Plasma optics technologies: State of the art and future perspective
-
摘要: 等离子体介质由于具有极高的储能密度、无光致损伤阈值和丰富的光学特性,利用它改善光束输出性能是发展高功率激光技术的一条重要技术路线。系统介绍了近年来等离子体光学的研究现状,并论述了今后等离子体光学的发展趋势。Abstract: Plasma optics is an important way for the development of high power laser technology because plasma medium has high energy storage density, no laser-induced damage threshold and rich optical properties. The research status of plasma optics in recent years is introduced, and the development trend of plasma optics in the future is discussed.
-
Key words:
- high power lasers /
- plasma optics /
- plasma amplification /
- plasma photonic crystal
-
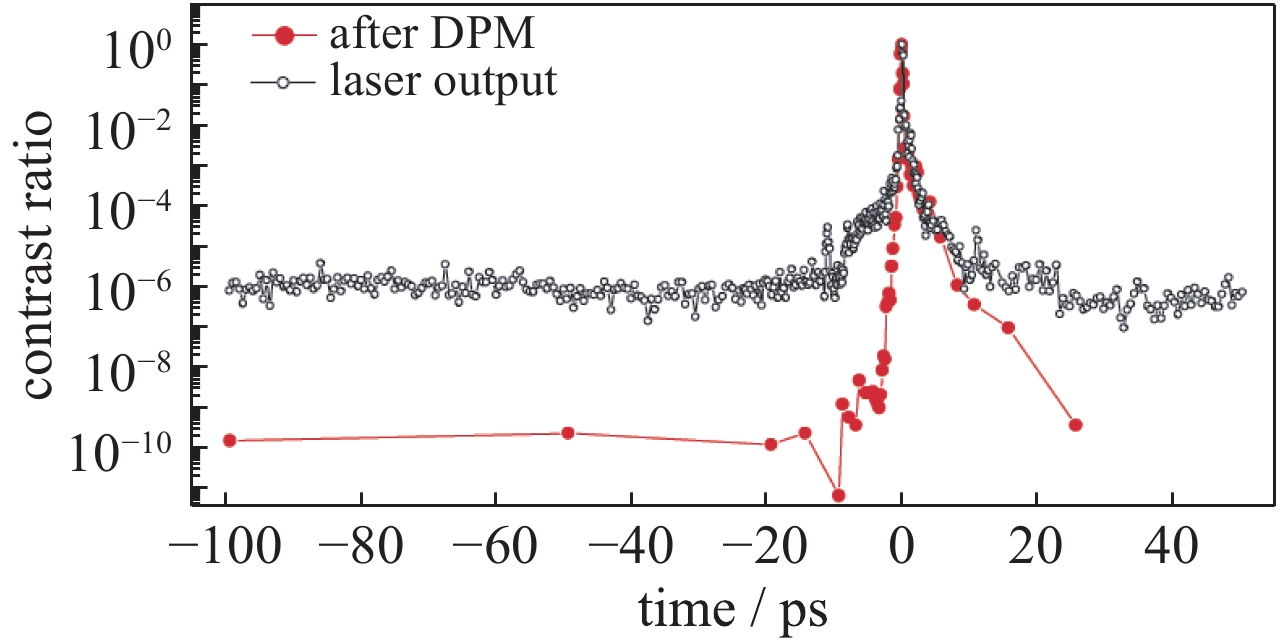
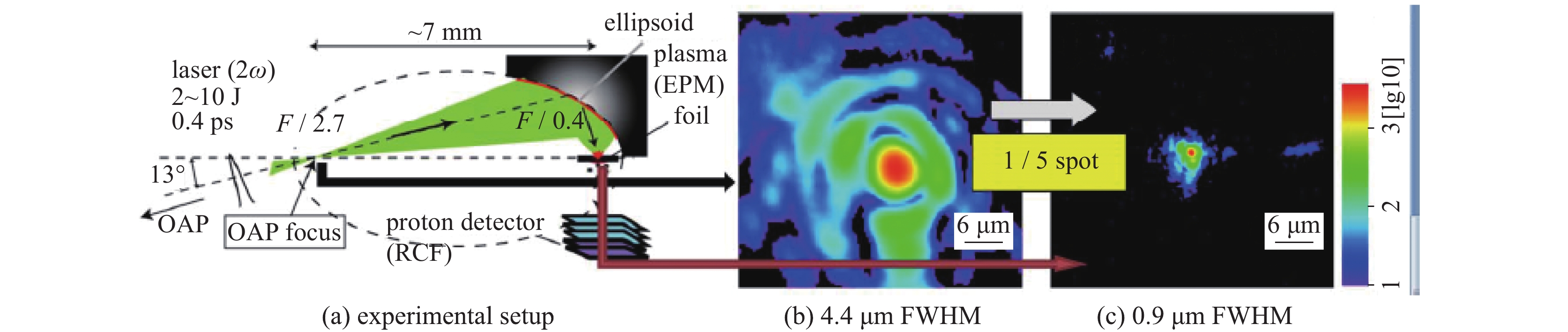
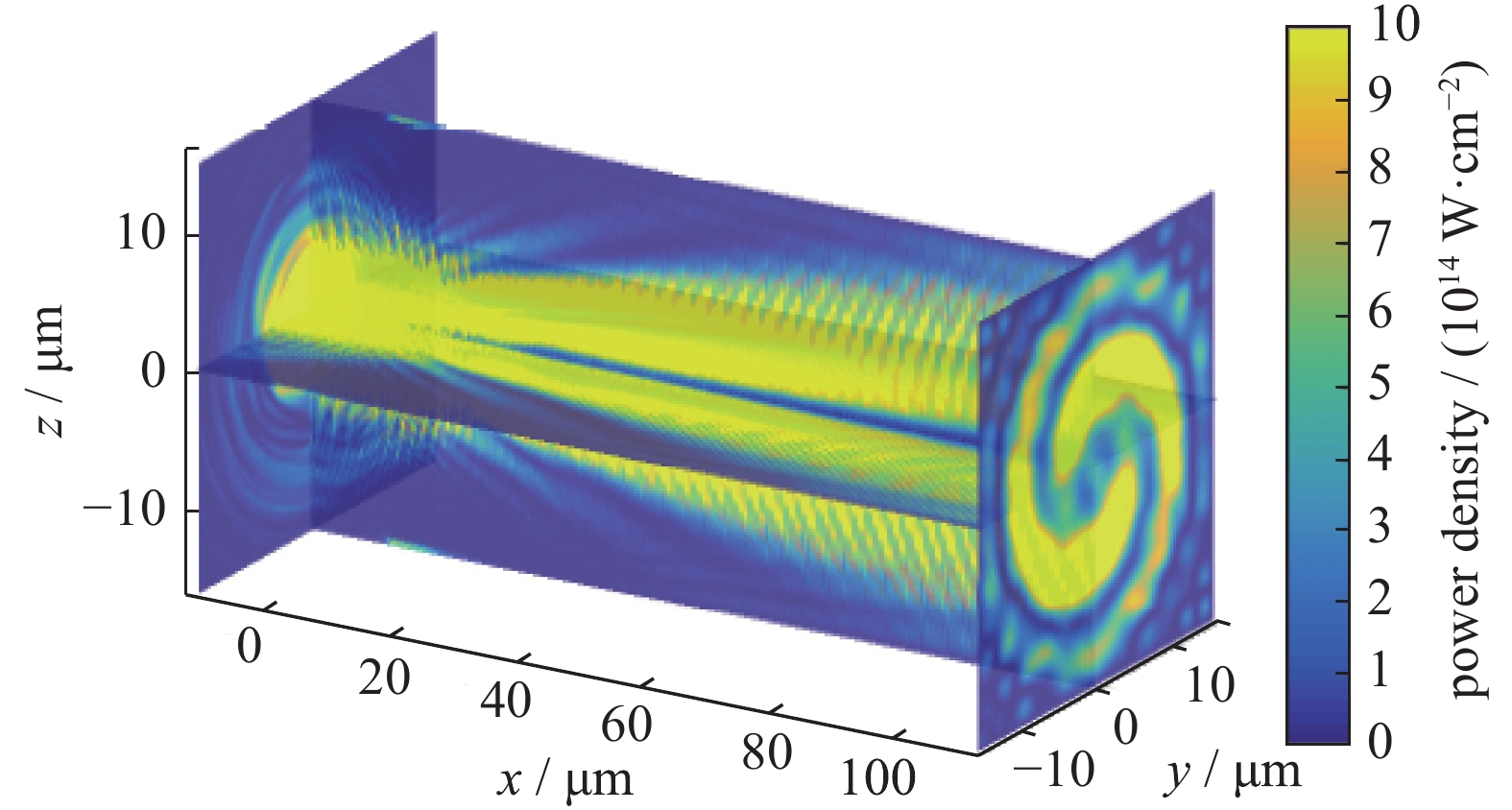
图 10 (a)利用凹面等离子体镜改善光束F数的实验示意图 (b)激光器自身输出F/2.7的光束焦斑 (c)利用等离子体凹面镜实现F/0.4的光束焦斑
Figure 10. (a) Experimental setup for tight focusing of ultrahigh-intensity laser pulses by low F-number confocal EPM. (b) Focal spot provided by the conventional F/2.7 output. (c) Focal spot in the output of the F/0.4, images are in common logarithm scale
-
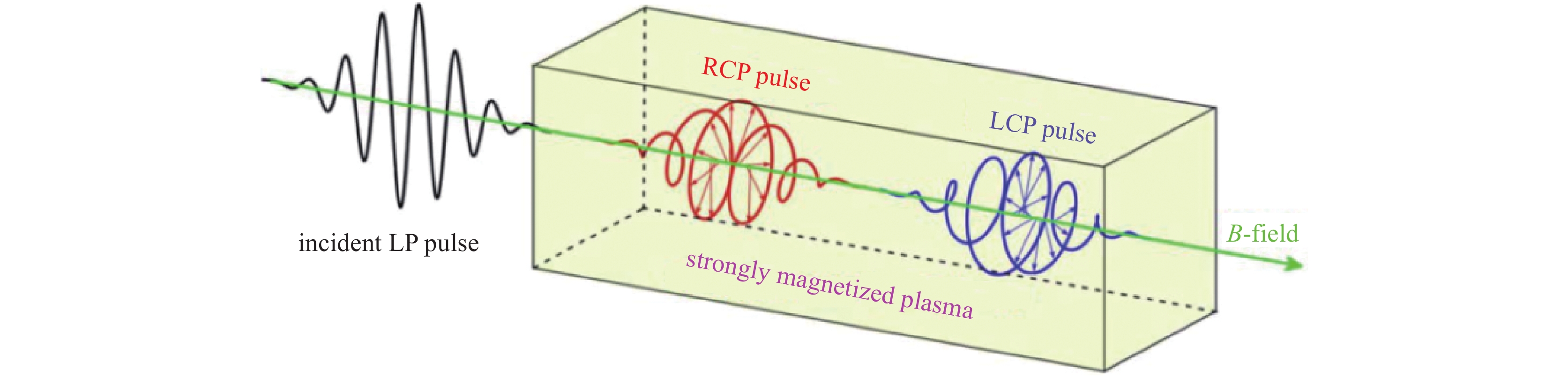
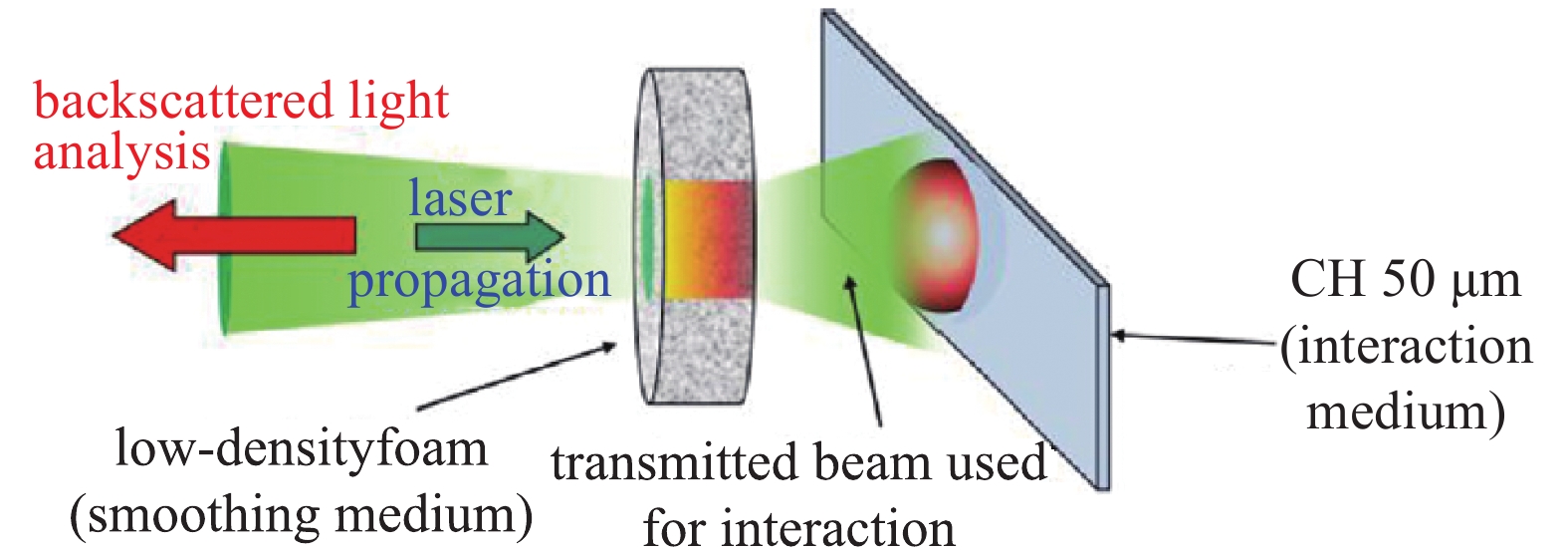
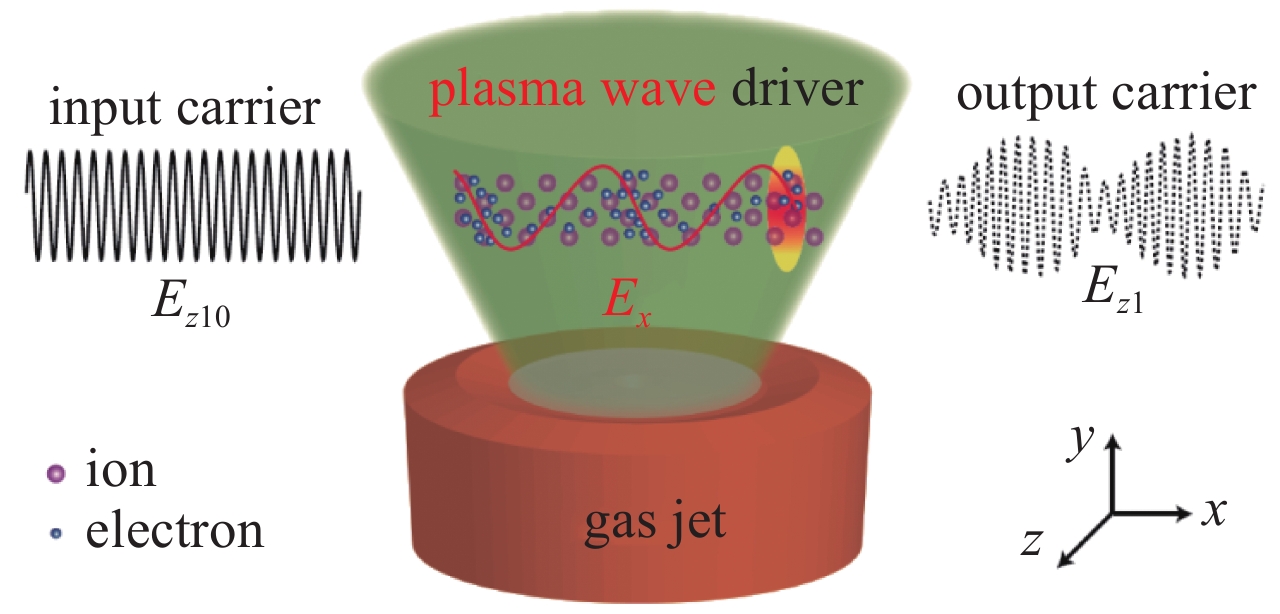
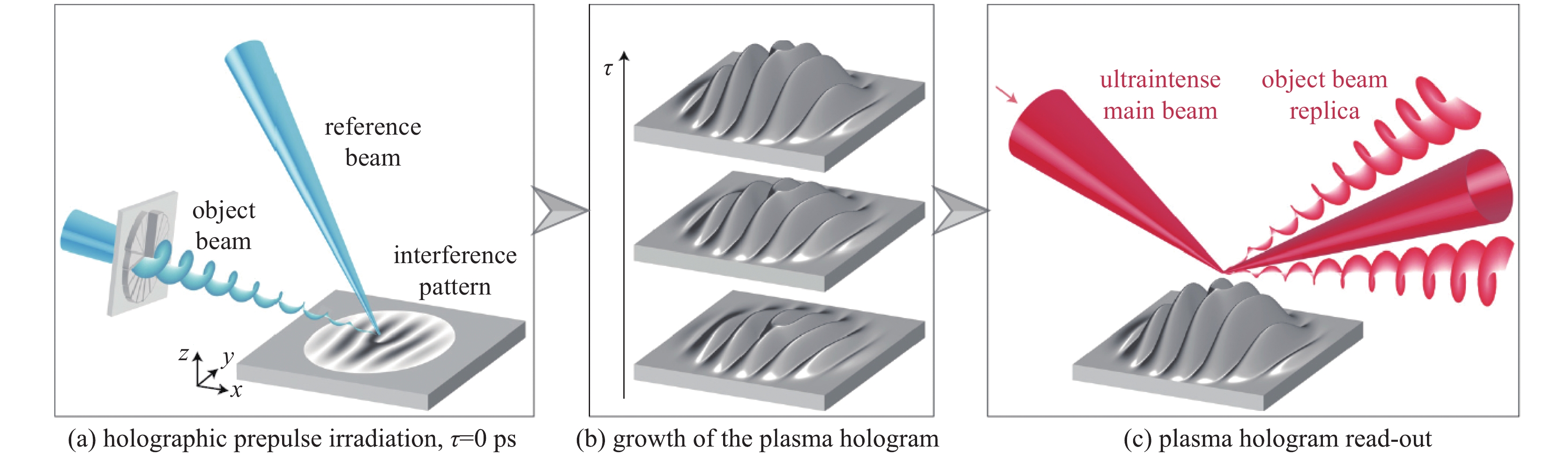
[1] Basov N G, Krohkin O H. The conditions of plasma heating by optical generation of radiation[C]//Proceedings of the 3rd International Congress on Quantum Electronics. New York: Columbia University Press, 1964: 1373. [2] 王淦昌. 利用大能量大功率的光激射器产生中子的建议[J]. 中国激光, 1987, 14(11):641-645. (Wang Ganchang. Suggestion of neutron generation with powerful lasers[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 1987, 14(11): 641-645 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0258-7025.1987.11.001 [3] Nuckolls J, Wood L, Thiessen A, et al. Laser compression of matter to super-high densities: Thermonuclear (CTR) applications[J]. Nature, 1972, 239(5368): 139-142. doi: 10.1038/239139a0 [4] 邵建达, 戴亚平, 许乔. 惯性约束聚变激光驱动装置用光学元器件的研究进展[J]. 光学 精密工程, 2016, 24(12):2889-2895. (Shao Jianda, Dai Yaping, Xu Qiao. Progress on optical components for ICF laser facility[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2016, 24(12): 2889-2895 doi: 10.3788/OPE.20162412.2889 [5] 魏晓峰, 郑万国, 张小民. 中国高功率固体激光技术发展中的两次突破[J]. 物理, 2018, 47(2):73-83. (Wei Xiaofeng, Zheng Wanguo, Zhang Xiaomin. Two breakthroughs in the development of high power solid-state laser technology in China[J]. Physics, 2018, 47(2): 73-83 doi: 10.7693/wl20180202 [6] 郑万国, 魏晓峰, 朱启华, 等. 神光-Ⅲ主机装置成功实现60 TW/180 kJ三倍频激光输出[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2016, 28:019901. (Zheng Wanguo, Wei Xiaofeng, Zhu Qihua, et al. SG-Ⅲ laser facility has successfully achieved 60 TW/180 kJ ultraviolet laser (351 nm) output[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2016, 28: 019901 [7] Maywar D N, Kelly J H, Waxer L J, et al. OMEGA EP high-energy petawatt laser: progress and prospects[J]. J Phys: Conf Ser, 2008, 112: 032007. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/112/3/032007 [8] André M L. The French Megajoule Laser Project (LMJ)[J]. Fusion Engineering and Design, 1999, 44(1/4): 43-49. [9] Moses, E I. The National Ignition Facility (NIF): A path to fusion energy[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2008, 49: 1795-1802. doi: 10.1016/j.enconman.2007.10.029 [10] Daniel C. Ignition facility misses goal, ponders new course[J]. Science, 2012, 337(9): 1444. [11] Hurricane O A, Kline J L, Meezan N, et al. Deep dive topic: Approach to ignition[R]. LLNL-TR-674445, 2015. [12] Manes K R, Spaeth M L, Adams J J, et al. Damage mechanisms avoided or managed for NIF large optics[J]. Fusion Science and Technology, 2016, 69: 146-249. doi: 10.13182/FST15-139 [13] 马腾才. 等离子体物理原理[M]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学出版社, 1988.Ma Tengcai. Principles of plasma physics[M]. Hefei: China University of Science and Technology Press, 1988 [14] Maier S A. Plasmonics: Fundamentals and applications[M]. Berlin: Springer, 2017. [15] Sakai O, Tachibana K. Plasmas as metamaterials: a review[J]. Plasma Sources Sci Technol, 2012, 21: 013001. doi: 10.1088/0963-0252/21/1/013001 [16] Boley C D, Rhodes M A. Modeling of plasma behavior in a plasma electrode Pockels cell[J]. IEEE Trans Plasma Science, 1999, 27(3): 713-726. doi: 10.1109/27.774676 [17] Backus S, Kapteyn H C, Murname M M, et al. Prepulse suppression for high-energy ultrashort pulses using self-induced plasma shuttering from a fluid target[J]. Opt Express, 1993, 18(2): 134-136. [18] Ehrlich Y, Cohen C, Zigler A, et al. Guiding of high intensity laser pulses in straight and curved plasma channel experiments[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 1996, 77(20): 4186-4189. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.77.4186 [19] Kuo C C, Pai C H, Lin M W, et al. Enhancement of relativistic harmonic generation by an optically preformed periodic plasma waveguide[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 2007, 98: 033901. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.98.033901 [20] Litos M, Adli E, An W, et al. High-efficiency acceleration of an electron beam in a plasma wakefield accelerator[J]. Nature, 2014, 515(7525): 92-95. doi: 10.1038/nature13882 [21] 於陆勒, 盛政明, 张杰. 均匀等离子体光栅的色散特性研究[J]. 物理学报, 2008, 57(10):6457-6464. (Yu Lule, Sheng Zhengming, Zhang Jie. Investigation on the dispersion characteristics of a uniform plasma grating[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2008, 57(10): 6457-6464 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3290.2008.10.062 [22] 陈伟, 叶艾, 任竞骁. 高功率激光器电光调Q技术研究[J]. 光学与光电技术, 2007, 5(1):27-300. (Chen Wei, Ye Ai, Ren Jingxiao. Electro-optic Q-switched technology of high power and high efficiency laser[J]. Optics & Optoelectronic Technology, 2007, 5(1): 27-300 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3392.2007.01.007 [23] 王小发, 樊仲维, 余锦, 等. 高能量高效率钕玻璃再生放大器[J]. 中国激光, 2012, 39:0802002. (Wang Xiaofa, Fan Zhongwei, Yu Jin, et al. High energy and high efficiency Nd glass regenerative amplifier[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2012, 39: 0802002 doi: 10.3788/CJL201239.0802002 [24] 范滇元, 余文炎. 高功率多程放大器[J]. 中国激光, 1980, 7(9):1-6. (Fan Dianyuan, Yu Wenyan. High power multi-pass amplifier[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 1980, 7(9): 1-6 [25] 张雄军, 郑建刚, 郑奎兴, 等. 用于多程放大系统光束反转器的等离子体电极电光开关[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2003, 15(2):150-154. (Zhang Xiongjun, Zheng Jiangang, Zheng Kuixing, et al. PEPC electro-optical switch used in beam reverser of multipass amplifier[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2003, 15(2): 150-154 [26] Zhang Jun, Wu Dengsheng, Zheng Jiangang, et al. Single-pulse driven, large-aperture, 2×1 array plasma-electrodes optical switch for SG-II upgrading facility[C]//Proc of SPIE. 2014: 929425. [27] Zhang Xiongjun, Wu Dengsheng, Zhang Jun, et al. One-pulse driven plasma Pockels cell with DKDP crystal for repetition-rate application[J]. Opt Express, 2009, 17: 17164. doi: 10.1364/OE.17.017164 [28] Zhang Jun, Zhang Xiongjun, Wu Dengsheng, et al. A reflecting Pockels cell with aperture scalable for high average power multipass amplifier systems[J]. Opt Express, 2010, 18: A185. doi: 10.1364/OE.18.00A185 [29] Zhang Jun, Zhang Xiongjun, Zheng Jiangang, et al. Aperture scalable, high average power capable, hybrid-electrode Pockels cell[J]. Opt Lett, 2017, 42(9): 1676. doi: 10.1364/OL.42.001676 [30] Strickland D, Mourou G. Compression of amplified chirped optical pulses[J]. Opt Commun, 1985, 56: 219. doi: 10.1016/0030-4018(85)90120-8 [31] Gomez C H, Blake S P, Chekhlov O, et al. The Vulcan 10 PW project[J]. J of Physics: Conf Series, 2010, 244: 032006. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/244/3/032006 [32] Malkin V M, Shvets G, Fisch N J. Fast compression of laser beams to highly overcritical powers[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 1999, 82(22): 4448-4451. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.82.4448 [33] Shvets G, Fisch N J, Pukhov A, et al. Super radiant amplification of an ultrashort laser pulse in a plasma by a counter propagating pump[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 1998, 81(22): 4879-4882. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.81.4879 [34] Ping Y, Cheng W, Suckewer S, et al. Amplification of ultrashort laser pulses by a resonant Raman scheme in a gas-jet plasma[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 2004, 92: 175007. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.92.175007 [35] Pai C H, Lin M W, Ha L C, et al. Backward Raman amplification in a plasma waveguide[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 2008, 101: 065005. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.101.065005 [36] Cheng W, Avitzour Y, Ping Y, et al. Reaching the nonlinear regime of Raman amplification of ultrashort laser pulses[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 2005, 94: 045003. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.94.045003 [37] Kirkwood R K, Ping Y, Wilks S C, et al. Observation of amplification of light by Langmuir waves and its saturation on the electron kinetic timescale[J]. J Plasma Phys, 2011, 77: 521-528. doi: 10.1017/S0022377810000681 [38] Weber S, Riconda C, Lancia L, et al. Amplification of ultrashort laser pulses by Brillouin backscattering in plasmas[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 2013, 111: 055004. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.111.055004 [39] Edwards M R, Jia Q, Mikhailova J M, et al. Short-pulse amplification by strongly coupled stimulated Brillouin scattering[J]. Phys Plasmas, 2016, 23: 083122. doi: 10.1063/1.4961429 [40] Zuo Y L, Wei X F, Zhou K N, et al. Enhanced laser-induced plasma channels in air[J]. Chinese Physics B, 2016, 25(3): 256-261. [41] Wu Z H, Wei X F, Zuo Y L, et al. Backward Raman amplification in plasmas with chirped wideband pump and seed pulses[J]. Chinese Physics B, 2015, 24(1): 298-302. [42] Lehmann G, Spatschek K-H. Transient plasma photonic crystals for high-power lasers[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 2016, 116: 225002. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.116.225002 [43] Turnbull D P, Michel P, Ralph J, et al. Multibeam seeded Brillouin sidescatter in inertial confinement fusion experiments[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 2015, 114: 125001. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.114.125001 [44] Kirkwood R K, Turnbull D P, Chapman T, et al. Plasma-based beam combiner for very high fluence and energy[J]. Nature Physics, 2018, 14: 80-84. doi: 10.1038/nphys4271 [45] Gold D M. Direct measurement of prepulse suppression by use of a plasma shutter[J]. Opt Lett, 1994, 19(24): 2006-2008. [46] Price D F, More R M, Walling R S, et al. Absorption of ultrashort laser pulses by solid targets heated rapidly to temperatures 1-1000 eV[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 1995, 75(2): 252-255. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.75.252 [47] Ziener Ch, Foster P S, Divall E J, et al. Specular reflectivity of plasma mirrors as a function of intensity, pulse duration, and angle of incidence[J]. J of Appl Phys, 2003, 93(1): 768-770. doi: 10.1063/1.1525062 [48] Bulanov S S, Macchi A, Maksimchuk A, et al. Electromagnetic pulse reflection at self-generated plasma mirrors: Laser pulse shaping and high order harmonic generation[J]. Phys Plasma, 2007, 14: 093105. doi: 10.1063/1.2776906 [49] Doumy G, Quéré F, Gobert O, et al. Complete characterization of a plasma mirror for the production of high-contrast ultraintense laser pulses[J]. Phys Rev E, 2004, 69: 026402. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.69.026402 [50] Wittmann T, Geindre J P, Audebert P, et al. Towards ultrahigh-contrast ultraintense laser pulses—Complete characterization of a double plasma-mirror pulse cleaner[J]. Rev Sci Instrum, 2006, 77: 083019. [51] Thaury C, Quere F, Geindre J P, et al. Plasma mirrors for ultrahigh-intensity optics[J]. Nature Physics, 2007, 3: 424-429. doi: 10.1038/nphys595 [52] Gibbon P. Plasma physics: Cleaner petawatts with plasma optics[J]. Nature Physics, 2007, 3: 369-370. doi: 10.1038/nphys639 [53] Nakatsutsumi M, Kon A, Buffechoux S, et al. Fast focusing of short-pulse lasers by innovative plasma optics toward extreme intensity[J]. Opt Lett, 2010, 35(13): 2314-2316. doi: 10.1364/OL.35.002314 [54] 李平, 王伟, 赵润昌, 等. 基于焦斑空间频率全域优化的偏振匀滑设计[J]. 物理学报, 2014, 63:215202. (Li Ping, Wang Wei, Zhao Runchang, et al. Polarization smoothing design for improving the whole spatial frequency at focal spot[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2014, 63: 215202 doi: 10.7498/aps.63.215202 [55] Liu Z J, Zheng C Y, Cao L H, et al. Decreasing Brillouin and Raman scattering by alternating-polarization light[J]. Phys Plasmas, 2017, 24(3): 032701. doi: 10.1063/1.4977910 [56] Arita Y, Mazilu M, Dholakia K. Laser-induced rotation and cooling of a trapped microgyroscope in vacuum[J]. Nat Commun, 2013, 4: 2374. doi: 10.1038/ncomms3374 [57] Zhang L, Shen B, Zhang X, et al. Deflection of a reflected intense vortex laser beam[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 2016, 117: 113904. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.117.113904 [58] Michel P, Rozmus W, Williams E A, et al. Saturation of multi-laser beams laser-plasma instabilities from stochastic ion heating[J]. Phys Plasmas, 2013, 20: 056308. doi: 10.1063/1.4802828 [59] Michel P, Divol L, Turnbul l D, et al. , Dynamic control of the polarization of intense laser beams via optical wave mixing in plasma[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 2014, 113: 205001. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.113.205001 [60] Turnbull D, Michel P, Chapman T, et al. High power dynamic polarization control using plasma photonics[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 2016, 116: 205001. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.116.205001 [61] Turnbull D, Goyon C, Kemp G E, et al. Refractive index seen by a probe beam interacting with a laser-plasma system[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 2017, 118: 015001. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.118.015001 [62] Weng Suming, Zhao Qian, Sheng Zhengming, et al. Extreme case of Faraday effect: magnetic splitting of ultrashort laser pulses in plasmas[J]. Optica, 2017, 4(9): 1086. doi: 10.1364/OPTICA.4.001086 [63] Liu Ming, Zhang Xiang. Nano-optics: plasmon-boosted magneto-optics[J]. Nat Photonics, 2013, 7: 429-430. doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2013.134 [64] Skupsky S, Short R W, Kessler T, et al. Improved laser-beam uniformity using the angular dispersion of frequency-modulated light[J]. J Appl Phys, 1989, 66(8): 3456-3462. doi: 10.1063/1.344101 [65] 钱列加. 宽频带激光的啁啾匹配型三次谐波转换[J]. 光学学报, 1995, 15(6):662-664. (Qian Liejia. Chirp matched third harmonic conversion for broad-band lasers[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 1995, 15(6): 662-664 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2239.1995.06.005 [66] Loiseau P, Morice O, Teychenné D, et al. Laser-beam smoothing induced by stimulated Brillouin scattering in an inhomogeneous plasma[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 2006, 97: 205001. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.97.205001 [67] Maximov A V, Ourdev I G, Pesme D, et al. Plasma induced smoothing of a spatially incoherent laser beam and reduction of backward stimulated Brillouin scattering[J]. Phys Plasma, 2001, 8(4): 1319. doi: 10.1063/1.1352056 [68] Grech M, Riazuelo G, Pesme D, et al. Coherent forward stimulated-Brillouin scattering of a spatially incoherent laser beam in a plasma and its effect on beam spray[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 2009, 102: 155001. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.102.155001 [69] Fuchs J, Labaune C, Bandulet H, et al. Reduction of the coherence time of an intense laser pulse propagating through a plasma[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 2002, 88: 195003. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.88.195003 [70] Yahia V, Masson-Laborde P E, Depierreux S, et al. Reduction of stimulated Brillouin backscattering with plasma beam smoothing[J]. Phys Plasma, 2015, 22: 042707. doi: 10.1063/1.4918942 [71] Grech M, Tikhonchuk V T, Riazuelo G, et al. Plasma induced laser beam smoothing below the filamentation threshold[J]. Phys Plasma, 2006, 13: 093104. doi: 10.1063/1.2337791 [72] Yu L L, Zhao Y, Qian L J, et al. Plasma optical modulators for intense lasers[J]. Nat Commun, 2016(6): 11893. [73] Leblanc A, Denoeud A, Chopineau L, et al. Plasma holograms for ultrahigh-intensity optics[J]. Nature Phys, 2017, 13: 440-443. doi: 10.1038/nphys4007 [74] Monchocé S, Kahaly S, Leblanc A, et al. Optically controlled solid-density transient plasma gratings[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 2014, 112: 145008. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.112.145008 [75] Peng H, Marquès J R, Lancia L. et al, Plasma optics in the context of high intensity lasers[J]. Matter and Radiation at Extremes, 2019, 4: 065401. doi: 10.1063/1.5091550 [76] Qu K, Jia Q, Fisch N J. Plasma Q-plate for generation and manipulation of intense optical vortices[J]. Phys Rev E, 2017, 96(5): 053207. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.96.053207 -




 下载:
下载: