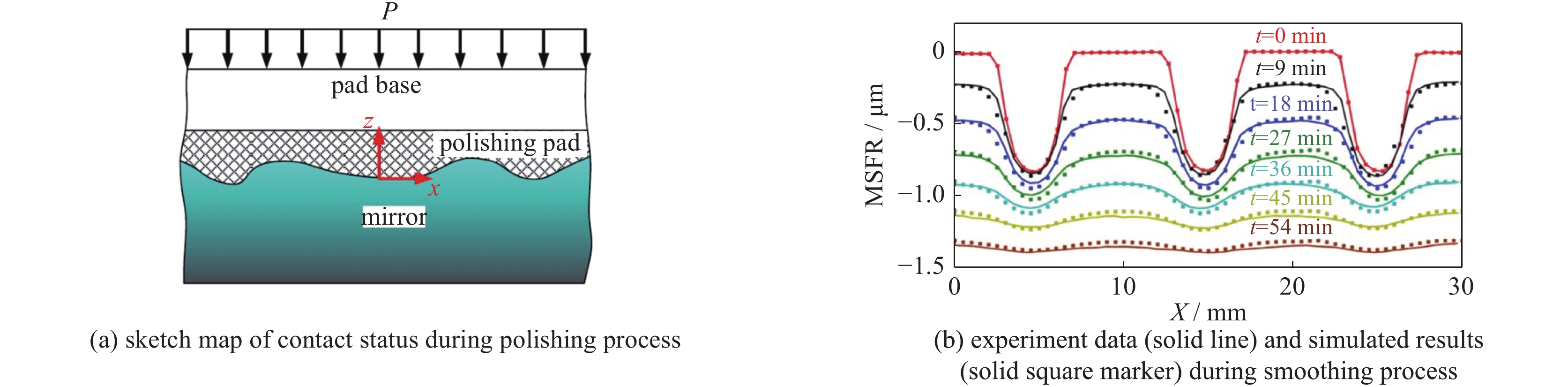
| [1] |
Wang Ganchang. Suggestion of neutron generation with powerful lasers[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 1987, 22(11): 7.
|
| [2] |
Hogan W J, Moses E I, Warner B E, et al. The National Ignition Facility[J]. Optical Engineering, 2002, 43(12): 21-51.
|
| [3] |
Zheng Wanguo, Zhang Xiaomin, Wei Xiaofeng, et al. Status of the SG-Ⅲ solid-state laser facility[C]//The Fifth International Conference on Inertial Fusion Sciences and Applications, 2008, 112: 032009.
|
| [4] |
Campbell J H, Hawley-Fedder R A, Stolz C J, et al. NIF optical materials and fabrication technologies: an overview[C]//Proc of SPIE. 2004, 5341: 1-18.
|
| [5] |
Baisden P A, Atherton L J, Hawley RA, et al. Large optics for the National Ignition Facility[J]. Fusion Science & Technology, 2016, 69(1): 614-620.
|
| [6] |
Suratwala T I, Miller P E, Bude J D, et al. HF based etching processes for improving laser damage resistance of fused silica optical surfaces[J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2011, 94(2): 416-428. doi: 10.1111/j.1551-2916.2010.04112.x
|
| [7] |
Wood R M. Laser-induced damage of optical materials[M].London: Institute of Physics Publishing, 2003.
|
| [8] |
Liao Wenlin, Dai Yifan, Xie Xuhui, et al. Morphology evolution of fused silica surface during ion beam figuring of high-slope optical components[J]. Applied Optics, 2013, 52(16): 3719-3725. doi: 10.1364/AO.52.003719
|
| [9] |
Liao Wenlin, Dai Yifan, Xie Xuhui. Nanopatterning of optical surfaces during low-energy ion beam sputtering[J]. Optical Engineering, 2014, 53: 065108.
|
| [10] |
Liao Wenlin, Dai Yifan, Xie Xuhui, et al. Deterministic ion beam material adding technology for high-precision optical surfaces[J]. Applied Optics, 2013, 52(6): 1302-1309. doi: 10.1364/AO.52.001302
|
| [11] |
Liao Wenlin, Dai Yifan, Xie Xuhui, et al. Combined figuring technology for high-precision optical surfaces using a deterministic ion beam material adding and removal method[J]. Optical Engineering, 2013, 52: 010503.
|
| [12] |
Peng Wenqiang, Guan Chaoliang, Li Shengyi. Ultrasmooth surface polishing based on the hydrodynamic effect[J]. Applied Optics, 2013, 52(25): 6411-6416. doi: 10.1364/AO.52.006411
|
| [13] |
Peng Wenqiang, Li Shengyi, Guan Chaoliang, et al. Ultra-precision optical surface fabricated by hydrodynamic effect polishing combined with magnetorheological finishing[J]. Optik, 2018, 156: 374-383. doi: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2017.11.055
|
| [14] |
Peng Wenqiang, Guan Chaoliang, Li Shengyi, et al. The improvement of laser induced damage resistance of optical workpiece surface by hydrodynamic effect polishing[C]//Proc of SPIE. 2016: 968315.
|
| [15] |
Nie Xuqing, Li Shengyi, Shi Feng, et al. Generalized numerical pressure distribution model for smoothing polishing of irregular midspatial frequency errors[J]. Applied Optics, 2014, 53(6): 1020-1027. doi: 10.1364/AO.53.001020
|
| [16] |
Nie Xuqing, Li Shengyi, Hu Hao, et al. Control of mid-spatial frequency errors considering the pad groove feature in smoothing polishing process[J]. Applied Optics, 2014, 53(28): 6332-6339. doi: 10.1364/AO.53.006332
|
| [17] |
Nie Xuqing, Li Shengyi, Song Ci, et al. Combined fabrication process for high-precision aspheric surface based on smoothing polishing and magnetorheological finishing[C]//Proc of SPIE. 2014: 928111.
|
| [18] |
Shi Feng, Shu Yong, Dai Yifan, et al. Magnetorheological elastic super-smooth finishing for high-efficiency manufacturing of ultraviolet laser resistant optics[J]. Optical Engineering, 2013, 52: 075104.
|
| [19] |
Shi Feng, Tian Ye, Peng Xiaoqiang, et al. Combined technique of elastic magnetorheological finishing and HF etching for high-efficiency improving of the laser-induced damage threshold of fused silica optics[J]. Applied Optics, 2014, 53(5): 598-604.
|
| [20] |
Shi Feng, Zhong Yaoyu, Dai Yifan, et al. Investigation of surface damage precursor evolutions and laser-induced damage threshold improvement mechanism during Ion beam etching of fused silica[J]. Optics Express, 2016, 24(18): 20842-20854. doi: 10.1364/OE.24.020842
|
| [21] |
Xu Mingjin, Dai Yifan, Zhou Lin, et al. Investigation of surface characteristics evolution and laser damage performance of fused silica during ion-beam sputtering[J]. Optical Materials, 2016, 58: 151-157. doi: 10.1016/j.optmat.2016.03.034
|
| [22] |
Xu Mingjin, Shi Feng, Zhou Lin, et al. Investigation of laser-induced damage threshold improvement mechanism during ion beam sputtering of fused silica[J]. Optics Express, 2017, 25(23): 29260-29271. doi: 10.1364/OE.25.029260
|





 下载:
下载: