Research progress on generation and application of the magnetic field of intense laser-driven coil target
-
摘要:
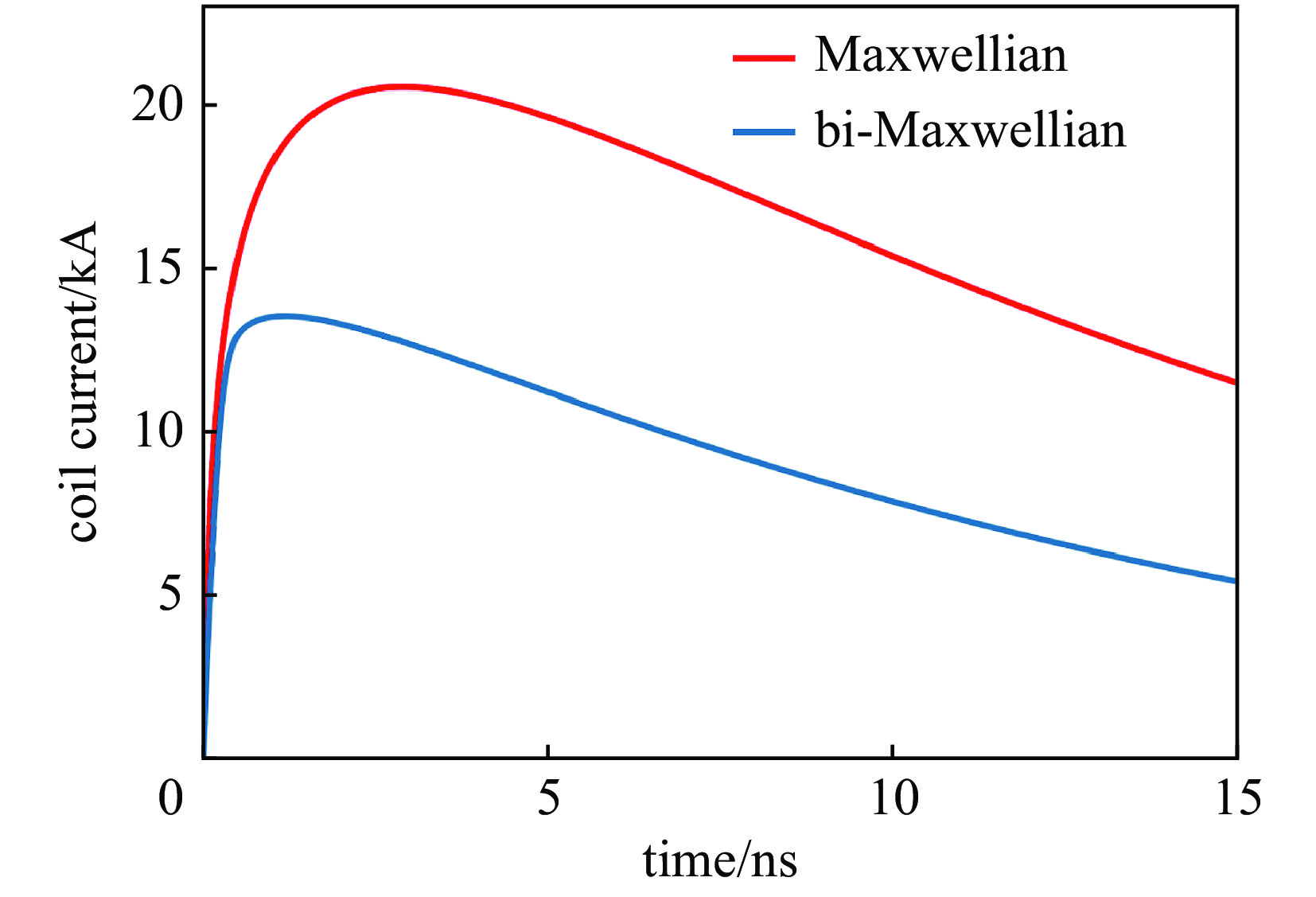
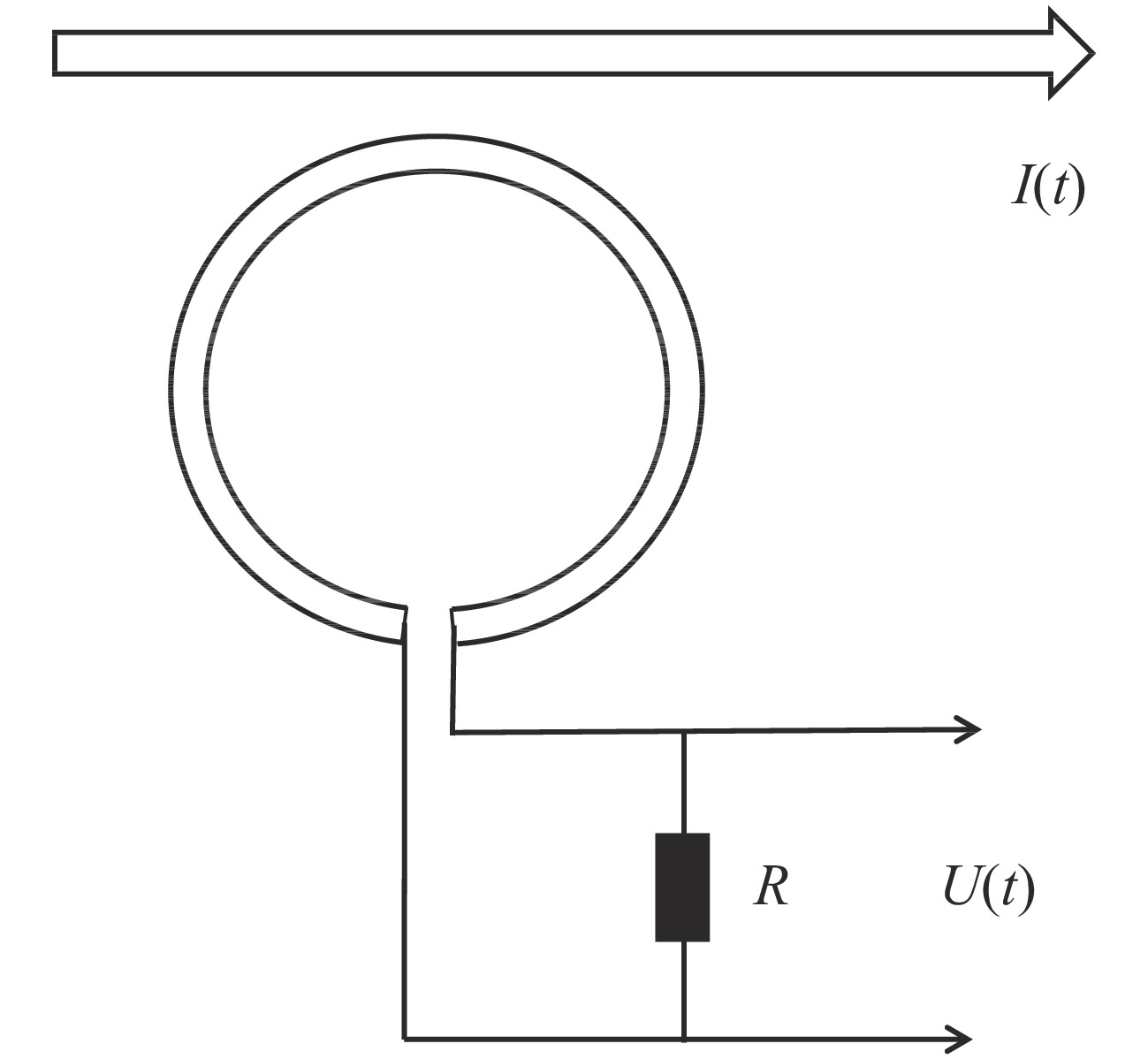
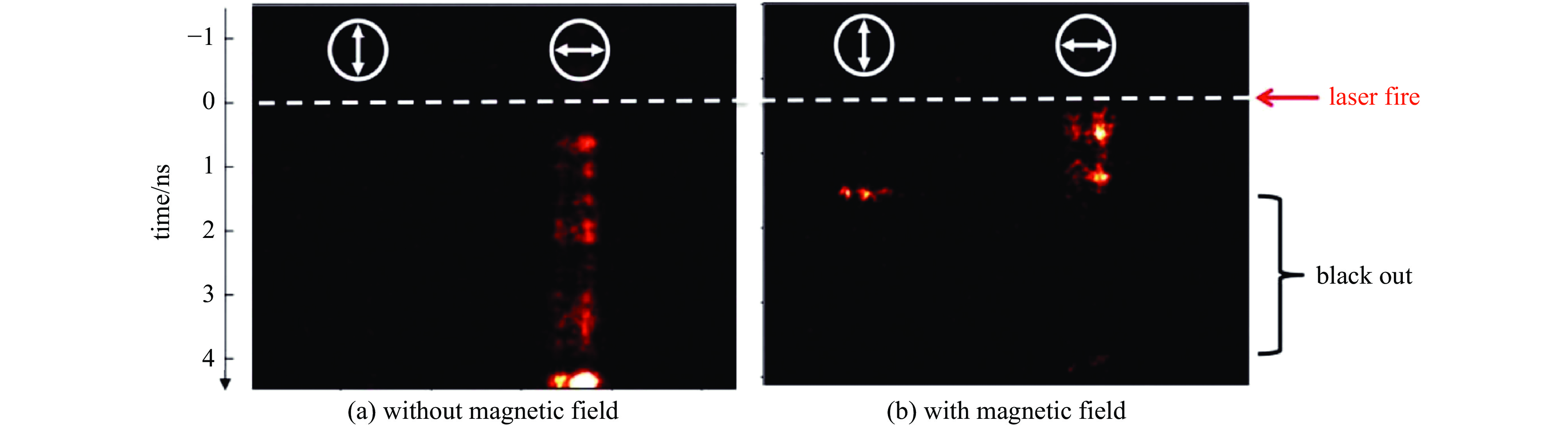
介绍了以强激光驱动电容线圈靶的实验方法产生磁场的基本模型及其发展过程。对比了实验室中常用的三种磁场诊断方法,包含:B-dot、法拉第旋转以及质子背光,发现前两种方法在实验中仅可以获得距离靶较远处的有限个磁场值,通过结合模拟工具获得靶处的磁场值与测量点的值跨越几个数量级,容易产生误差;质子背光诊断可以在实验中获得全局磁场信息,能够较好地满足线圈靶磁场诊断的需求。由于线圈靶磁场强且可持续时间长,在时空分布上具有一定可控性,因此我们将其应用到了磁重联的研究中,并成功获得了重联出流等特征。另外线圈靶在带电粒子的约束和磁流体动力学研究等多方面也得到了应用。
Abstract:It has been experimentally proved that the intense laser-driven capacitor-coil target can generate a strong magnetic field of several hundred Tesla. The basic model of the magnetic field generated by this experimental method and its development process are introduced. Comparisons are made between three magnetic field diagnostic methods commonly used in laboratory, including: B-dot, Faraday rotation and proton backlight, it is found that the first two methods can only obtain a limited number of magnetic field values far away from the target in the experiment. The values of the magnetic field at the target obtained by the simulation tool and the value of the measurement point cover a span of several orders of magnitude, which is prone to errors; the proton backlight diagnosis can obtain the global magnetic field information in the experiment, which can better meet the needs of the magnetic field diagnosis of the coil target. Because the magnetic field of the coil target is strong and sustainable for a long time, and has a certain controllability in space-time distribution, we applied it to the study of magnetic reconnection, and have successfully obtained the reconnection characteristics, such as outflow. In addition, the coil target has also been applied in many aspects, such as the confinement of charged particles and the study of magnetohydrodynamics, which will provide new ideas for the research of related problems in laboratory.
-
Key words:
- intense laser /
- strong magnetic field /
- high-energy-density physics
-
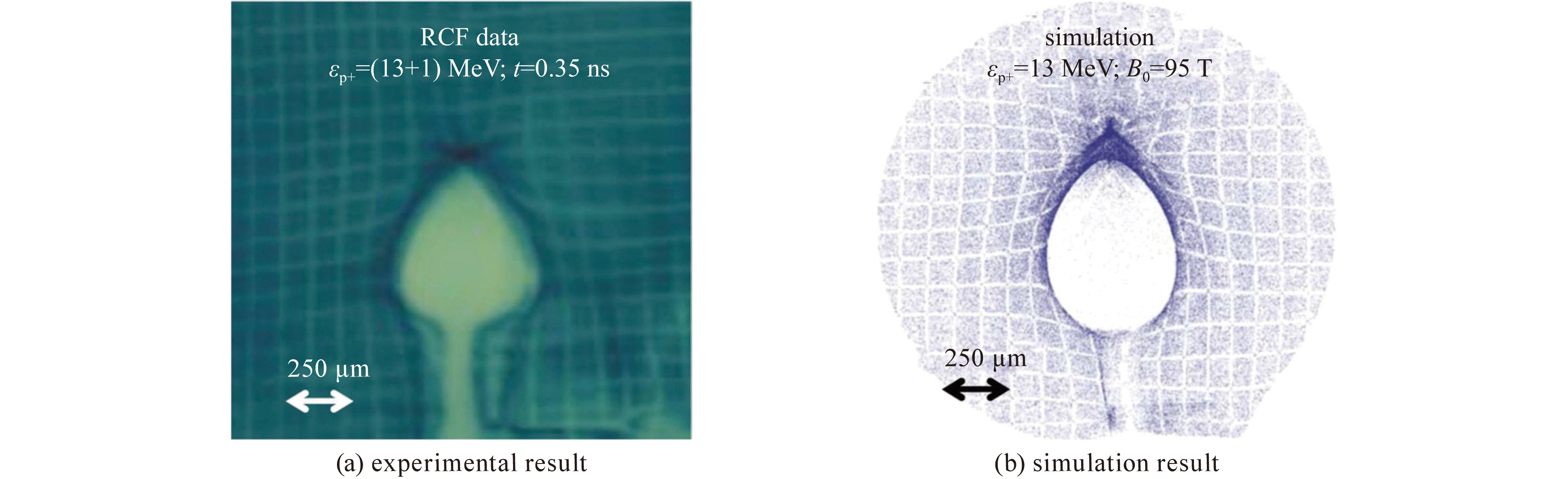
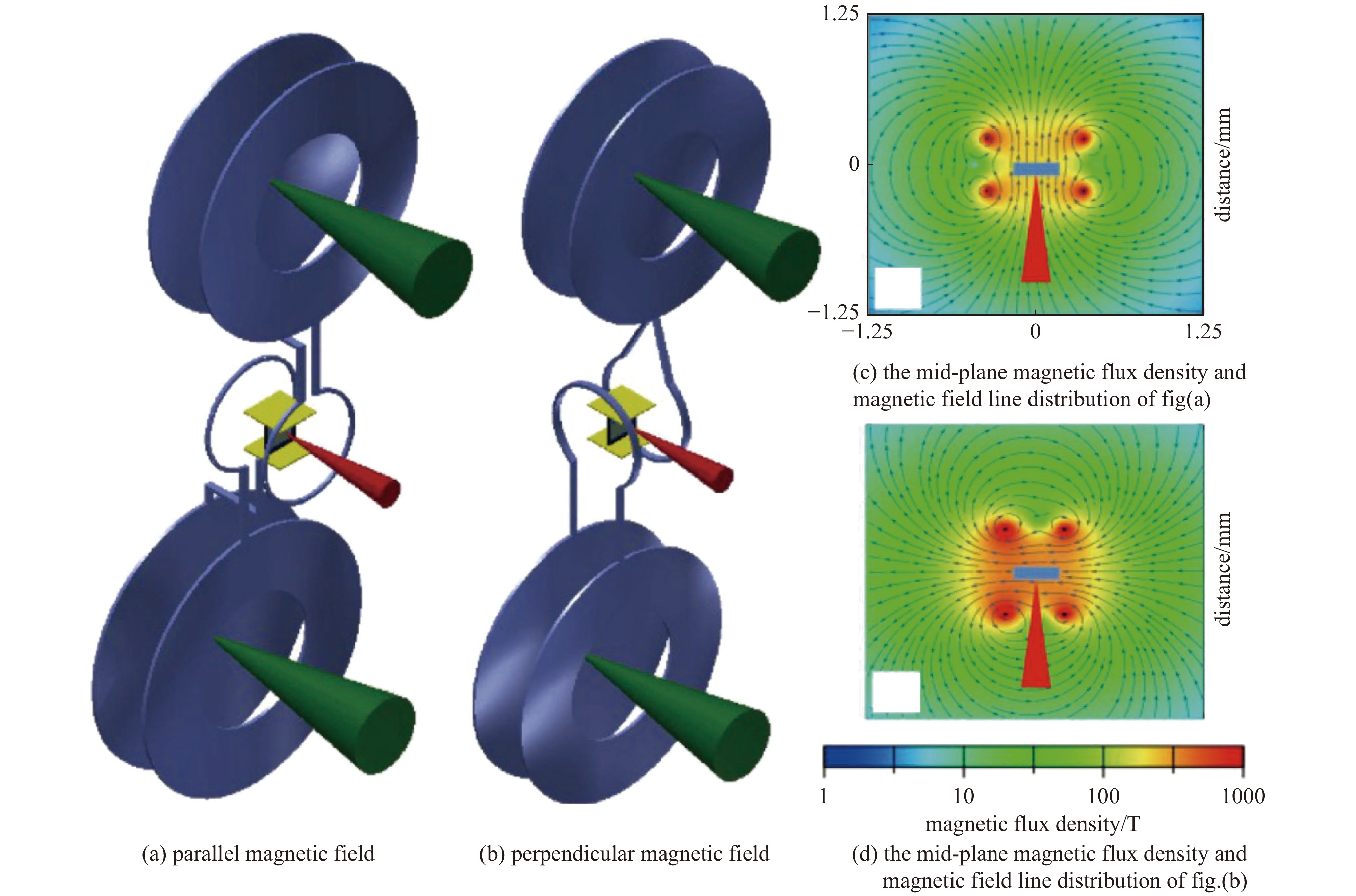
图 9 研究 HEDP 在外部磁场中的流体动力学的实验示意图[18]
Figure 9. Schematic diagram of the experiment to study the hydrodynamics of HEDP in an external magnetic field
-
[1] Shibata K, Magara T. Solar flares: magnetohydrodynamic processes[J]. Living Rev Sol Phys, 2011, 8: 6. [2] Yuan Feng, Zhang Bing. Episodic jets as the central engine of gamma-ray bursts[J]. Astrophys J, 2012, 757: 56. doi: 10.1088/0004-637X/757/1/56 [3] Meinecke J, Doyle H W, Miniati F, et al. Turbulent amplification of magnetic fields in laboratory laser-produced shock waves[J]. Nat Phys, 2014, 10(7): 520-524. doi: 10.1038/nphys2978 [4] Balbus S A, Hawley J F. A powerful local shear instability in weakly magnetized disks. I-Linear analysis. II-Nonlinear evolution[J]. Astrophys J, 1991, 376: 214-233. doi: 10.1086/170270 [5] Nilson P M, Willingale L, Kaluza M C, et al. Magnetic reconnection and plasma dynamics in two-beam laser-solid interactions[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 2006, 97: 255001. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.97.255001 [6] Li C K, Séguin F H, Frenje J A, et al. Observation of megagauss-field topology changes due to magnetic reconnection in laser-produced plasmas[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 2007, 99: 055001. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.99.055001 [7] Zhong Jiayong, Li Yutong, Wang Xiaogang, et al. Modelling loop-top X-ray source and reconnection outflows in solar flares with intense lasers[J]. Nat Phys, 2010, 6(12): 984-987. doi: 10.1038/nphys1790 [8] http://www.naturechina.com.cn/nchina/2010/101201/full/nchina.2010.136.html. [9] Daido H, Miki F, Mima K, et al. Generation of a strong magnetic field by an intense CO2 laser pulse[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 1986, 56(8): 846-849. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.56.846 [10] Courtois C, Ash A D, Chambers D M, et al. Creation of a uniform high magnetic-field strength environment for laser-driven experiments[J]. J Appl Phys, 2005, 98: 054913. doi: 10.1063/1.2035896 [11] Santos J J, Bailly-Grandvaux M, Giuffrida L, et al. Laser-driven platform for generation and characterization of strong quasi-static magnetic fields[J]. New J Phys, 2015, 17: 083051. doi: 10.1088/1367-2630/17/8/083051 [12] Wang Weiwu, Cai Hongbo, Teng Jian, et al. Efficient production of strong magnetic fields from ultraintense ultrashort laser pulse with capacitor-coil target[J]. Phys Plasmas, 2018, 25: 083111. doi: 10.1063/1.5000991 [13] Pei Xiaoxing, Zhong Jiayong, Sakawa Y, et al. Magnetic reconnection driven by Gekko XII lasers with a Helmholtz capacitor-coil target[J]. Phys Plasmas, 2016, 23: 032125. doi: 10.1063/1.4944928 [14] Zhang Jie, Wang Weimin, Yang Xiaohu, et al. Double-cone ignition scheme for inertial confinement fusion[J]. Philos Trans Roy Soc A: Math, Phys Eng Sci, 2020, 378: 20200015. [15] Cai Hongbo, Zhu Shaoping, He Xiantu. Effects of the imposed magnetic field on the production and transport of relativistic electron beams[J]. Phys Plasmas, 2013, 20: 072701. doi: 10.1063/1.4812631 [16] Bailly-Grandvaux M, Santos J J, Bellei C, et al. Guiding of relativistic electron beams in dense matter by laser-driven magnetostatic fields[J]. Nat Commun, 2018, 9: 102. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-02641-7 [17] Arefiev A, Toncian T, Fiksel G. Enhanced proton acceleration in an applied longitudinal magnetic field[J]. New J Phys, 2016, 18: 105011. doi: 10.1088/1367-2630/18/10/105011 [18] Matsuo K, Nagatomo H, Zhang Zhe, et al. Magnetohydrodynamics of laser-produced high-energy-density plasma in a strong external magnetic field[J]. Phys Rev E, 2017, 95: 053204. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.95.053204 [19] Yuan Xiaoxia, Zhong Jiayong, Zhang Zhe, et al. Low-β magnetic reconnection driven by the intense lasers with a double-turn capacitor-coil[J]. Plasma Phys Control Fusion, 2018, 60: 065009. doi: 10.1088/1361-6587/aabaa9 [20] Fiksel G, Fox W, Gao Lan, et al. A simple model for estimating a magnetic field in laser-driven coils[J]. Appl Phys Lett, 2016, 109: 134103. doi: 10.1063/1.4963763 [21] Korobkin V V, Motylev S L. On a possibility of using laser radiation for generation of strong magnetic fields[J]. Sov Tech Phys Lett, 1979, 5: 474. [22] Goyon C, Pollock B B, Turnbull D P, et al. Ultrafast probing of magnetic field growth inside a laser-driven solenoid[J]. Phys Rev E, 2017, 95: 033208. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.95.033208 [23] Tikhonchuk V T, Bailly-Grandvaux M, Santos J J, et al. Quasistationary magnetic field generation with a laser-driven capacitor-coil assembly[J]. Phys Rev E, 2017, 96: 023202. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.96.023202 [24] Williams G J, Patankar S, Mariscal D A, et al. Laser intensity scaling of the magnetic field from a laser-driven coil target[J]. J Appl Phys, 2020, 127: 083302. doi: 10.1063/1.5117162 [25] Morita H, Pollock B B, Goyon C S, et al. Dynamics of laser-generated magnetic fields using long laser pulses[J]. Phys Rev E, 2021, 103: 033201. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.103.033201 [26] 王为武, 单连强, 田超, 等. 一种脉冲强电流条件下导线电阻测量方法[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2020, 32:082001 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202032.200057Wang Weiwu, Shan Lianqiang, Tian Chao, et al. A method for estimating coil resistance with pulsed strong electric current[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2020, 32: 082001 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202032.200057 [27] 谭榕容, 冉汉政, 程刚. 基于B-Dot的kA级短脉冲电流测量方法[J]. 太赫兹科学与电子信息学报, 2015, 13(6):990-994,999 doi: 10.11805/TKYDA201506.0990Tan Rongrong, Ran Hanzheng, Cheng Gang. Measurement of kA-level short pulse current based on B-Dot[J]. Journal of Terahertz Science and Electronic Information Technology, 2015, 13(6): 990-994,999 doi: 10.11805/TKYDA201506.0990 [28] Zhu Baojun, Li Yutong, Yuan Dawei, et al. Strong magnetic fields generated with a simple open-ended coil irradiated by high power laser pulses[J]. Appl Phys Lett, 2015, 107: 261903. doi: 10.1063/1.4939119 [29] Fujioka S, Zhang Zhe, Ishihara K, et al. Kilotesla magnetic field due to a capacitor-coil target driven by high power laser[J]. Sci Rep, 2013, 3: 1170. doi: 10.1038/srep01170 [30] Yamada M, Ji Hantao, Hsu S, et al. Study of driven magnetic reconnection in a laboratory plasma[J]. Phys Plasmas, 1997, 4(5): 1936-1944. doi: 10.1063/1.872336 [31] Ji Hantao, Daughton W. Phase diagram for magnetic reconnection in heliophysical, astrophysical, and laboratory plasmas[J]. Phys Plasmas, 2011, 18: 111207. doi: 10.1063/1.3647505 [32] Chien A, Gao Lan, Ji Hantao, et al. Study of a magnetically driven reconnection platform using ultrafast proton radiography[J]. Phys Plasmas, 2019, 26: 062113. doi: 10.1063/1.5095960 [33] Stone J M, Gardiner T. Nonlinear evolution of the magnetohydrodynamic Rayleigh-Taylor instability[J]. Phys Fluids, 2007, 19: 094104. doi: 10.1063/1.2767666 [34] Morita H, Arefiev A, Toncian T, et al. Application of laser-driven capacitor-coil to target normal sheath acceleration[J]. High Energy Density Phys, 2020, 37: 100874. doi: 10.1016/j.hedp.2020.100874 [35] Tan Junhao, Li Yifei, Zhu Baojun, et al. Short-period high-strength helical undulator by laser-driven bifilar capacitor coil[J]. Opt Express, 2019, 27(21): 29676-29684. doi: 10.1364/OE.27.029676 [36] 张杰, 赵刚. 实验室天体物理学简介[J]. 物理, 2000, 29(7):393-396 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-4148.2000.07.003Zhang Jie, Zhao Gang. Introduction to laboratory astrophysics[J]. Physics, 2000, 29(7): 393-396 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-4148.2000.07.003 -




 下载:
下载: