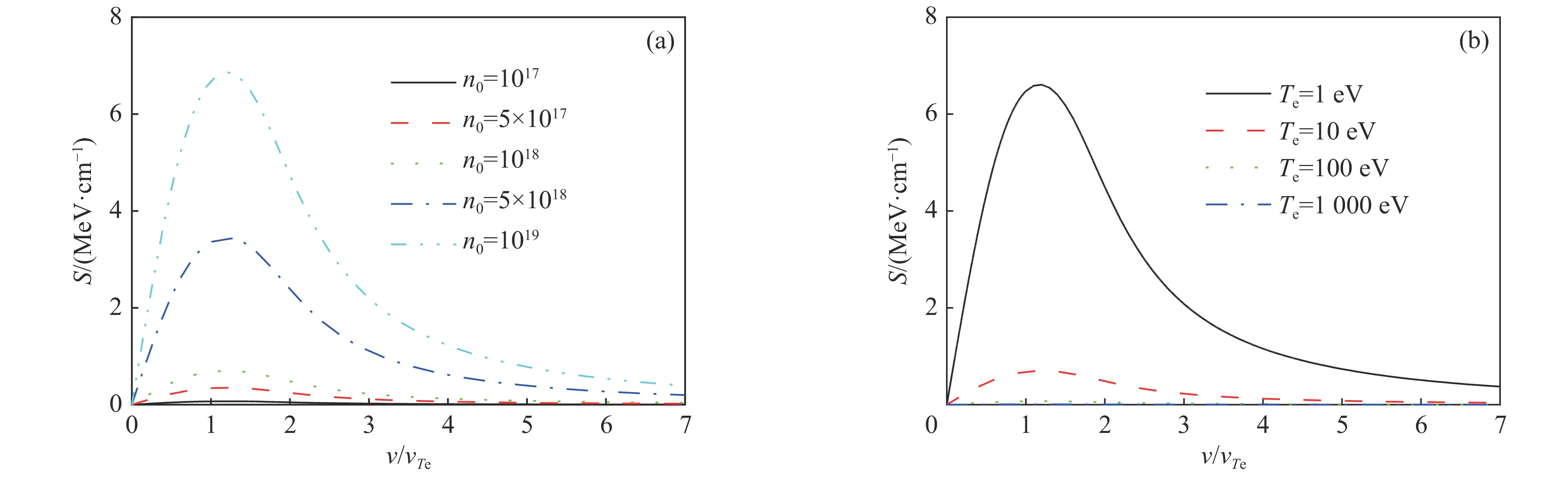
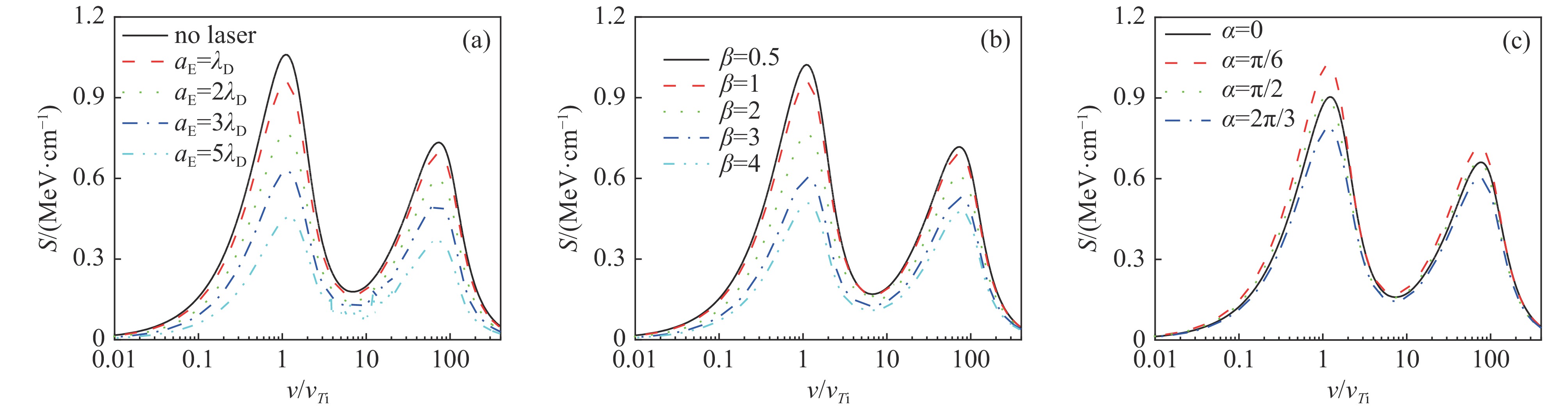
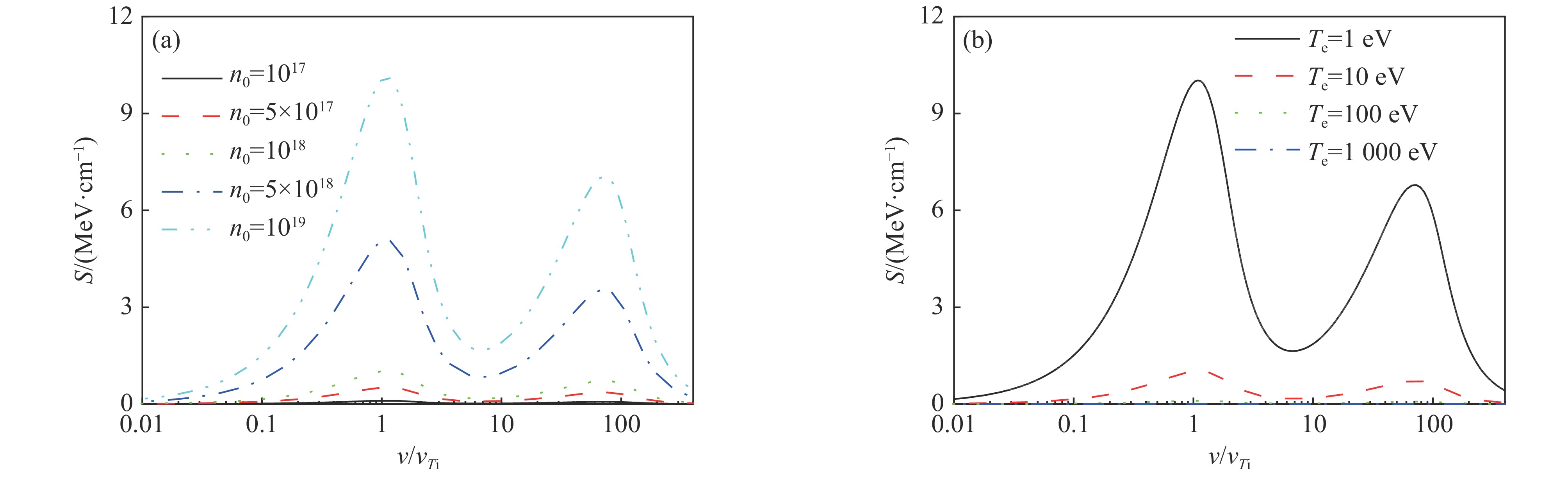
| [1] |
Eliezer S, Murakami M, Martinez Val J M. Equation of state and optimum compression in inertial fusion energy[J]. Laser and Particle Beams, 2007, 25(4): 585-592. doi: 10.1017/S0263034607000699
|
| [2] |
Barriga-Carrasco M D. Target electron collision effects on energy loss straggling of protons in an electron gas at any degeneracy[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2008, 15: 033103. doi: 10.1063/1.2888525
|
| [3] |
Cook R C, Kozioziemski B J, Nikroo A, et al. National Ignition Facility target design and fabrication[J]. Laser and Particle Beams, 2008, 26(3): 479-487. doi: 10.1017/S0263034608000499
|
| [4] |
Golubev A, Basko M, Fertman A, et al. Dense plasma diagnostics by fast proton beams[J]. Physical Review E, 1998, 57(3): 3363-3367. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.57.3363
|
| [5] |
Alviri V M, Asem M M. Hadron therapy based on laser acceleration in the plasma channel using oxygen ionization[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 183262-183291. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2952916
|
| [6] |
Higginson A, Gray R J, King M, et al. Near-100 MeV protons via a laser-driven transparency-enhanced hybrid acceleration scheme[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9: 724. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-03063-9
|
| [7] |
Vieux G, Brunetti E, Cipiccia S, et al. Towards a high efficiency amplifier based on Raman amplification[J]. Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 2020, 62: 014018. doi: 10.1088/1361-6587/ab56de
|
| [8] |
Williams G J, Tommasini R, Lemos N, et al. High-energy differential-filtering photon spectrometer for ultraintense laser-matter interactions[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2018, 89: 10F116. doi: 10.1063/1.5039383
|
| [9] |
Bulanov S V, Khoroshkov V S. Feasibility of using laser ion accelerators in proton therapy[J]. Plasma Physics Reports, 2002, 28(5): 453-456. doi: 10.1134/1.1478534
|
| [10] |
Ledingham K W D, Galster W, Sauerbrey R. Laser-driven proton oncology—a unique new cancer therapy?[J]. The British Journal of Radiology, 2007, 80(959): 855-858. doi: 10.1259/bjr/29504942
|
| [11] |
Kluge T, Rödel M, Metzkes-Ng J, et al. Observation of ultrafast solid-density plasma dynamics using femtosecond X-ray pulses from a free-electron laser[J]. Physical Review X, 2018, 8: 031068.
|
| [12] |
Parigger C G. Laser-plasma and stellar astrophysics spectroscopy[J]. Contributions of the Astronomical Observatory Skalnaté Pleso, 2020, 50(1): 15-31.
|
| [13] |
Remington B A, Arnett D, Paul R, et al. Modeling astrophysical phenomena in the laboratory with intense lasers[J]. Science, 1999, 284(5419): 1488-1493. doi: 10.1126/science.284.5419.1488
|
| [14] |
Bulanov S V, Esirkepov T Z, Kando M, et al. On the problems of relativistic laboratory astrophysics and fundamental physics with super powerful lasers[J]. Plasma Physics Reports, 2015, 41(1): 1-51. doi: 10.1134/S1063780X15010018
|
| [15] |
Jia Shaokui, Zhou Jiaqi, Wang Xing, et al. Cold-target electron-ion-coincidence momentum-spectroscopy study of electron-impact single and double ionization of N2 and O2 molecules[J]. Physical Review A, 2023, 107: 032819. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.107.032819
|
| [16] |
Frenje J A. Nuclear diagnostics for inertial confinement fusion (ICF) plasmas[J]. Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 2019, 62: 023001.
|
| [17] |
Ren Jieru, Ma Bubo, Liu Lirong, et al. Target density effects on charge transfer of laser-accelerated carbon ions in dense plasma[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2023, 130: 095101. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.130.095101
|
| [18] |
Ren Jieru, Deng Zhigang, Qi Wei, et al. Observation of a high degree of stopping for laser-accelerated intense proton beams in dense ionized matter[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11: 5157. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-18986-5
|
| [19] |
胡章虎, 王琼, 宋远红, 等. 带电粒子与磁化等离子体相互作用的极化效应及能量损失[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2008, 20(11):1919-1922Hu Zhanghu, Wang Qiong, Song Yuanhong, et al. Polarization effect and energy loss in interactions of charged particles with magnetized plasmas[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2008, 20(11): 1919-1922
|
| [20] |
Brandt W, Kitagawa M. Effective stopping-power charges of swift ions in condensed matter[J]. Physical Review B, 1982, 25(9): 5631-5637. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.25.5631
|
| [21] |
D’Avanzo J, Hofmann I, Lontano M. Effective charge in heavy ion stopping in classical collisionless plasmas[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 1996, 3(11): 3885-3889. doi: 10.1063/1.871576
|
| [22] |
Arista N R, Galvo R O M, Miranda L C M. Laser-field effects on the interaction of charged particles with a degenerate electron gas[J]. Physical Review A, 1989, 40(7): 3808-3816. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.40.3808
|
| [23] |
Wang Guiqiu, Song Yuanhong, Wang Younian, et al. Influence of a laser field on Coulomb explosions and stopping power for swift molecular ions interacting with solids[J]. Physical Review A, 2002, 66: 042901. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.66.042901
|
| [24] |
D’Avanzo J, Lontano M, Tome’ E, et al. Heavy-ion interaction in a nonisothermal plasma with two-ion correlation effects[J]. Physical Review E, 1995, 52(1): 919-931. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.52.919
|
| [25] |
Wang Guiqiu, Wang Younian. Influence of strong laser fields on Coulomb explosions energy losses of correlated-ion clusters in plasmas[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2004, 11(3): 1187-1193. doi: 10.1063/1.1645794
|





 下载:
下载: