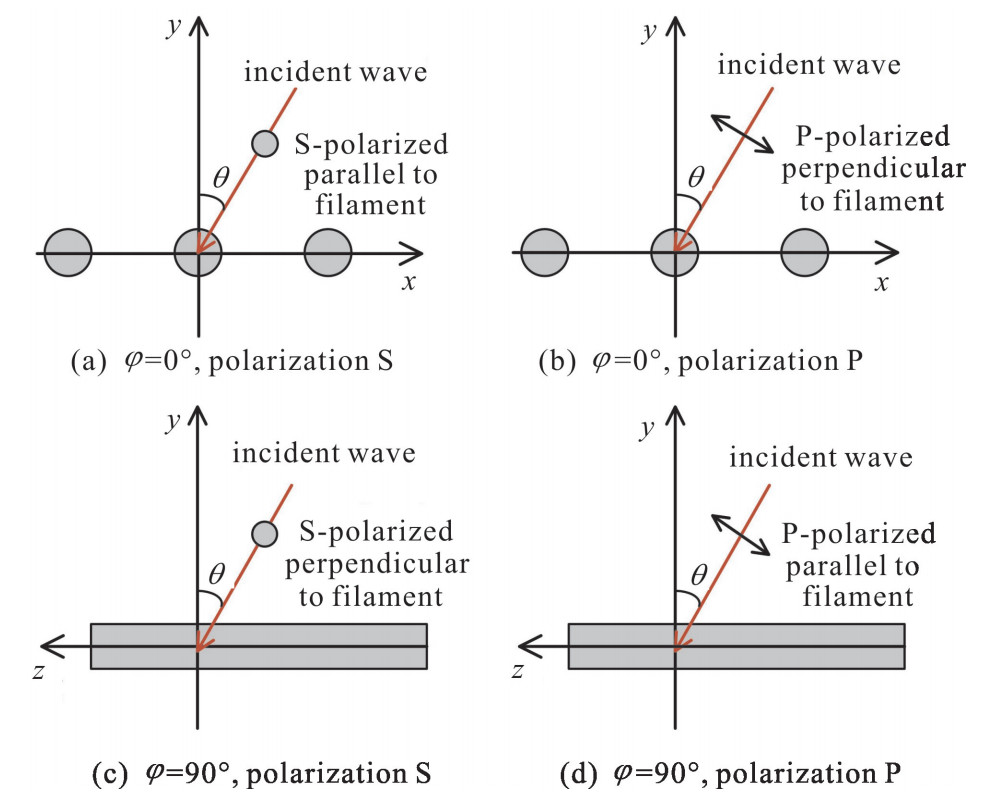
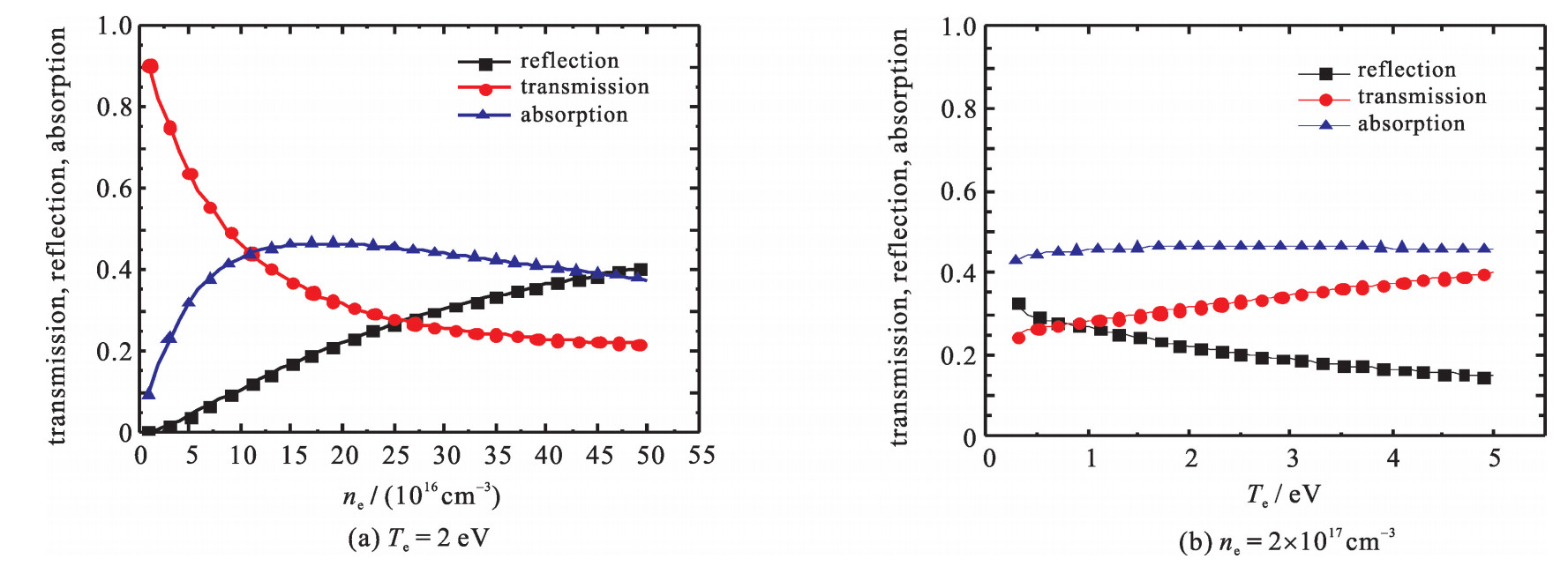
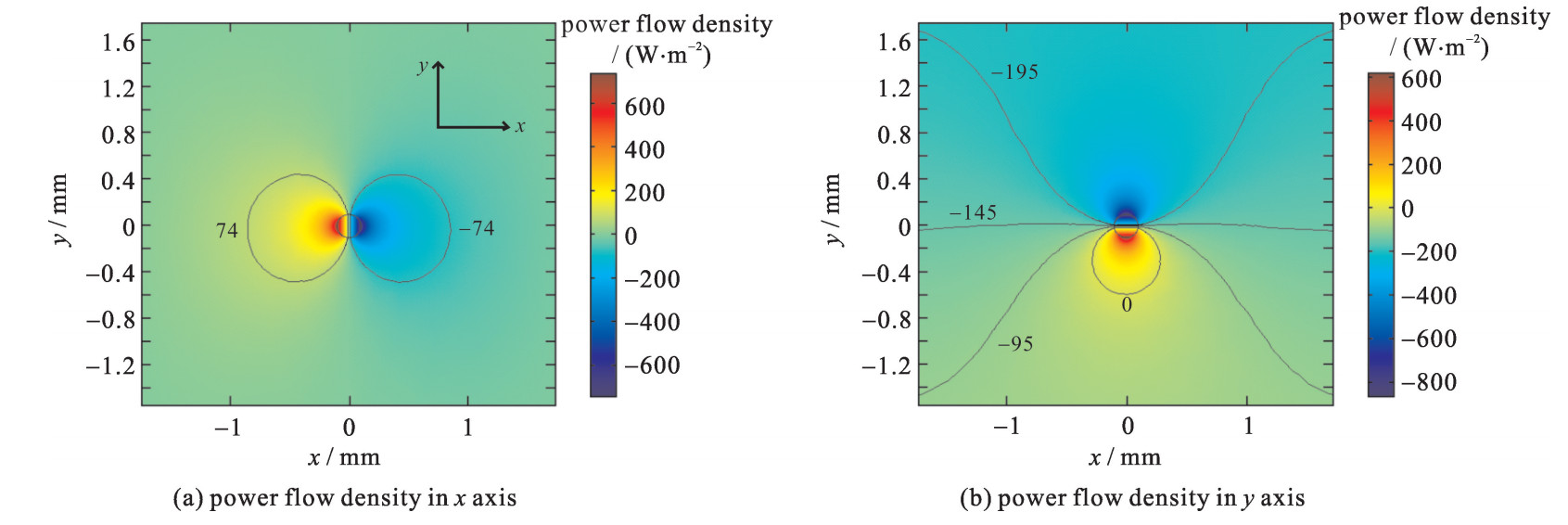
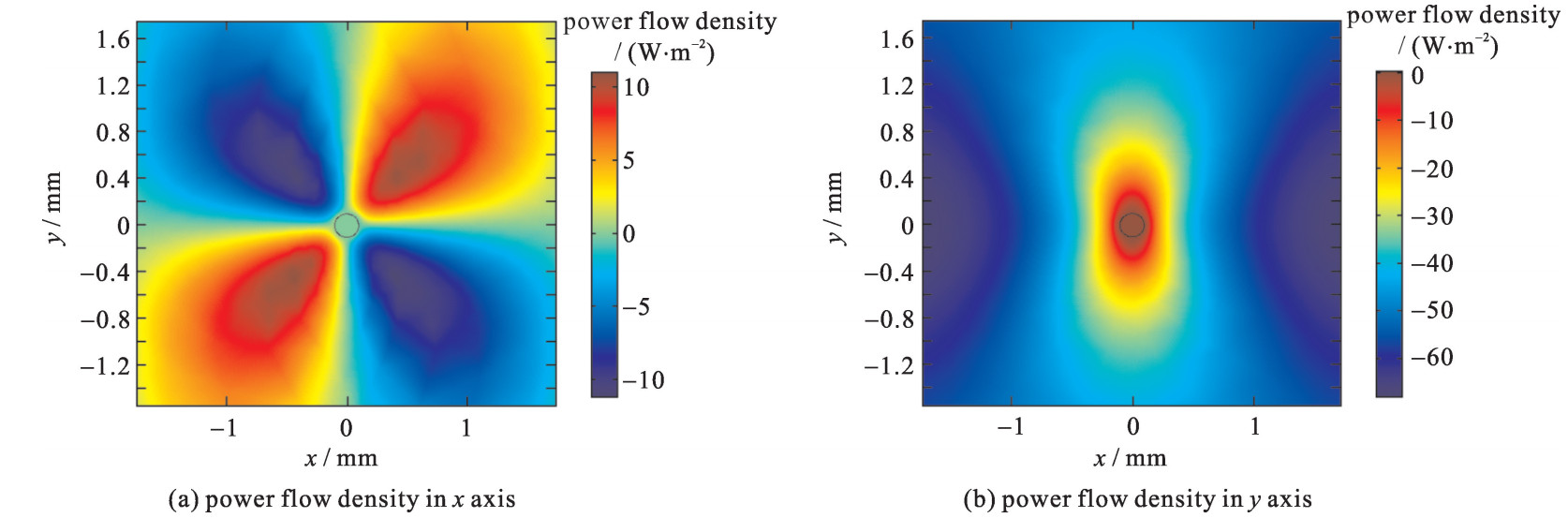
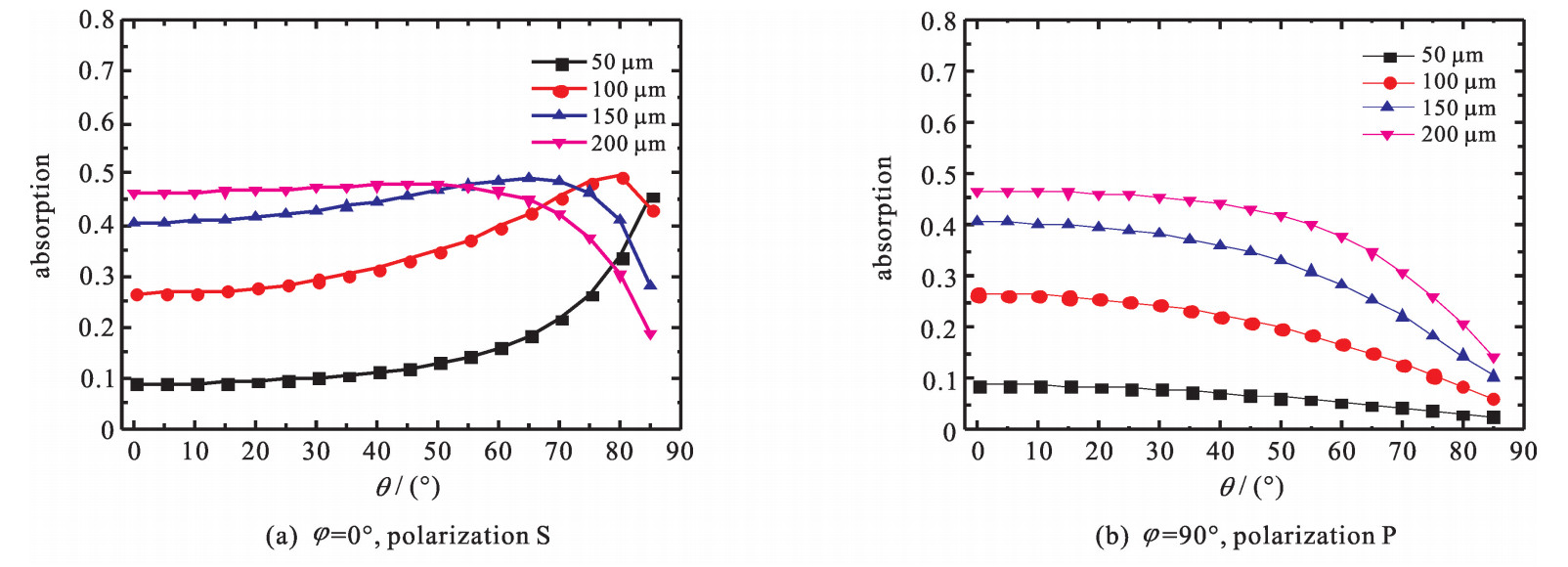
| [1] |
Rodriguez M, Bourayou R, Méjean G, et al. Kilometer-range nonlinear propagation of femtosecond laser pulses[J]. Physical Review E, 2004, 69: 036607. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.69.036607
|
| [2] |
Schillinger H, Sauerbrey R. Electrical conductivity of long plasma channels in air generated by self-guided femtosecond laser pulses[J]. Applied Physics B, 1999, 68(4): 753-756. doi: 10.1007/s003400050699
|
| [3] |
王海涛, 范承玉, 沈红, 等. 飞秒光丝中等离子体密度时间演化特征[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2012, 24(5): 1024-1028. doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20122405.1024Wang Haitao, Fan Chengyu, Shen Hong, et al. Temporal evolution of plasma density in femtosecond light filaments. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2012, 24(5): 1024-1028 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20122405.1024
|
| [4] |
Courvoisier F, Boutou V, Kasparian J, et al. Ultraintense light filaments transmitted through clouds[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2003, 83(2): 213-215. doi: 10.1063/1.1592615
|
| [5] |
Méchain G, Méjean G, Ackermann R, et al. Propagation of fs TW laser filaments in adverse atmospheric conditions[J]. Applied Physics B, 2005, 80(7): 785-789. doi: 10.1007/s00340-005-1825-2
|
| [6] |
Silaeva E P, Kandidov V P. Propagation of a high-power femtosecond pulse filament through a layer of aerosol[J]. Atmospheric and Oceanic Optics, 2009, 22(1): 26-34. doi: 10.1134/S1024856009010059
|
| [7] |
高慧. 超快激光光丝阵列产生机理研究[D]. 天津: 南开大学, 2013.Gao Hui. Ultrafast laser filament array generation. Tianjin: Nankai University, 2013
|
| [8] |
Musin R R, Shneider M N, Zheltikov A M, et al. Guiding radar signals by arrays of laser-induced filaments: Finite-difference analysis[J]. Applied Optics, 2007, 46(23): 5593-5597. doi: 10.1364/AO.46.005593
|
| [9] |
Chateauneuf M, Payeur S, Dubois J, et al. Microwave guiding in air by a cylindrical filament array waveguide[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2008, 92: 091104. doi: 10.1063/1.2889501
|
| [10] |
Shneider M N, Zheltikov A M, Miles R B. Long-lived laser-induced microwave plasma guides in the atmosphere: self-consistent plasma-dynamic analysis and numerical simulations[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2010, 108: 033113. doi: 10.1063/1.3457150
|
| [11] |
Marian A, Morsli M E, Vidal F, et al. The interaction of polarized microwaves with planar arrays of femtosecond laser-produced plasma filaments in air[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2013, 20: 023301. doi: 10.1063/1.4792160
|
| [12] |
Alshershby M, Hao Z, Camino A, et al. Modeling a femtosecond filament array waveguide for guiding pulsed infrared laser radiation[J]. Optics Communications, 2013, 296: 87-94. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2012.12.067
|
| [13] |
Camino A, Xi T, Hao Z, et al. Femtosecond filament array generated in air[J]. Applied Physics B, 2015, 121(3): 363-368. doi: 10.1007/s00340-015-6238-2
|
| [14] |
Bogatskaya A V, Popov A M, Smetanin I V. Amplification and guiding of microwave radiation in a plasma channel created by an ultrashort high-intensity laser pulse in noble gases[J]. Journal of Russian Laser Research, 2014, 35(5): 437-446. doi: 10.1007/s10946-014-9445-0
|
| [15] |
Bogatskaya A V, Hou B, Popov A M, et al. Nonequilibrium laser plasma of noble gases: Prospects for amplification and guiding of the microwave radiation[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2016, 23: 374001.
|
| [16] |
Kartashov D, Shneider M N. Femtosecond filament initiated, microwave heated cavity-free nitrogen laser in air[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2017, 121: 113303. doi: 10.1063/1.4978745
|
| [17] |
Prade B, Houard A, Larour J, et al. Transfer of microwave energy along a filament plasma column in air[J]. Applied Physics B, 2017, 123(1): 40. doi: 10.1007/s00340-016-6616-4
|
| [18] |
吴莹. 激光等离子体的微波干扰和诊断研究[D]. 南京: 南京理工大学, 2009.Wu Ying. Studies on microwave interference and microwave measure of laser-induced plasma. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Science and Technology, 2009
|
| [19] |
弗朗西斯·F·陈. 等离子体物理学导论[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2016.Chen F F. Introduction to plasma physics. Beijing: Science Press, 2016
|
| [20] |
Huba J D. NRL (Naval Research Laboratory) plasma formulary, revised[R]. NRL/PU/6790-16-614, 2016.
|
| [21] |
张亚春, 何湘, 沈中华, 等. 进气道内衬筒形等离子体隐身性能三维模拟[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2015, 27: 052005. doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201527.052005Zhang Yachun, He Xiang, Shen Zhonghua, et al. Three-dimensional simulation of plasma stealth for cylindrical inlet. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2015, 27: 052005 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201527.052005
|
| [22] |
庄钊文, 袁乃昌, 刘少斌, 等. 等离子体隐身技术[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2005.Zhuang Zhaowen, Yuan Naichang, Liu Shaobin, et al. Plasma Stealth Technology. Beijing: Science Press, 2005
|




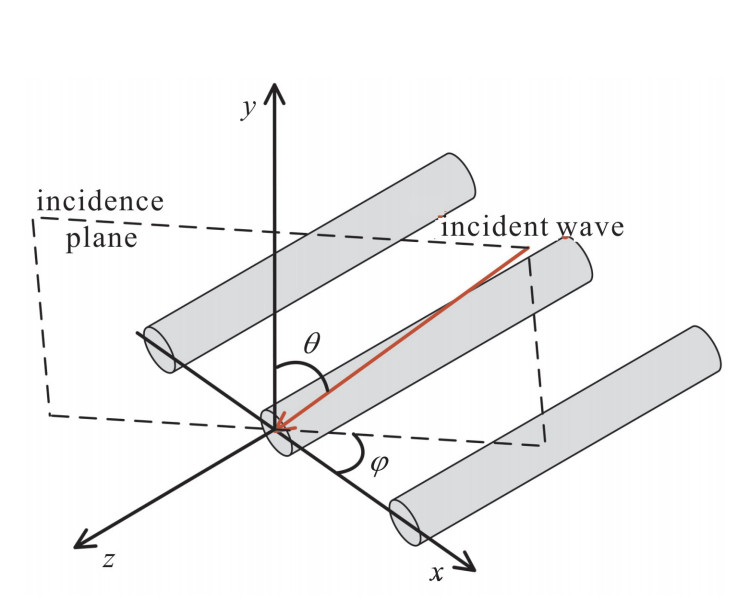
 下载:
下载: