Analysis of high-altitude electromagnetic pulse effect on wireless communication network from hierarchical perspective
-
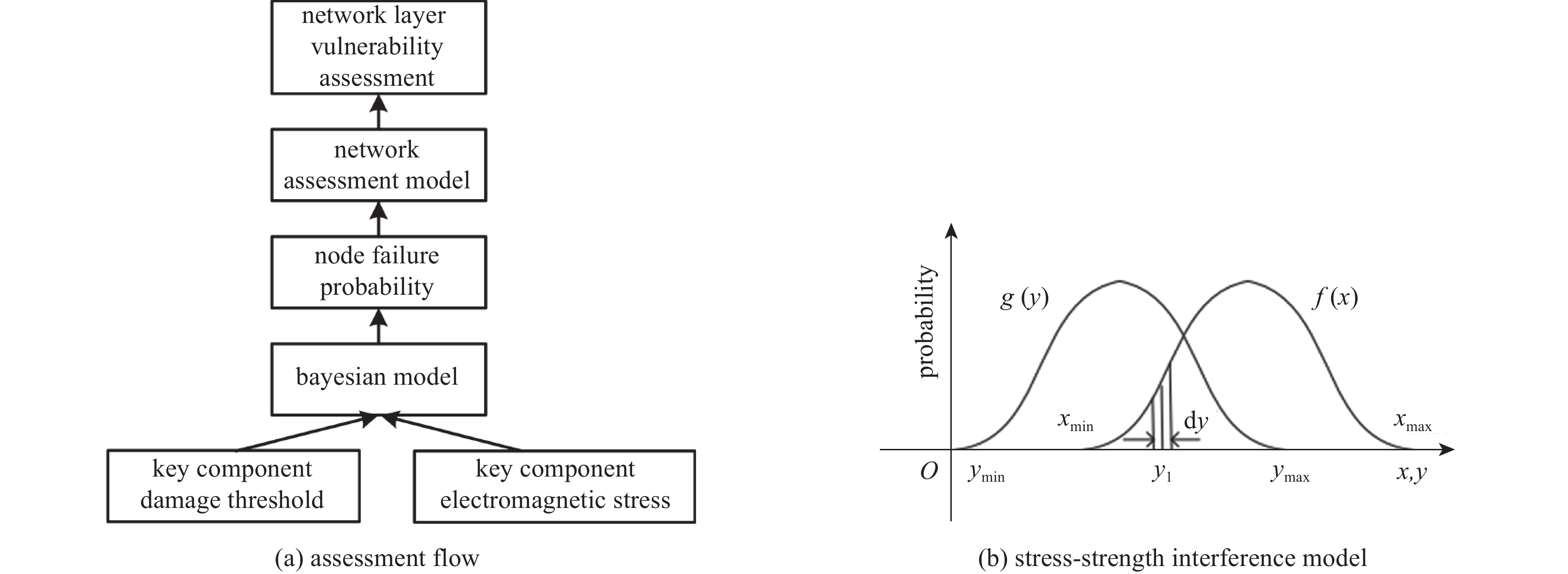
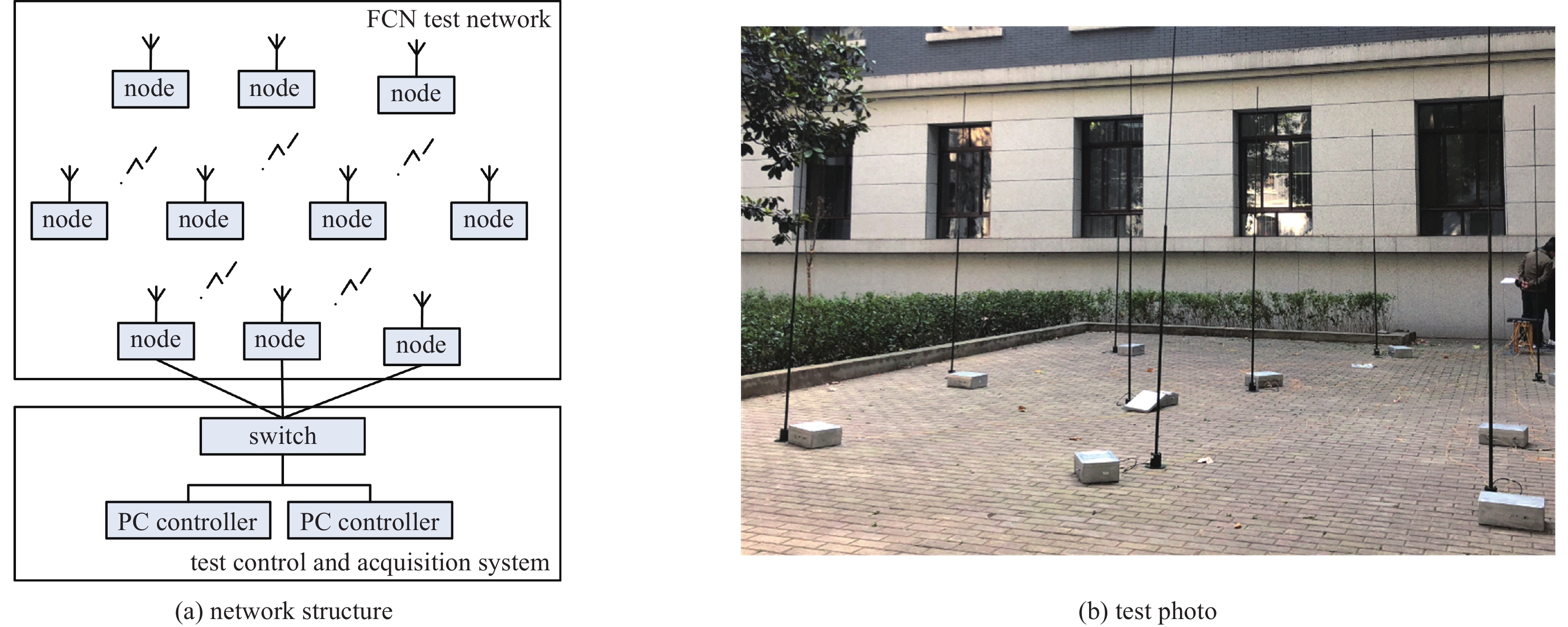
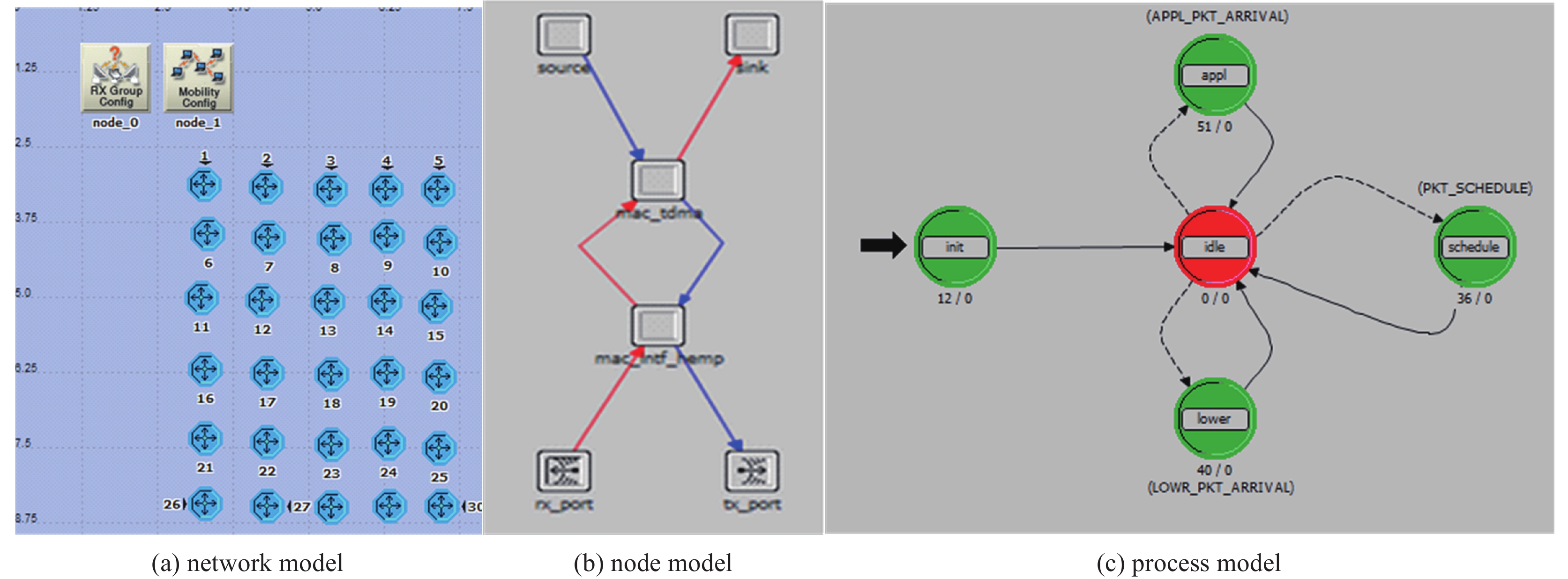
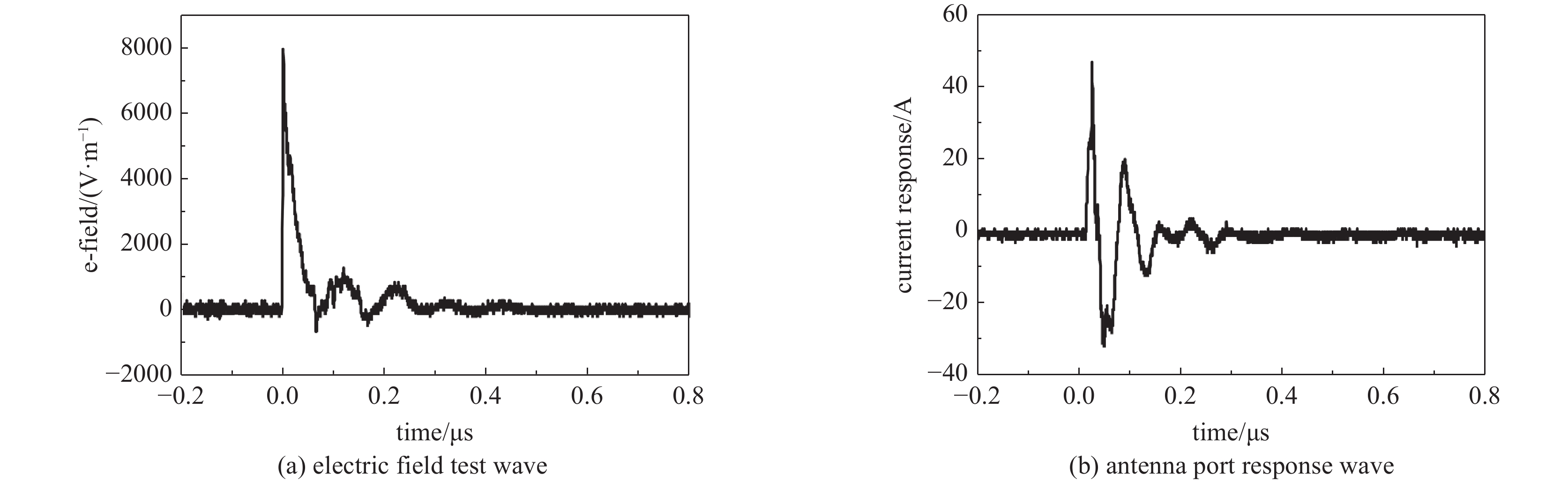
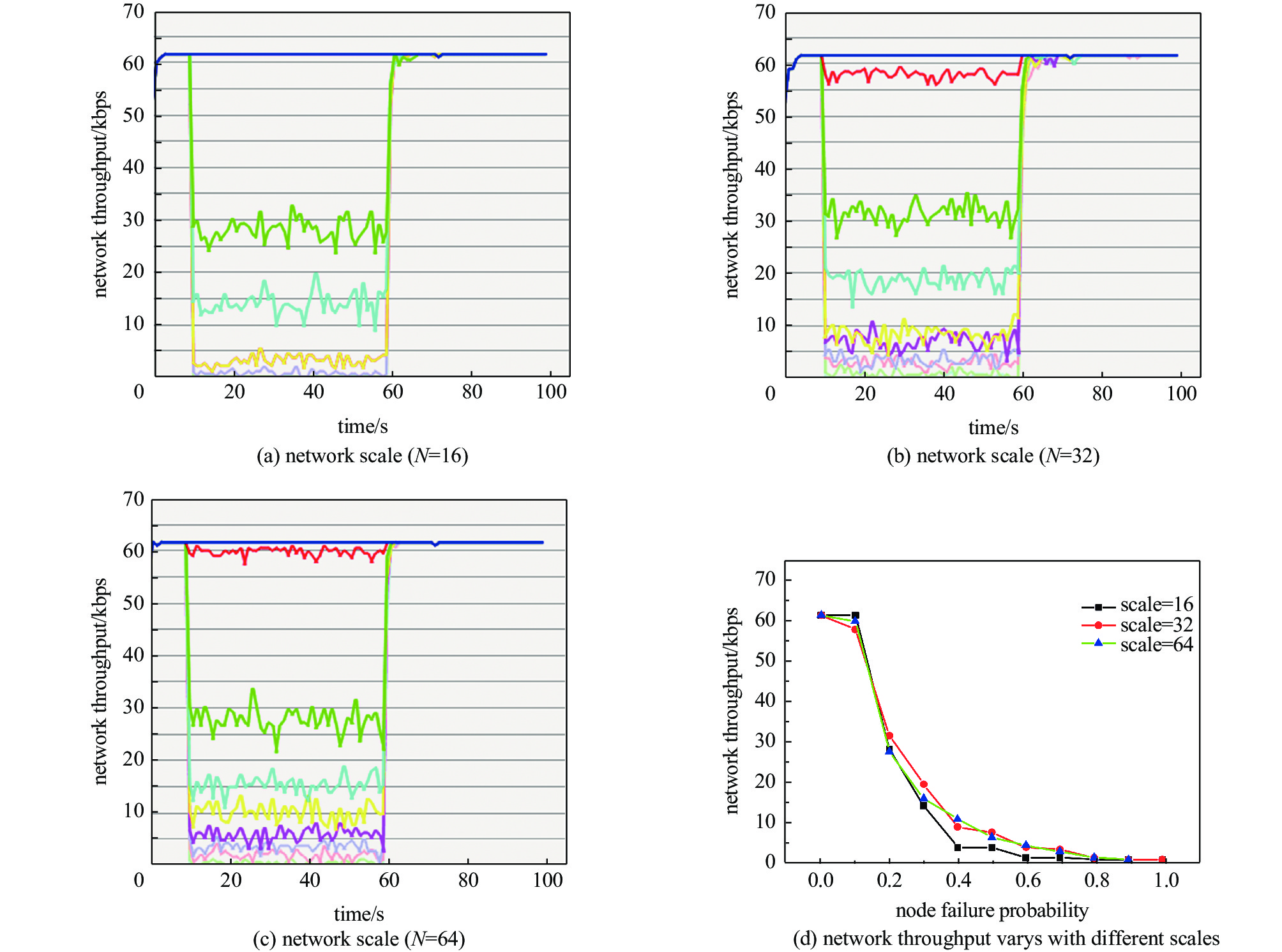
摘要: 从分层视角研究无线通信网络高空电磁脉冲效应,提出了一种具有层级属性的网络级效应评估方法。设计研制了一种无线通信网络效应试验仿真平台,网络使用典型全连通拓扑结构,网络节点使用超外差式收发机,网络运行在超短波频段。开展了小型网络脉冲辐照效应试验和效应机理分析,网络仿真研究了网络规模不同条件下节点失效概率对网络性能的影响。得到以下结论:(1)设备级效应对低层级效应具备一定冗余容错能力,这取决于效应评价指标的选择和损伤组件的功能属性;(2)网络级效应对设备级效应具有潜在放大效果,个别节点失效可能造成网络性能严重下降甚至瘫痪。Abstract: To study the representation of high altitude electromagnetic pulse effect in communication network from a hierarchical perspective, a network-level effect assessment method with hierarchical feature was proposed. A network effect test and simulation platform for wireless network was designed and developed. The platform employs a typically fully-connected network, in which the communication node is designed based on the framework of superheterodyne transceivers with operating on very high frequency ranges. The effect of pulse irradiation test on this network platform was tested and its effect mechanism was analyzed. The influence of node failure probability on network performance under different network scales was studied by using OPNET software. The following conclusions are drawn: (1) The equipment-level effect has a certain redundant fault-tolerance for the lower-level damage effect, which depends on the selection of effect assessment indicators and the function properties of the damaged components; (2) The network-level effect has a potential effect on the equipment-level effect, and the failure of individual nodes may cause serious degradation or even paralysis of the whole network.
-
表 1 基于层级关系的效应现象列表
Table 1. List of effect phenomena based on hierarchy
layer effect(indicator) effect type network throughput declined rapidly performance degradation equipment receive sensitivity declined by 30~50 dB performance degradation component LNA grain declined by 30~50 dB damage device the internal triodes of LNA have different degrees of breakdown damage -
[1] 毛从光, 程引会, 谢彦召. 高空电磁脉冲技术基础[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2019Mao Congguang, Cheng Yinhui, Xie Yanzhao. Fundamentals of high altitude electromagnetic pulse technology[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2019 [2] 周璧华, 陈彬, 石立华. 电磁脉冲及其工程防护[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2003Zhou Bihua, Chen Bin, Shi Lihua. EMP and EMP protection[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2003 [3] Giri D V, Hoad R, Sabath F. High-power electromagnetic effects on electronic systems[M]. Norwood: Artech House, 2020: 20-30. [4] Foster J S Jr, Gjelde E, Graham W R, et al. Report of the commission to assess the threat to the United States from electromagnetic pulse (EMP) attack: critical national infrastructures[R]. EMP Commission USA, 2008. [5] GJB538-88, 半导体器件电磁脉冲损伤阈值试验方法[S]GJB538-88, 半导体器件电磁脉冲损伤阈值试验方法[S]. (GJB538-88, Test method for electromagnetic pulse damage threshold of semiconductor devices[S] [6] 汪海洋, 周翼鸿, 李家胤, 等. 低噪声放大器有意电磁干扰效应(英文)[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2011, 23(11):2865-2871. (Wang Haiyang, Zhou Yihong, Li Jiayin, et al. LNA malfunctions under intentional electromagnetic interference[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2011, 23(11): 2865-2871 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20112311.2865 [7] 任兴荣. 半导体器件的电磁损伤效应与机理研究[D]. 西安: 西安电子科技大学, 2014Ren Xingrong. Research on the electromagnetic damage effects and mechanisms of semiconductor devices[D]. Xi’an: Xidian University, 2014 [8] 王洋. 接收机前端低噪声放大器设计及其电磁脉冲防护研究[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2011Wang Yang. Design and electromagnetic pulse protection research of receiver front-end LNA[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2011 [9] Camp M, Gerth H, Garbe H, et al. Predicting the breakdown behavior of microcontrollers under EMP/UWB impact using a statistical analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electromagnetic Compatibility, 2004, 46(3): 368-379. doi: 10.1109/TEMC.2004.831816 [10] Nitsch D, Camp M, Sabath F, et al. Susceptibility of some electronic equipment to HPEM threats[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electromagnetic Compatibility, 2004, 46(3): 380-389. doi: 10.1109/TEMC.2004.831842 [11] Coburn W O, Nguyen E, Reyzer R J, et al. High-altitude electromagnetic pulse survivability assessment of the Harris RF-3200 transceiver[R]. AD-A258 347, Adelphi, MD: Harry Diamond Laboratories, 1992. [12] Hoad R, Carter N J, Herke D, et al. Trends in EM susceptibility of IT equipment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electromagnetic Compatibility, 2004, 46(3): 390-395. doi: 10.1109/TEMC.2004.831815 [13] Hoad R, Carter N J, Herke D, et al. An investigation into radiated susceptibility of IT networks[C]//Proceedings of the International Symposium on Electromagnetic Compatibility. Eindhoven, The Netherland: QinetiQ, Electromagnetic Compatibility Group, 2004. [14] IEC TR 61000-1-3, Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) –part 1-3: general – the effects of high-altitude EMP (HEMP) on civil equipment and systems[S]. [15] IEC 61000-5-9, Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) - part 5-9: installation and mitigation guidelines – system-level susceptibility assessments for HEMP and HPEM[S]. [16] Frank H, Frisch I. Analysis and design of survivable networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communication Technology, 1970, 18(5): 501-519. doi: 10.1109/TCOM.1970.1090419 [17] 魏福林. 野战地域通信网拓扑层抗毁性研究[D]. 郑州: 解放军信息工程大学, 2006Wei Fulin. Research on invulnerability based on topological structure of regional communication networks[D]. Zhengzhou: Information Engineering University, 2006 [18] Mao Congguang, Canavero F. System-level vulnerability assessment for EME: from fault tree analysis to Bayesian networks—part I: methodology framework[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electromagnetic Compatibility, 2016, 58(1): 180-187. doi: 10.1109/TEMC.2015.2484067 [19] Mao Congguang, Canavero F G, Cui Zhitong, et al. System-level vulnerability assessment for EME: from fault tree analysis to Bayesian networks-part II: illustration to microcontroller system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electromagnetic Compatibility, 2016, 58(1): 188-196. doi: 10.1109/TEMC.2015.2502591 -





 下载:
下载: