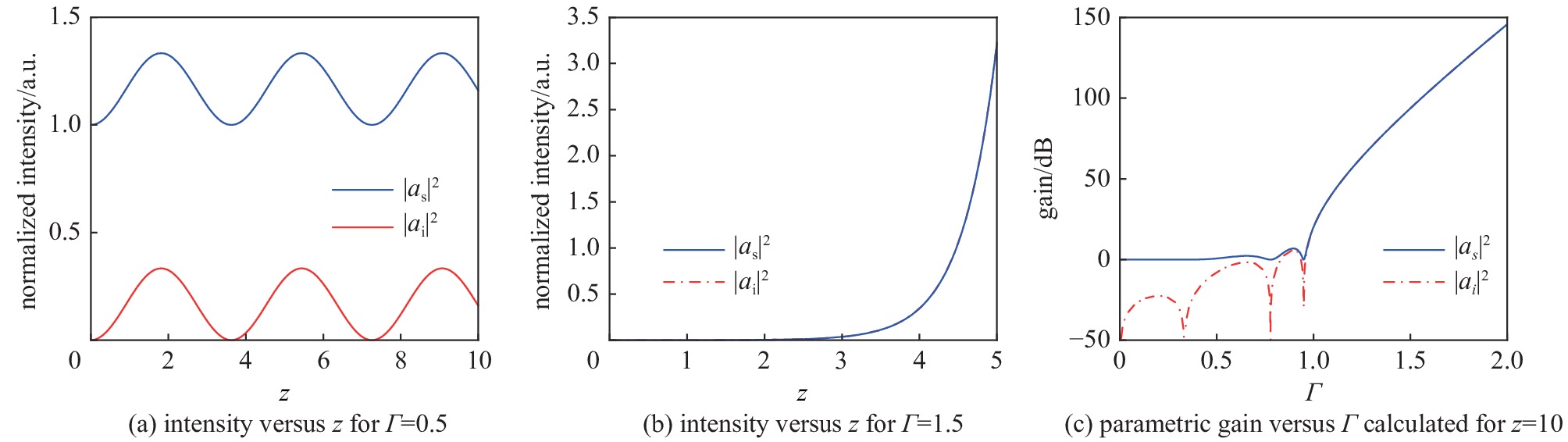
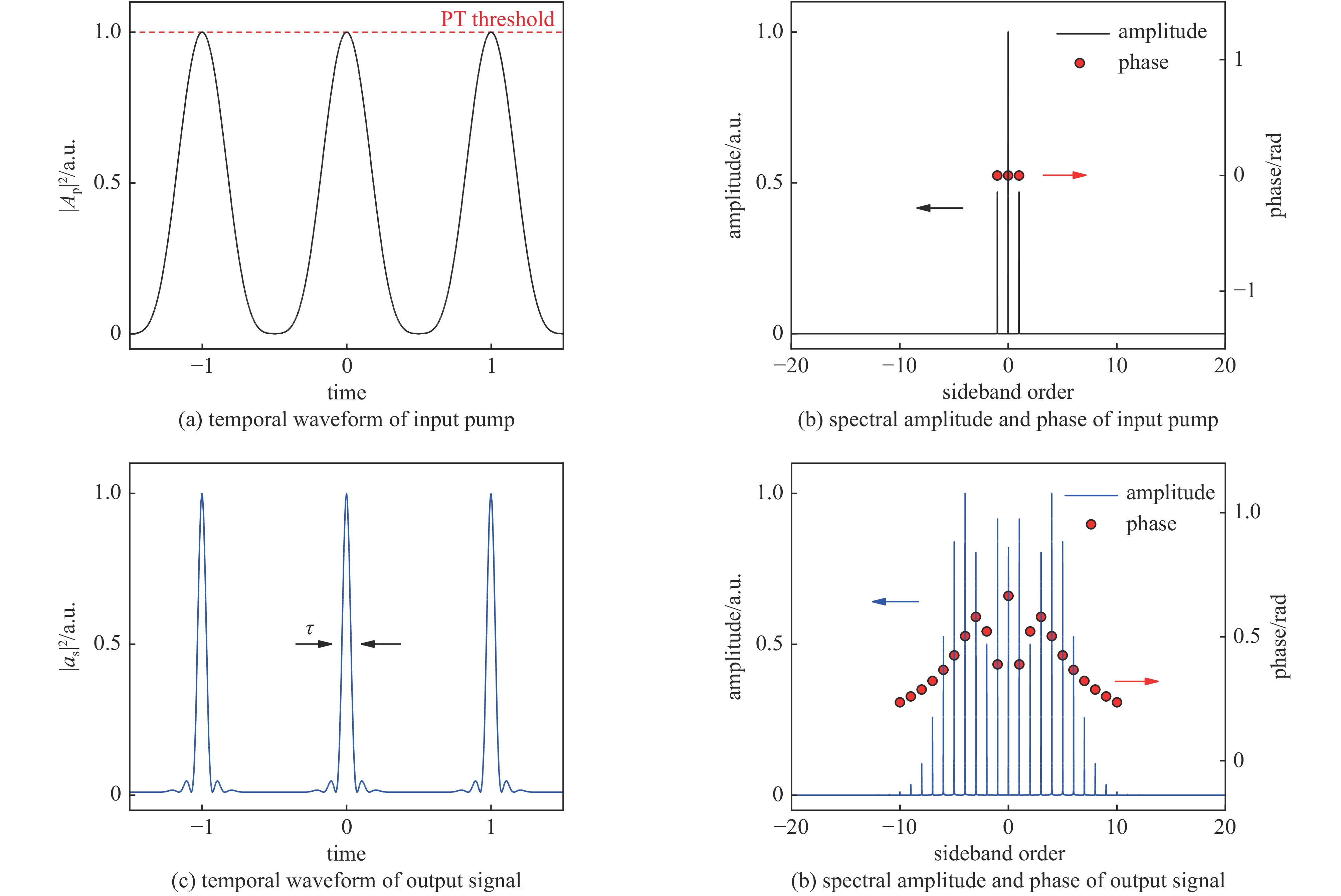
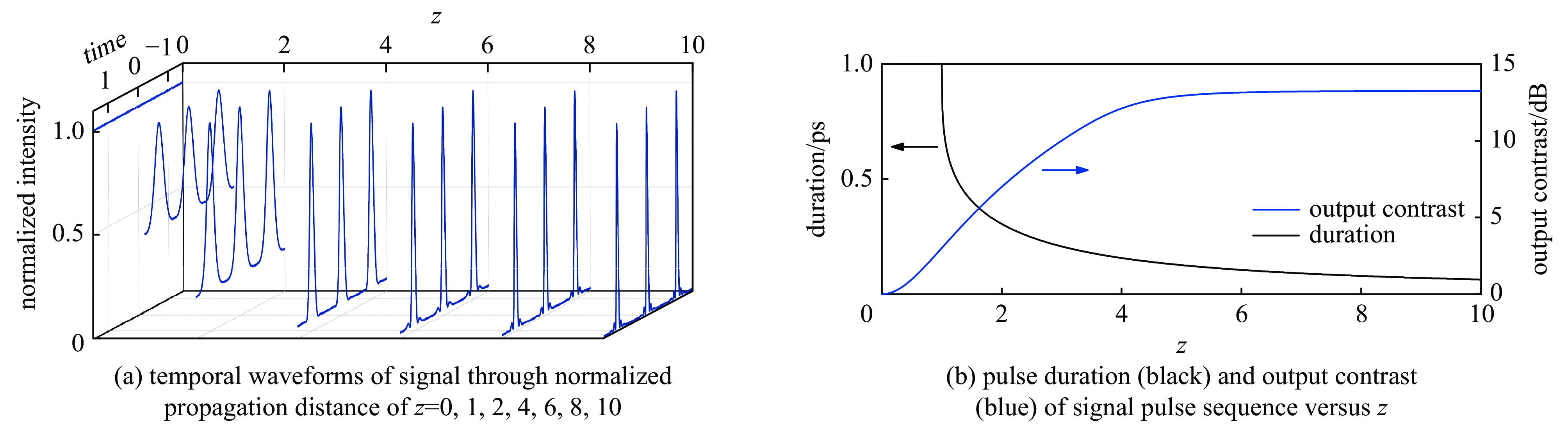
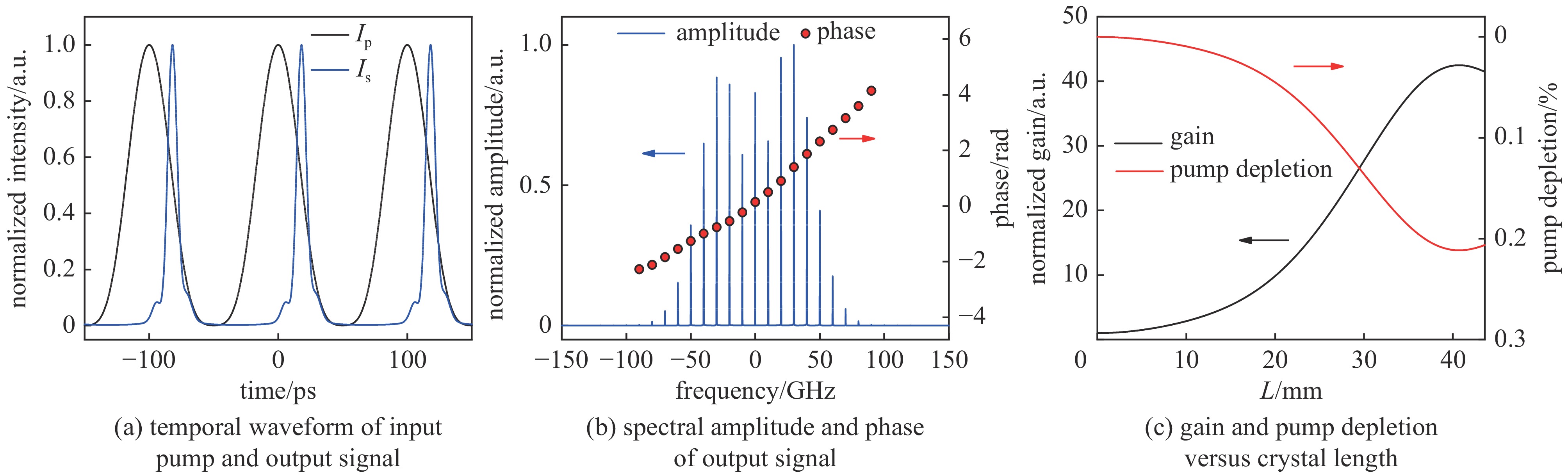
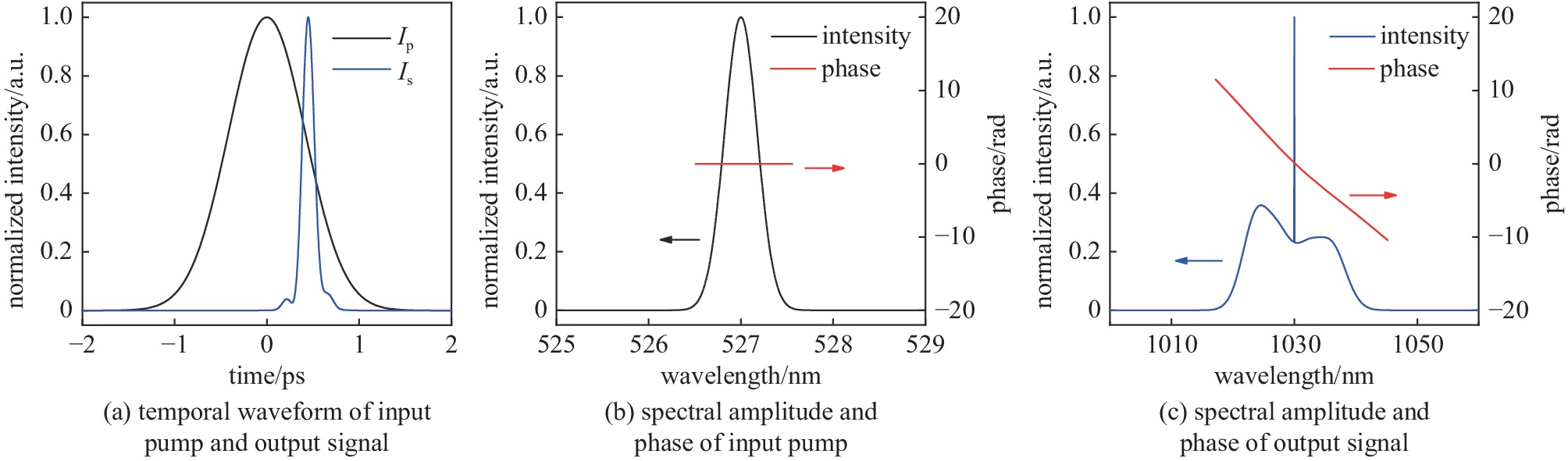
| [1] |
Udem T, Holzwarth R, Hänsch T W. Optical frequency metrology[J]. Nature, 2002, 416(6877): 233-237. doi: 10.1038/416233a
|
| [2] |
Hasegawa A, Tappert F. Transmission of stationary nonlinear optical pulses in dispersive dielectric fibers. I. Anomalous dispersion[J]. Appl Phys Lett, 1973, 23(3): 142-144. doi: 10.1063/1.1654836
|
| [3] |
Peyman G A. Method for modifying corneal curvature: 4840175[P]. 1989-06-20.
|
| [4] |
McCracken R A, Charsley J M, Reid D T. A decade of astrocombs: recent advances in frequency combs for astronomy [Invited][J]. Opt Express, 2017, 25(13): 15058-15078. doi: 10.1364/OE.25.015058
|
| [5] |
IMT Vision—Framework and overall objectives of the future development of IMT for 2020 and beyond[R]. ITU-R M. 2083-0, 2015.
|
| [6] |
Bender C M, Boettcher S. Real spectra in non-Hermitian Hamiltonians having PT symmetry[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 1998, 80(24): 5243-5246. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.80.5243
|
| [7] |
Guo A, Salamo G J, Duchesne D, et al. Observation of PT-symmetry breaking in complex optical potentials[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 2009, 103: 093902. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.103.093902
|
| [8] |
Rüter C E, Makris K G, El-Ganainy R, et al. Observation of parity–time symmetry in optics[J]. Nat Phys, 2010, 6(3): 192-195. doi: 10.1038/nphys1515
|
| [9] |
Wiersig J. Enhancing the sensitivity of frequency and energy splitting detection by using exceptional points: application to microcavity sensors for single-particle detection[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 2014, 112: 203901. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.112.203901
|
| [10] |
Lai Y H, Lu Y K, Suh M G, et al. Observation of the exceptional-point-enhanced Sagnac effect[J]. Nature, 2019, 576(7785): 65-69. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1777-z
|
| [11] |
Ramezani H, Kottos T, El-Ganainy R, et al. Unidirectional nonlinear PT-symmetric optical structures[J]. Phys Rev A, 2010, 82: 043803. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.82.043803
|
| [12] |
Antonosyan D A, Solntsev A S, Sukhorukov A A. Parity-time anti-symmetric parametric amplifier[J]. Opt Lett, 2015, 40(20): 4575-4578. doi: 10.1364/OL.40.004575
|
| [13] |
Ma Jingui, Wang Jing, Yuan Peng, et al. Quasi-parametric amplification of chirped pulses based on a Sm3+-doped yttrium calcium oxyborate crystal[J]. Optica, 2015, 2(11): 1006-1009. doi: 10.1364/OPTICA.2.001006
|
| [14] |
Zhong Q, Ahmed A, Dadap J I, et al. Parametric amplification in quasi-PT symmetric coupled waveguide structures[J]. New J Phys, 2016, 18: 125006. doi: 10.1088/1367-2630/18/12/125006
|
| [15] |
Flemens N, Moses J. Hermitian nonlinear wave mixing controlled by a PT-symmetric phase transition[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 2022, 129: 153901. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.129.153901
|
| [16] |
Witte S, Eikema K S E. Ultrafast optical parametric chirped-pulse amplification[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics, 2012, 18(1): 296-307. doi: 10.1109/JSTQE.2011.2118370
|
| [17] |
Özdemir Ş K, Rotter S, Nori F, et al. Parity–time symmetry and exceptional points in photonics[J]. Nat Mater, 2019, 18(8): 783-798. doi: 10.1038/s41563-019-0304-9
|
| [18] |
Mücke O D, Sidorov D, Dombi P, et al. Scalable Yb-MOPA-driven carrier-envelope phase-stable few-cycle parametric amplifier at 1.5 μm[J]. Opt Lett, 2009, 34(2): 118-120. doi: 10.1364/OL.34.000118
|
| [19] |
Ganeev R A, Kulagin I A, Ryasnyansky A I, et al. Characterization of nonlinear optical parameters of KDP, LiNbO3 and BBO crystals[J]. Opt Commun, 2004, 229(1/6): 403-412.
|
| [20] |
Gayer O, Sacks Z, Galun E, et al. Temperature and wavelength dependent refractive index equations for MgO-doped congruent and stoichiometric LiNbO3[J]. Appl Phys B, 2008, 91(2): 343-348. doi: 10.1007/s00340-008-2998-2
|




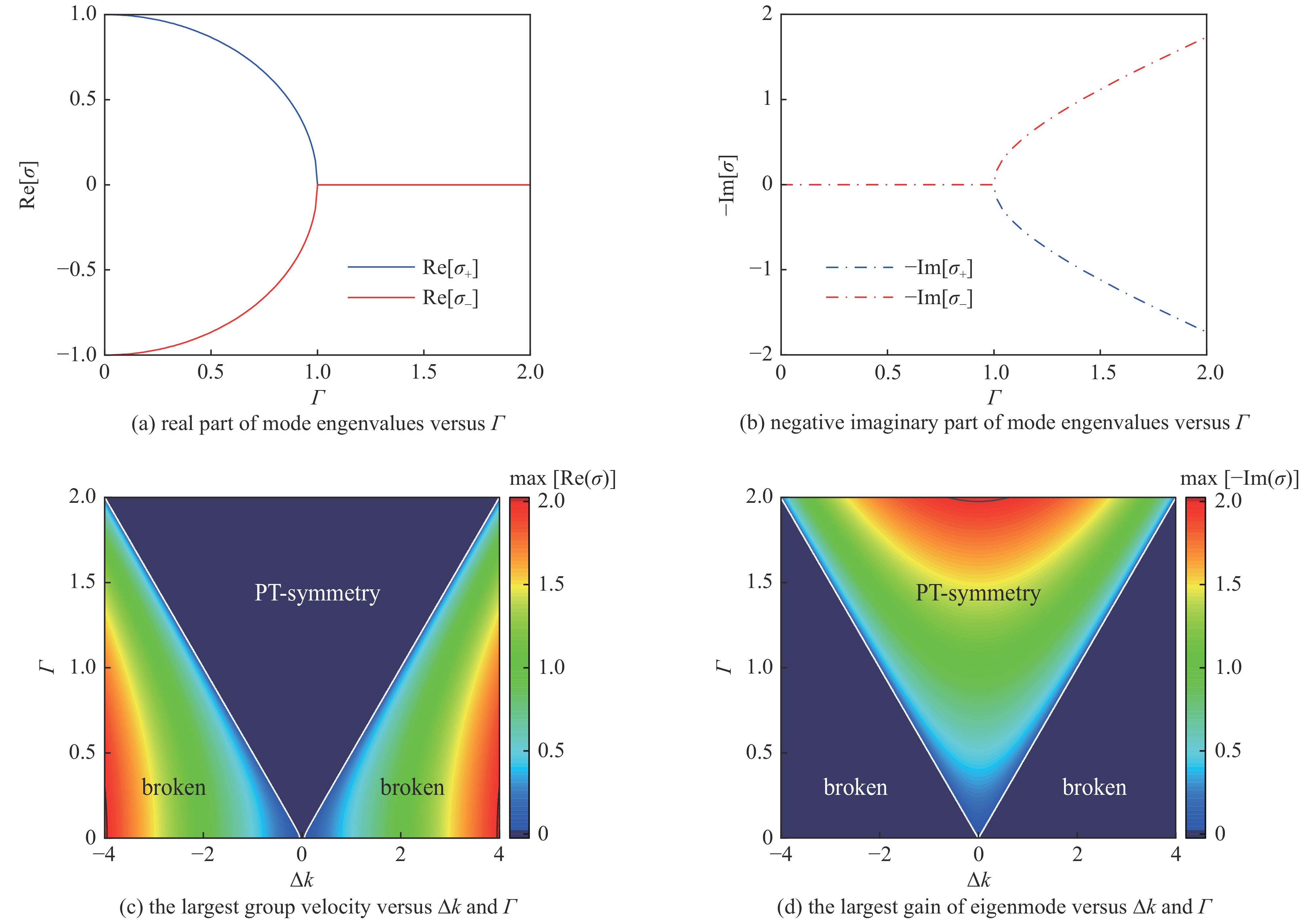
 下载:
下载: