Research on influence of cutting parameters on frequency characteristics of KDP surface topography
-
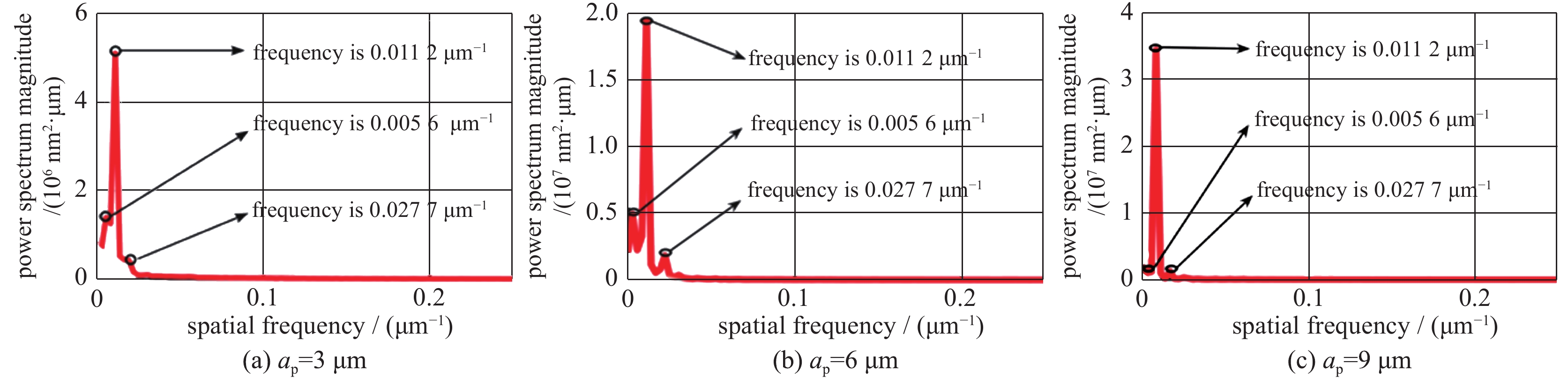
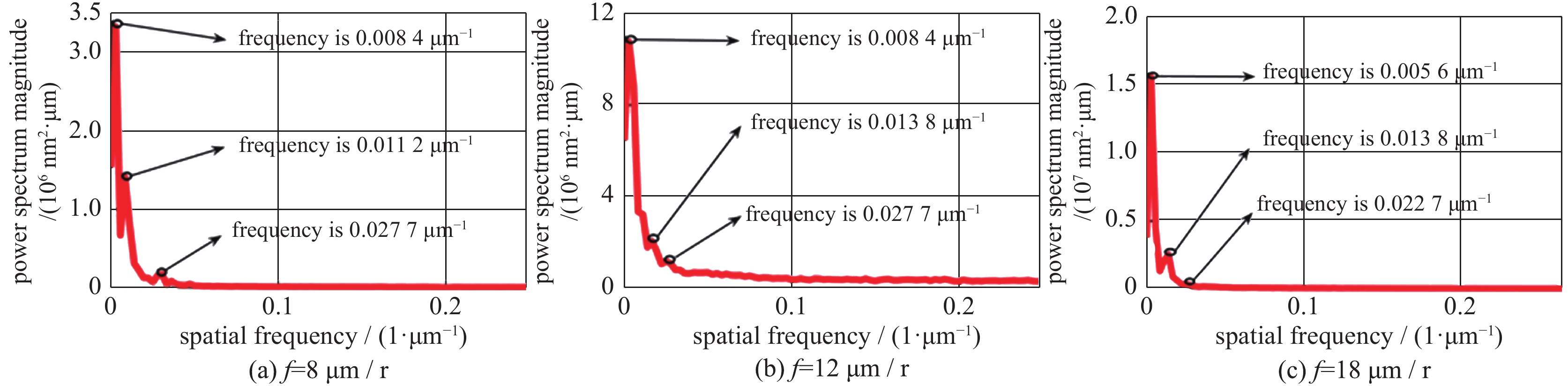
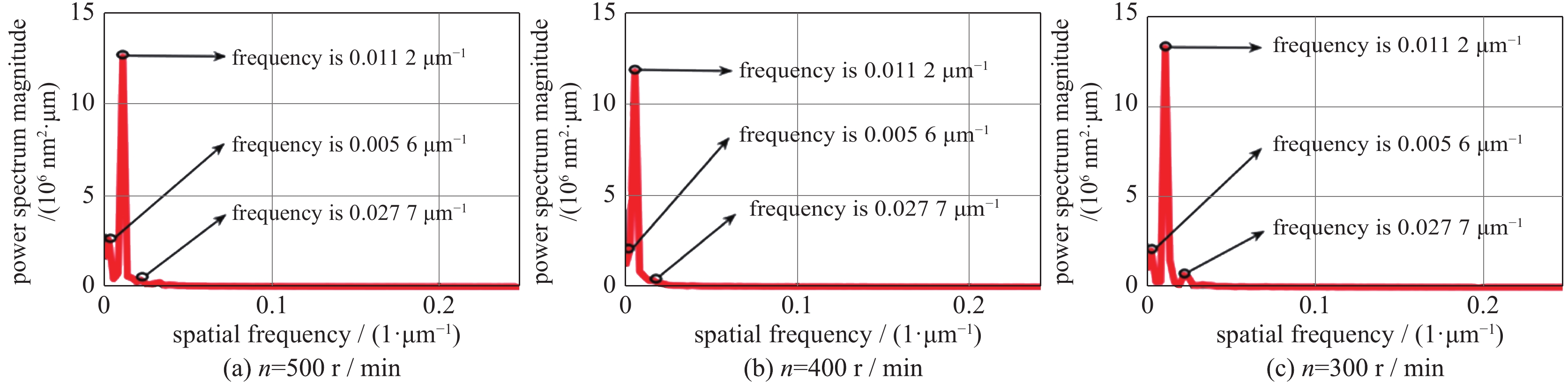
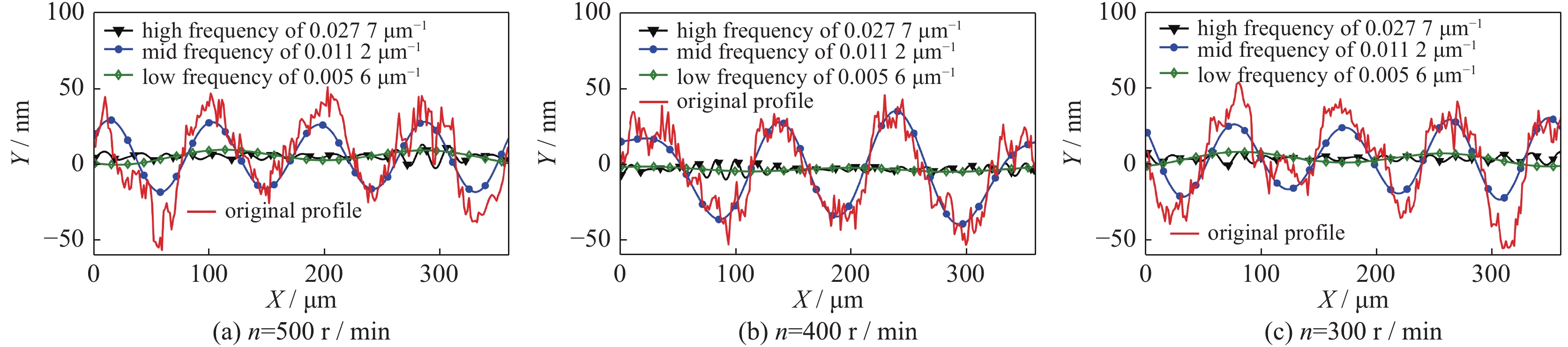
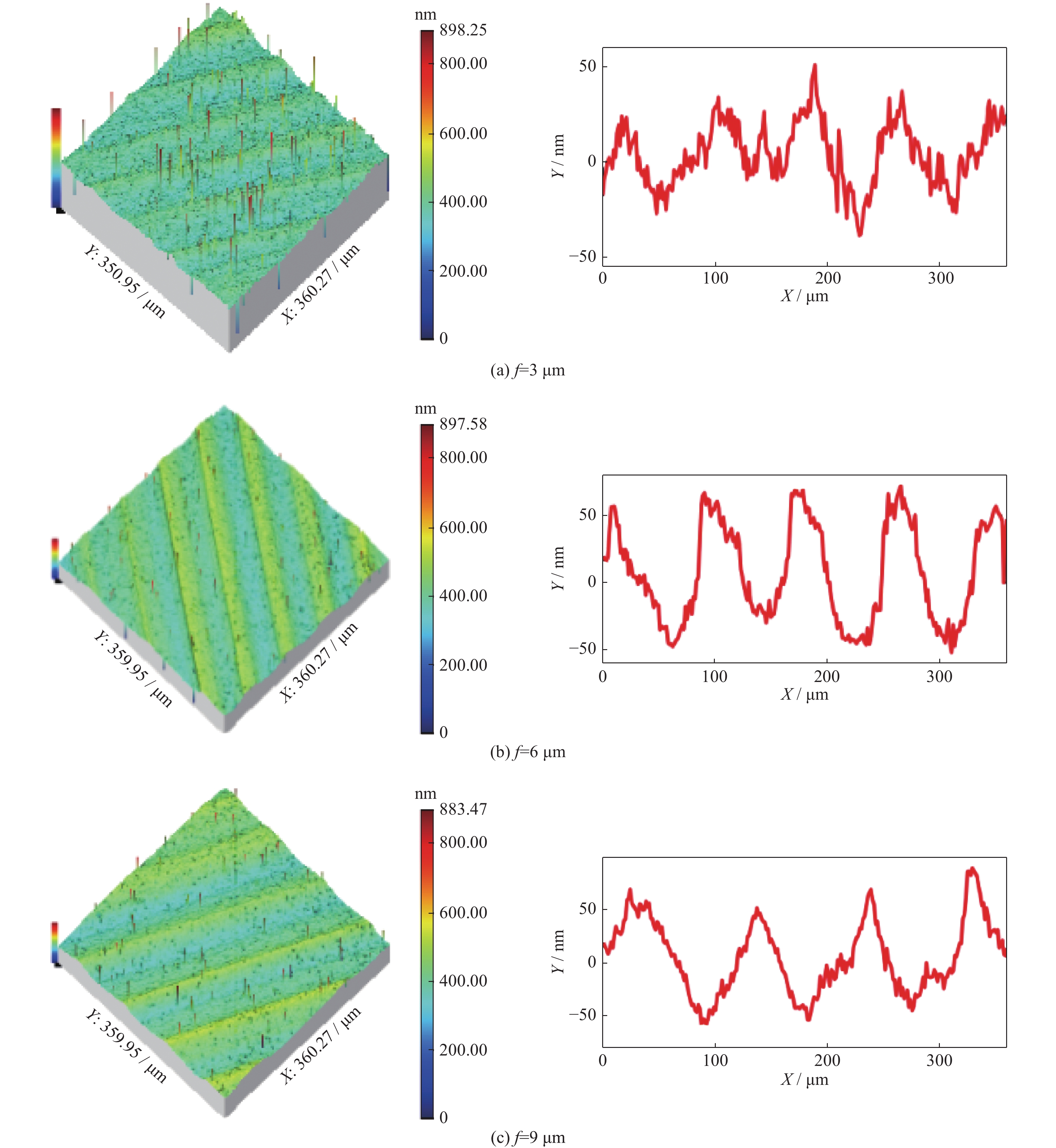
摘要: 针对采用单点金刚石超精加工的KDP晶体光学表面,研究了切削参数对微观形貌频率特征的影响。通过功率谱密度获得表面轮廓频率分布,并用连续小波重构加工过程中随切削用量变化的微观轮廓频率特征。结果表明:切削参数对微观形貌的影响具体表现在实际频率特征上,中频特征波长及幅值反映了切深及转速变化,随切深及转速增加,幅值变大;低频特征反映了进给量变化,随着进给量变小,频率及幅值变小;高频特征是加工过程中振动及材料各向异性的具体表现。
-
关键词:
- 频率特征 /
- 表面形貌 /
- 切削参数 /
- 功率谱密度(PSD) /
- 连续小波变换(CWT)
Abstract: The influence of cutting parameters on the frequency characteristics of optical crystal surface has been studied. The experiment of single point diamond turning was adopted to process KDP crystal. The frequency distribution of surface profile was obtained by power spectral density. The continuous wavelet method was used to evaluate the influence of cutting depth, feed rate and spindle speed on machined surface. The results show that the frequency characteristics reflect the effects of cutting parameters on surface topography. The wavelength and amplitude of mid frequency embody the change of cutting depth and spindle speed, and the amplitude increases with the increase of cutting depth and speed. Low frequency reflects the change of feed rate, and the amplitude becomes small as feed rate decreases. High frequency is the manifestation of vibration and material anisotropy in processing. Therefore the analysis of frequency characteristics on surface topography provides a reference for selecting the optimal process parameters. -
表 1 圆弧刃天然单晶金刚石车刀参数
Table 1. Parameters of diamond turning tool
nose radius r/mm edge radius rn/nm rake angle γ0/(°) clearance angle α0/(°) 3.2 150 0 9 表 2 切削参数及其轮廓均方根比较
Table 2. Cutting parameters and RMS of contour
No.(group) spindle speed n/(r/min) feed rate f /(μm/r) depth of cut ap/μm RMS of contour Rq/nm 1 400 10 3 17 6 35 9 37 2 300 8 3 15 12 24 18 27 3 500 10 5 25 400 24 300 26 表 3 尺度因子及其计算过程参数
Table 3. Scale a and its parameters of calculations
frequency f/μm−1 size L/μm number N waviness central frequency fs mexihat central frequency fc sampling period Δ scale a low 0.005 6 360 256 0.015 8 0.25 1.412 11.209 3 0.008 4 0.023 7 7.472 9 mid 0.011 2 0.031 2 5.674 8 0.013 8 0.038 8 4.563 2 high 0.027 7 0.077 9 2.272 8 -
[1] Wang Hui, Zhang Zheng, Liu Tianye, et al. Surface error modeling, evaluation and optimization of large optics in inertial confinement fusion laser system[J]. Fusion Eng Des, 2018, 137: 61-70. doi: 10.1016/j.fusengdes.2018.08.005 [2] NayarB K. Nonlinear optical properties of organic molecules and crystals[M]. Elsevier, 2012. [3] Tie Guipeng, Dai Yifan, Guan Chaoliang, et al. Research on full-aperture ductile cutting of KDP crystals using spiral turning technique[J]. J Mater Process Tech, 2013, 213(12): 2137-2144. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2013.06.006 [4] Chen Ni, Chen Mingjun, Wu Chunya, et al. The design and optimization of micro polycrystalline diamond ball end mill for repairing micro-defects on the surface of KDP crystal[J]. Precis Eng, 2016, 43: 345-355. doi: 10.1016/j.precisioneng.2015.08.015 [5] Li Zhanjie, Jin Gang, Fang Fengzhou, et al. Ultrasonically assisted single point diamond turning of optical mold of tungsten carbide[J]. Micromachines, 2018, 9(2): 77-87. doi: 10.3390/mi9020077 [6] Cheng Jian, Xiao Yong, Liu Qi, et al. Effect of surface scallop tool marks generated in micro-milling repairing process on the optical performance of potassium dihydrogen phosphate crystal[J]. Mater Design, 2018, 157: 447-456. doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2018.07.057 [7] Wang Yongqiang, Yin Shaohui, Huang Han, et al. Magnetorheological polishing using a permanent magnetic yoke with straight air gap for ultra-smooth surface planarization[J]. Precis Eng, 2015, 40: 309-317. doi: 10.1016/j.precisioneng.2014.11.001 [8] Ji Fang, Xu Min, Wang Baorui, et al. Preparation of methoxyl poly (ethylene glycol) (MPEG)-coated carbonyl iron particles (CIPs) and their application in potassium dihydrogen phosphate (KDP) magnetorheological finishing (MRF)[J]. Appl Surf Sci, 2015, 353: 723-727. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.06.063 [9] Peng Wenqiang, Li Shenyi, Guan Chaoliang, et al. Ultra-precision optical surface fabricated by hydrodynamic effect polishing combined with magnetorheological finishing[J]. Optik-International Journal for Light and Electron Optics, 2018, 156: 374-383. doi: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2017.11.055 [10] Clark W I, Shih A J, Hardin C W, et al. Fixed abrasive diamond wire machining—part I: Process monitoring and wire tension force[J]. Int J Mach Tool Manu, 2003, 43(5): 523-532. doi: 10.1016/S0890-6955(02)00215-8 [11] Pang Qilong, Kuang Liangjie, Xu Youlin, et al. Study on the extraction and reconstruction of arbitrary frequency topography from precision machined surfaces[J]. P I Mech Eng B-J Eng, 2019, 233(7): 1772-1780. [12] Chen Ni, Chen Mingjun, Wu Chunya, et al. Cutting surface quality analysis in micro ball end-milling of KDP crystal considering size effect and minimum undeformed chip thickness[J]. Precis Eng, 2017, 50: 410-420. doi: 10.1016/j.precisioneng.2017.06.015 [13] Chen Ni, Chen Mingjun, Guo Yanqiu, et al. Effect of cutting parameters on surface quality in ductile cutting of KDP crystal using self-developed micro PCD ball end mill[J]. Int J Adv Manuf Tech, 2015, 78(1/4): 221-229. [14] Zheng Wei, Zhou Ming, Zhou Li. Influence of process parameters on surface topography in ultrasonic vibration-assisted end grinding of SiCp/Al composites[J]. Int J Adv Manuf Tech, 2017, 91(5/8): 2347-2358. [15] Wang Shengfei, An Chenhui, Zhang Feihu, et al. An experimental and theoretical investigation on the brittle ductile transition and cutting force anisotropy in cutting KDP crystal[J]. Int J Mach Tool Manu, 2016, 106: 98-108. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2016.04.009 [16] Tian Fujing, Yin Ziqiang, Li Shengyi. Theoretical and experimental investigation on modeling of surface topography influenced by the tool-workpiece vibration in the cutting direction and feeding direction in single-point diamond turning[J]. Int J Adv Manuf Tech, 2016, 86(9/12): 2433-2439. [17] Wang Xuezhi, Yu Tianbiao, Dai Yuanxing, et al. Kinematics modeling and simulating of grinding surface topography considering machining parameters and vibration characteristics[J]. Int J Adv Manuf Tech, 2016, 87: 2459-2470. doi: 10.1007/s00170-016-8660-y [18] Krolczyk G M, Maruda R W, Krolczyk J B, et al. Parametric and nonparametric description of the surface topography in the dry and MQCL cutting conditions[J]. Measurement, 2018, 121: 225-239. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2018.02.052 [19] Zhang Qing, Zhang Song, Shi Wenhao. Modeling of surface topography based on relationship between feed per tooth and radial depth of cut in ball-end milling of AISI H13 steel[J]. Int J Adv Manuf Tech, 2018, 95(9/12): 4199-4209. [20] Wei Weihua, Li Yuantong, Xue Tongming, et al. Research on milling forces during high-speed milling of wood-plastic composites[J]. BioResources, 2018, 14(1): 769-779. [21] Wei Weihua, Li Yuantong, Mei Changtong, et al. The research progress of machining mechanisms in milling wood-based materials[J]. BioResources, 2018, 13(1): 2139-2149. [22] Itoh T, Yamauchi N. Surface morphology characterization of pentacene thin film and its substrate with under-layers by power spectral density using fast Fourier transform algorithms[J]. Appl Surf Sci, 2007, 253(14): 6196-6202. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2007.01.056 [23] Nieslony P, Krolczyk G M, Wojciechowski S, et al. Surface quality and topographic inspection of variable compliance part after precise turning[J]. Appl Surf Sci, 2018, 434: 91-101. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.10.158 -




 下载:
下载: