Energy loss spectra of Arq+(q=0-12) ions in grazing incidence on single-crystal copper surface
-
摘要: 采用蒙特卡罗模拟方法,对低速高电荷态Arq+离子掠射到单晶铜表面时的能损谱与表面结构的依赖关系进行研究。在能损计算中,包含了四种可能的能损机制。对于Ar原子沿着晶列方向掠射时,发现能损谱为一两峰结构,其中在能损比较大的区间新出现一个明显的小峰结构。通过研究Arq+以不同条件掠射到表面的能损,对观察到的沟道效应进行论述。能损谱的计算结果与实验结果吻合得比较好。Abstract: By performing a Monte Carlo simulation, energy spectra as a function of surface structure for slow highly charged Arq+ ions in grazing incidence on a single-crystal copper surface were studied. Four possible mechanisms were taken into account in energy loss calculation. The energy loss spectrum consisting of two peak structure with an obvious small peak at higher energy loss side was found for Ar atoms grazing along low-index direction. The channeling effect observed in the energy loss of Arq+ ions grazing from surface was discussed. The calculated energy loss spectra agree reasonably well with those of experiment.
-
Key words:
- Monte Carlo /
- energy loss /
- highly charged ion /
- grazing incidence
-
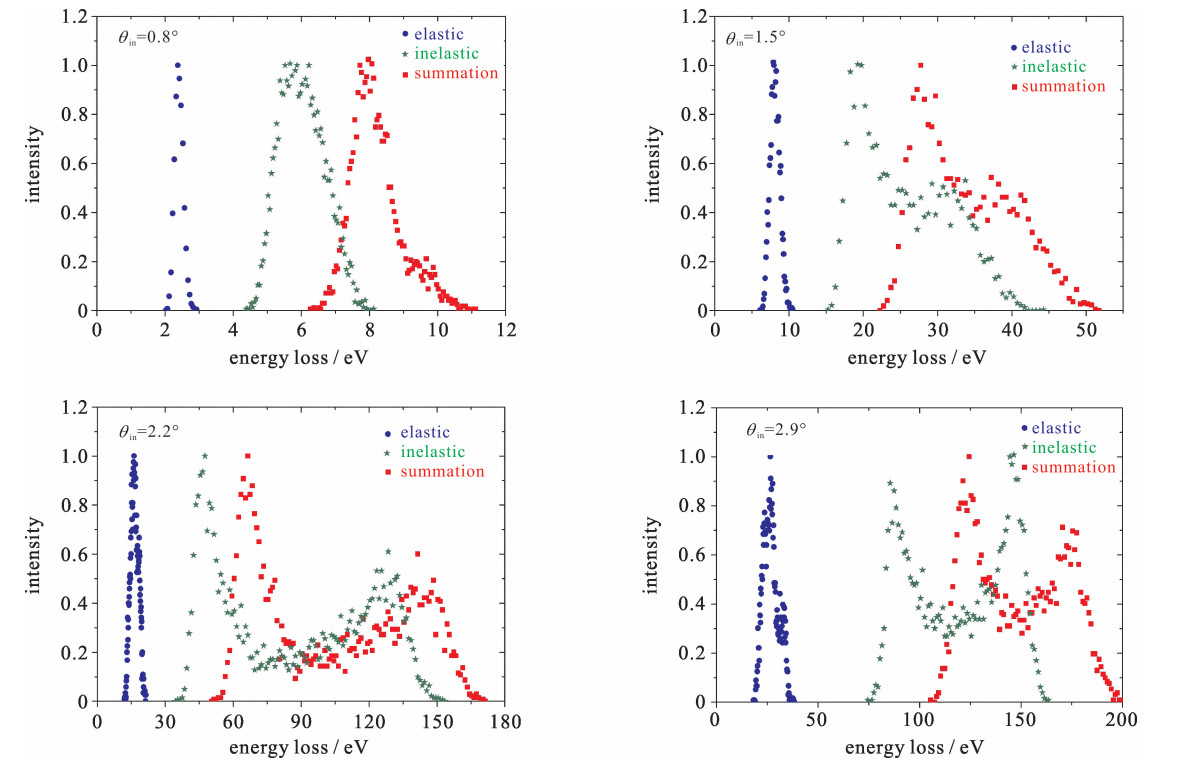
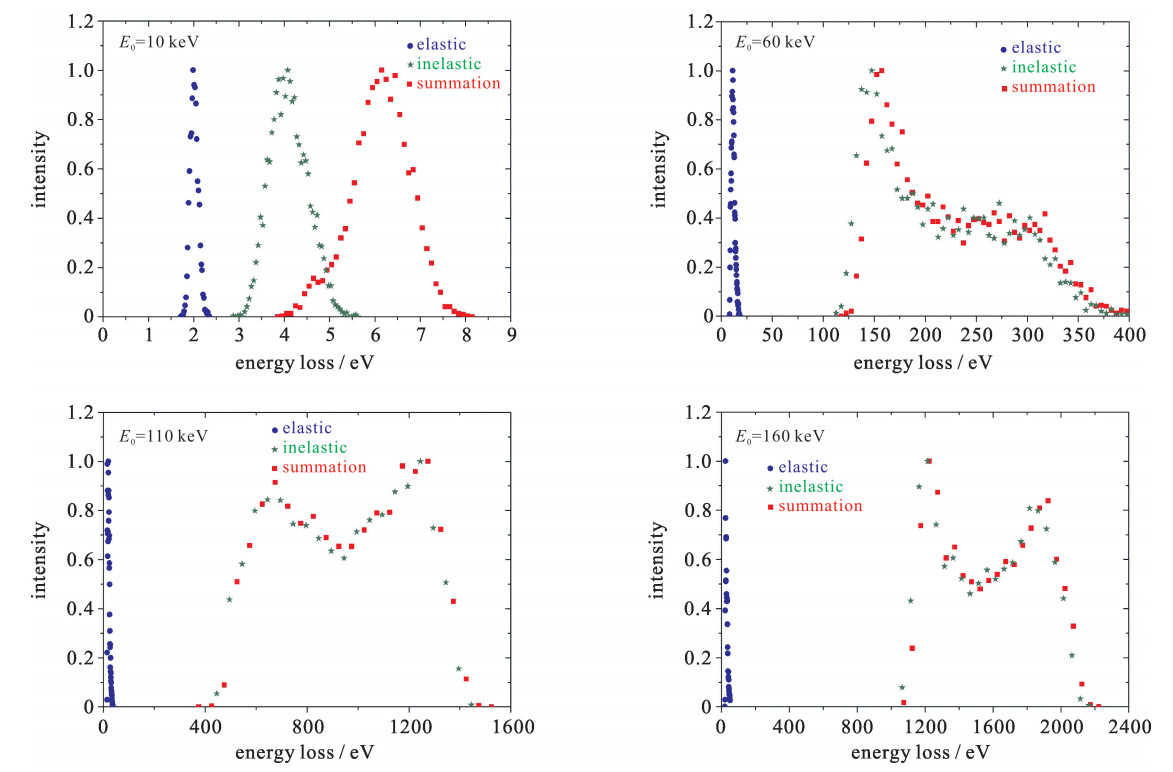
Figure 1. Energy loss spectra for 12 keV Ar scattering from single-crystal copper surface under an incidence angle of θin=2.2°
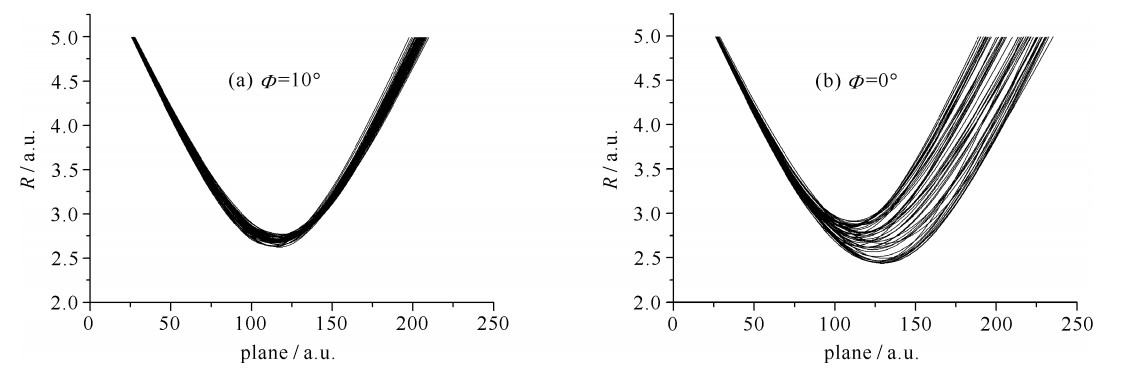
The azimuthal orientation of the target surface was chosen by azimuthal angles
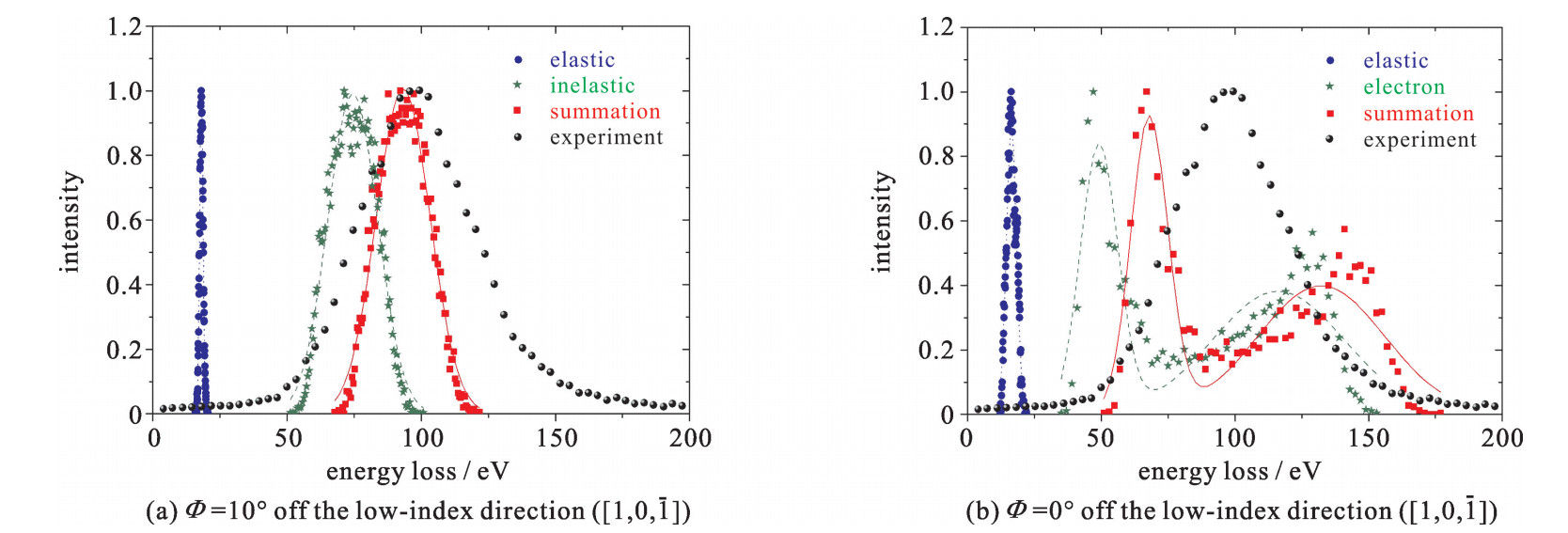
Full circles: experimental results of Ref. [18]. Curves: the present calculations fitted by Gaussian functions
(Dotted curve: elastic energy loss; dashed curves: inelastic energy loss; solid curves: summation of energy loss, i.e., total energy loss) -
[1] Briand J P, de Billy L, Charles P, et al. Subfemtosecond study of the hypersatellite cascade in "hollow" atoms[J]. Phys Rev A, 1991, 43: 565-567. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.43.565 [2] Limburg J, Schippers S, Hughes I, et al. Velocity dependence of KLL Auger emission from hollow atoms formed during collisions of hydrogenic N6+ ions on surfaces[J]. Phys Rev A, 1995, 51: 3873-3882. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.51.3873 [3] Briand J P, Etat B, Schnerifer D, et al. Time for the empty L shell of a hollow atom to be filled[J]. Phys Rev A, 1996, 53: 2194-2197. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.53.2194 [4] Winecki S, Cocke C L, Fry D, et al. Neutralization and equilibration of highly charged argon ions at grazing incidence on a graphite surface[J]. Phys Rev A, 1996, 53: 4228-4236. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.53.4228 [5] Briand J P, Giardino G, Borsoni G, et al. Decay of hollow atoms above and below a surface[J]. Phys Rev A, 1996, 54: 4136-4142. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.54.4136 [6] Winecki S, Stöckli M P, Cocke C L. Rapid neutralization and charge equilibration of highly charged ions at grazing incidence on a surface[J]. Phys Rev A, 1997, 56: 538-542. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.56.538 [7] Hughes I G, Burgdorfer J, Folkerts L, et al. Separation of kinetic and potential electron emission arising from slow multicharged ion-surface interactions[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 1993, 71: 291-294. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.71.291 [8] Lemell C, Stöckl J, Burgdörfer J, et al. Multicharged ion impact on clean Au(111): Suppression of kinetic electron emission in glancing angle scattering[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 1998, 81: 1965-1968. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.81.1965 [9] Luo Xianwen, Hu Bitao, Zhang Chengjun, et al. Electron and X ray emission of slow highly charged Arq+ ions in grazing incidence on an Al(111) surface[J]. Phys Rev A, 2010, 81: 052902-052913. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.81.052902 [10] Winter H, Aumayr F. Interaction of slow HCI with solid surfaces: What do we know, what should we know?[J]. Physica Scripta, 2001, T92: 15-21. [11] HuangW, Lebius H, Schuch R, et al. Energy loss in larger-angle scattering of slow highly charged Ar ions from a Au surface[J]. Phys Rev A, 1998, 58: 2962-2969. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.58.2962 [12] Susuki Y, Fritz M, Kimura K, et al. Energy loss and dissociation of 10-MeV/amu H3+ ions in carbon foils[J]. Phys Rev A, 1995, 51: 3868-3872. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.51.3868 [13] Juaristi J I, Arnau A, Echenique P M, et al. Charge state dependence of the energy loss of slow ions in metals[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 1999, 82: 1048-1051. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.82.1048 [14] Ziegler J F, Biersack J P, Littmark U. The stopping and ranges of ions in matter[M]. New York: Pergamon Press, 1985. [15] WinterH, Mertens A, Pfandzelter R, et al. Energy transfer of keV Ne atoms to the lattice of a LiF(001) surface under channeling[J]. Phys Rev A, 2002, 66: 022902-022908. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.66.022902 [16] Winter H P, Aumayr F, Lemell C, et al. Kinetic electron emission by grazing atom scattering from clean flat metal surfaces[J]. Nucl Instr and Meth B, 2007, 256: 455-463. doi: 10.1016/j.nimb.2006.12.044 [17] Mertens A, Winter H. Energy transfer from fast atomic projectiles to a crystal lattice under channeling conditions[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 2000, 85: 2825-2828. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.85.2825 [18] Lederer S, Winter H, Winter H P. Energy loss and electron emission during grazing scattering of fast noble gas atom from an Al(111) surface[J]. Nucl Instr and Meth B, 2007, 258: 87-90. doi: 10.1016/j.nimb.2006.12.095 [19] Luo Xianwen, Hu Bitao, Zhang Chengjun. Fragmentation and energy loss in grazing scattering of copper clusters Cun from a single-crystal Al(111) surface[J]. Phys Rev A, 2012, 85: 043201. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.85.043201 [20] Kurz H, Töglhofer K, Winter H P, et al. Electron emission from slow hollow atoms at a clean metal surface[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 1992, 69: 1140-1143. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.69.1140 [21] Limburg J, Das J, Schippers S, et al. Coster-Kronig transitions in hollow atoms created during highly charged ion-surface interactions[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 1994, 73: 786-789. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.73.786 [22] Stolterfoht N, Köhrbruck R, Grether M, et al. Models for L-shell filling of slow hollow atoms moving below a surface[J]. Nucl Instr and Meth B, 1995, 99: 4-7. doi: 10.1016/0168-583X(95)00207-3 [23] Stolterfoht N, Arnau A, Grether M, et al. Multiple-cascade model for the filling of hollow Ne atoms moving below an Al surface[J]. Phys Rev A, 1995, 52: 445-449. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.52.445 [24] Limburg J, Schippers S, Hoekstra R, et al. Do hollow atoms exist in front of an insulating LiF(100) surface[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 1995, 75: 217-219. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.75.217 [25] Briand J P, Thuriez S, Giardino G. Observation of hollow atoms or ions above insulator and metal surface[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 1996, 77: 1452-1455. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.77.1452 [26] Grether M, Niemann D, Spieler A, et al. Formation and filling of hollow Ne atoms below an Al surface[J]. Phys Rev A, 1997, 56: 3794-3803. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.56.3794 [27] Thomaschewski J, Bleck-Neuhaus J, Grether M, et al. Hollow nitrogen atoms probing the jellium edge in front of Au(111) surface[J]. Phys Rev A, 1998, 57: 3665-3672. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.57.3665 [28] Stolterfoht N, Bremer J H, Muino R D. Formation and cascading decay of hollow Ar atoms at a Si surface[J]. Interaction Journal of Mass Spectrometry, 1999, 192: 425-436. doi: 10.1016/S1387-3806(99)00106-2 [29] Khemliche H, Schlathölter T, Hoekstra R, et al. Hollow atom dynamics on LiF covered Au(111): Role of the surface electronic structure[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 1998, 81: 1219-1222. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.81.1219 [30] Stolterfoht N, Niemann D, Hoffmann V, et al. Plasmon production by the decay of hollow Ne atoms near an Al surface[J]. Phys Rev A, 2000, 61: 964-967. [31] Schlathölter T, Narmann A, Robin A, et al. Sputtering of hollow atoms from carbon surfaces[J]. Phys Rev A, 2000, 62: 190-195. [32] Diamant R, Huotari S, Hamalainen K, et al. Evolution from threshold of a hollow atom's X-ray emission spectrum: the Cu hypersatellites[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 2000, 84: 3278-3281. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.84.3278 [33] Tong X M, Kato D, Watanabe T, et al. Energy structure of hollow atoms or ions in the bulk of metallic materials[J]. Phys Rev A, 2001, 63: 052505-052512. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.63.052505 [34] WinterH, Aumayr F. Topic review: Hollow atoms[J]. J Phys B, 1999, 32: R39-R65. doi: 10.1088/0953-4075/32/7/005 [35] Arnau A, Köhrbruck R, Grether M, et al. Molecular-orbital model for slow hollow atoms colliding with atoms in a solid[J]. Phys Rev A, 1995, 51: R3399-R3404. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.51.R3399 [36] BriandJ P, Billy L, Charles P, et al. Production of hollow atoms by the excitation of highly charged ions in interaction with a metallic surface[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 1990, 65: 159-162. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.65.159 [37] Burgdörfer J, Lerner P, Meyer F W. Above-surface neutralization of highly charged ions: The classical over-the-barrier model[J]. Phys Rev A, 1991, 44: 5674-5685. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.44.5674 [38] Ducree J J, Casali F, Thumm U. Extended classical over-barrier model for collision of highly charged ions with conducting and insulating surfaces[J]. Phys Rev A, 1998, 57: 338-350. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.57.338 [39] Ducree J, Andra H J, Thumm U. Neutralization of hyperthermal multiply charged ions at surfaces: comparison between the extended dynamical over barrier model and experiment[J]. Phys Rev A, 1999, 60: 3029-3043. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.60.3029 [40] Bridwell L B, Hay H J, Pender L F, et al. Excitation of swift heavy ions in foil targets. Ⅳ. Preequilibrium energy losses and mean charge states[J]. Aust J phys, 1988, 41: 681-692. doi: 10.1071/PH880681 [41] Burgdorfer J, Meyer F. Image acceleration of multiply charged ions by metallic surfaces[J]. Phys Rev A, 1993, 47: R20-R22. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.47.R20 [42] Song Yuan-Hong, Wang You-Nian, Miskovic Z L. Energy loss of heavy ions specularly reflected from surfaces under glancing-angle incidence[J]. Phys Rev A, 2001, 63: 052902. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.63.052902 [43] Wang Y N, Liu W K. Energy loss of ions moving near a solid surface[J]. Phys Rev A, 1996, 54: 636-640. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.54.636 [44] Fetterman A, Sinclair L, Tanushev N. Simulation of the channeling of ions from MeV C60 in crystalline solids[J]. J Phys B, 2007, 40: 2055-2064. doi: 10.1088/0953-4075/40/11/008 [45] Auth C, Mertens A, Winter H, et al. Threshold in the stopping of slow protons scattered from the surface of a wide-band-gap insulator[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 1998, 81: 4831-4834. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.81.4831 [46] Borisov A, Mertens A, Winter H. Evidence for the stopping of slow ions by excitation of optical phonons in insulators[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 1999, 83: 5378-5381. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.83.5378 -




 下载:
下载: