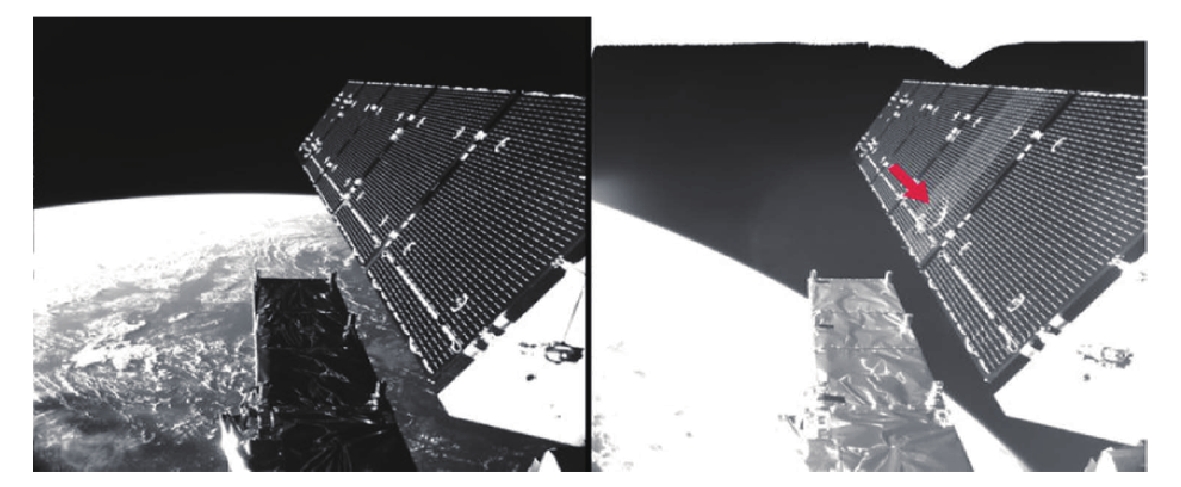
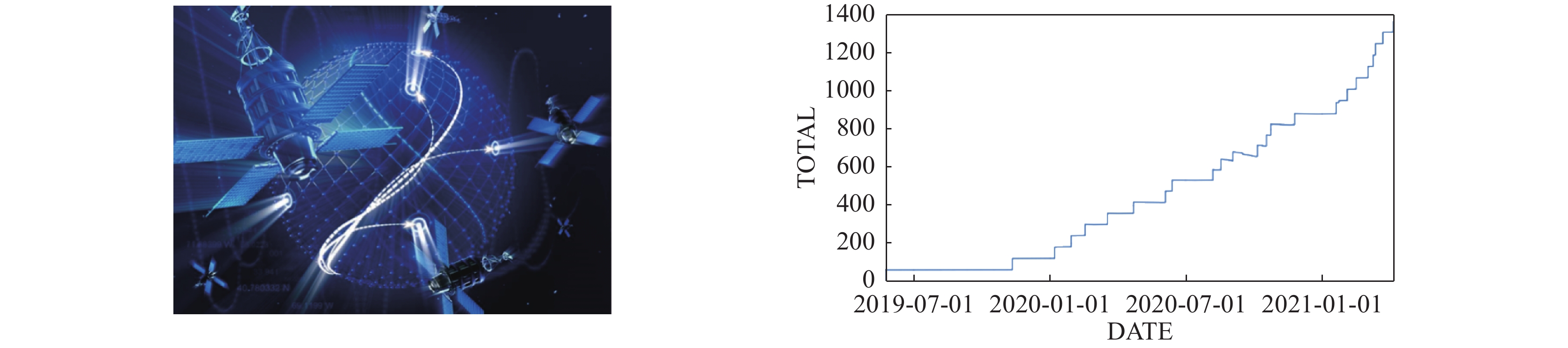
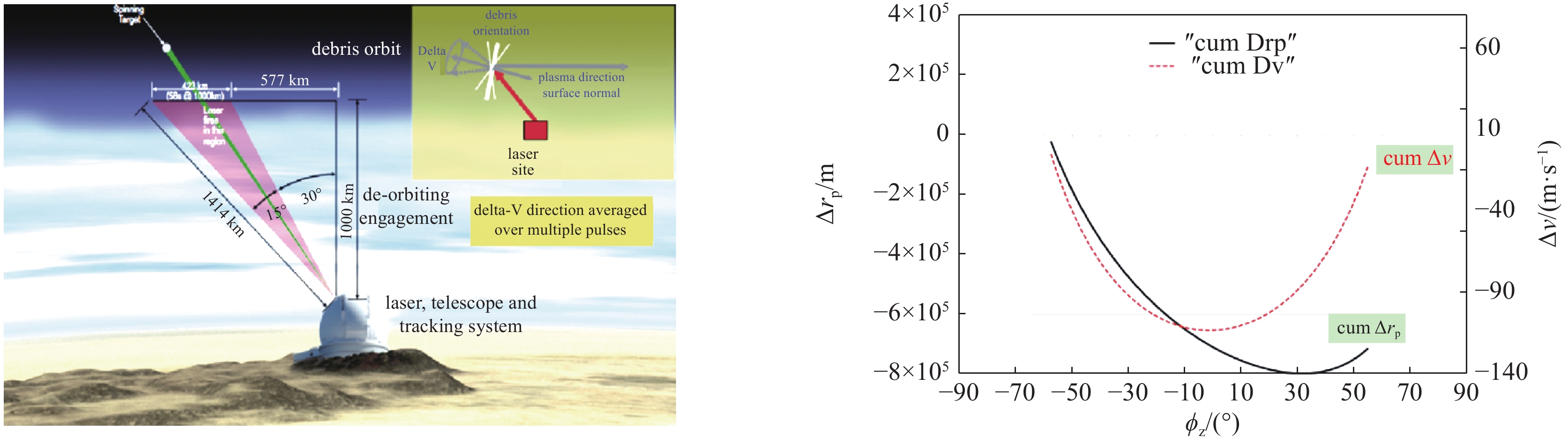
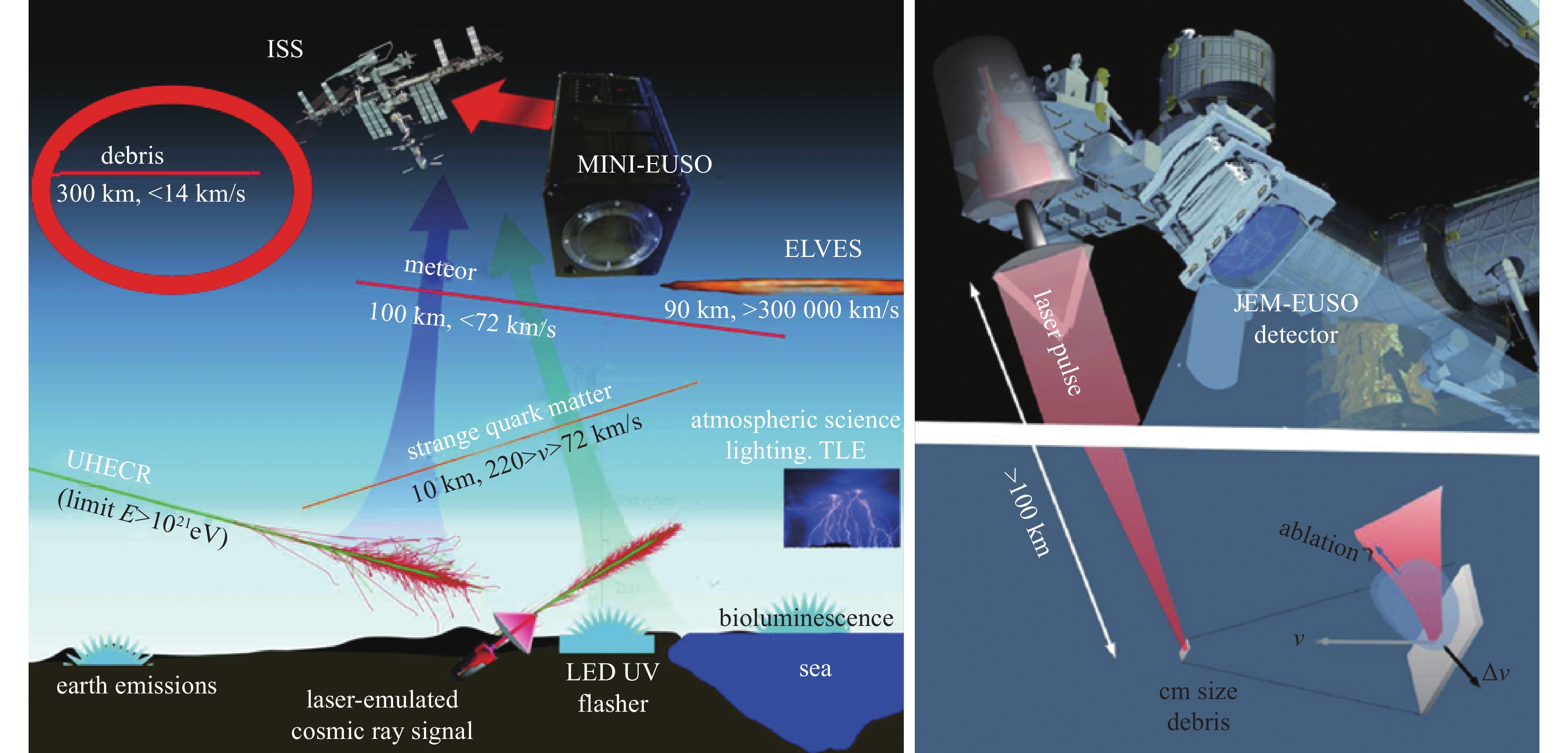
Removal of space debris by pulsed laser: Overview and future perspective
-
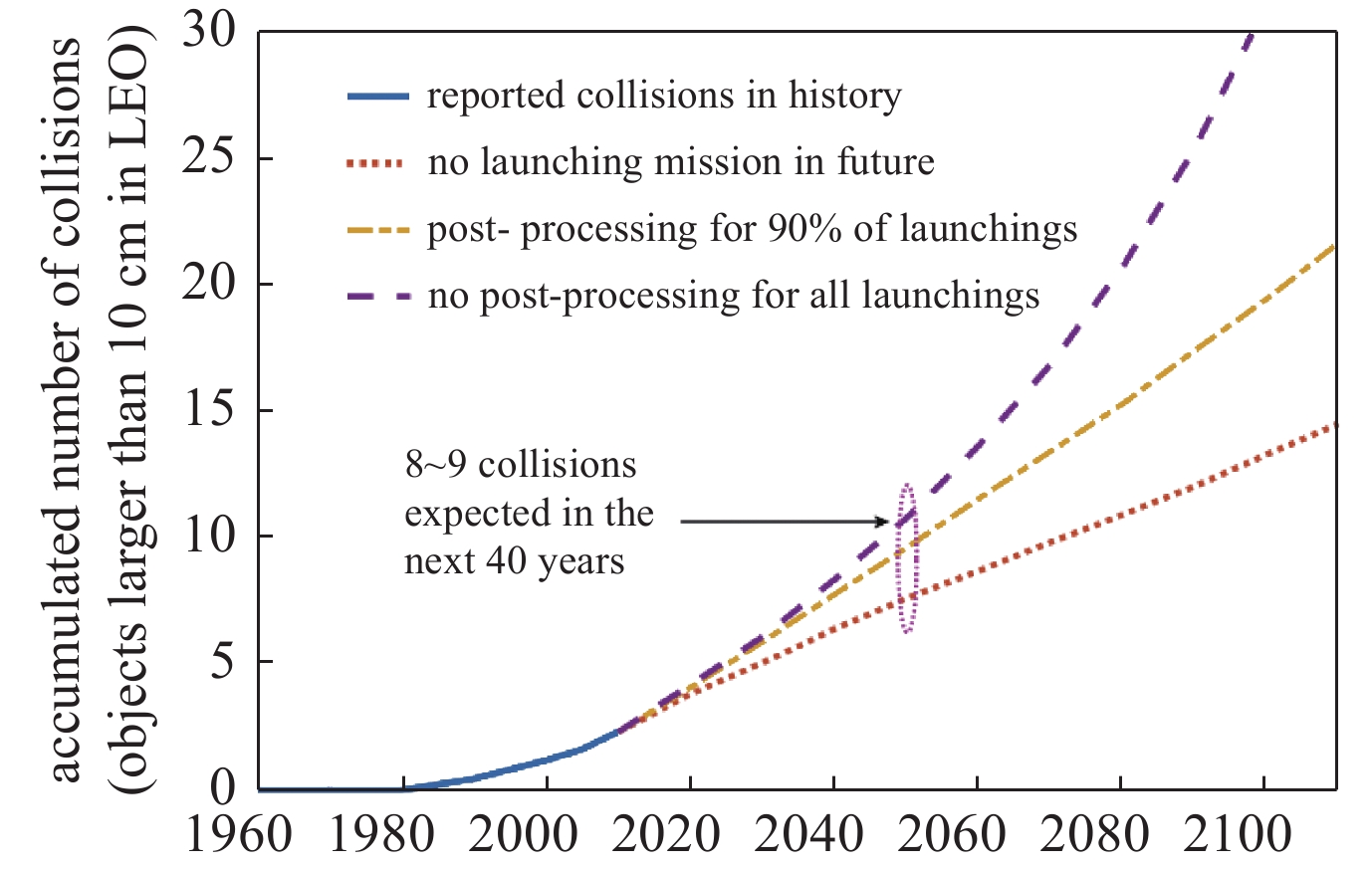
摘要: 近年来,近地轨道的空间碎片问题对航天应用的威胁日益严峻。通过主动移除技术手段减少在轨空间碎片的数量,从而保障空间资源的可持续开发和航天器的安全运行,已成为相关领域研究的热点。溯源了空间碎片问题的产生及沿革,分析基于不同技术途径的主动移除方案的特点。重点研究了脉冲激光主动移除空间碎片的关键技术与科学问题,总结了现阶段的技术发展情况,并对未来天基激光移除空间碎片的发展方向给出了建议。Abstract: In recent years, the space debris has posed severe threat for aerospace applications. Active removal of space debris has been extensively investigated to preserve the sustainable development of space resources and maintain the safety of spacecrafts. In this paper, the origin and development of space debris problem is studied, and the characteristics of different active removal techniques are discussed. Besides, the technical difficulties and the scientific problem of space debris removal by using pulsed laser system is further studied, and the development of the method is reviewed. At last, this paper suggests potential development of space-based laser for removing space debris in the future.
-
Key words:
- space debris /
- plasma plume /
- laser removal technique /
- irradiation effect
-
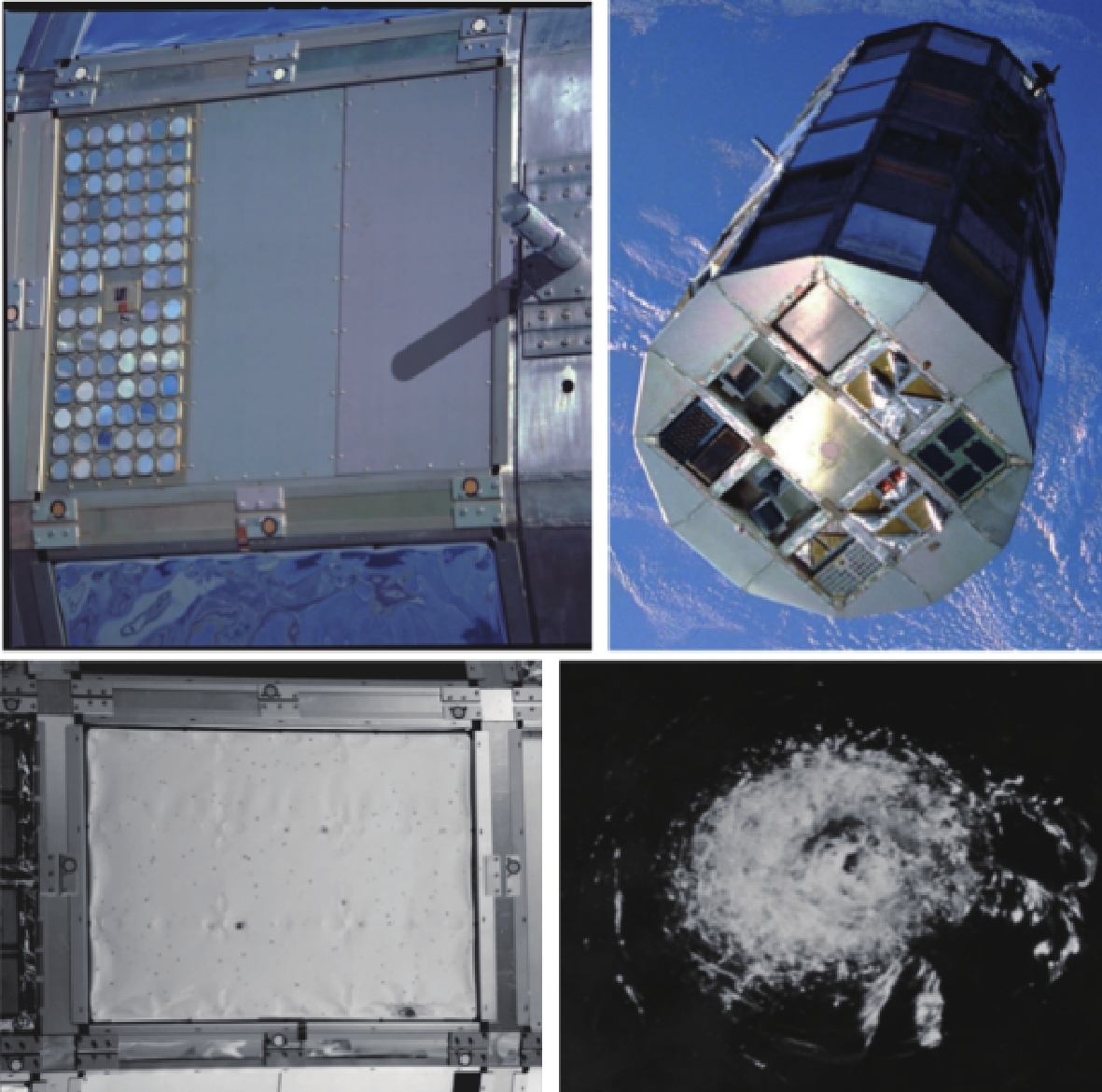
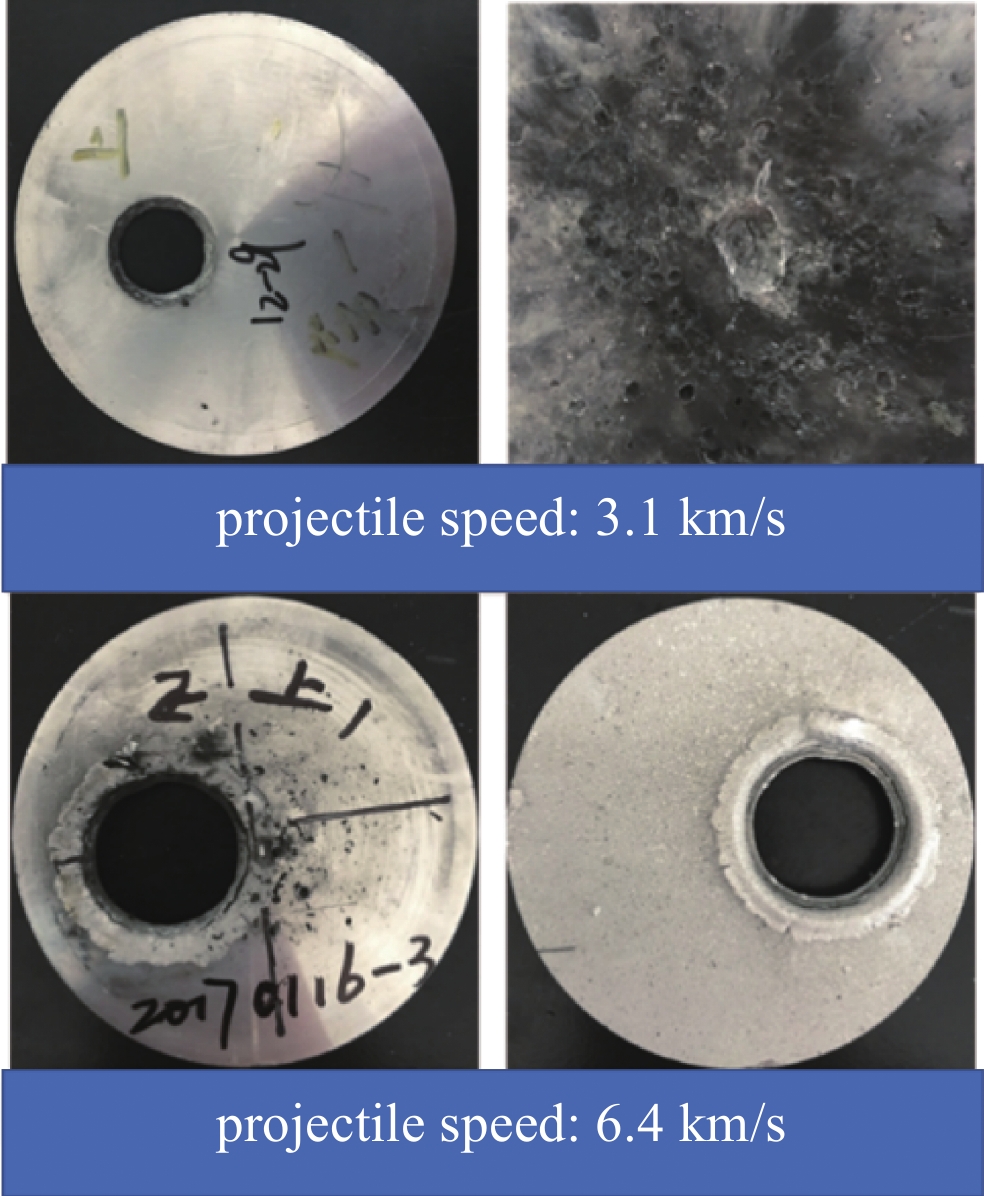
表 1 1992—1997美国航天飞机空间碎片碰撞情况统计
Table 1. Collisions of space debris with US space shuttle during 1992 to 1997
material of space debris number of collisions impact depth/mm position of collision Ti 1 0.57 observation window coating material(polymer) 3 0.57~1.1 hatch door, radiator Al 5 0.24~2.1 observation window, antenna, sealing system,
PLB door, bracket trunnionstainless steel 5 1.0~2.8 radiator meteoroids 4 0.4~1.4 radiation pipeline, antenna, sealing system -
[1] 郑永超, 赵思思, 李同, 等. 激光空间碎片移除技术发展与展望[J]. 空间碎片研究, 2020, 20(4):1-10. (Zheng Yongchao, Zhao Sisi, Li Tong, et al. Current status and development of laser active debris removal technology[J]. Space Debris Research, 2020, 20(4): 1-10 [2] Le May S, Gehly S, Carter B A, et al. Space debris collision probability analysis for proposed global broadband constellations[J]. Acta Astronautica, 2018, 151: 445-455. doi: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2018.06.036 [3] 王钊, 杨东春, 康志宇. 空间碎片主动移除任务的相关法律问题[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报(社会科学版), 2015, 28(2):44-48. (Wang Zhao, Yang Dongchun, Kang Zhiyu. Legal matters about space debris removing[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics (Social Sciences Edition), 2015, 28(2): 44-48 [4] Kessler D J. Collisional cascading: the limits of population growth in low earth orbit[J]. Advances in Space Research, 1991, 11(12): 63-66. doi: 10.1016/0273-1177(91)90543-S [5] 江海, 刘静. 空间碎片与空间交通管理[J]. 空间碎片研究, 2019, 19(1):39-44. (Jiang Hai, Liu Jing. Space debris and space traffic management[J]. Space Debris Research, 2019, 19(1): 39-44 [6] Klinkrad H. Space debris: models and risk analysis[M]. Berlin: Springer, 2006. [7] 罗刚桥. 空间碎片减缓措施及其研究对策[J]. 中国空间科学技术, 2001, 21(6):33-42. (Luo Gangqiao. The mitigation measures of space debris and the strategy of study[J]. Chinese Space Science and Technology, 2001, 21(6): 33-42 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-758X.2001.06.006 [8] Šilha J. Space debris: optical measurements[M]//Kabáth P, Jones D, Skarka M. Reviews in Frontiers of Modern Astrophysics. Cham: Springer, 2020: 1-21. [9] Pool R. Scrapheap in the sky [Technology space debris][J]. Engineering & Technology, 2021, 16(3): 44-47. [10] 龚自正, 杨继运, 代福, 等. CAST空间碎片超高速撞击试验研究进展[J]. 航天器环境工程, 2009, 26(4):301-306. (Gong Zizheng, Yang Jiyun, Dai Fu, et al. M/OD hypervelocity impact tests carried out in CAST[J]. Spacecraft Environment Engineering, 2009, 26(4): 301-306 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1379.2009.04.001 [11] 罗斌强, 张旭平, 郝龙, 等. 7 km/s以上超高速发射技术研究进展[J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2021, 41:021401. (Luo Binqiang, Zhang Xuping, Hao Long, et al. Advances on the techniques of ultrahigh-velocity launch above 7 km/s[J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2021, 41: 021401 [12] 王国语. 空间碎片管辖权及主动清除的法律依据[J]. 北京理工大学学报(社会科学版), 2014, 16(6):103-109. (Wang Guoyu. The jurisdiction of space debris and the legal basis of active space debris removal[J]. Journal of Beijing Institute of Technology (Social Sciences Edition), 2014, 16(6): 103-109 [13] 李怡勇, 陈勇, 李智, 等. 对一种利用人造粉尘清除空间碎片新方法的理论分析[J]. 空间科学学报, 2015, 35(1):77-85. (Li Yiyong, Chen Yong, Li Zhi, et al. Theoretic analysis on a new technique of dust-based active debris removal[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2015, 35(1): 77-85 [14] 王小锭, 张烽, 申麟, 等. 空间平台电动力绳系离轨装置技术研究[J]. 空间碎片研究, 2020, 20(2):22-31. (Wang Xiaoding, Zhang Feng, Shen Lin, et al. An EDT de-orbiting equipment for spacecraft[J]. Space Debris Research, 2020, 20(2): 22-31 [15] Mark C P, Kamath S. Review of active space debris removal methods[J]. Space Policy, 2019, 47: 194-206. doi: 10.1016/j.spacepol.2018.12.005 [16] Kelly P W, Bevilacqua R, Mazal L, et al. TugSat: removing space debris from geostationary orbits using solar sails[J]. Journal of Spacecraft and Rockets, 2018, 55(2): 437-450. doi: 10.2514/1.A33872 [17] Colombo C, Rossi A, Vedova F D, et al. Drag and solar sail deorbiting: re-entry time versus cumulative collision probability[C]//68th International Astronautical Congress (IAC 2017). IAF, 2017: 3535-3553. [18] Soulard R, Quinn M N, Tajima T, et al. ICAN: a novel laser architecture for space debris removal[J]. Acta Astronautica, 2014, 105(1): 192-200. doi: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2014.09.004 [19] Sänger E. On the theory of photon rocket[J]. Engineer Archive, 1953, 21(3): 213-226. doi: 10.1007/BF00535829 [20] Kantrowitz A. Propulsion to orbit by ground-based laser[J]. Astronautics and Aeronautics, 1972, 10(5): 74-76. [21] Phipps C R, Albrecht G, Friedman H, et al. ORION: clearing near-Earth space debris using a 20-kW, 530-nm, Earth-based, repetitively pulsed laser[J]. Laser and Particle Beams, 1996, 14(1): 1-44. doi: 10.1017/S0263034600009733 [22] Van Der Pas N, Lousada J, Terhes C, et al. Target selection and comparison of mission design for space debris removal by DLR׳s advanced study group[J]. Acta Astronautica, 2014, 102: 241-248. doi: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2014.06.020 [23] Shan Minghe, Guo Jian, Gill E. Review and comparison of active space debris capturing and removal methods[J]. Progress in Aerospace Sciences, 2016, 80: 18-32. doi: 10.1016/j.paerosci.2015.11.001 [24] 杜配冰, 刘钰, 陈志华, 等. 基于多项式混沌的激光大气传输湍流效应不确定度量化[J]. 现代应用物理, 2021, 12(2):29-34. (Du Peibing, Liu Yu, Chen Zhihua, et al. Uncertainty quantification for turbulence effect of laser propagation in atmosphere based on polynomial chaos[J]. Modern Applied Physics, 2021, 12(2): 29-34 [25] 赵璐, 王静, 郭苗军, 等. 基于微扰法研究涡旋光束在大气中传输的热晕效应[J]. 光电子·激光, 2021, 32(5):532-540. (Zhao Lu, Wang Jing, Guo Miaojun, et al. The thermal blooming effect of vortex beam propagation in the atmosphere is studied by perturbation method[J]. Journal of Optoelectronics·Laser, 2021, 32(5): 532-540 [26] Schall W O. Laser radiation for cleaning space debris from lower earth orbits[J]. Journal of Spacecraft and Rockets, 2002, 39(1): 81-91. doi: 10.2514/2.3785 [27] Vasile M, Maddock C, Saunders C. Orbital debris removal with solar concentrators[C]//61st International Astronautical Congress. 2010. [28] Vetrisano M, Thiry N, Vasile M. Detumbling large space debris via laser ablation[C]//2015 IEEE Aerospace Conference. IEEE, 2015: 1-10. [29] 杨武霖, 陈川, 余谦, 等. 天基激光驱动空间碎片降轨效果仿真研究[J]. 航天器环境工程, 2018, 35(3):217-222. (Yang Wulin, Chen Chuan, Yu Qian, et al. Simulation of space debris de-orbiting by space-based laser ablation[J]. Spacecraft Environment Engineering, 2018, 35(3): 217-222 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1379.2018.03.003 [30] 吴波, 金星. 激光辐照下圆锥体空间碎片的激光烧蚀力与力矩分析方法[J]. 空间碎片研究, 2019, 19(4):28-33. (Wu Bo, Jin Xing. Laser ablation force and moment analysis method for conical space debris under laser irradiation[J]. Space Debris Research, 2019, 19(4): 28-33 [31] Bennet F, Conan R, D'Orgeville C, et al. Adaptive optics for laser space debris removal[C]//Proceedings of SPIE 8447. Adaptive Optics Systems III. 2012: 844744. [32] Liedahl D A, Rubenchik A, Libby S B, et al. Pulsed laser interactions with space debris: target shape effects[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2013, 52(5): 895-915. doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2013.05.019 [33] Phipps C R. Laser space debris removal: now, not later[C]//Proceedings of SPIE 9255. XX International Symposium on High-Power Laser Systems and Applications 2014. 2015: 92553Q. [34] Phipps C R. L’ADROIT–A spaceborne ultraviolet laser system for space debris clearing[J]. Acta Astronautica, 2014, 104(1): 243-255. doi: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2014.08.007 [35] Phipps C R, Bonnal C. A spaceborne, pulsed UV laser system for re-entering or nudging LEO debris, and re-orbiting GEO debris[J]. Acta Astronautica, 2016, 118: 224-236. doi: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2015.10.005 [36] 陈川, 杨武霖, 余谦, 等. 激光驱动接力移除空间碎片的小卫星星座及可行性研究[J]. 宇航学报, 2019, 40(2):156-163. (Chen Chuan, Yang Wulin, Yu Qian, et al. A laser driven relay small satellite constellation for space debris active removal and feasibility study[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2019, 40(2): 156-163 [37] 赵剑衡. 激光清除空间碎片分析[C]//第十四届全国物理力学学术会议缩编文集. 2016: 1.Zhao Jianheng. Analysis on laser removal of space debris[C]//Condensed Proceedings of the 14th National Conference on Physical Mechanics. 2016: 1. [38] 金云声, 张兴卫, 谭福礼, 等. 干涉式冲量摆测试装置及其双精度数据处理方法[J]. 光学学报, 2017, 37:0512001. (Jin Yunsheng, Zhang Xingwei, Tan Fuli, et al. Testing device based on interferometric ballistic pendulum and its double precision data processing method[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2017, 37: 0512001 doi: 10.3788/AOS201737.0512001 [39] 叶继飞, 洪延姬. 基于扭秤的激光干涉差动测量微小冲量方法[J]. 应用光学, 2013, 34(6):990-994. (Ye Jifei, Hong Yanji. Laser interference differential measurement of micro impulse based on torsion balance[J]. Journal of Applied Optics, 2013, 34(6): 990-994 [40] Afanas’ev Y V, Basov N G, Krokhin O N, et al. Gas-dynamic processes in irradiation of solids[J]. Soviet Physics Technical Physics, 1969, 14(5): 669-676. [41] Sprangle P, Esarey E, Ting A. Nonlinear theory of intense laser-plasma interactions[J]. Physical Review Letters, 1990, 64(17): 2011-2014. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.64.2011 [42] Holmes B S, Maher W E, Hall R B. Laser-target interaction near the plasma-formation threshold[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1980, 51(11): 5699-5707. doi: 10.1063/1.327569 [43] Shih C Y, Wu Chengping, Shugaev M V, et al. Atomistic modeling of nanoparticle generation in short pulse laser ablation of thin metal films in water[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2017, 489: 3-17. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2016.10.029 [44] Mahmood S, Rawat R S, Springham S V, et al. Material ablation and plasma plume expansion study from Fe and graphite targets in Ar gas atmosphere[J]. Applied Physics A, 2010, 101(4): 695-699. doi: 10.1007/s00339-010-5951-2 [45] Schmitz T A, Koch J, Günther D, et al. Characterization of aerosol plumes in nanosecond laser ablation of molecular solids at atmospheric pressure[J]. Applied Physics B, 2010, 100(3): 521-533. doi: 10.1007/s00340-010-4112-9 [46] 袁红, 童慧峰, 李牧, 等. 强激光加载真空中铝靶冲量耦合的数值模拟[J]. 激光技术, 2012, 36(4):520-523. (Yuan Hong, Tong Huifeng, Li Mu, et al. Numerical simulation of impulse coupling to aluminum in laser ablation in vacuum[J]. Laser Technology, 2012, 36(4): 520-523 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3806.2012.04.022 [47] Pakhomov A V, Gregory D A. Ablative laser propulsion: an old concept revisited[J]. AIAA Journal, 2000, 38(4): 725-727. doi: 10.2514/2.1021 [48] Phipps C R, Baker K L, Libby S B, et al. Removing orbital debris with pulsed lasers[J]. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2012, 1464(1): 468-480. [49] Phipps C R, Boustie M, Chevalier J M, et al. Laser impulse coupling measurements at 400 fs and 80 ps using the LULI facility at 1057 nm wavelength[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2017, 122: 193103. doi: 10.1063/1.4997196 [50] D'Souza B C. Development of impulse measurement techniques for the investigation of transient forces due to laser-induced ablation[D]. Los Angeles: University of Southern California, 2007. [51] Phipps C R Jr, Turner T P, Harrison R F, et al. Impulse coupling to targets in vacuum by KrF, HF, and CO2 single-pulse lasers[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1988, 64(3): 1083-1096. doi: 10.1063/1.341867 [52] Phipps C, Luke J, Funk D, et al. Laser impulse coupling at 130 fs[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2006, 252(13): 4838-4844. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2005.07.079 [53] Munafò A, Alberti A, Pantano C, et al. A computational model for nanosecond pulse laser-plasma interactions[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2020, 406: 109190. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2019.109190 [54] Scharring S, Eisert L, Lorbeer R A, et al. Momentum predictability and heat accumulation in laser-based space debris removal[J]. Optical Engineering, 2018, 58: 011004. [55] 常浩, 金星, 叶继飞, 等. 激光功率密度对纳秒激光烧蚀冲量耦合影响的数值模拟[J]. 推进技术, 2013, 34(10):1426-1431. (Chang Hao, Jin Xing, Ye Jifei, et al. Numerical simulation of laser power density effect on nanosecond laser ablation impulse coupling[J]. Journal of Propulsion Technology, 2013, 34(10): 1426-1431 [56] 方英武, 赵尚弘, 杨丽薇, 等. 地基激光辐照近地轨道小尺度空间碎片作用规律研究[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2016, 45:229002. (Fang Yingwu, Zhao Shanghong, Yang Liwei, et al. Research on action rules of ground-based laser irradiating small scale space debris in LEO[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2016, 45: 229002 doi: 10.3788/irla201645.0229002 [57] 王卫杰, 李怡勇, 罗文, 等. 天基激光清除空间碎片任务分析[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2019, 41(6):1374-1382. (Wang Weijie, Li Yiyong, Luo Wen, et al. Mission analysis on removal of space debris with space-based laser[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2019, 41(6): 1374-1382 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001506X.2019.06.27 [58] 王治, 万峰, 吴剑锋, 等. 卫星总装过程异构数据物联集成技术研究[J]. 西北工业大学学报, 2020, 38(S1):44-52. (Wang Zhi, Wan Feng, Wu Jianfeng, et al. Research on integration technology of heterogeneous data of satellite assembly process[J]. Journal of Northwestern Polytechnical University, 2020, 38(S1): 44-52 -




 下载:
下载: