| [1] |
Migliaccio M, Gradoni G, Arnaut L R. Electromagnetic reverberation: the legacy of Paolo Corona[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electromagnetic Compatibility, 2016, 58(3): 643-652. doi: 10.1109/TEMC.2016.2546183
|
| [2] |
Tian Zhihao, Huang Yi, Shen Yaochun, et al. Efficient and accurate measurement of absorption cross section of a lossy object in reverberation chamber using two one-antenna methods[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electromagnetic Compatibility, 2016, 58(3): 686-693. doi: 10.1109/TEMC.2016.2527363
|
| [3] |
Xu Qian, Huang Yi, Xing Lei, et al. B-scan in a reverberation chamber[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2016, 64(5): 1740-1750. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2016.2535121
|
| [4] |
程二威, 王平平, 赵敏, 等. 边界形变混响室设计与性能评估[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2021, 33:123002Cheng Erwei, Wang Pingping, Zhao Min, et al. Design and performance evaluation of boundary deformation reverberation chamber[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2021, 33: 123002
|
| [5] |
姜林, 王庆国, 程二威. 机械搅拌混响室独立样本数建模及实验[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2013, 25(11):3050-3054 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20132511.3050Jiang Lin, Wang Qingguo, Cheng Erwei. Modelling and experimental study of the number of independent samples in reverberation chamber with mechanical stirring[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2013, 25(11): 3050-3054 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20132511.3050
|
| [6] |
Kim J S, Mittra R. Performance evaluation of a mode-stirred reverberation chamber using the finite difference time domain (FDTD) simulation[C]//Proceedings of 2021 Asia-Pacific Symposium on Electromagnetic Compatibility. 2012: 173-176.
|
| [7] |
Harima K, Yamanaka Y. FDTD analysis on the effect of stirrers in a reverberation chamber[C]//Proceedings of 1999 International Symposium on Electromagnetic Compatibility. 1999: 260-263.
|
| [8] |
Primiani V M, Moglie F. Reverberation chamber performance varying the position of the stirrer rotation axis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electromagnetic Compatibility, 2014, 56(2): 486-489. doi: 10.1109/TEMC.2013.2285313
|
| [9] |
Bastianelli L, Primiani V M, Moglie F. Stirrer efficiency as a function of its axis orientation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electromagnetic Compatibility, 2015, 57(6): 1732-1735. doi: 10.1109/TEMC.2015.2477465
|
| [10] |
Moglie F, Bastianelli L, Primiani V M. Reliable finite-difference time-domain simulations of reverberation chambers by using equivalent volumetric losses[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electromagnetic Compatibility, 2016, 58(3): 653-660. doi: 10.1109/TEMC.2016.2548520
|
| [11] |
Carlberg U, Kildal P S, Carlsson J. Numerical study of position stirring and frequency stirring in a loaded reverberation chamber[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electromagnetic Compatibility, 2009, 51(1): 12-17. doi: 10.1109/TEMC.2008.2011818
|
| [12] |
Zhao Huapeng, Shen Zhongxiang. Fast wideband analysis of reverberation chambers using hybrid discrete singular convolution-method of moments and adaptive frequency sampling[J] IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 2015, 51: 7206804.
|
| [13] |
IEC 61000-4-21, Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) - Part 4-21: testing and measurement techniques—reverberation chamber test methods[S].
|
| [14] |
Xu Qian, Huang Yi, Xing Lei, et al. Average absorption coefficient measurement of arbitrarily shaped electrically large objects in a reverberation chamber[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electromagnetic Compatibility, 2016, 58(6): 1776-1779. doi: 10.1109/TEMC.2016.2587679
|
| [15] |
Carlberg U, Kildal P S, Wolfgang A, et al. Calculated and measured absorption cross sections of lossy objects in reverberation chamber[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electromagnetic Compatibility, 2004, 46(2): 146-154. doi: 10.1109/TEMC.2004.826878
|
| [16] |
Xu Qian, Huang Yi, Xing Lei, et al. Extract the decay constant of a reverberation chamber without satisfying Nyquist criterion[J]. IEEE Microwave and Wireless Components Letters, 2016, 26(3): 153-155. doi: 10.1109/LMWC.2016.2526027
|
| [17] |
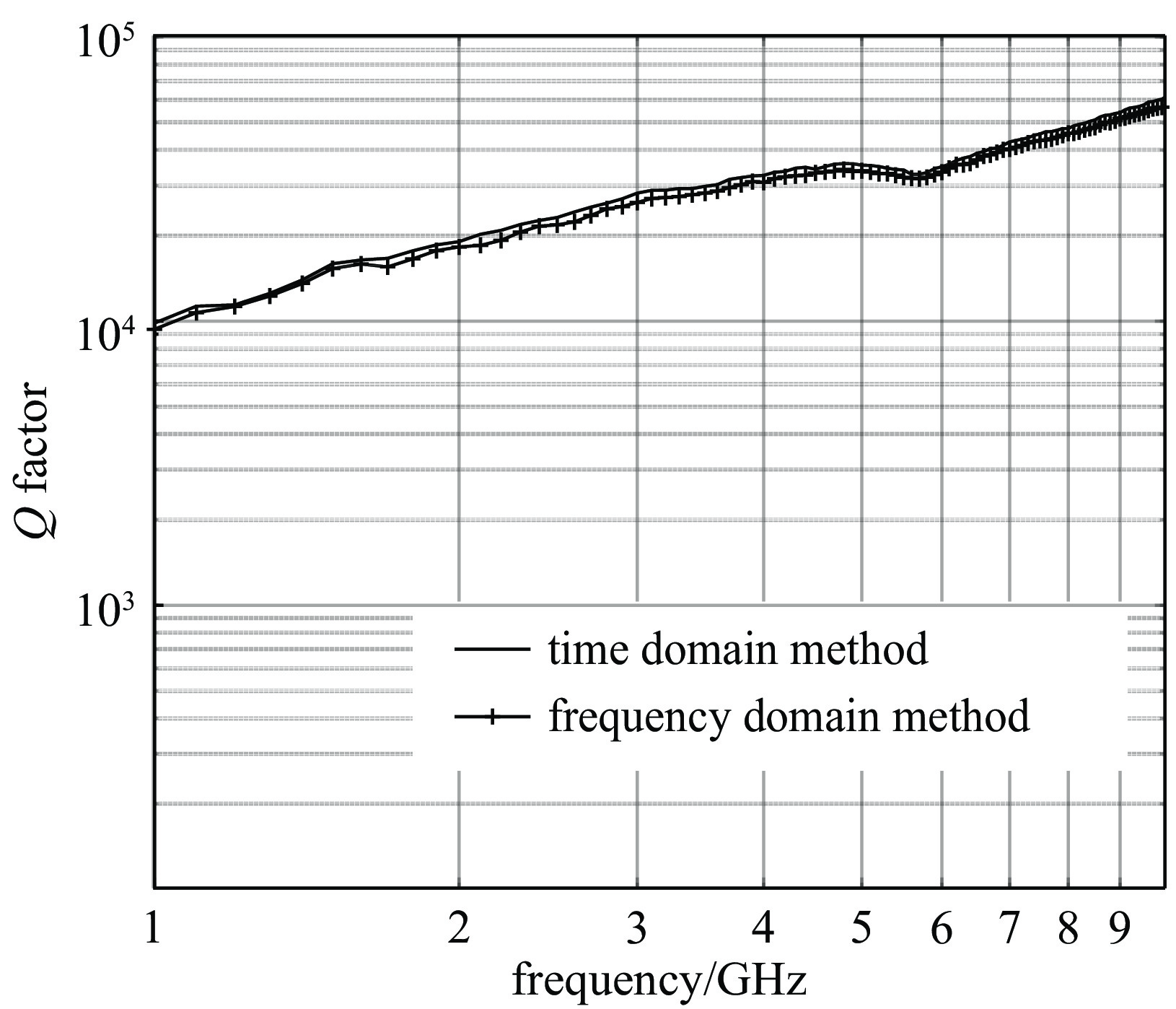
Cui Y, Wei G, Wang S, et al. Fast calculation of reverberation chamber Q-factor[J]. Electronics Letters, 2012, 48(18): 1116-1117. doi: 10.1049/el.2012.2106
|
| [18] |
Wang Song, Wu Zhancheng, Wei Guanghui, et al. A new method of evaluating reverberation chamber Q-factor with experimental validation[J]. Progress in Electromagnetics Research Letters, 2013, 36: 103-112. doi: 10.2528/PIERL12090710
|
| [19] |
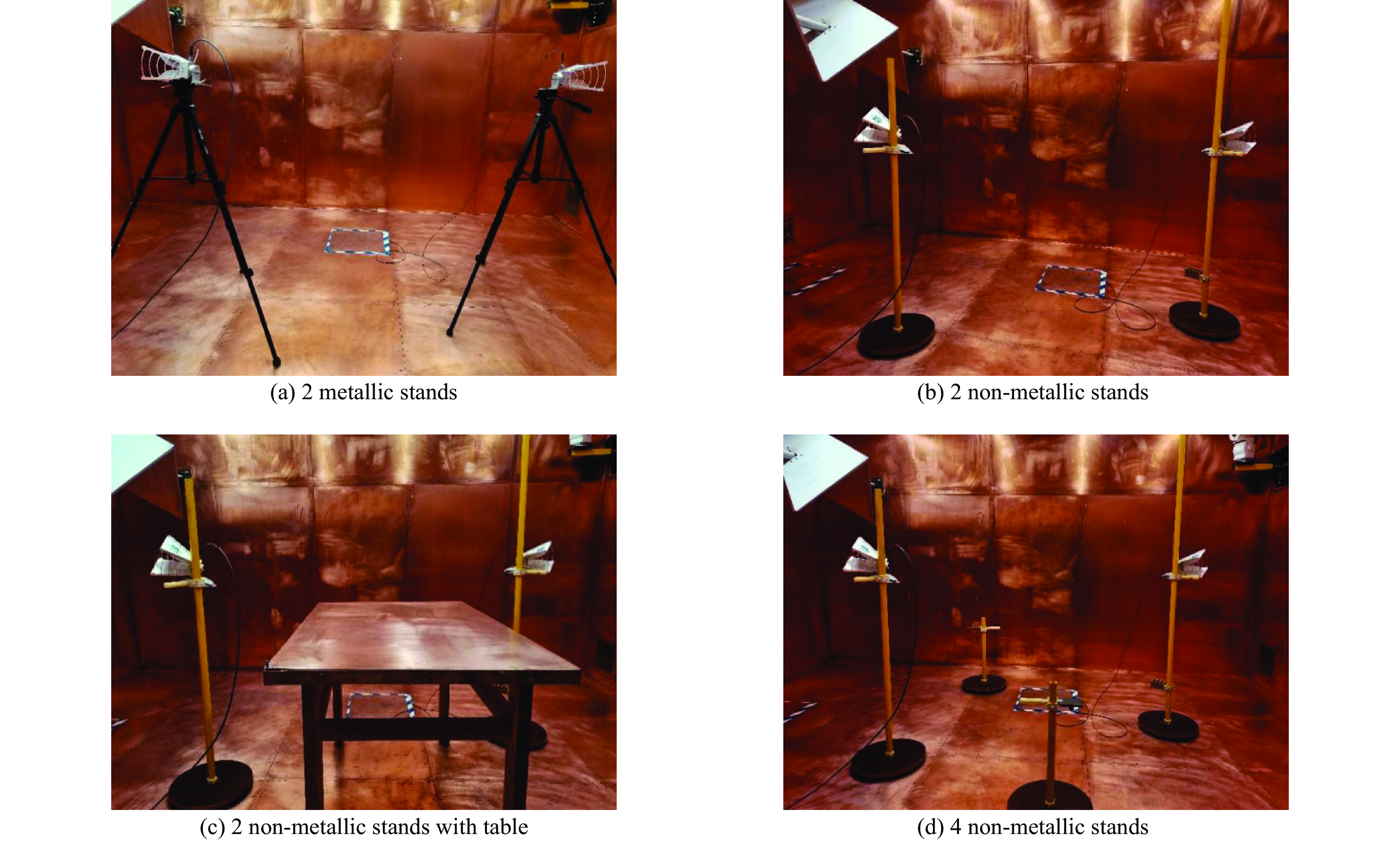
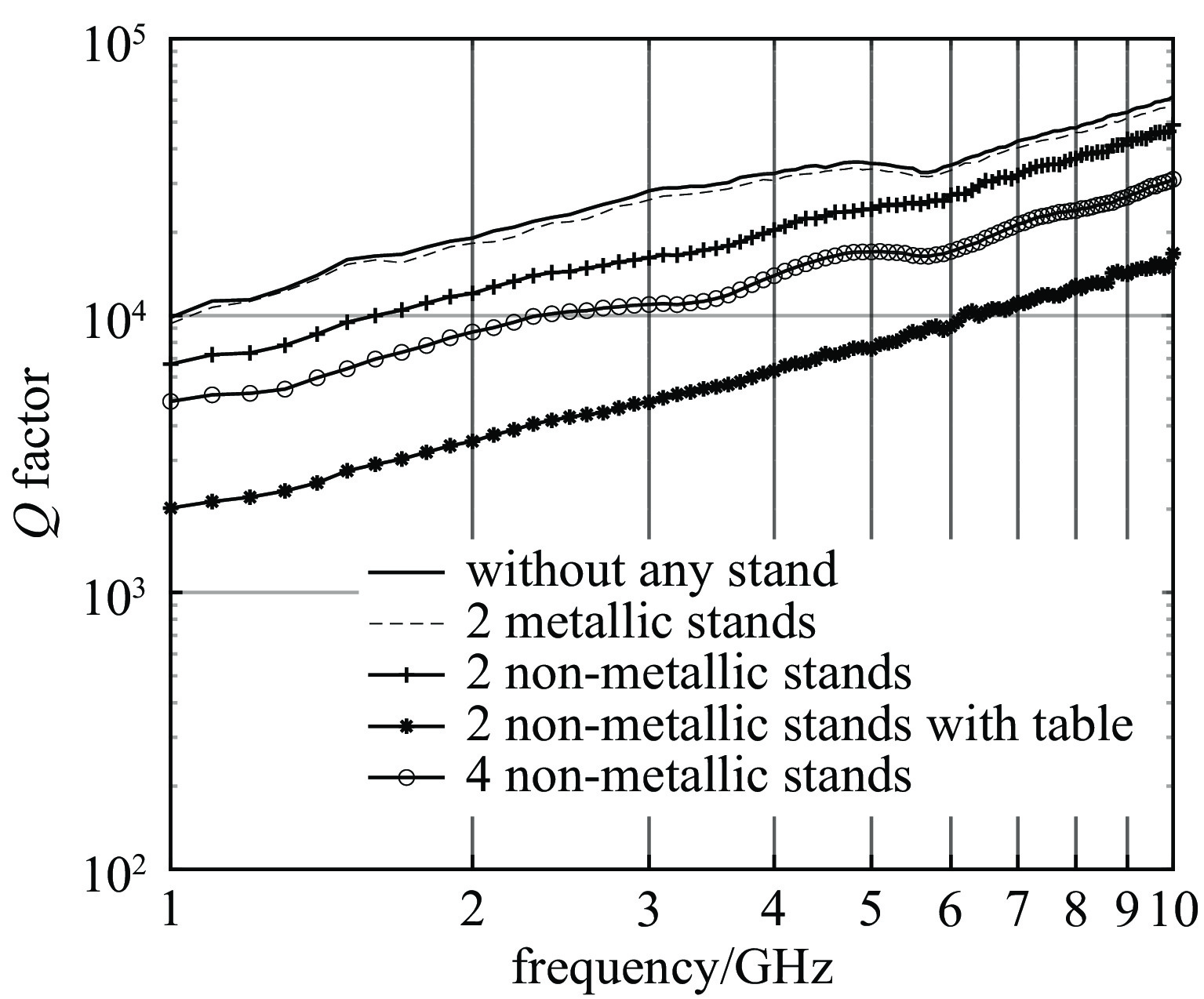
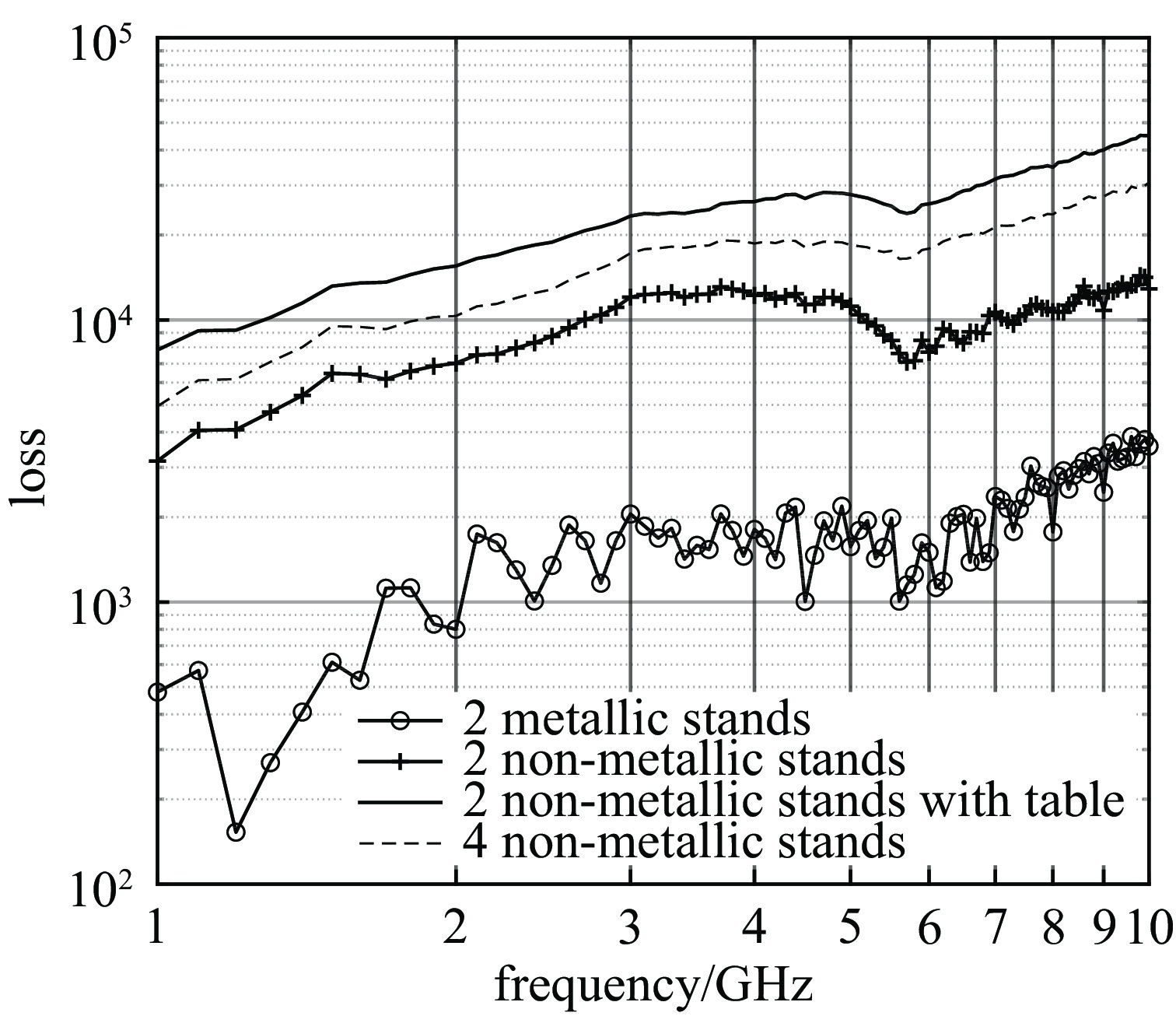
Clegg J, Marvin A C, Dawson J F, et al. Optimization of stirrer designs in a reverberation chamber[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electromagnetic Compatibility, 2005, 47(4): 824-832. doi: 10.1109/TEMC.2005.860561
|





 下载:
下载: