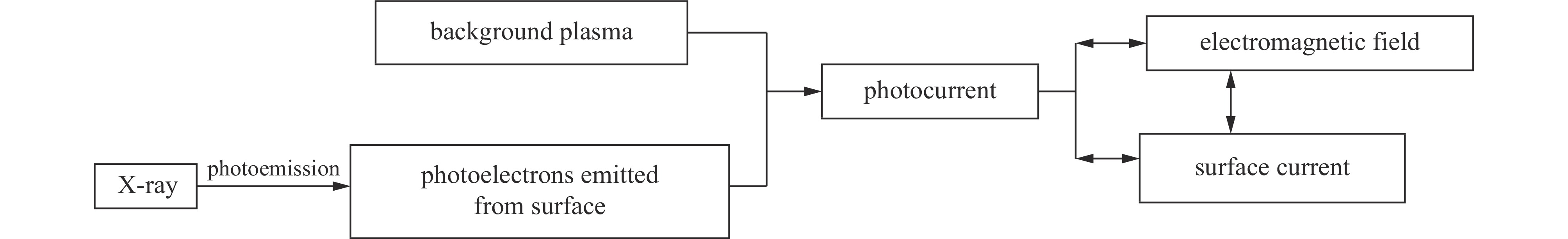
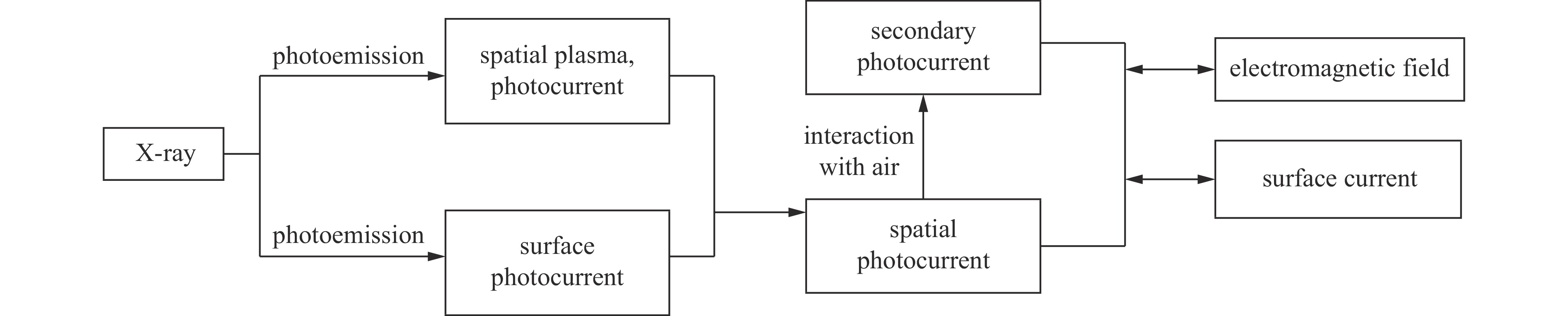
Simulation study of external system generated electromagnetic pulse in low pressure air or plasma
-
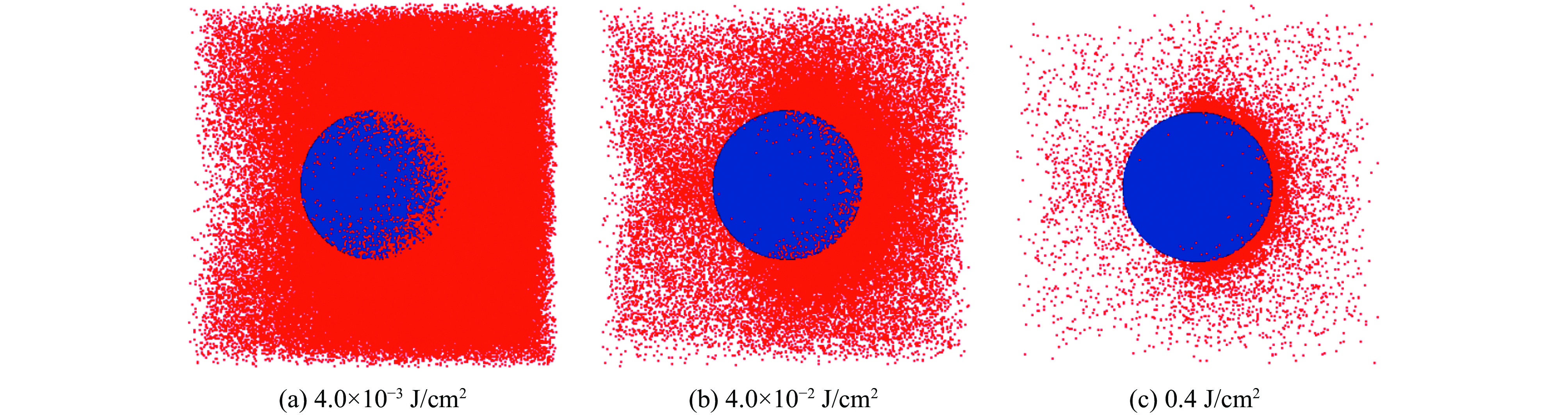
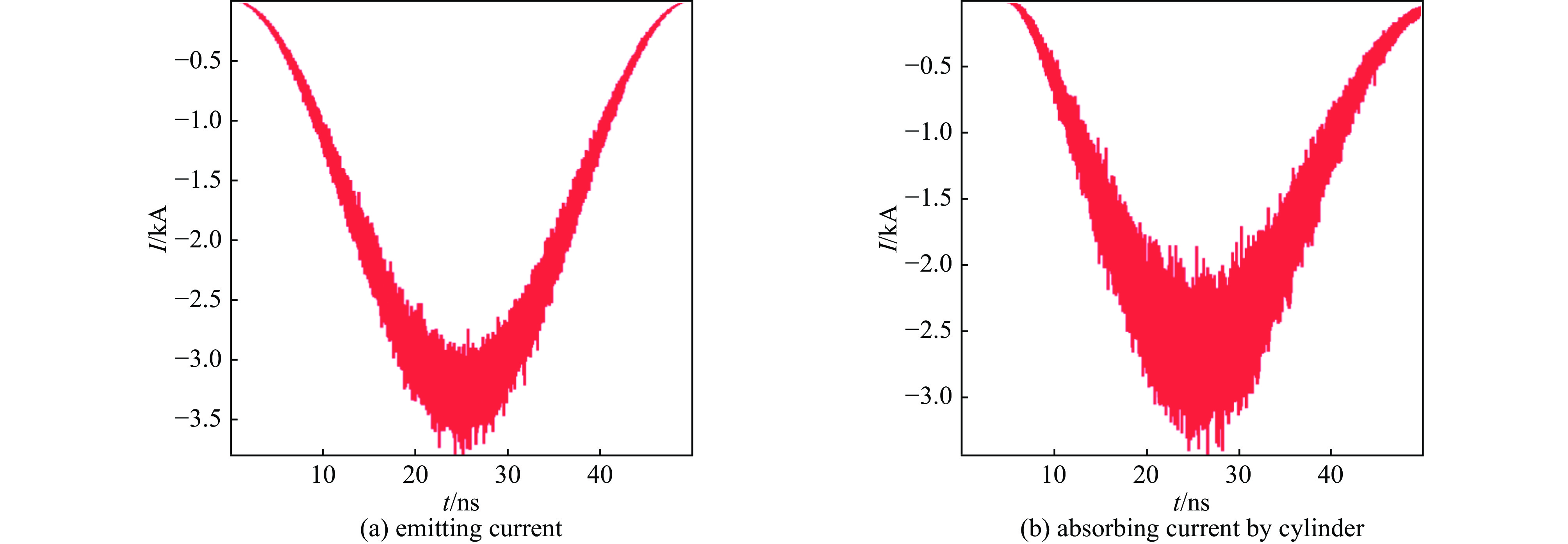
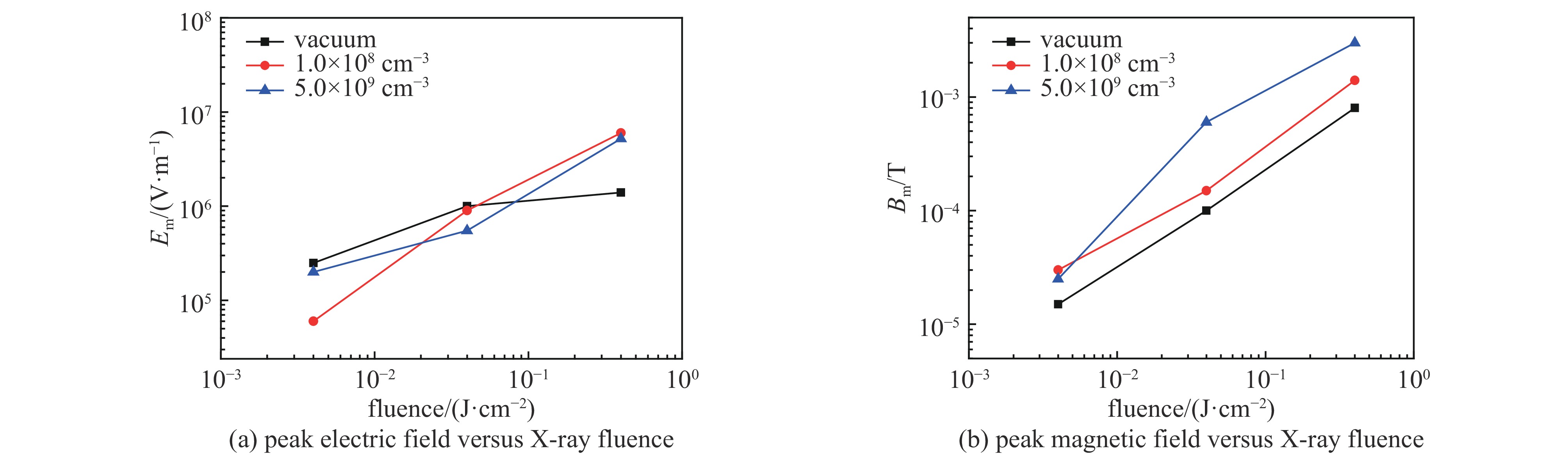
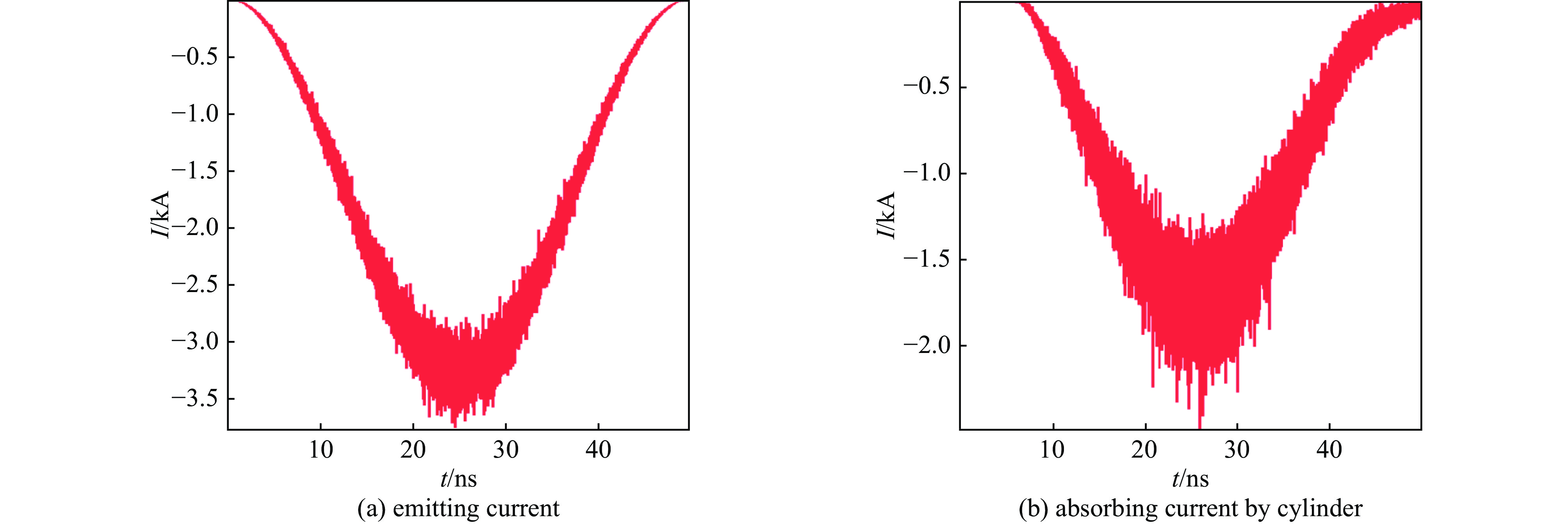
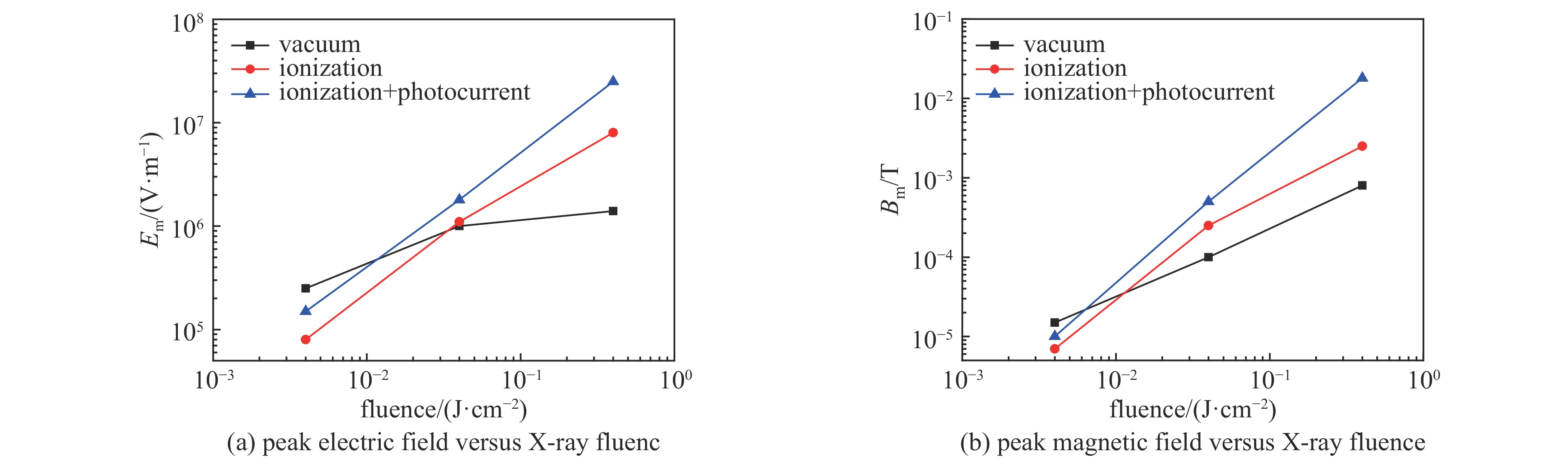
摘要: 为研究大气环境对系统电磁脉冲(SGEMP )的影响,针对海拔50~100 km的X射线能量沉积区,分别应用3维PIC程序及3维PIC-MCC程序各自开展预电离等离子体和稀薄空气条件下外SGEMP的建模与模拟研究,针对3种不同的X射线注量(4×10−3 J/cm2、4×10−2 J/cm2、0.4 J/cm2),分别取对应两种不同海拔高度(70 km和80~90 km)的本底等离子体及海拔56 km的稀薄空气条件进行模拟计算,并和真空中的计算结果进行对比,得出预电离等离子体及稀薄空气对外SGEMP的影响规律:当X射线注量较低时,等离子体使得磁场增大,电场减小,而稀薄空气对外SGEMP效应影响不明显;随着X射线注量增大,空间电荷非线性效应越来越明显,等离子体及稀薄空气都使得电场、磁场同时增大,且稀薄空气的增大效应更显著。Abstract: For examining effects of atmosphere on system generated electromagnetic pulse (SGEMP), the external SGEMP are simulated by the 3D PIC code in pre-ionized plasma and by the PIC-MCC code in low pressure air respectively in the X-ray energy deposition region (50 km to 100 km). For three fluences of X-ray (4×10−3 J/cm2、4×10−2 J/cm2、0.4 J/cm2), the simulations are done in pre-ionized plasma corresponding to two different altitudes (70 km and 80−90 km) and low pressure air corresponding to 56 km altitude each other, and the results are compared with those in vacuum. The variation laws of external SGEMP in pre-ionized plasma and low pressure air are received : the effects have relation to fluence of X-ray, when the fluence of X-ray is low, the magnetic field increases and the electric field decreases in the plasma environment, while the variations of external SGEMP are not obvious in low pressure air; with the fluence of X-ray increasing, the space charge nonlinear effects become more and more obvious, the electric field and magnetic field are enhanced together in both pre-ionized plasma and low pressure air, and the enhancement effects are more significant in low pressure air.
-
Key words:
- PIC code /
- system generated electromagnetic pulse /
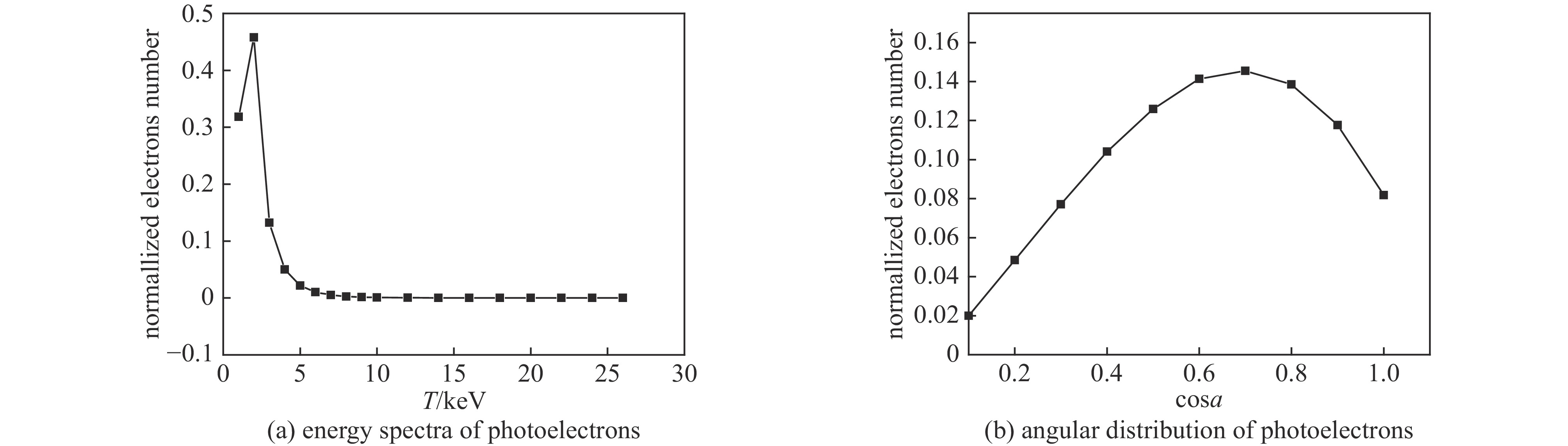
- photoelectron /
- secondary electron
-
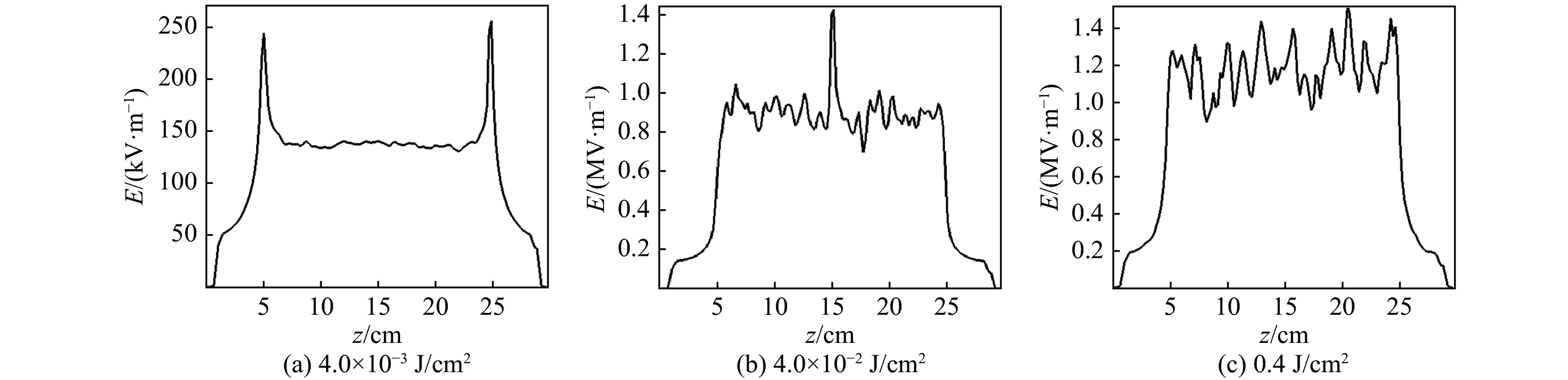
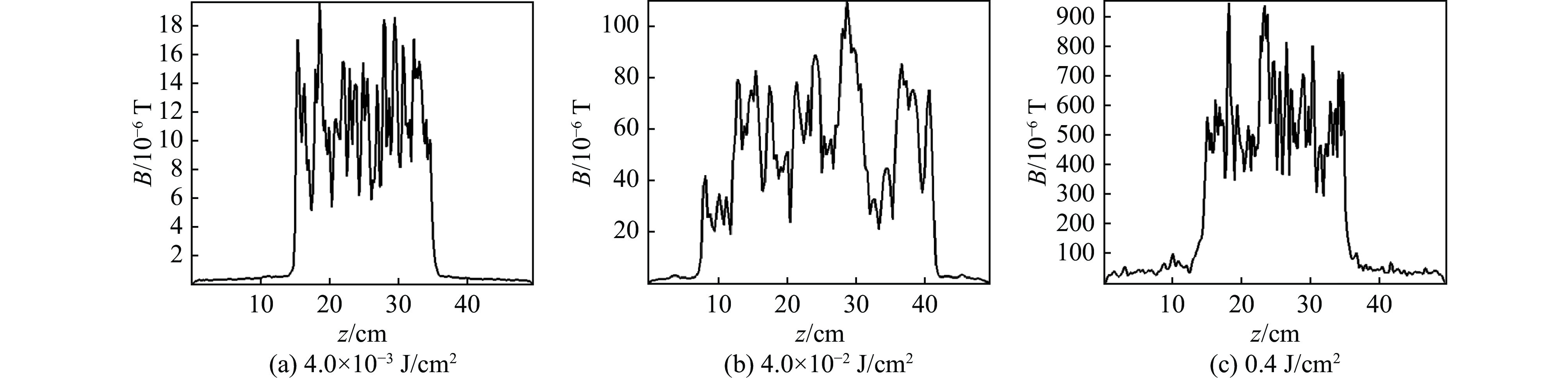
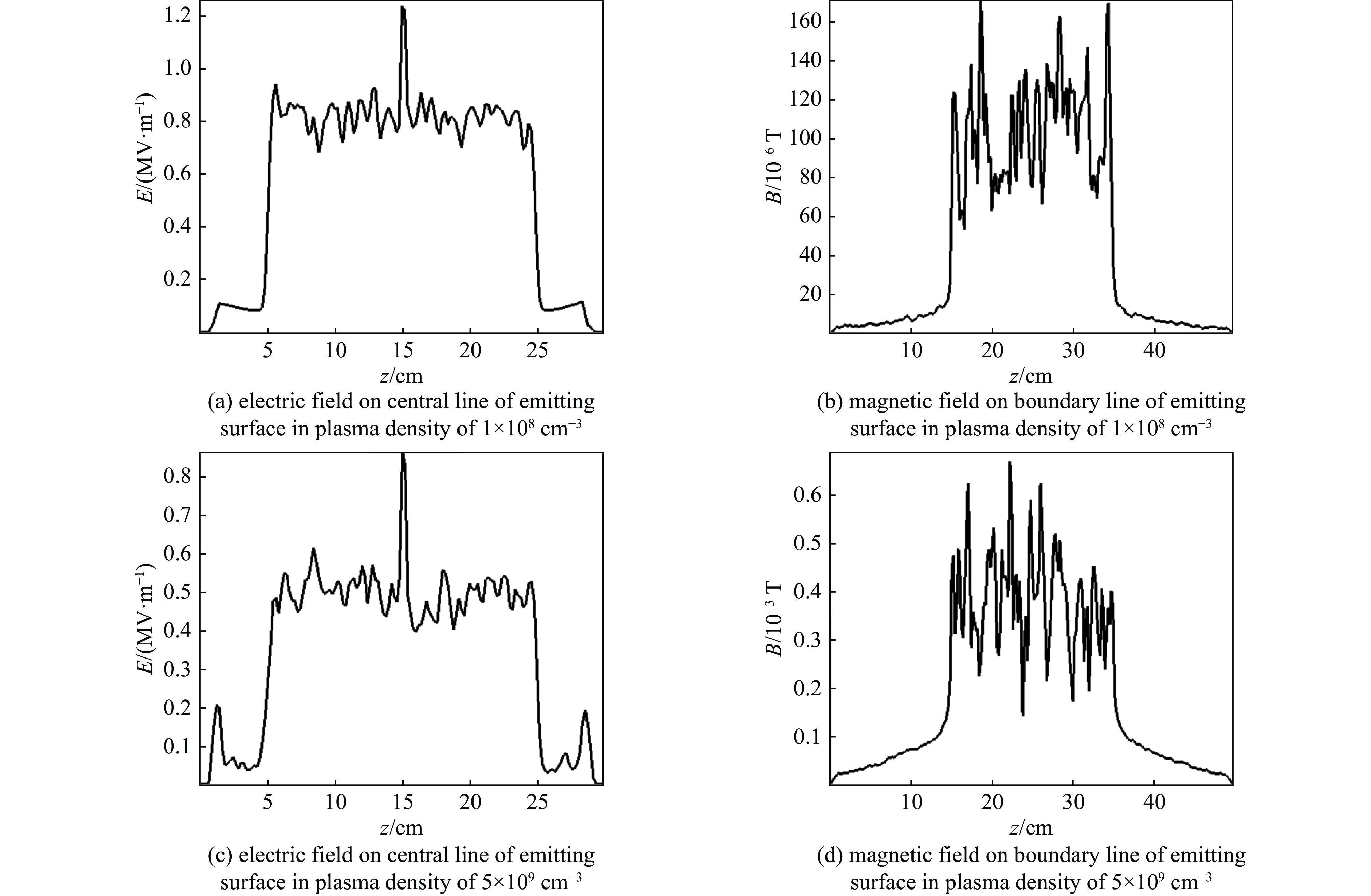
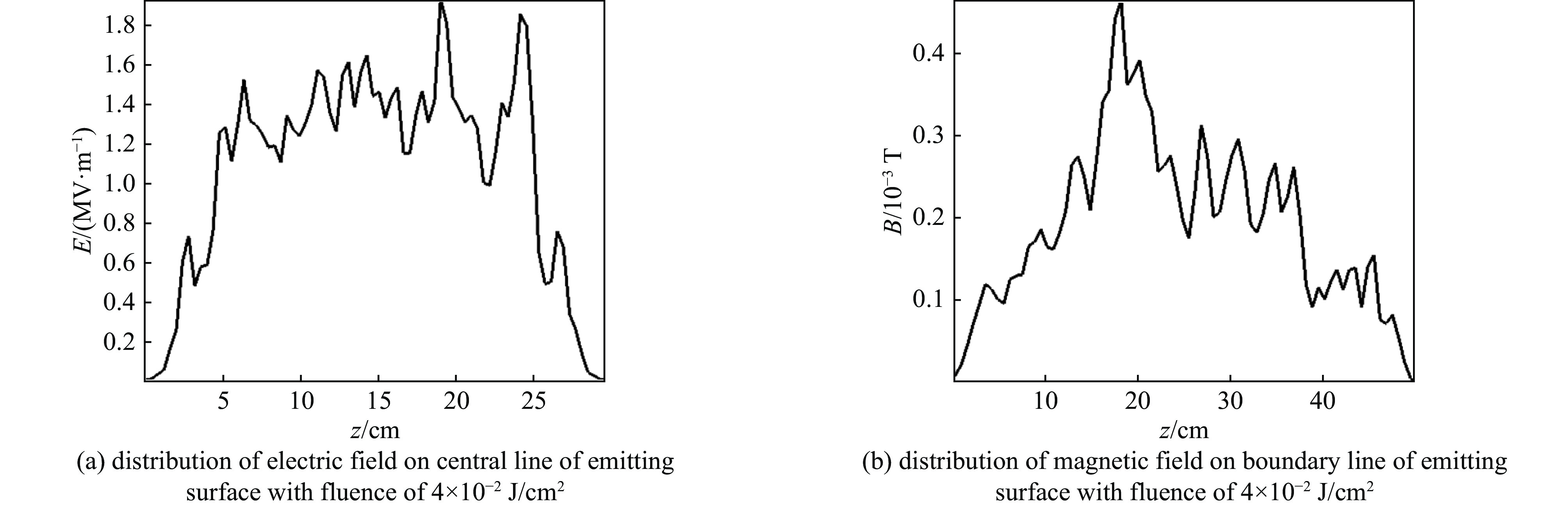
图 7 X射线注量为4×10−2 J/cm2 ,对应两种等离子体密度(1×108cm−3 、5×109 cm−3) 24 ns时,发射面中线(y=0,x=10.2 cm)上的电场分布和发射面边线(x=0,y=10.2 cm)上的磁场分布
Figure 7. Distribution of electric field on central line of emitting surface (y=0, x=10.2 cm) and magnetic field on boundary line of emitting surface (x=0, y=10.2 cm) with fluence of 4×10−2 J/cm2 respectively in different density plasma (1×108 cm−3, 5×109 cm−3) at 24 ns
图 11 X射线注量为4×10−2 J/cm2时由表面光电流和次级电子共同激发的SGEMP 在50 ns时发射面中线(y=0,x=10.2 cm)上的的电场分布和发射面边线(x=0,y=10.2 cm)上的磁场分布
Figure 11. Distribution of electric field on central line of emitting surface (y=0, x=10.2 cm) and magnetic field on boundary line of emitting surface (x=0, y=10.2 cm) with fluence of 4×10−2 J/cm2 excitated by both photocurrent emitting from surface and secondary electrons at 50 ns
图 13 X射线注量为4×10−2 J/cm2时由表面光电流、次级电子和空气光电流共同激发的SGEMP在50 ns时发射面中线(y=0,x=10.2 cm)上的的电场分布和发射面边线(x=0,y=10.2 cm)上的磁场分布
Figure 13. Distribution of electric field on central line of emitting surface (y=0, x=10.2 cm) and magnetic field on boundary line of emitting surface (x=0, y=10.2 cm) with fluence of 4×10−2 J/cm2 excitated by photocurrent emitting from both surface and air、secondary electrons together at 50 ns
-
[1] 王泰春, 贺云汉, 王玉芝. 电磁脉冲导论[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2011Wang Taichun, He Yunhan, Wang Yuzhi. Introduction to electromagnetic pulse[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2011 [2] Woods A J, Hobbs W E, Wenaas E P. Air effects on the external SGEMP response of a cylinder[J]. IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 1981, 28(6): 4467-4478. doi: 10.1109/TNS.1981.4335749 [3] Woods A J, Treadaway M J, Nunan S, et al. Air-enhanced SGEMP response—an experimental and analytical investigation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 1982, 29(6): 1793-1797. doi: 10.1109/TNS.1982.4336449 [4] Osborn D C, Stahl R H, Delmer T N. Large-area electron-beam experiments on space-charge neutralization in a cavity[J]. IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 1976, 23(6): 1964-1968. doi: 10.1109/TNS.1976.4328607 [5] Hinshelwood D, Swanekamp S B, Allen R J, et al. Electron-beam-gas interaction studies for code validation[C]//2015 Hardened Electronics and Radiation Technology Technical Interchange Meeting. 2015. [6] Zhang Hantian, Zhou Qianhong, Zhou Haijing, et al. Particle-in-cell simulations of low-pressure air plasma generated by pulsed X rays[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2021, 130: 173303. doi: 10.1063/5.0057841 [7] Gilbert R M, Klebers J, Bromborsky A. Air pressure effects on internal SGEMP: a benchmark experiment for computer code validation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 1977, 24(6): 2389-2398. doi: 10.1109/TNS.1977.4329225 [8] 孙会芳, 张芳, 董志伟. 圆柱体外SGEMP的三维数值模拟[J]. 计算物理, 2016, 33(4):434-440 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-246X.2016.04.007Sun Huifang, Zhang Fang, Dong Zhiwei. 3D simulation of external SGEMP of cylinder[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2016, 33(4): 434-440 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-246X.2016.04.007 [9] 董志伟, 孙会芳, 杨郁林, 等. 磁绝缘线振荡器阴极释气电离粒子模拟[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2016, 28:033023 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201628.033023Dong Zhiwei, Sun Huifang, Yang Yulin, et al. Particle simulation technology of MILO cathode outgassing ionization[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2016, 28: 033023 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201628.033023 [10] 张玲玉, 李瑞, 李刚, 等. JMCT光子-电子耦合输运模拟计算研究[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2017, 29:126007 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201729.170253Zhang Lingyu, Li Rui, Li Gang, et al. Simulation of JMCT photon-electron coupled transport[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2017, 29: 126007 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201729.170253 -





 下载:
下载: