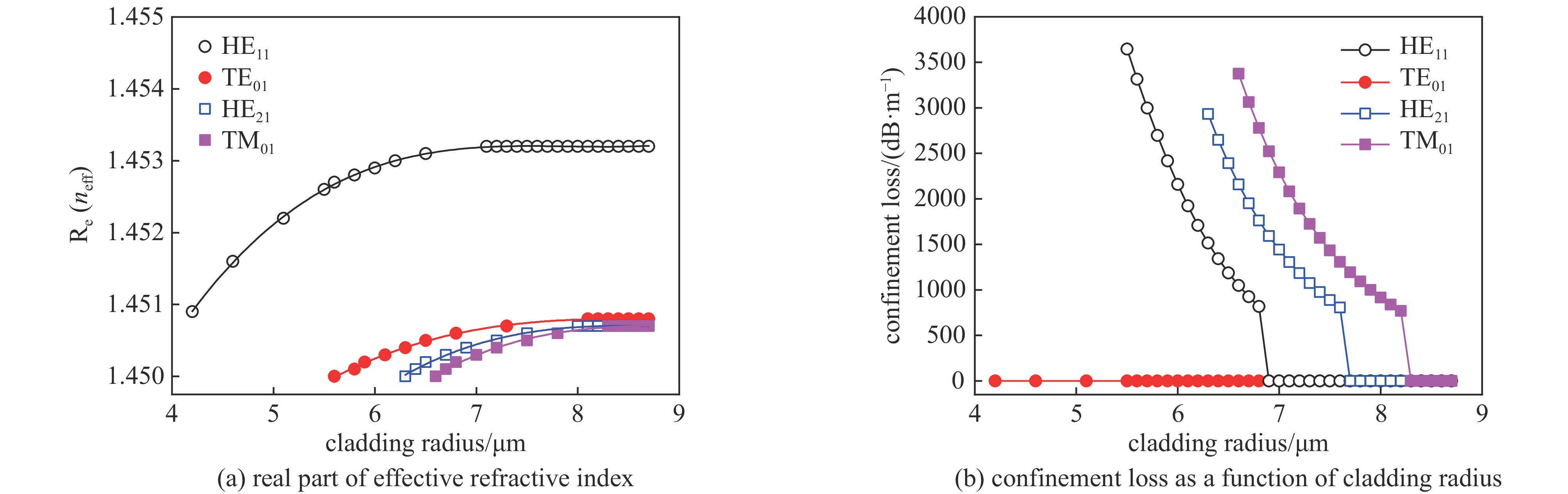
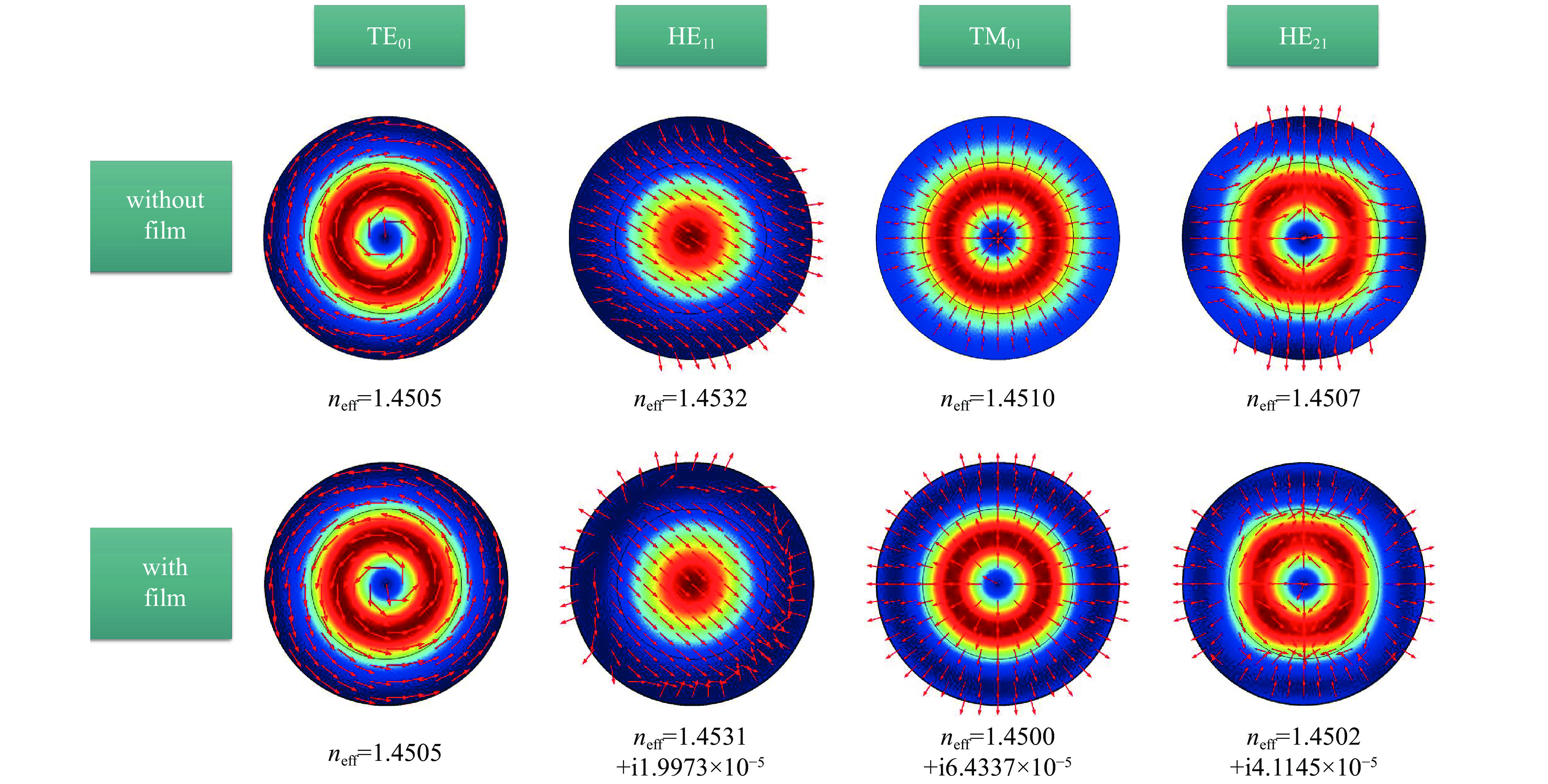
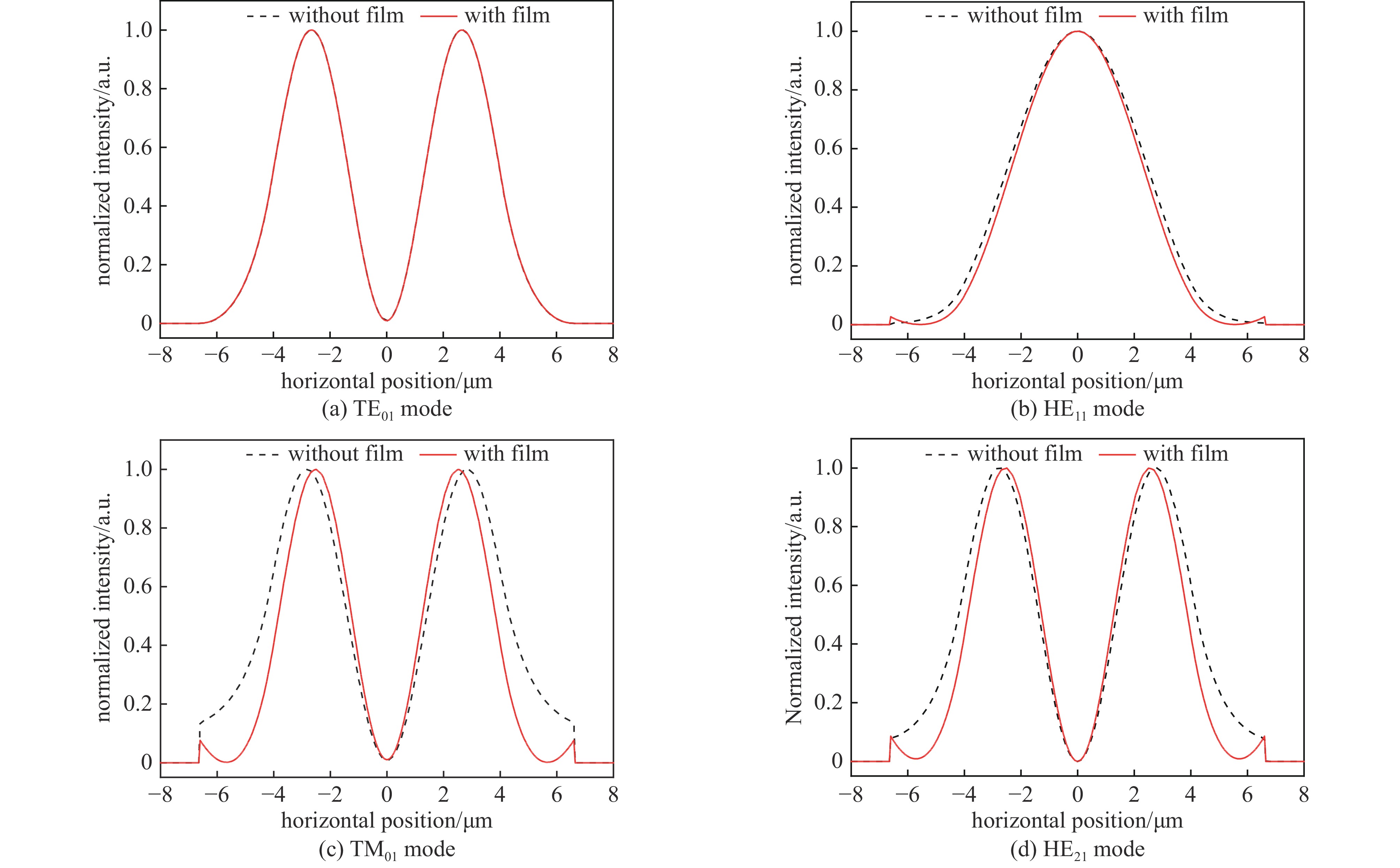
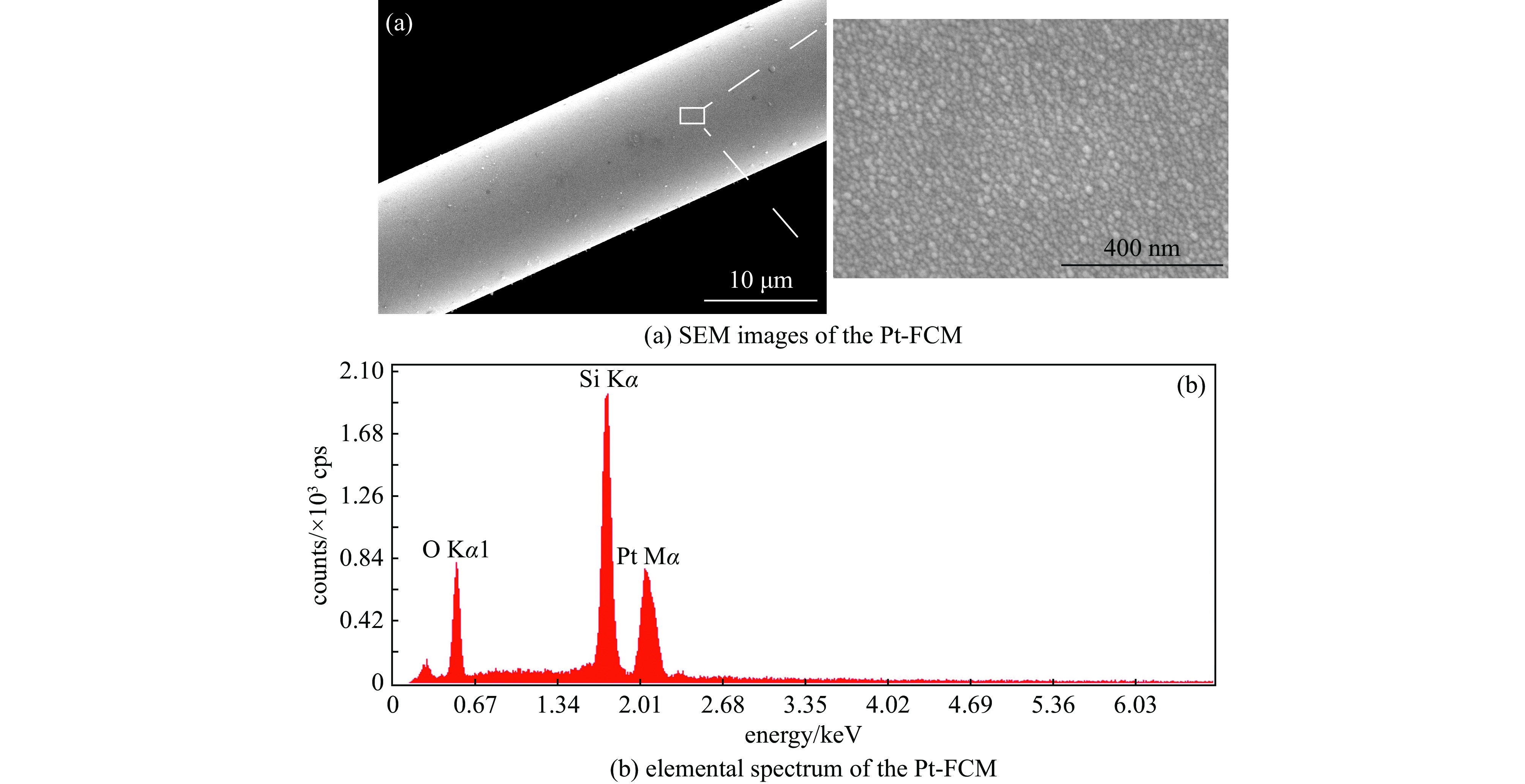
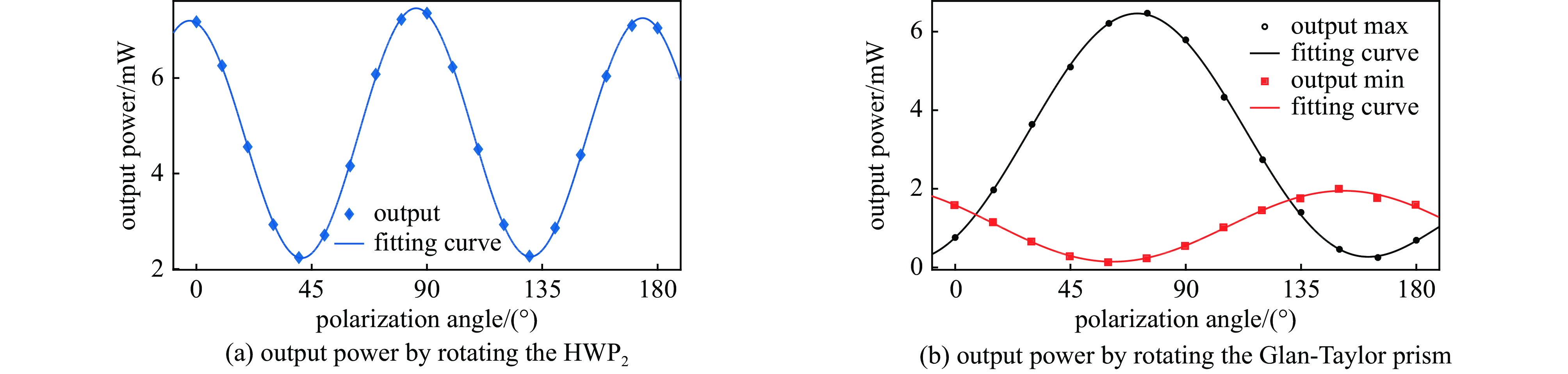
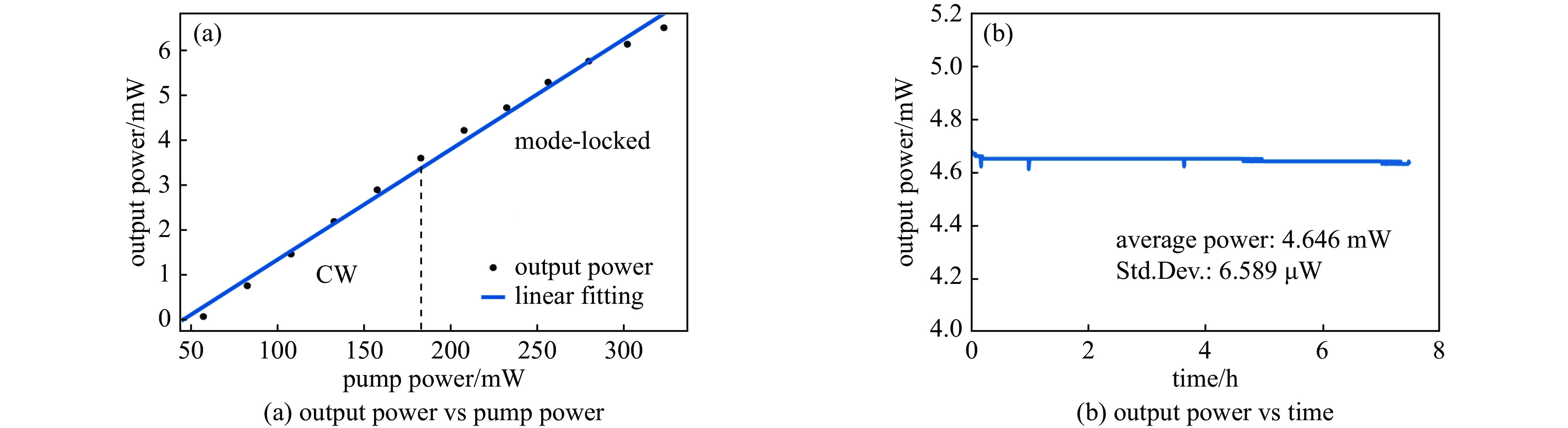
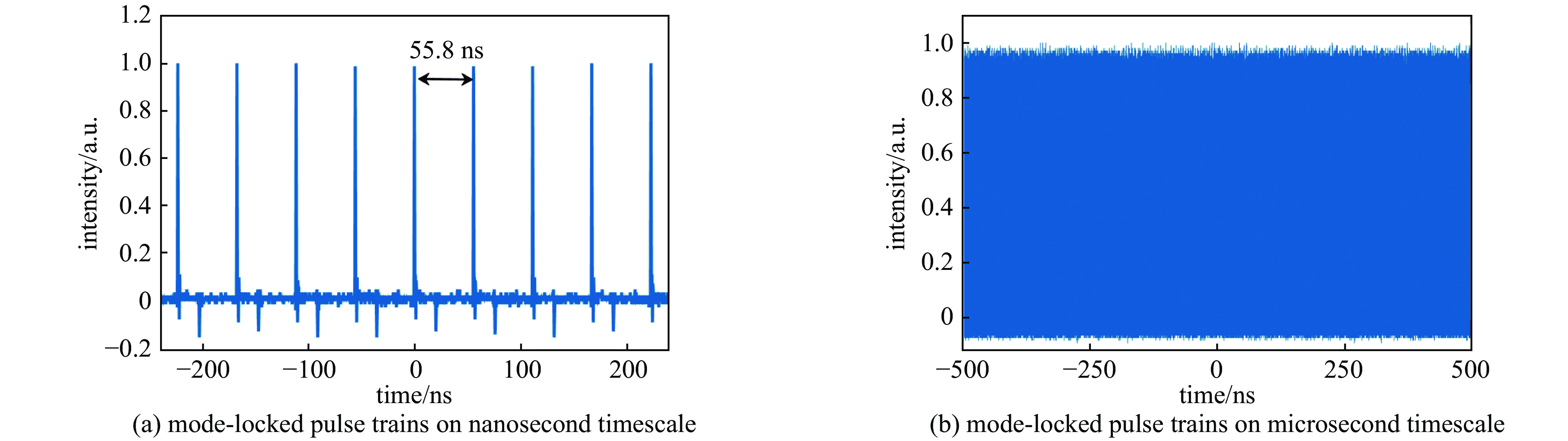
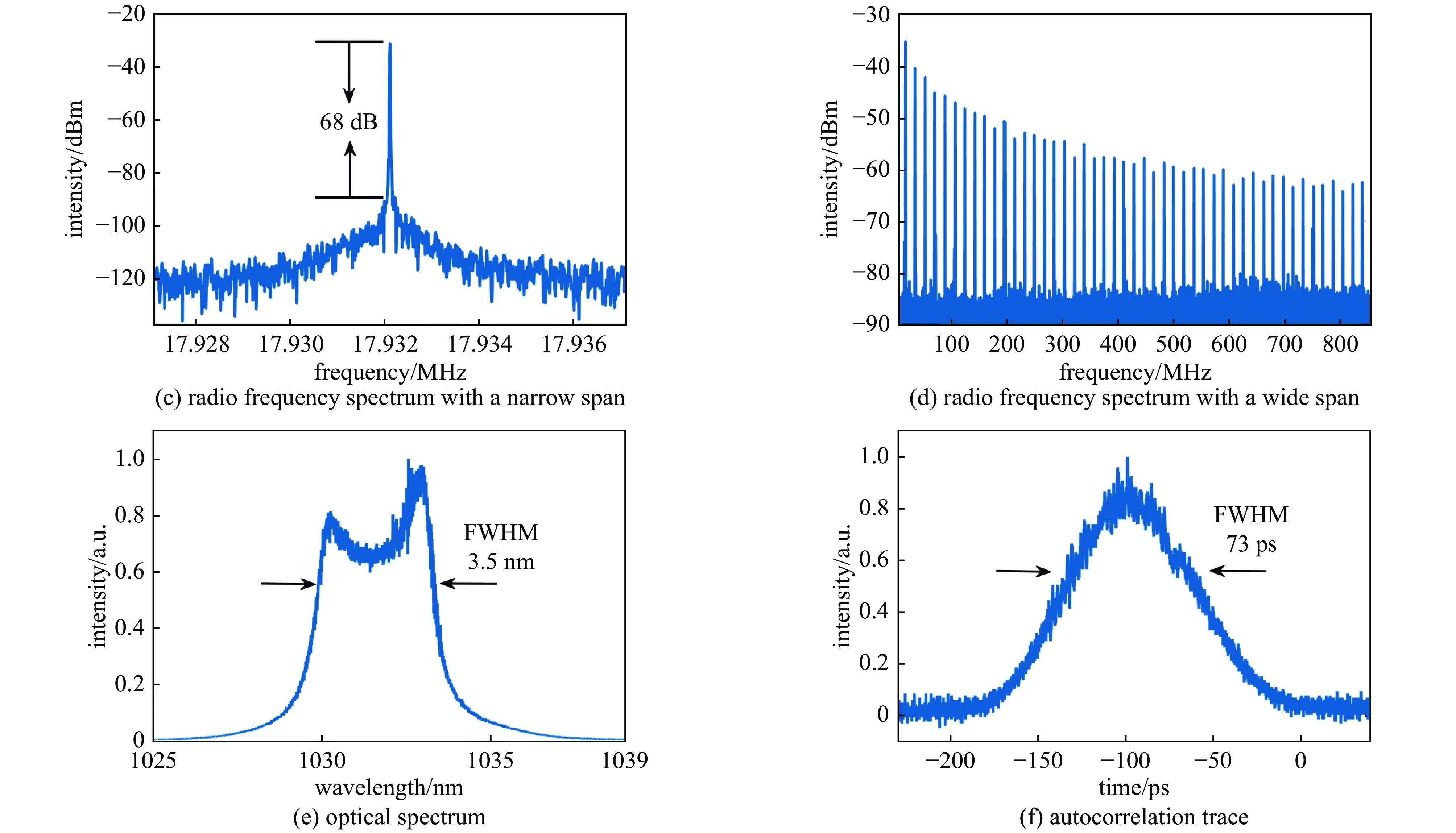
| [1] |
Phillips K C, Gandhi H H, Mazur E, et al. Ultrafast laser processing of materials: a review[J]. Advances in Optics and Photonics, 2015, 7(4): 684-712. doi: 10.1364/AOP.7.000684
|
| [2] |
Malinauskas M, Žukauskas A, Hasegawa S, et al. Ultrafast laser processing of materials: from science to industry[J]. Light: Science & Applications, 2016, 5: 16133.
|
| [3] |
Zipfel W R, Williams R M, Webb W W. Nonlinear magic: multiphoton microscopy in the biosciences[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2003, 21(11): 1369-1377. doi: 10.1038/nbt899
|
| [4] |
Lu Yu, Wong T T W, Chen Feng, et al. Compressed ultrafast spectral-temporal photography[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2019, 122: 193904. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.122.193904
|
| [5] |
Udem T, Holzwarth R, Hänsch T W. Optical frequency metrology[J]. Nature, 2002, 416(6877): 233-237. doi: 10.1038/416233a
|
| [6] |
Yoshii K, Nomura J, Taguchi K, et al. Optical frequency metrology study on nonlinear processes in a waveguide device for ultrabroadband comb generation[J]. Physical Review Applied, 2019, 11: 054031. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevApplied.11.054031
|
| [7] |
Martinez A, Sun Zhipei. Nanotube and graphene saturable absorbers for fibre lasers[J]. Nature Photonics, 2013, 7(11): 842-845. doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2013.304
|
| [8] |
Chen Bohua, Zhang Xiaoyan, Wu Kan, et al. Q-switched fiber laser based on transition metal dichalcogenides MoS2, MoSe2, WS2, and WSe2[J]. Optics Express, 2015, 23(20): 26723-26737. doi: 10.1364/OE.23.026723
|
| [9] |
Ahmad H, Reduan S A, Ali Z A, et al. C-band Q-switched fiber laser using titanium dioxide (TiO2) as saturable absorber[J]. IEEE Photonics Journal, 2016, 8: 1500107.
|
| [10] |
Luo Zhengqian, Huang Yizhong, Weng Jian, et al. 1.06 μm Q-switched ytterbium-doped fiber laser using few-layer topological insulator Bi2Se3 as a saturable absorber[J]. Optics Express, 2013, 21(24): 29516-29522. doi: 10.1364/OE.21.029516
|
| [11] |
Chen Yu, Jiang Guobao, Chen Shuqing, et al. Mechanically exfoliated black phosphorus as a new saturable absorber for both Q-switching and mode-locking laser operation[J]. Optics Express, 2015, 23(10): 12823-12833. doi: 10.1364/OE.23.012823
|
| [12] |
Ahmad H, Hassan H, Safaei R, et al. Q-switched fiber laser using carbon platinum saturable absorber on side-polished fiber[J]. Chinese Optics Letters, 2017, 15: 090601. doi: 10.3788/COL201715.090601
|
| [13] |
Guo Hao, Feng Ming, Song Feng, et al. Q-switched erbium-doped fiber laser based on silver nanoparticles as a saturable absorber[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2015, 28(2): 135-138.
|
| [14] |
Jiang Tao, Xu Yang, Tian Qijun, et al. Passively Q-switching induced by gold nanocrystals[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2012, 101: 151122. doi: 10.1063/1.4759120
|
| [15] |
Kang Zhe, Guo Xingyuan, Jia Zhixu, et al. Gold nanorods as saturable absorbers for all-fiber passively Q-switched erbium-doped fiber laser[J]. Optical Materials Express, 2013, 3(11): 1986-1991. doi: 10.1364/OME.3.001986
|
| [16] |
Kang Zhe, Li Q, Gao X J, et al. Gold nanorod saturable absorber for passive mode-locking at 1 μm wavelength[J]. Laser Physics Letters, 2014, 11: 035102. doi: 10.1088/1612-2011/11/3/035102
|
| [17] |
Gao Yachen, Zhang Xueru, Li Yuliang, et al. Saturable absorption and reverse saturable absorption in platinum nanoparticles[J]. Optics Communications, 2005, 251(4/6): 429-433.
|
| [18] |
Yuzaile Y R, Awang N A, Zalkepali N U H H, et al. Pulse compression in Q-switched fiber laser by using platinum as saturable absorber[J]. Optik, 2019, 179: 977-985. doi: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2018.11.057
|
| [19] |
Ganeev R A, Tugushev R I, Usmanov T. Application of the nonlinear optical properties of platinum nanoparticles for the mode locking of Nd: glass laser[J]. Applied Physics B, 2009, 94(4): 647-651. doi: 10.1007/s00340-009-3371-9
|
| [20] |
Zhang Yimin, Li Hongxun, Dai Chuansheng, et al. All-fiber high-order mode laser using a metal-clad transverse mode filter[J]. Optics Express, 2018, 26(23): 29679-29686. doi: 10.1364/OE.26.029679
|
| [21] |
Dong Chunhua, Zou Changling, Ren Xifeng, et al. In-line high efficient fiber polarizer based on surface plasmon[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2012, 100: 041104. doi: 10.1063/1.3678591
|





 下载:
下载: