Progress of experimental research on micro-ejection diagnosis of metal materials under intense laser loading
-
摘要:
强激光加载下金属材料产生的微喷射现象及其内在的机理分析是冲击压缩科学与工程领域研究的前沿问题,相关研究对于认识材料在极端载荷条件下的动力学行为具有重要意义。近年来国内外科学家们基于各大激光装置开展了大量微喷射诊断实验研究,在喷射物性质、金属界面不稳定性增长以及微喷混合问题等方面取得了一系列重要进展。通过回顾微喷静态和动态诊断实验的研究历程,对微喷诊断实验研究方法的重要应用作了详细介绍,同时对微喷产生的主要作用机制、影响因素以及微喷混合等问题进行回顾、梳理和总结。根据当前国内外微喷诊断实验发展趋势,归纳总结目前微喷诊断实验研究结果中仍存在的不足,并对微喷射实验研究未来发展方向进行展望。
Abstract:The micro-ejection phenomenon and its internal mechanism analysis of metal materials under intense laser shock are the frontier issues in the field of shock compression science and engineering. Related research is of great significance for understanding the dynamic behavior of materials under extreme loading conditions. With the continuous development of laser technology, scientists at home and abroad have carried out numerous micro-ejection diagnostic experiments based on some large laser devices in various countries in recent years, and made a series of significant progress in the properties of ejection, the growth of instability at the metal interface and the mixing mechanism of ejection. By reviewing the research history of ejecta static and dynamic diagnostic experiments, this paper describes the main mechanism of ejection, influencing factors and ejecta interface mixing mechanism in detail, and then it reviews, classifies and summarizes the important applications of micro-ejection experimental diagnostic methods. Finally, according to the current development trend of ejecta diagnostic experiments at home and abroad, the deficiencies in the current ejection experimental research results are summarized, and the future development direction of ejection experimental research is prospected.
-
Key words:
- micro-ejection /
- shock wave /
- recovery /
- dynamic diagnostics /
- X-ray radiography
-
-
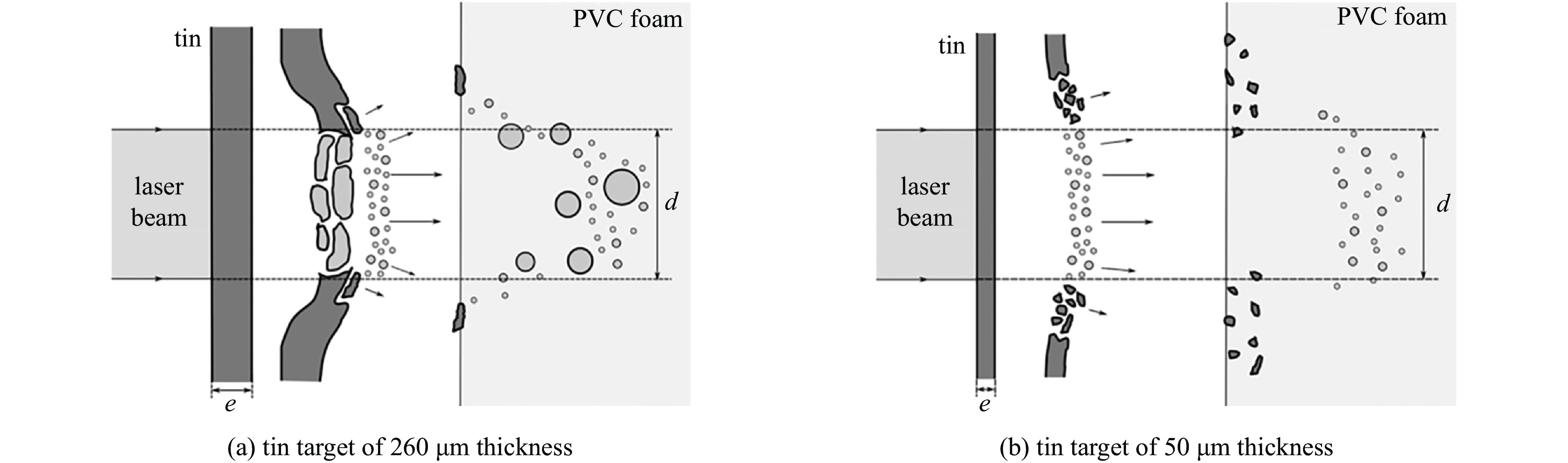
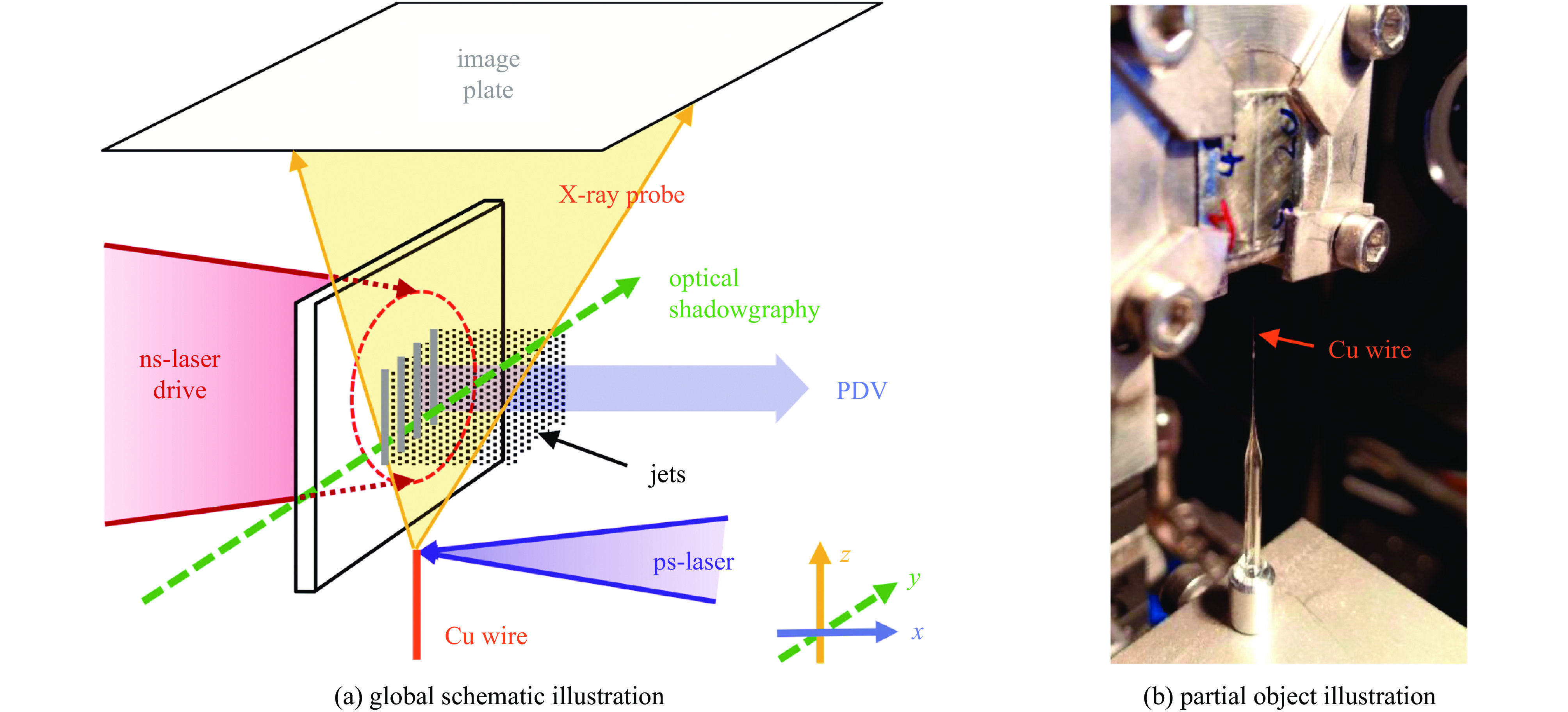
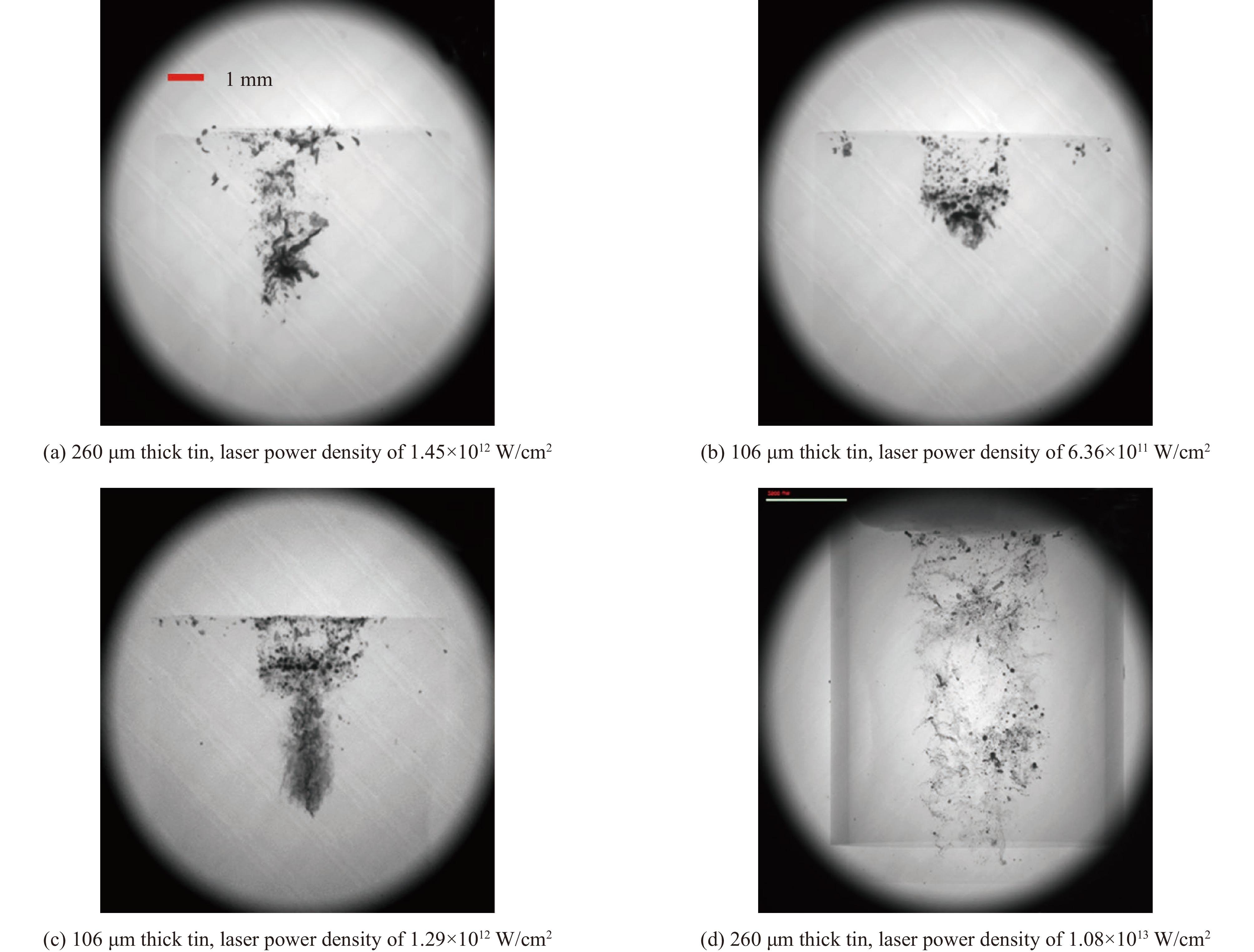
[1] De Rességuier T, Signor L, Dragon A, et al. Experimental investigation of liquid spall in laser shock-loaded tin[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2007, 101: 013506. doi: 10.1063/1.2400800 [2] Walsh J M, Shreffler R G, Willig F J. Limiting conditions for jet formation in high velocity collisions[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1953, 24(3): 349-359. doi: 10.1063/1.1721278 [3] Jones A H, Isbell W M, Maiden C J. Measurement of the very-high-pressure properties of materials using a light-gas gun[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1966, 37(9): 3493-3499. doi: 10.1063/1.1708887 [4] Remiot C, Chapron P, Demay B. A flash X-ray radiography diagnostic for studing surface phenomena under shock loading[J]. AIP Conference Proceedings, 1994, 309(1): 1763-1766. [5] Andriot P, Chapron P, Olive F. Ejection of material from shocked surfaces of tin, tantalum and lead-alloys[J]. AIP Conference Proceedings, 1982, 78(1): 505-509. [6] 韩长生, 经福谦, 丁儆, 等. 不同加载速率下铝自由面微粒子喷射现象研究[J]. 高压物理学报, 1989, 3(2):97-106Han Changsheng, Jing Fuqian, Ding Jing, et al. Study on the phenomena of the mass ejection from the free surface of aluminum at different dynamic loading rates[J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 1989, 3(2): 97-106. [7] Buttler W T, Oró D M, Olson R T, et al. Second shock ejecta measurements with an explosively driven two-shockwave drive[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2014, 116: 103519. doi: 10.1063/1.4895053 [8] Chen Yongtao, Hong Renkai, Chen Haoyu, et al. Experimental examination of ejecta production on shock-melted Sn targets under various surface roughnesses[J]. Journal of Dynamic Behavior of Materials, 2017, 3(2): 174-179. doi: 10.1007/s40870-016-0089-8 [9] Andriyash A V, Astashkin M V, Baranov V K, et al. Application of photon Doppler velocimetry for characterization of ejecta from shock-loaded samples[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2018, 123: 243102. doi: 10.1063/1.5029958 [10] Stöffler D, Gault D E, Wedekind J, et al. Experimental hypervelocity impact into quartz sand: distribution and shock metamorphism of ejecta[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1975, 80(29): 4062-4077. doi: 10.1029/JB080i029p04062 [11] Asay J R. Effect of shock wave risetime on material ejection from aluminum surfaces[R]. Albuquerque: Sandia National Laboratories, 1977. [12] Vogan W S, Anderson W W, Grover M, et al. Piezoelectric characterization of ejecta from shocked tin surfaces[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2005, 98: 113508. doi: 10.1063/1.2132521 [13] Li C K, Séguin F H, Frenje J A, et al. Study of direct-drive capsule implosions in inertial confinement fusion with proton radiography[J]. Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 2009, 51: 014003. doi: 10.1088/0741-3335/51/1/014003 [14] Tamura H, Kohama T, Kondo K, et al. Femtosecond-laser-induced spallation in aluminum[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2001, 89(6): 3520-3522. doi: 10.1063/1.1346996 [15] Pedrini G, Osten W, Gusev M E. High-speed digital holographic interferometry for vibration measurement[J]. Applied Optics, 2006, 45(15): 3456-3462. doi: 10.1364/AO.45.003456 [16] 汪伟, 李作友, 李欣竹, 等. 用超高速阴影摄影技术研究微喷射现象[J]. 应用光学, 2008, 29(4):526-529 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2082.2008.04.010Wang Wei, Li Zuoyou, Li Xinzhu, et al. Study on micro-jet on ultra-high speed shadow photography[J]. Journal of Applied Optics, 2008, 29(4): 526-529. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2082.2008.04.010 [17] Kirugulige M S, Tippur H V, Denney T S. Measurement of transient deformations using digital image correlation method and high-speed photography: application to dynamic fracture[J]. Applied Optics, 2007, 46(22): 5083-5096. doi: 10.1364/AO.46.005083 [18] De Rességuier T, Signor L, Dragon A, et al. Dynamic fragmentation of laser shock-melted tin: experiment and modelling[J]. International Journal of Fracture, 2010, 163(1/2): 109-119. [19] Ohira S, Fujioka S, Sunahara A, et al. X-ray backlight measurement of preformed plasma by kJ-class petawatt LFEX laser[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2012, 112: 063301. doi: 10.1063/1.4752872 [20] Zhao Cang, Fezzaa K, Cunningham R W, et al. Real-time monitoring of laser powder bed fusion process using high-speed X-ray imaging and diffraction[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7: 3602. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-03761-2 [21] Calta N P, Martin A A, Hammons J A, et al. Pressure dependence of the laser-metal interaction under laser powder bed fusion conditions probed by in situ X-ray imaging[J]. Additive Manufacturing, 2020, 32: 101084. doi: 10.1016/j.addma.2020.101084 [22] Buttler W T, Lamoreaux S K, Schulze R K, et al. Ejecta transport, breakup and conversion[J]. Journal of Dynamic Behavior of Materials, 2017, 3(2): 334-345. doi: 10.1007/s40870-017-0114-6 [23] Buttler W T, Cooley J C, Hammerberg J E, et al. Studies of reactive and nonreactive metals-ejecta-transporting nonreactive and reactive gases and vacuum[J]. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2020, 2272: 120003. [24] Durand O, Soulard L, Colombet L, et al. Influence of the phase transitions of shock-loaded tin on microjetting and ejecta production using molecular dynamics simulations[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2020, 127: 175901. doi: 10.1063/5.0003744 [25] Soulard L, Durand O. Observation of phase transitions in shocked tin by molecular dynamics[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2020, 127: 165901. doi: 10.1063/5.0003089 [26] Germann T C, Hammerberg J E, Lee Holian B. Large-scale molecular dynamics simulations of ejecta formation in copper[J]. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2004, 706(1): 285-288. [27] 王裴, 何安民, 邵建立, 等. 强冲击作用下金属界面物质喷射与混合问题数值模拟和理论研究[J]. 中国科学: 物理学 力学 天文学, 2018, 48(9): 106-116Wang Pei, He Anmin, Shao Jianli, et al. Numerical and theoretical investigations of shock-induced material ejection and ejecta-gas mixing[J]. Scientia Sinica (Physica, Mechanica & Astronomica), 2018, 48(9): 106-116. [28] 邵建立, 何安民, 王裴. 微喷射现象数值模拟研究进展概述[J]. 高压物理学报, 2019, 33:030110 doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.20190786Shao Jianli, He Anmin, Wang Pei. Brief review of research progress on numerical simulation of ejection phenomena[J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2019, 33: 030110. doi: 10.11858/gywlxb.20190786 [29] Zellner M B, Vunni G B. Photon Doppler velocimetry (PDV) characterization of shaped charge jet formation[J]. Procedia Engineering, 2013, 58: 88-97. doi: 10.1016/j.proeng.2013.05.012 [30] Georgievskaya A, Raevsky V A. Estimation of spectral characteristics of particles ejected from the free surfaces of metals and liquids under a shock wave effect[J]. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2012, 1426(1): 1007-1010. [31] Dimonte G, Terrones G, Cherne F J, et al. Ejecta source model based on the nonlinear Richtmyer-Meshkov instability[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2013, 113: 024905. doi: 10.1063/1.4773575 [32] Cherne F J, Hammerberg J E, Andrews M J, et al. On shock driven jetting of liquid from non-sinusoidal surfaces into a vacuum[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2015, 118: 185901. doi: 10.1063/1.4934645 [33] 何安民, 刘军, 邵建立, 等. 基于强度介质Richtmyer-Meshkov不稳定性理论的微缺陷喷射模型[J]. 计算物理, 2018, 35(5):505-514 doi: 10.19596/j.cnki.1001-246x.7721He Anmin, Liu Jun, Shao Jianli, et al. Theoretical ejecta model for elastic-plastic solids based on Richtmyer-Meshkov instability[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 2018, 35(5): 505-514. doi: 10.19596/j.cnki.1001-246x.7721 [34] Durand O, Soulard L. Large-scale molecular dynamics study of jet breakup and ejecta production from shock-loaded copper with a hybrid method[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2012, 111: 044901. doi: 10.1063/1.3684978 [35] Shao Jianli, Wang Pei, He Anmin, et al. Molecular dynamics study on the failure modes of aluminium under decaying shock loading[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2013, 113: 163507. doi: 10.1063/1.4802671 [36] He Anmin, Wang Pei, Shao Jianli. Molecular dynamics simulations of ejecta size distributions for shock-loaded Cu with a wedged surface groove[J]. Computational Materials Science, 2015, 98: 271-277. doi: 10.1016/j.commatsci.2014.11.020 [37] He Anmin, Liu Jun, Liu Chao, et al. Numerical and theoretical investigation of jet formation in elastic-plastic solids[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2018, 124: 185902. doi: 10.1063/1.5051527 [38] Soulard L, Durand O, Prat R, et al. High velocity impact of a spherical particle on a surface: theory and simulation of the jet formation[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2021, 129: 205104. doi: 10.1063/5.0046250 [39] Xu Yihua, Xu Ruicong, Cheng Hui, et al. Numerical simulation of jet breakup phenomenon during severe accident of sodium-cooled fast reactor using MPS method[J]. Annals of Nuclear Energy, 2022, 172: 109087. doi: 10.1016/j.anucene.2022.109087 [40] DeMaria A J, Stetser D A, Heynau H. Self mode-locking of lasers with saturable absorbers[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 1966, 8(7): 174-176. doi: 10.1063/1.1754541 [41] Strickland D, Mourou G. Compression of amplified chirped optical pulses[J]. Optics Communications, 1985, 55(6): 447-449. doi: 10.1016/0030-4018(85)90151-8 [42] Bahk S W, Rousseau P, Planchon T A, et al. Generation and characterization of the highest laser intensities (1022 W/cm2)[J]. Optics Letters, 2004, 29(24): 2837-2839. doi: 10.1364/OL.29.002837 [43] Eliezer S. The interaction of high-power lasers with plasmas[J]. Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 2003, 45: 181. doi: 10.1088/0741-3335/45/2/701 [44] 宾建辉, 雷安乐, 余玮. 等离子体初始温度对强激光与等离子体相互作用中的高能质子产生的影响[J]. 中国激光, 2009, 36(6):1416-1419 doi: 10.3788/CJL20093606.1416Bin Jianhui, Lei Anle, Yu Wei. Influence of initial plasma temperature on energetic proton generation from laser-plasma interactions[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2009, 36(6): 1416-1419. doi: 10.3788/CJL20093606.1416 [45] 马文君, 刘志鹏, 王鹏杰, 等. 激光加速高能质子实验研究进展及新加速方案[J]. 物理学报, 2021, 70:084102 doi: 10.7498/aps.70.20202115Ma Wenjun, Liu Zhipeng, Wang Pengjie, et al. Experimental progress of laser-driven high-energy proton acceleration and new acceleration schemes[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2021, 70: 084102. doi: 10.7498/aps.70.20202115 [46] 周维民, 于明海, 张天奎, 等. 基于皮秒拍瓦激光的高分辨X射线背光照相研究[J]. 中国激光, 2020, 47:0500010 doi: 10.3788/CJL202047.0500010Zhou Weimin, Yu Minghai, Zhang Tiankui, et al. High-resolution X-ray backlight radiography using picosecond petawatt laser[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2020, 47: 0500010. doi: 10.3788/CJL202047.0500010 [47] 曹丙花, 张宇盟, 范孟豹, 等. 太赫兹超分辨率成像研究进展[J]. 中国光学, 2022, 15(3):405-417 doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0198Cao Binghua, Zhang Yumeng, Fan Mengbao, et al. Research progress of terahertz super-resolution imaging[J]. Chinese Optics, 2022, 15(3): 405-417. doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0198 [48] 谭智勇, 万文坚, 黎华, 等. 基于太赫兹量子级联激光器的实时成像研究进展[J]. 中国光学, 2017, 10(1):68-76 doi: 10.3788/co.20171001.0068Tan Zhiyong, Wan Wenjian, Li Hua, et al. Progress in real-time imaging based on terahertz quantum-cascade lasers[J]. Chinese Optics, 2017, 10(1): 68-76. doi: 10.3788/co.20171001.0068 [49] 张佳茹, 管迎春. 超快激光制备生物医用材料表面功能微结构的现状及研究进展[J]. 中国光学, 2019, 12(2):199-213 doi: 10.3788/co.20191202.0199Zhang Jiaru, Guan Yingchun. Surface functional microstructure of biomedical materials prepared by ultrafast laser: a review[J]. Chinese Optics, 2019, 12(2): 199-213. doi: 10.3788/co.20191202.0199 [50] Cauble R, Phillion D W, Hoover T J, et al. Demonstration of 0.75 Gbar planar shocks in X-ray driven colliding foils[J]. Physical Review Letters, 1993, 70(14): 2102-2105. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.70.2102 [51] Smith R F, Eggert J H, Jeanloz R, et al. Ramp compression of diamond to five terapascals[J]. Nature, 2014, 511(7509): 330-333. doi: 10.1038/nature13526 [52] Li Kebin, Li Xiaojie, Wang Xiaohong, et al. A simple electrometric method for parametric determination of Jones-Wilkins-Lee equation of state from underwater explosion test[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2018, 124: 215906. doi: 10.1063/1.5049497 [53] Jones D R, Fensin S J, Ndefru B G, et al. Spall fracture in additive manufactured tantalum[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2018, 124: 225902. doi: 10.1063/1.5063930 [54] Wang Xiaofeng, Liu Yang, Shi Tongya, et al. Strain rate dependence of mechanical property in a selective laser melted 17-4 PH stainless steel with different states[J]. Materials Science and Engineering:A, 2020, 792: 139776. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2020.139776 [55] Luo Shengnian, An Qi, Germann T C, et al. Shock-induced spall in solid and liquid Cu at extreme strain rates[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2009, 106: 013502. doi: 10.1063/1.3158062 [56] Esarey E, Schroeder C B, Leemans W P. Physics of laser-driven plasma-based electron accelerators[J]. Reviews of Modern Physics, 2009, 81(3): 1229-1285. doi: 10.1103/RevModPhys.81.1229 [57] Tian Chao, Yu Minghai, Shan Lianqiang, et al. Radiography of direct drive double shell targets with hard X-ray generated by a short pulse laser[J]. Nuclear Fusion, 2019, 59: 046012. doi: 10.1088/1741-4326/aafe30 [58] 税敏, 于明海, 储根柏, 等. 激光加载下金属锡材料微喷颗粒与低密度泡沫混合实验研究[J]. 物理学报, 2019, 68:076201 doi: 10.7498/aps.68.20182280Shui Min, Yu Minghai, Chu Genbai, et al. Observation of ejecta tin particles into polymer foam through high-energy X-ray radiograpy using high-intensity short-pulse laser[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2019, 68: 076201. doi: 10.7498/aps.68.20182280 [59] Signor L, De Rességuier T, Dragon A, et al. Investigation of fragments size resulting from dynamic fragmentation in melted state of laser shock-loaded tin[J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2010, 37(8): 887-900. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2010.03.001 [60] Prudhomme G, De Rességuier T, Roland C, et al. Velocity and mass density of the ejecta produced from sinusoidal grooves in laser shock-loaded tin[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2020, 128: 155903. doi: 10.1063/5.0022940 [61] De Rességuier T, Signor L, Dragon A, et al. Spallation in laser shock-loaded tin below and just above melting on release[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2007, 102: 073535. doi: 10.1063/1.2795436 [62] Lescoute E, De Rességuier T, Chevalier J M, et al. Soft recovery technique to investigate dynamic fragmentation of laser shock-loaded metals[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2009, 95: 211905. doi: 10.1063/1.3268437 [63] Morard G, De Rességuier T, Vinci T, et al. High-power laser shock-induced dynamic fragmentation of iron foils[J]. Physical Review B, 2010, 82: 174102. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.82.174102 [64] Loison D, De Rességuier T, Dragon A. Micro-tomography to characterize size distribution of fragments created by laser shock-induced micro-spallation of metallic sample[J]. Applied Mechanics and Materials, 2014, 556: 225-231. [65] Lescoute E, De Rességuier T, Chevalier J M, et al. Ejection of spalled layers from laser shock-loaded metals[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2010, 108: 093510. doi: 10.1063/1.3500317 [66] 辛建婷, 谷渝秋, 李平, 等. 强激光加载下金属材料微喷回收诊断[J]. 物理学报, 2012, 61:236201 doi: 10.7498/aps.61.236201Xin Jianting, Gu Yuqiu, Li Ping, et al. Study on metal ejection under laser shock loading[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2012, 61: 236201. doi: 10.7498/aps.61.236201 [67] Gauch J M. Image segmentation and analysis via multiscale gradient watershed hierarchies[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 1999, 8(1): 69-79. doi: 10.1109/83.736688 [68] Vese L A, Chan T F. A multiphase level set framework for image segmentation using the Mumford and Shah model[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2002, 50(3): 271-293. doi: 10.1023/A:1020874308076 [69] He Weihua, Xin Jianting, Chu Genbai, et al. Investigation of fragment sizes in laser-driven shock-loaded tin with improved watershed segmentation method[J]. Optics Express, 2014, 22(16): 18924-18933. doi: 10.1364/OE.22.018924 [70] 辛建婷, 赵永强, 储根柏, 等. 强激光加载下锡材料微喷颗粒与气体混合回收实验研究及颗粒度分析[J]. 物理学报, 2017, 66:186201 doi: 10.7498/aps.66.186201Xin Jianting, Zhao Yongqiang, Chu Genbai, et al. Experimental investigation of tin fragments mixing with gas subjected to laser driven shock[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2017, 66: 186201. doi: 10.7498/aps.66.186201 [71] De Rességuier T, Signor L, Dragon A, et al. On the dynamic fragmentation of laser shock-melted tin[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2008, 92: 131910. doi: 10.1063/1.2906907 [72] Franzkowiak J E, Prudhomme G, Mercier P, et al. PDV-based estimation of ejecta particles’ mass-velocity function from shock-loaded tin experiment[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2018, 89: 033901. doi: 10.1063/1.4997365 [73] Seisson G, Prudhomme G, Frugier P A, et al. Dynamic fragmentation of graphite under laser-driven shocks: identification of four damage regimes[J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2016, 91: 68-79. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2015.12.012 [74] Olbinado M P, Cantelli V, Mathon O, et al. Ultra high-speed X-ray imaging of laser-driven shock compression using synchrotron light[J]. Journal of Physics D:Applied Physics, 2018, 51: 055601. doi: 10.1088/1361-6463/aaa2f2 [75] Pradel P, Malaise F, De Rességuier T, et al. Fast X-ray radiography to study the dynamic compaction mechanisms in a rigid polyurethane foam under plate impact[J]. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2020, 2272: 110010. [76] 赵永强, 辛建婷, 席涛, 等. 强激光加载下材料微层裂过程研究进展[J]. 激光杂志, 2017, 38(10):1-7Zhao Yongqiang, Xin Jianting, Xi Tao, et al. Progress on material micro-spalling under intense laser-driven loading[J]. Laser Journal, 2017, 38(10): 1-7. [77] Kalantar D H, Belak J F, Collins G W, et al. Direct observation of the α− ε transition in shock-compressed iron via nanosecond X-ray diffraction[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2005, 95: 075502. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.95.075502 [78] Lindl J. Development of the indirect-drive approach to inertial confinement fusion and the target physics basis for ignition and gain[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 1995, 2(11): 3933-4024. doi: 10.1063/1.871025 [79] Lindl J D, Amendt P, Berger R L, et al. The physics basis for ignition using indirect-drive targets on the National Ignition Facility[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2004, 11(2): 339-491. doi: 10.1063/1.1578638 [80] Tommasini R, Hatchett S P, Hey D S, et al. Development of Compton radiography of inertial confinement fusion implosions[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2011, 18: 056309. doi: 10.1063/1.3567499 [81] Schick D, Borchert M, Braenzel J, et al. Laser-driven resonant magnetic soft-X-ray scattering for probing ultrafast antiferromagnetic and structural dynamics[J]. Optica, 2021, 8(9): 1237-1242. doi: 10.1364/OPTICA.435522 [82] Bhan L, Covington C, Varga K. Signatures of atomic structure in subfemtosecond laser-driven electron dynamics in nanogaps[J]. Physical Review B, 2022, 105: 085416. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.105.085416 [83] Zhu Wei, Fauseweh B, Chacon A, et al. Ultrafast laser-driven many-body dynamics and Kondo coherence collapse[J]. Physical Review B, 2021, 103: 224305. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.103.224305 [84] Zhu Qihua, Zhou Kainan, Su Jingqin, et al. The Xingguang-III laser facility: precise synchronization with femtosecond, picosecond and nanosecond beams[J]. Laser Physics Letters, 2018, 15: 015301. doi: 10.1088/1612-202X/aa94e9 [85] Park H S, Chambers D M, Chung H K, et al. High-energy Kα radiography using high-intensity, short-pulse lasers[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2006, 13: 056309. doi: 10.1063/1.2178775 [86] Kulpe S, Dierolf M, Günther B, et al. Dynamic K-edge subtraction fluoroscopy at a compact inverse-Compton synchrotron X-ray source[J]. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10: 9612. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-66414-x [87] De Rességuier T, Roland C, Prudhomme G, et al. Picosecond radiography combined with other techniques to investigate microjetting from laser shock-loaded grooves[J]. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2018, 1979: 080011. [88] Chu Genbai. High-energy X-ray radiography of laser shock loaded metal dynamic fragmentation using high-intensity short-pulse laser[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2018, 89(11): 115106. doi: 10.1063/1.5034401 [89] 叶雁, 李军, 朱鹏飞, 等. 脉冲X光照相在微物质喷射诊断中的应用[J]. 高压物理学报, 2013, 27(3):398-402Ye Yan, Li Jun, Zhu Pengfei, et al. Flash X-ray radiography for diagnosing the ejecta from shocked metal surface[J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2013, 27(3): 398-402. [90] Xin Jianting, He Anmin, Liu Wenbin, et al. X-ray radiography of microjetting from grooved surfaces in tin sample subjected to laser driven shock[J]. Journal of Micromechanics and Microengineering, 2019, 29: 095011. doi: 10.1088/1361-6439/ab2c56 [91] Roland C, De Rességuier T, Sollier A, et al. Ejection of micron-scale fragments from triangular grooves in laser shock-loaded copper samples[J]. Journal of Dynamic Behavior of Materials, 2017, 3(2): 156-163. doi: 10.1007/s40870-016-0087-x [92] Sollier A, Lescoute E. Characterization of the ballistic properties of ejecta from laser shock-loaded samples using high resolution picosecond laser imaging[J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2020, 136: 103429. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2019.103429 [93] Dimonte G, Ramaprabhu P. Simulations and model of the nonlinear Richtmyer–Meshkov instability[J]. Physics of Fluids, 2010, 22: 014104. doi: 10.1063/1.3276269 [94] Monfared S K, Oró D M, Grover M, et al. Experimental observations on the links between surface perturbation parameters and shock-induced mass ejection[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2014, 116: 063504. doi: 10.1063/1.4891449 [95] 陈永涛, 洪仁楷, 汤铁钢, 等. 熔化状态下锡样品微喷射现象的诊断[J]. 高压物理学报, 2016, 30(4):323-327Chen Yongtao, Hong Renkai, Tang Tiegang, et al. Experimental diagnostic of ejecta on Sn sample in shock melting[J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2016, 30(4): 323-327. [96] De Rességuier T, Prudhomme G, Roland C, et al. Material ejection from surface defects in laser shock-loaded metallic foils[J]. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2020, 2272: 120023. [97] Prudhomme G, Franzkowiak J E, De Rességuier T, et al. Ejecta from periodical grooves in tin foils under laser-driven shock loading[J]. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2018, 1979: 080010. [98] Zellner M B, Grover M, Hammerberg J E, et al. Effects of shock-breakout pressure on ejection of micron-scale material from shocked tin surfaces[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2007, 102: 013522. doi: 10.1063/1.2752130 [99] He Weihua, Xi Tao, Shui Min, et al. High-energy X-ray radiography investigation on the ejecta physics of laser shock-loaded tin[J]. AIP Advances, 2019, 9: 085002. doi: 10.1063/1.5109748 [100] Elias P, Chapron P, Mondot M. Experimental study of the slowing down of shock-induced matter ejection into argon gas[M]//Schmidt S C, Johnson J N, Davison L W. Shock Compression of Condensed Matter-1989. Amsterdam: North-Holland, 1990. [101] Oro D M, Hammerberg J E, Buttler W T, et al. A class of ejecta transport test problems[J]. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2012, 1426(1): 1351-1354. [102] 税敏, 杨曦, 于明海, 等. 锡-泡沫界面不稳定性增长与混合实验研究[J]. 中国激光, 2021, 48:0703002 doi: 10.3788/CJL202148.0703002Shui Min, Yang Xi, Yu Minghai, et al. Instability growth of tin-foam interface and mixing experiment[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2021, 48: 0703002. doi: 10.3788/CJL202148.0703002 -




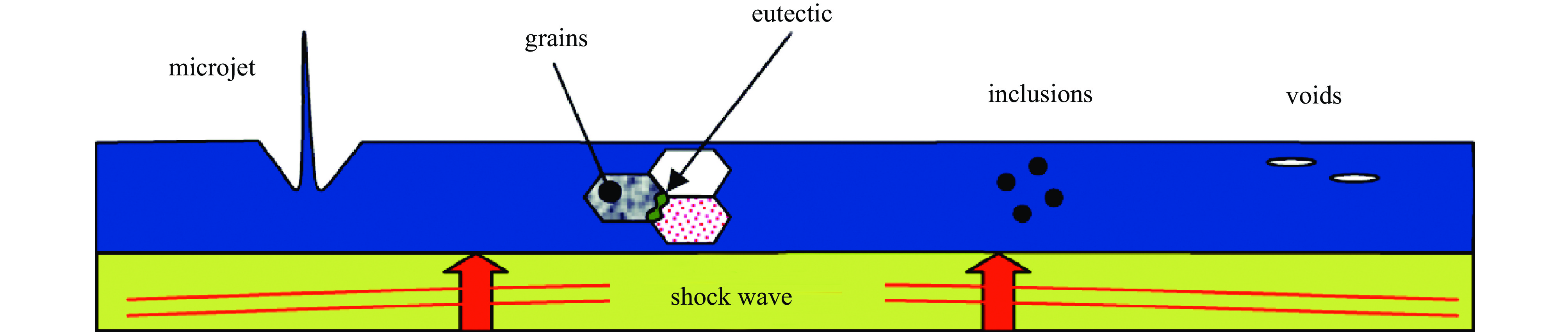
 下载:
下载: