Data compression for optical spectrum-encoding imaging system
-
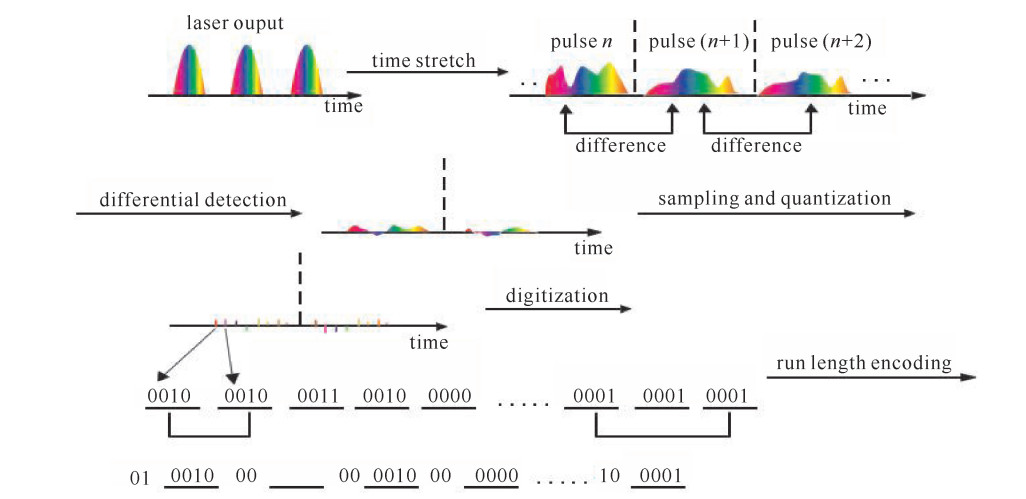
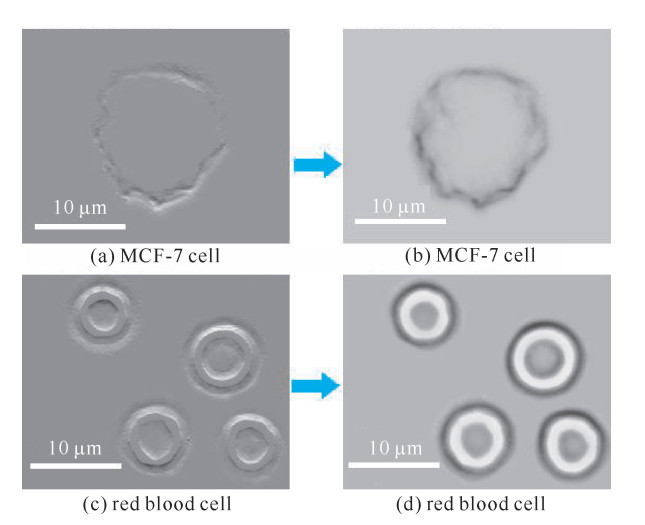
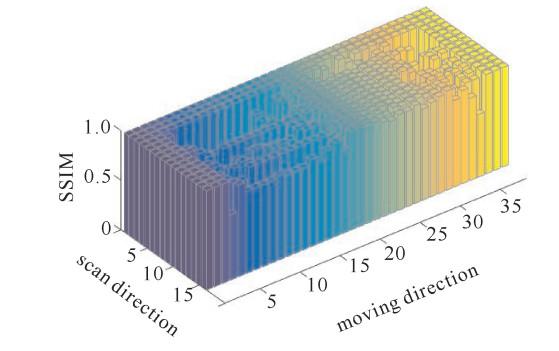
摘要: 利用时间拉伸显微成像系统观察并记录非重复动态随机现象,在其超高成像速度和高空间分辨率下必定会产生大量的数据。一种基于差分检测和游程编码的数据压缩方法,可以有效地解决时间拉伸成像系统的数据存储问题。差分检测可以消除连续相同的信号,只检测出相邻信号的差异,从而提高游程编码算法的有效性。实验中,采用扫描频率为77.76 MHz的时间拉伸显微成像对分辨率板、人红细胞和人乳腺癌细胞线性扫描成像。实验结果表明,数据压缩比可以达到8.47,对比分析发现经过差分检测方法可以获得更高的压缩比。另外,通过计算重建后的图像与原图的结构相似性(SSIM)值发现,经过数据压缩后高质量的图像可以被重建。Abstract: Serial time-stretch imaging technique with its high line-scan rate can observe and record fast non-repetitive events. However, it is inevitable that a fast imaging system would generate a massive amount of data. This paper proposes a data compression methodbased on differential detection and run-length encoding for time-stretch imaging technique, which can efficiently solve the existing problem of data volume in the back-end digital signal processing. Differential detection can eliminate identical signals and only distinguish the difference between consecutive scans, while the run-length encoding algorithm is suitable for encoding the same repeated signals, to further improve the effectiveness of run-length encoding algorithm. In the experiment, a 77.76 MHz line-scan imaging system is demonstrated with the resolution test target, red blood cell and MCF cell. It turns out that the compression rate of 8.47 is proved. Through analysis, it is found that the method with differential detection can achieve higher compression rate than the method without differential detection, especially when the sampling resolution is low. The structured similarity index measurement(SSIM) calculation between the original image and the reconstructed image shows high quality images can be reconstructed after compression by the proposed method.
-
表 1 实验仪器的关键参数
Table 1. Key parameters of experiment apparatus
center wavelength of laser/nm 10 dB width of laser/nm pulsewidth/fs repetition rate of pulse/MHz groove density of diffraction grating/(line·mm-1) 1557 8 80 77.76 600 focal length of convex lens1/mm focal length of convex lens2/mm dispersion coefficient /(ps·nm-1·km-1) length of DCF/km bandwidth of balanced photodetection/GHz 15 60 130 12.1 50 bandwidth of oscilloscope/GHz sampling rate of oscilloscope/(Gs·s-1) delay of TODL/ns 4 20 12.86 -
[1] 王哲斌, 杨冬, 张惠鸽, 等. 光学条纹相机时间扫描性能应用[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2012, 24(8): 1836-1840. doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20122408.1836Wang Zhebin, Yang Dong, Zhang Huige, et al. Sweep time performance of optic streak camera. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2012, 24(8): 1836-1840 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20122408.1836 [2] 李剑, 但加坤, 赵新才, 等. 超高速激光纹影技术测量脉冲功率驱动的磁重联现象[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2014, 26: 092006. doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201426.092006Li Jian, Dan Jiakun, Zhao Xincai, et al. Measurement of magnetic reconnection driven by pulse power using ultra high speed laser schlieren technology. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2014, 26: 092006 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201426.092006 [3] Goda K, Tsia K K, Jalali B. Serial time-encoded amplified imaging for real-time observation of fast dynamic phenomena[J]. Nature, 2009, 458(7242): 1145-1149. doi: 10.1038/nature07980 [4] Tsia K K, Goda K, Capewell D, et al. Performance of serial time-encoded amplified microscope[J]. Optics Express, 2010, 18(10): 10016-10028. doi: 10.1364/OE.18.010016 [5] 陈宏伟, 邢芳俭, 王雨西, 等. 超快平面显微成像技术[J]. 数据采集与处理, 2014, 29(6): 895-900. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJCJ201406005.htmChen Hongwei, Xing Fangjian, Wang Yuxi, et al. Ultra-fast surface microscopic imaging technique. Journal of Data Acquisition and Processing, 2014, 29(6): 895-900 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJCJ201406005.htm [6] 焦小毅, 林静, 程晓明, 等. 时间序列编码放大显微系统的成像方法研究[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2016, 28: 101008. doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201628.160103Jiao Xiaoyi, Lin Jing, Cheng Xiaoming, et al. Imaging method for serial time-encoded amplified microscope. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2016, 28: 101008 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201628.160103 [7] Mahjoubfar A, Churkin D V, Barland S, et al. Time stretch and its applications[J]. Nature Photonics, 2017, 11(6): 341-351. doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2017.76 [8] Mahjoubfar A, Goda K, Betts G, et al. Optically amplified detection for biomedical sensing and imaging[J]. J Opt Soc Am A, 2013, 30(10): 2124-2132. doi: 10.1364/JOSAA.30.002124 [9] Lei C, Ito T, Ugawa M, et al. High-throughput label-free image cytometry and image-based classification of live Euglena gracilis[J]. Biomedical Optics Express, 2016, 7(7): 2703-2708. doi: 10.1364/BOE.7.002703 [10] Roussel E, Evain C, Le Parquier M, et al. Observing microscopic structures of a relativistic object using a time-stretch strategy[J]. Science Report, 2015, 5: 10330. [11] Chen C L, Mahjoubfar A, Jalali B. Optical data compression in time stretch imaging[J]. PlOS ONE, 2015, 10(4): e0125106. [12] Guo Q, Chen H, Weng Z, et al. Compressive sensing based high-speed time-stretch optical microscopy for two-dimensional image acquisition[J]. Optics Express, 2015, 23(23): 29639-29646. [13] Dai Bo, Zhuo Ran, Yin Songchao, et al. Ultrafast imaging with anti-aliasing based on optical time-division multiplexing[J]. Optics Letters, 2016, 41(5): 882-885. -





 下载:
下载: