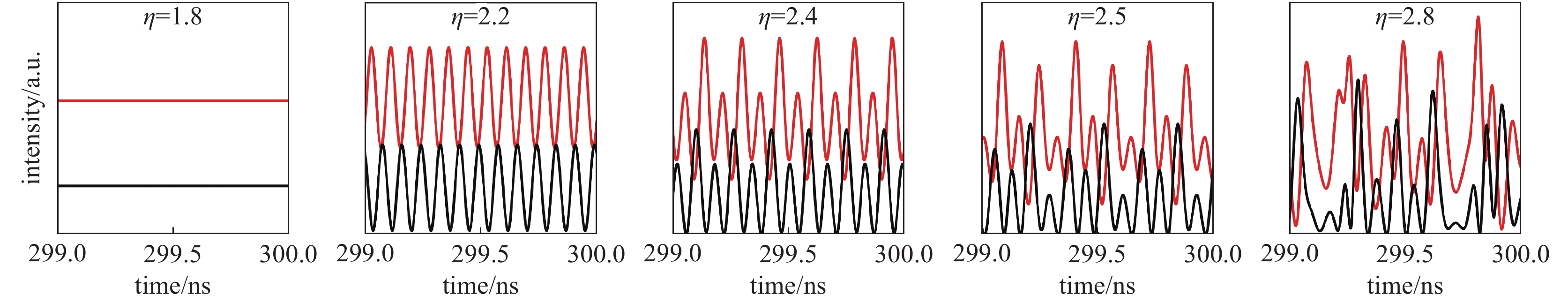
图 1 自旋VCSEL的时序图
Figure 1. Intensity time sequence of the spin-VCSEL
optical field decay rate κ=300 ns−1; linear dichroism γa=0; linear birefringence γp=10π ns−1; spin-flip relaxation rate γs=30 ns−1; decay rate of N (N is normalized carrier concentration) γ=1 ns−1; linewidth enhancement factor α=3; pump ellipticity P=−0.1. The other parameters of VCSEL are the same as those in Fig. 1
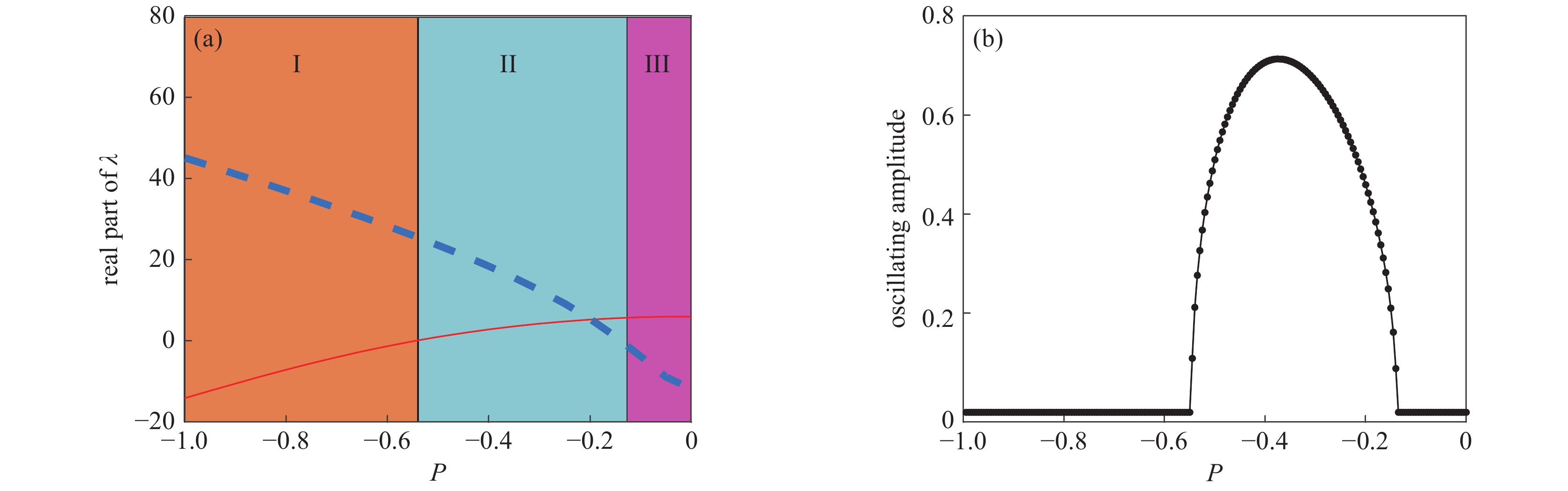
图 4 二维分岔图
Figure 4. Bifurcation diagrams (κ=230 ns−1, γa=0, γp=8.8π ns−1, γs=30 ns−1, γ=0.68 ns−1, α=4, P=−0.1 [39])
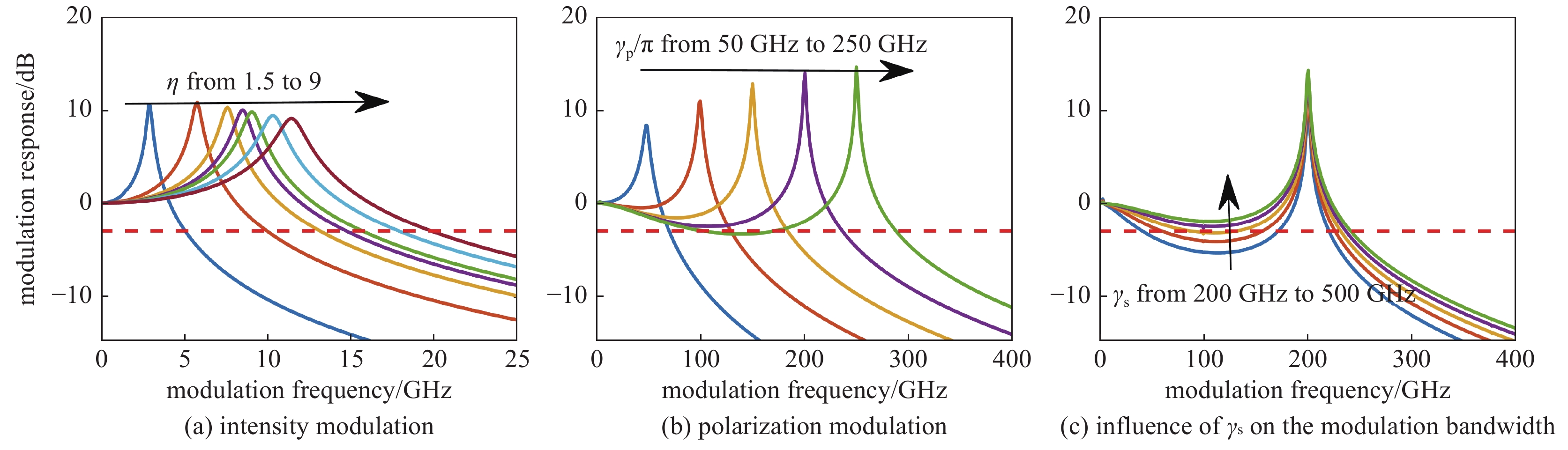
图 6 强度调制、偏振调制和自旋反转弛豫速率的影响
Figure 6. Simulated intensity modulation and polarization modulation (κ=325 ns−1, γa=0, γs=450 ns−1, γ=1 ns−1, α=5, P=0 [22])
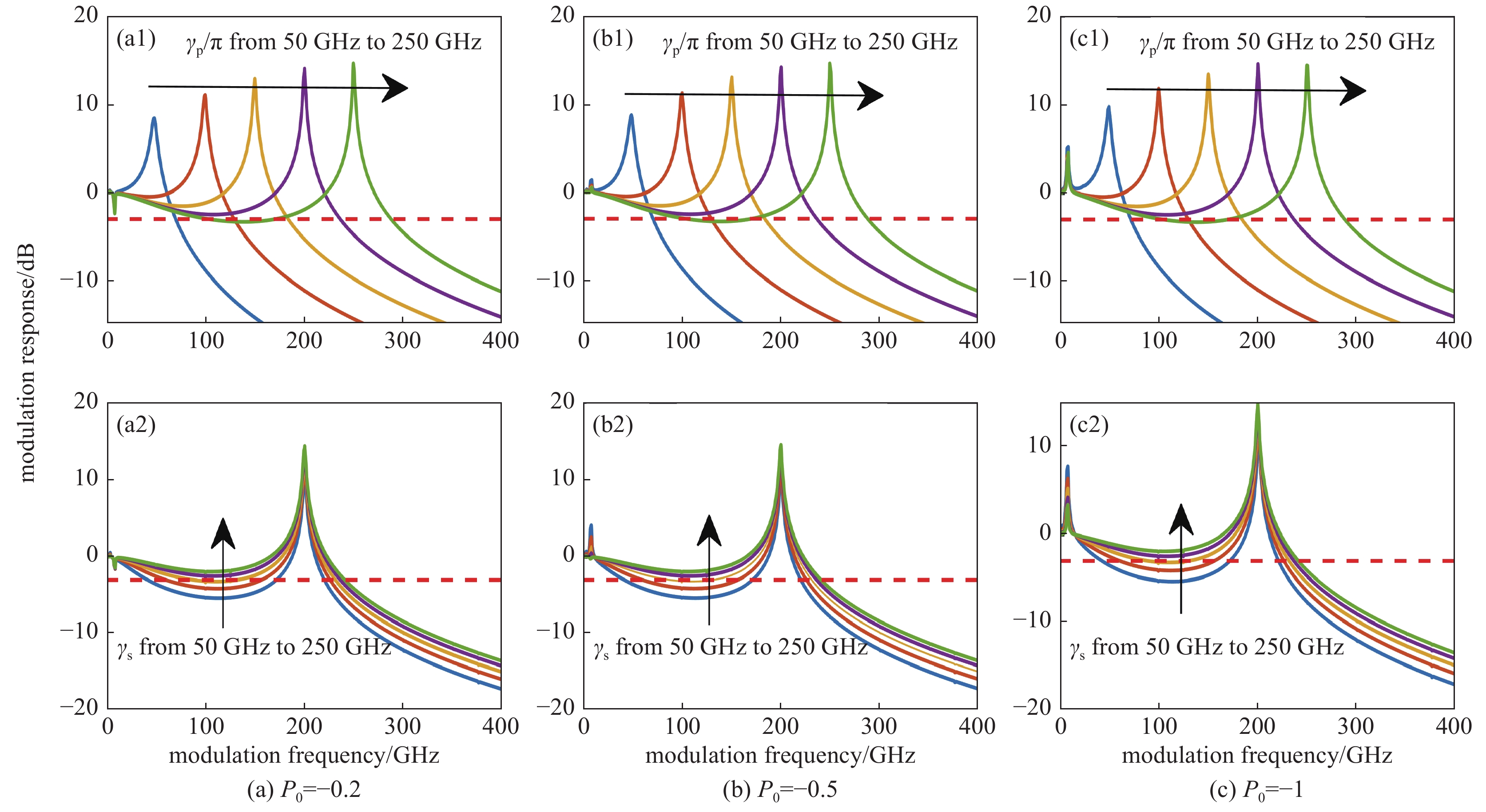
图 7 不同偏振椭圆率下的偏振调制
Figure 7. Polarization modulation response at various polarization ellipticity (κ=325 ns−1, γa=0, γs=450 ns−1, γ=1 ns−1, α=5, η=5.4[22])
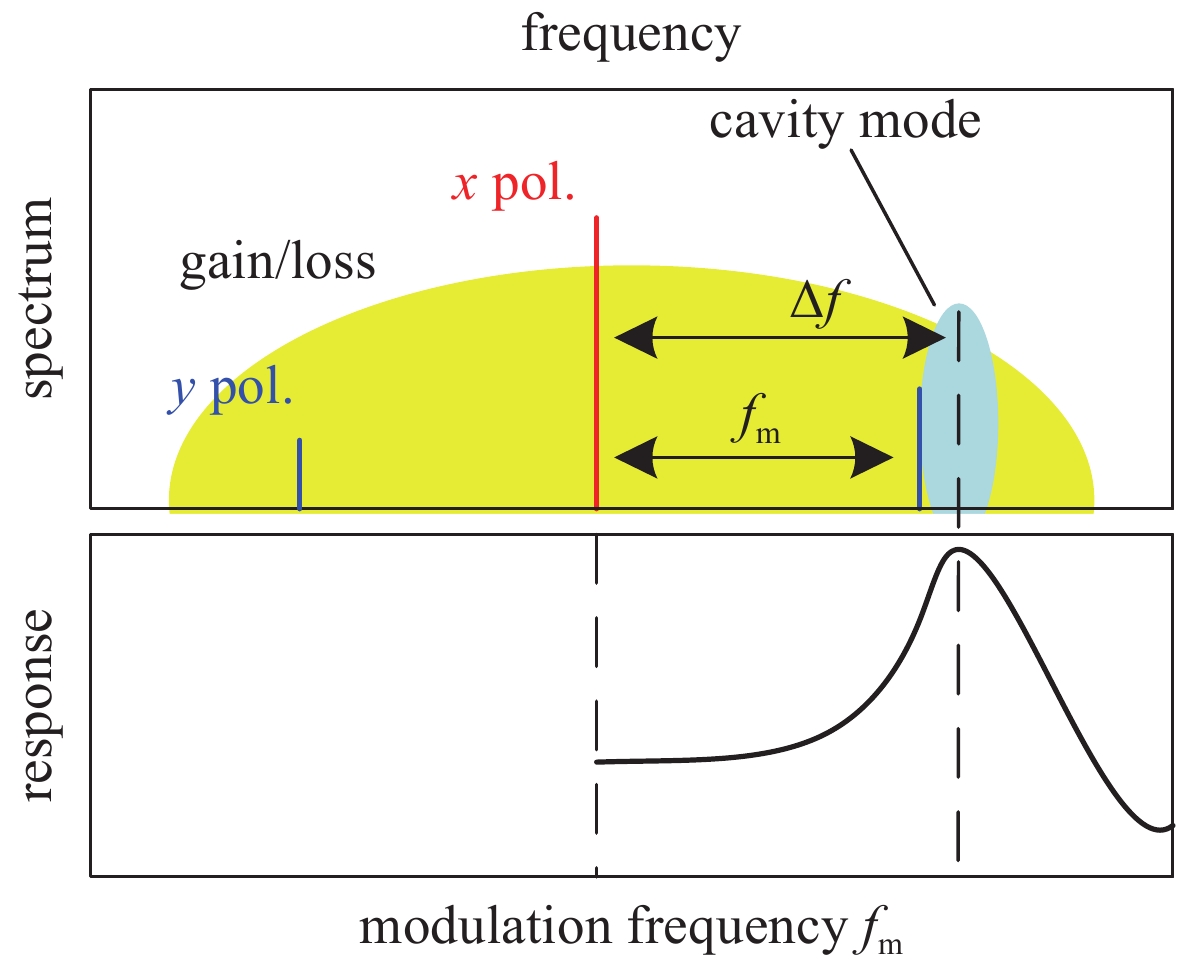
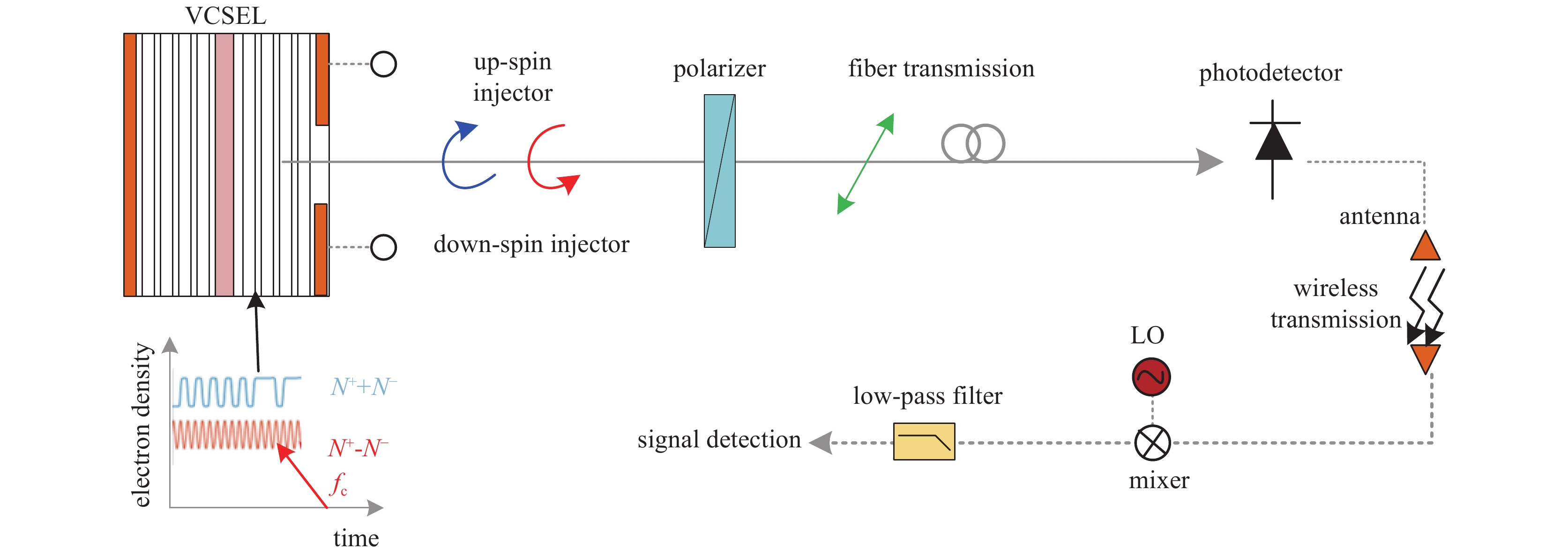
图 10 自旋VCSEL的光子微波产生系统以及光谱与频谱示意图
Figure 10. Schematic of the proposed photonic microwave generation system and optical spectra and radio-frequency spectra
feedback strength kf=1.1 ns−1 and feedback delay time τ=4 ns. κ=300 ns−1, γa=0, γs=30 ns−1, γp=40π ns−1, γ=1 ns−1, α=3, η=2, P=−0.5 [40]
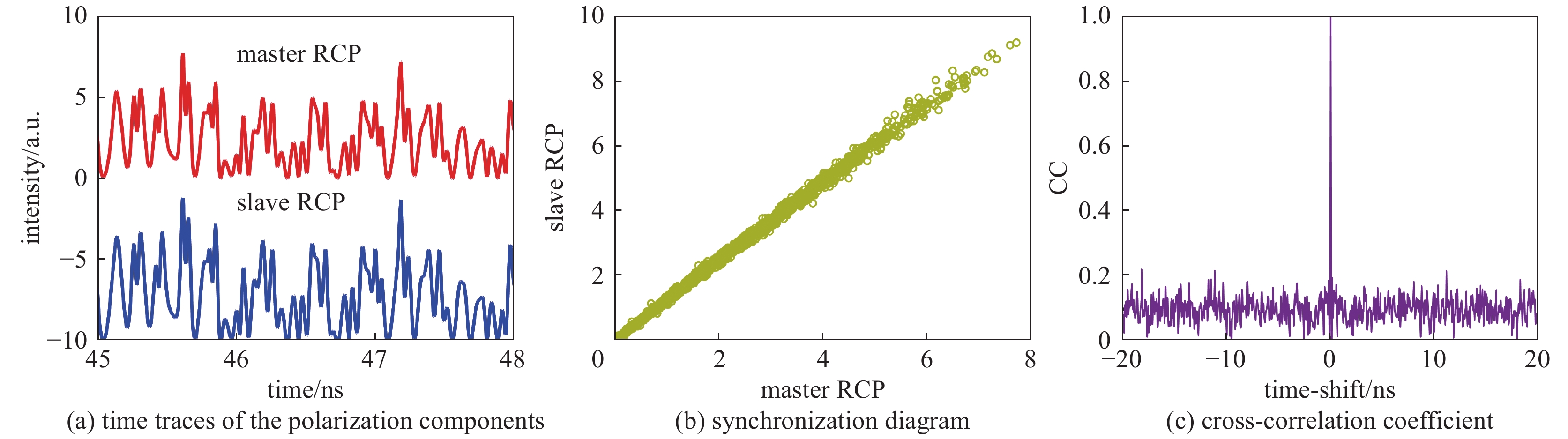
图 11 主从激光器的混沌时间序列
Figure 11. Cross-correlation between the master laser and slave laser
κ=250 ns−1, γa=0, γs=30 ns−1, γp=8.8π ns−1, γ=0.68 ns−1, α=4, kinj=100 ns−1, Δf=−20 GHz, ηM,S=6, and PM,S=−0.1[71]
图 12 调制自旋VCSEL的泵浦振幅和偏振态
Figure 12. Modulated pump magnitude and polarization of the master spin-VCSEL (PM,S=−0.1)
Modulated pump magnitude of the master spin-VCSEL. Recovered message from (a) the total intensity and (c) the RCP. (b) and (d) the corresponding eye diagrams. The bit rate is 4 Gb/s. Modulated pump polarization of the master spin-VCSEL. Recovered message from (e) the total intensity and (g) the RCP. (f) and (h) the corresponding eye diagrams. The bit rate is 3 Gb/s[71]. The other parameters are the same as those in Fig. 8
-
[1] Gerhardt N C, Hofmann M R. Spin-controlled vertical-cavity surface-emitting lasers[J]. Advances in Optical Technologies, 2012, 2012: 268949. [2] Adams M J, Alexandropoulos D. Parametric analysis of spin-polarized VCSELs[J]. IEEE Journal of Quantum Electronics, 2009, 45(6): 744-749. doi: 10.1109/JQE.2009.2013107 [3] Holub M, Shin J, Saha D, et al. Electrical spin injection and threshold reduction in a semiconductor laser[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2007, 98: 146603. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.98.146603 [4] Alharthi S S, Hurtado A, Al Seyab R K, et al. Control of emitted light polarization in a 1310 nm dilute nitride spin-vertical cavity surface emitting laser subject to circularly polarized optical injection[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2014, 105: 181106. doi: 10.1063/1.4901192 [5] Alharthi S S, Hurtado A, Korpijarvi V M, et al. Circular polarization switching and bistability in an optically injected 1300 nm spin-vertical cavity surface emitting laser[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2015, 106: 021117. doi: 10.1063/1.4905923 [6] Basu D, Saha D, Bhattacharya P. Optical polarization modulation and gain anisotropy in an electrically injected spin laser[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2009, 102: 093904. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.102.093904 [7] Schires K, Al Seyab R, Hurtado A, et al. Optically-pumped dilute nitride spin-VCSEL[J]. Optics Express, 2012, 20(4): 3550-3555. doi: 10.1364/OE.20.003550 [8] Li Nianqiang, Alexandropoulos D, Susanto H, et al. Stability analysis of quantum-dot spin-VCSELs[J]. Electronics, 2016, 5: 83. doi: 10.3390/electronics5040083 [9] Alharthi S S, Orchard J, Clarke E, et al. 1300 nm optically pumped quantum dot spin vertical external-cavity surface-emitting laser[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2015, 107: 151109. doi: 10.1063/1.4933334 [10] Li M Y, Jähme H, Soldat H, et al. Birefringence controlled room-temperature picosecond spin dynamics close to the threshold of vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser devices[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2010, 97: 191114. doi: 10.1063/1.3515855 [11] Adams M, Li Nianqiang, Cemlyn B, et al. Algebraic expressions for the polarisation response of spin-VCSELs[J]. Semiconductor Science and Technology, 2018, 33: 064002. doi: 10.1088/1361-6641/aabda3 [12] Lee J, Oszwałdowski R, Gøthgen C, et al. Mapping between quantum dot and quantum well lasers: from conventional to spin lasers[J]. Physical Review B, 2012, 85: 045314. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.85.045314 [13] Žutić I, Fabian J, Sarma S D. Spintronics: fundamentals and applications[J]. Reviews of Modern Physics, 2004, 76(2): 323-410. doi: 10.1103/RevModPhys.76.323 [14] Žutić I, Xu Gaofeng, Lindemann M, et al. Spin-lasers: spintronics beyond magnetoresistance[J]. Solid State Communications, 2020, 316-317: 113949. doi: 10.1016/j.ssc.2020.113949 [15] Soldat H, Li Mingyuan, Gerhardt N C, et al. Room temperature spin relaxation length in spin light-emitting diodes[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2011, 99: 051102. doi: 10.1063/1.3622662 [16] Schires K, Al Seyab R, Hurtado A, et al. Instabilities in optically-pumped 1300nm dilute nitride spin-VCSELs: experiment and theory[C]//Proceedings of IEEE Photonics Conference 2012. Burlingame: IEEE, 2012: 870-871. [17] Höpfner H, Lindemann M, Gerhardt N C, et al. Controlled switching of ultrafast circular polarization oscillations in spin-polarized vertical-cavity surface-emitting lasers[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2014, 104: 022409. doi: 10.1063/1.4862330 [18] Lindemann M, Pusch T, Michalzik R, et al. Frequency tuning of polarization oscillations: toward high-speed spin-lasers[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2016, 108: 042404. doi: 10.1063/1.4940713 [19] Torre M S, Susanto H, Li Nianqiang, et al. High frequency continuous birefringence-induced oscillations in spin-polarized vertical-cavity surface-emitting lasers[J]. Optics Letters, 2017, 42(8): 1628-1631. doi: 10.1364/OL.42.001628 [20] Yokota N, Takeuchi R, Yasaka H, et al. Lasing polarization characteristics in 1.55-μm spin-injected VCSELs[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2017, 29(9): 711-714. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2017.2681129 [21] Yokota N, Nisaka K, Yasaka H, et al. Spin polarization modulation for high-speed vertical-cavity surface-emitting lasers[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2018, 113: 171102. doi: 10.1063/1.5040914 [22] Lindemann M, Xu Gaofeng, Pusch T, et al. Ultrafast spin-lasers[J]. Nature, 2019, 568(7751): 212-215. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1073-y [23] Frougier J, Baili G, Sagnes I, et al. Accurate measurement of the residual birefringence in VECSEL: Towards understanding of the polarization behavior under spin-polarized pumping[J]. Optics Express, 2015, 23: 9573-9588. doi: 10.1364/OE.23.009573 [24] Etou K, Hiura S, Park S, et al. Room-temperature spin-transport properties in an In0.5Ga0.5As quantum dot spin-polarized light-emitting diode[J]. Physical Review Applied, 2021, 16: 014034. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevApplied.16.014034 [25] Michalzik R. VCSELs: fundamentals, technology and applications of vertical-cavity surface-emitting lasers[M]. Berlin Heidelberg: Springer, 2013: 166. [26] Sarma S D, Fabian J, Hu Xuedong, et al. Spin electronics and spin computation[J]. Solid State Communications, 2001, 119(4/5): 207-215. [27] Sarma S D, Fabian J, Hu Xuedong, et al. Spintronics: electron spin coherence, entanglement, and transport[J]. Superlattices and Microstructures, 2000, 27(5/6): 289-295. [28] Parkin S P S, Kaiser C, Panchula A, et al. Giant tunnelling magnetoresistance at room temperature with MgO (100) tunnel barriers[J]. Nature Materials, 2004, 3(12): 862-867. doi: 10.1038/nmat1256 [29] Alharthi S S, Al Seyab R K, Henning I D, et al. Simulated dynamics of optically pumped dilute nitride 1300 nm spin vertical-cavity surface-emitting lasers[J]. IET Optoelectronics, 2014, 8(2): 117-121. doi: 10.1049/iet-opt.2013.0044 [30] Alharthi S S. Nonlinear dynamics of solitary and optically-injected spin vertical-cavity lasers[D]. Essex: University of Essex, 2016: 82-180. [31] Virte M, Panajotov K, Thienpont H, et al. Deterministic polarization chaos from a laser diode[J]. Nature Photonics, 2013, 7(1): 60-65. doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2012.286 [32] Raddo T R, Panajotov K, Borges B H V, et al. Strain induced polarization chaos in a solitary VCSEL[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7: 14032. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-14436-3 [33] Alexandropoulos D, Al-Seyab R, Henning I, et al. Instabilities in quantum-dot spin-VCSELs[J]. Optics Letters, 2012, 37(10): 1700-1702. doi: 10.1364/OL.37.001700 [34] Li Nianqiang, Susanto H, Cemlyn B R, et al. Mapping bifurcation structure and parameter dependence in quantum dot spin-VCSELs[J]. Optics Express, 2018, 26(11): 14636-14649. doi: 10.1364/OE.26.014636 [35] Song Tingting, Xie Yiyuan, Ye Yichen, et al. Numerical analysis of nonlinear dynamics based on spin-VCSELs with optical feedback[J]. Photonics, 2021, 8: 10. doi: 10.3390/photonics8010010 [36] Saha D, Basu D, Bhattacharya P. High-frequency dynamics of spin-polarized carriers and photons in a laser[J]. Physical Review B, 2010, 82: 205309. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.82.205309 [37] Al-Seyab R, Alexandropoulos D, Henning I D, et al. Instabilities in spin-polarized vertical-cavity surface-emitting lasers[J]. IEEE Photonics Journal, 2011, 3(5): 799-809. doi: 10.1109/JPHOT.2011.2165205 [38] Gerhardt N C, Li M Y, Jähme H, et al. Ultrafast spin-induced polarization oscillations with tunable lifetime in vertical-cavity surface-emitting lasers[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2011, 99: 151107. doi: 10.1063/1.3651339 [39] Li Nianqiang, Susanto H, Cemlyn B, et al. Stability and bifurcation analysis of spin-polarized vertical-cavity surface-emitting lasers[J]. Physical Review A, 2017, 96: 013840. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.96.013840 [40] Huang Yu, Zhou Pei, Li Nianqiang. Broad tunable photonic microwave generation in an optically pumped spin-VCSEL with optical feedback stabilization[J]. Optics Letters, 2021, 46(13): 3147-3150. doi: 10.1364/OL.431184 [41] Huang Yu, Zhou Pei, Li Nianqiang. High-speed secure key distribution based on chaos synchronization in optically pumped QD spin-polarized VCSELs[J]. Optics Express, 2021, 29(13): 19675-19689. doi: 10.1364/OE.426126 [42] Vaughan M, Susanto H, Henning I, et al. Dynamics of laterally-coupled pairs of spin-VCSELs[J]. IEEE Journal of Quantum Electronics, 2020, 56: 2400310. [43] Lindemann M, Pusch T, Michalzik R, et al. Investigations on polarization oscillation amplitudes in spin-VCSELs[C]//Proceedings of SPIE 10122, Vertical-Cavity Surface-Emitting Lasers XXI. San Francisco: SPIE, 2017: 101220O. [44] Susanto H, Schires K, Adams M J, et al. Spin-flip model of spin-polarized vertical-cavity surface-emitting lasers: asymptotic analysis, numerics, and experiments[J]. Physical Review A, 2015, 92: 063838. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.92.063838 [45] Martin-Regalado J, Prati F, Miguel M S, et al. Polarization properties of vertical-cavity surface-emitting lasers[J]. IEEE Journal of Quantum Electronics, 1997, 33(5): 765-783. doi: 10.1109/3.572151 [46] Gahl A, Balle S, Miguel M S. Polarization dynamics of optically pumped VCSELs[J]. IEEE Journal of Quantum Electronics, 1999, 35(3): 342-351. doi: 10.1109/3.748839 [47] Homayounfar A, Adams M J. Analysis of SFM dynamics in solitary and optically-injected VCSELs[J]. Optics Express, 2007, 15(17): 10504-10519. doi: 10.1364/OE.15.010504 [48] Lee J, Falls W, Oszwaldowski R, et al. Spin modulation in semiconductor lasers[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2010, 97: 041116. doi: 10.1063/1.3473759 [49] Panajotov K, Nagler B, Verschaffelt G, et al. Impact of in-plane anisotropic strain on the polarization behavior of vertical-cavity surface-emitting lasers[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2000, 77(11): 1590-1592. doi: 10.1063/1.1309019 [50] Pusch T, La Tona E, Lindemann M, et al. Monolithic vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser with thermally tunable birefringence[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2017, 110: 151106. doi: 10.1063/1.4980025 [51] Pusch T, Lindemann M, Gerhardt N C, et al. Vertical-cavity surface-emitting lasers with birefringence splitting above 250 GHz[J]. Electronics Letters, 2015, 51(20): 1600-1602. doi: 10.1049/el.2015.2149 [52] Pusch T, Debernardi P, Lindemann M, et al. Vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser with integrated surface grating for high birefringence splitting[J]. Electronics Letters, 2019, 55(19): 1055-1057. doi: 10.1049/el.2019.1441 [53] Zhu Ninghua, Shi Zhan, Zhang Zhike, et al. Directly modulated semiconductor lasers[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics, 2018, 24(1): 1-19. [54] Zhou Daibing, Liang Song, Zhao Lingjuan, et al. High-speed directly modulated widely tunable two-section InGaAlAs DBR lasers[J]. Optics Express, 2017, 25(3): 2341-2346. doi: 10.1364/OE.25.002341 [55] Rosales R, Zorn M, Lott J A. 30-GHz bandwidth with directly current-modulated 980-nm oxide-aperture VCSELs[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2017, 29(23): 2107-2110. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2017.2764626 [56] Xu Gaofeng, Cao J D, Labinac V, et al. Intensity equations for birefringent spin lasers[J]. Physical Review B, 2020, 103: 045306. [57] Huang Yu, Zhou Pei, Torre M S, et al. Optically pumped spin-VCSELs: toward high-frequency polarization oscillations and modulation[J]. IEEE Journal of Quantum Electronics, 2021, 57: 2400212. [58] Junior P E F, Xu Gaofeng, Lee J, et al. Toward high-frequency operation of spin lasers[J]. Physical Review B, 2015, 92: 075311. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.92.075311 [59] Drong M, Fördös T, Jaffrès H Y, et al. Spin-VCSELs with local optical anisotropies: toward terahertz polarization modulation[J]. Physical Review Applied, 2021, 15: 014041. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevApplied.15.014041 [60] Kini R N, Nontapot K, Khodaparast G A, et al. Time resolved measurements of spin and carrier dynamics in InAs films[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2008, 103: 064318. doi: 10.1063/1.2899091 [61] Blansett E L, Raymer M G, Khitrova G, et al. Ultrafast polarization dynamics and noise in pulsed vertical-cavity surface-emitting lasers[J]. Optics Express, 2001, 9(6): 312-318. doi: 10.1364/OE.9.000312 [62] Yokota N, Ikeda K, Yasaka H. Spin-injected birefringent VCSELs for analog radio-over-fiber systems[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2021, 33(6): 297-300. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2021.3059697 [63] Guo Xingxing, Xiang Shuiying, Zhang Yahui, et al. High-speed neuromorphic reservoir computing based on a semiconductor nanolaser with optical feedback under electrical modulation[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics, 2020, 26: 1500707. [64] Vatin J, Rontani D, Sciamanna M. Enhanced performance of a reservoir computer using polarization dynamics in VCSELs[J]. Optics Letters, 2018, 43(18): 4497-4500. doi: 10.1364/OL.43.004497 [65] Bueno J, Brunner D, Soriano M C, et al. Conditions for reservoir computing performance using semiconductor lasers with delayed optical feedback[J]. Optics Express, 2017, 25(3): 2401-2412. doi: 10.1364/OE.25.002401 [66] Yang Yigong, Zhou Pei, Li Nianqiang. Time-delayed reservoir computing based on an optically pumped spin VCSEL for high-speed processing[J]. submitted to Noninear Dynamic. [67] Harkhoe K, Verschaffelt G, Van der Sande G. Neuro-inspired computing with spin-VCSELs[J]. Applied Sciences, 2021, 11: 4232. doi: 10.3390/app11094232 [68] Wang Cheng, Raghunathan R, Schires K, et al. Optically injected InAs/GaAs quantum dot laser for tunable photonic microwave generation[J]. Optics Letters, 2016, 41(6): 1153-1156. doi: 10.1364/OL.41.001153 [69] Chan S C, Hwang S K, Liu Jiaming. Period-one oscillation for photonic microwave transmission using an optically injected semiconductor laser[J]. Optics Express, 2007, 15(22): 14921-14935. doi: 10.1364/OE.15.014921 [70] Lin Xiaodong, Xia Guangqiong, Yang Tilian, et al. Photonic microwave generation based on an OISL by subharmonic modulation from an OEO[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2019, 31(22): 1846-1849. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2019.2949278 [71] Li Nianqiang, Susanto H, Cemlyn B, et al. Secure communication systems based on chaos in optically pumped spin-VCSELs[J]. Optics Letters, 2017, 42(17): 3494-3497. doi: 10.1364/OL.42.003494 [72] Huang Yu, Zhou Pei, Li Nianqiang. Chaos synchronization in optically pumped quantum-dot spin-VCSELs[C]//Proceedings of SPIE 11763, Seventh Symposium on Novel Photoelectronic Detection Technology and Applications. Kunming: SPIE, 2021: 117636I. [73] Jiang Ning, Xue Chenpeng, Liu Ding, et al. Secure key distribution based on chaos synchronization of VCSELs subject to symmetric random-polarization optical injection[J]. Optics Letters, 2017, 42(6): 1055-1058. doi: 10.1364/OL.42.001055 [74] Yokota N, Yasaka H. Spin laser local oscillators for homodyne detection in coherent optical communications[J]. Micromachines, 2021, 12: 573. doi: 10.3390/mi12050573 -




 下载:
下载: