Design, simulation and optimization of magnet supports in 4th generation synchrotron light sources
-
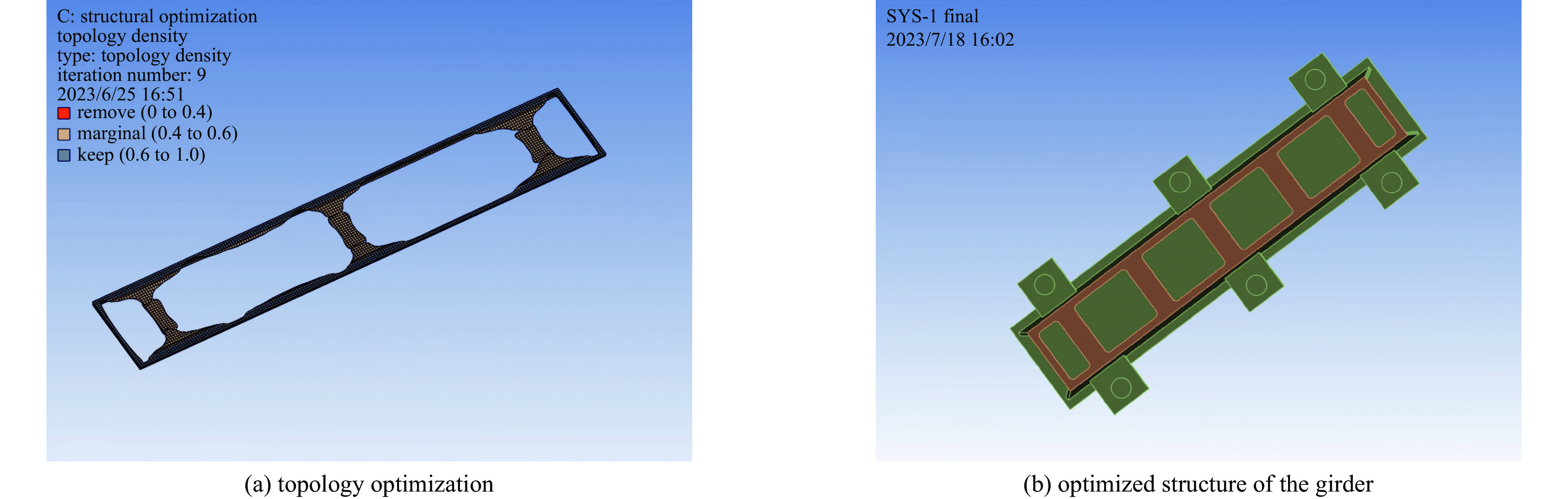
摘要: 储存环机械支撑的静力变形、调节精度决定各物理元件的定位精度,其动态响应特性间接影响着束流的稳定性,机械支撑是各物理元件的安装基础,保证磁铁、真空室、束测元件正确地安装、运行,发挥出相应的物理性能。主要从支撑的静力变形和固有频率两个方面对机械支撑进行优化设计。以深圳产业光源(SILF)共架支撑为例,利用SolidWorks和Ansys软件对储存环磁铁机械支撑进行设计、拓扑优化。详细阐述了储存环机械支撑设计、优化的过程,并将最终优化完成的支撑模型与磁铁模型进行装配,在尽量接近真实工况的基础上对整体支撑进行仿真计算,以确保支撑整体能够达到设计指标。Abstract: The static deformation and adjustment precision of the storage ring's mechanical support determine the positioning accuracy of each physical component. The dynamic response characteristics of these components affect the stability of the beam current. Therefore, mechanical support serves as the installation foundation for all physical components, ensuring the correct installation and operation of magnets, vacuum chambers, beam diagnostics, and other elements, thereby enabling them to exhibit their corresponding physical performance. Therefore, designing mechanical support with high stability holds extraordinary significance. Taking the Shenzhen Innovation Light source Facility (SILF) as an example, this article utilizes SolidWorks and Ansys software to design and optimize the magnets support of the storage ring. The process of mechanical support design and optimization simulation for the storage ring is elaborated in detail. The final design is assembled with the magnet model, and the overall support is simulated and validated as closely as possible to the real operating conditions to ensure compliance with the parameter requirements of the physical design.
-
表 1 部分光源支撑形式及准直的要求
Table 1. The type of girder and collimation requirements
ring lattice girder adjustment the first-order frequency/Hz alignment accuracy
between magnets/μmalignment accuracy
between girder/μmESRF-EBS 7BA common girder wedge 49(actual measurement) 50 50 APS-U 7BA common girder wedge 36.3(actual measurement) 30 100 Sirius 5BA common girder wedge 168(actual measurement) 40 80 Diamond 6BA common girder cam 16.3(actual measurement) 50 100 SLS-II 7BA common girder cam — 50 100 MAXIV 7BA common girder screw 39(actual measurement) 30 100 HEPS 7BA common girder wedge 54(design parameter) 30 50 表 2 SILF储存环的主要参数
Table 2. Main parameters of the SILF storage ring
beam energy/GeV circumstance/m number of cells natural emittance/(pm·rad) transverse tunes momentum compaction factor damping time/ms 3.0 696 28 89 68.26/24.22 6.6×10−5 34.97/43/74/25.01 表 3 横梁高度与截面角组合
Table 3. Combination of girder height and cross-section angle
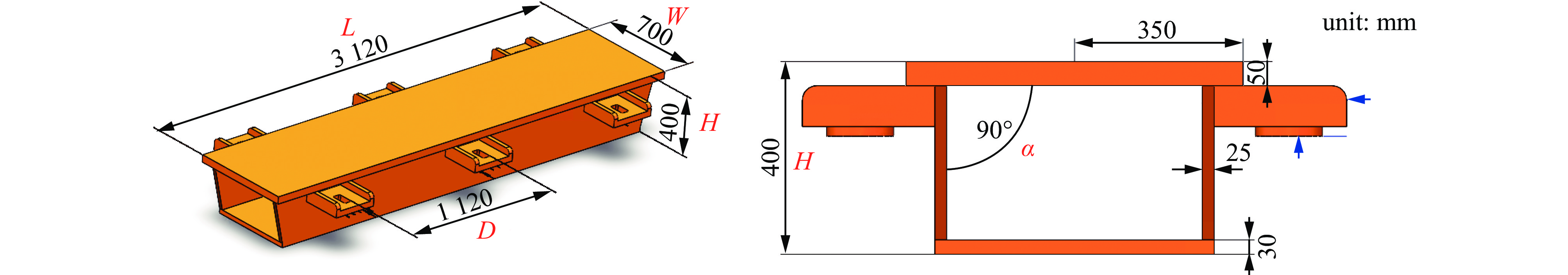
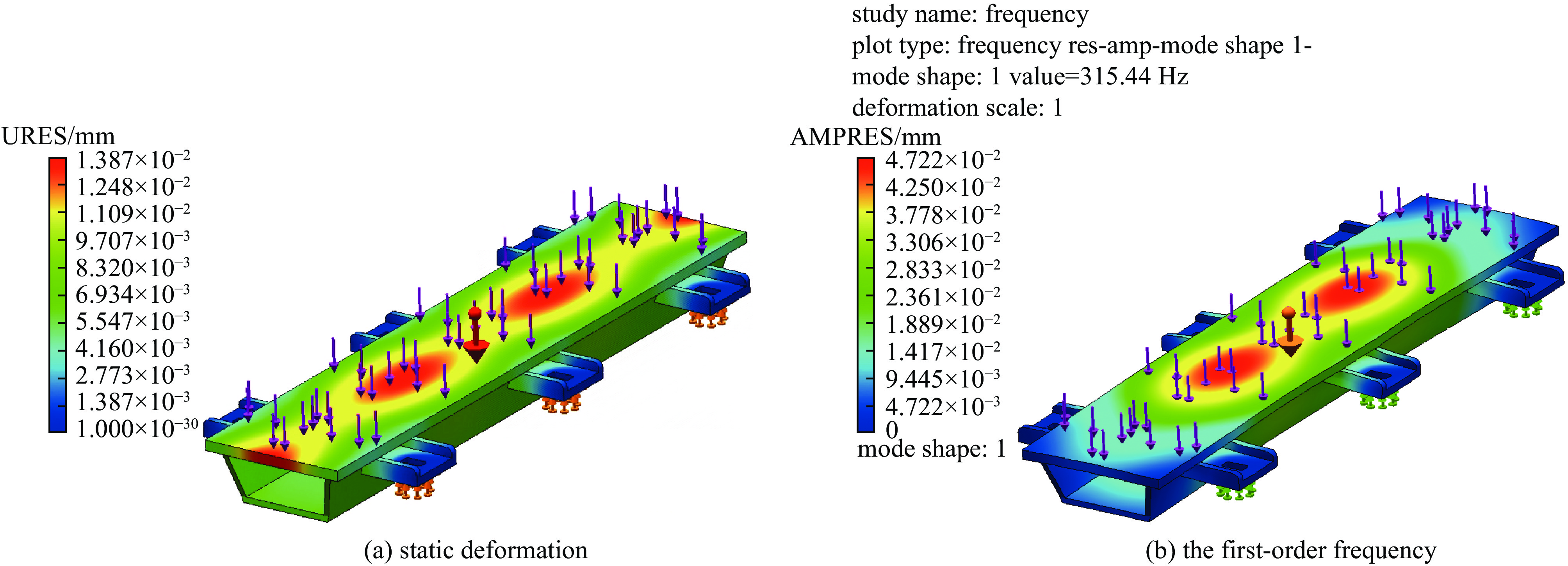
case H/mm α/(°) case H/mm α/(°) case H/mm α/(°) case H/mm α/(°) 1 300 65 12 500 70 23 350 80 34 550 85 2 350 65 13 550 70 24 400 80 35 600 85 3 400 65 14 600 70 25 450 80 36 300 90 4 450 65 15 300 75 26 500 80 37 350 90 5 500 65 16 350 75 27 550 80 38 400 90 6 550 65 17 400 75 28 600 80 39 450 90 7 600 65 18 450 75 29 300 85 40 500 90 8 300 70 19 500 75 30 350 85 41 550 90 9 350 70 20 550 75 31 400 85 42 600 90 10 400 70 21 600 75 32 450 85 11 450 70 22 300 80 33 500 85 表 4 横梁最大静力变形量和一阶固有模态值
Table 4. Static deformation and the first-order frequency of the girder
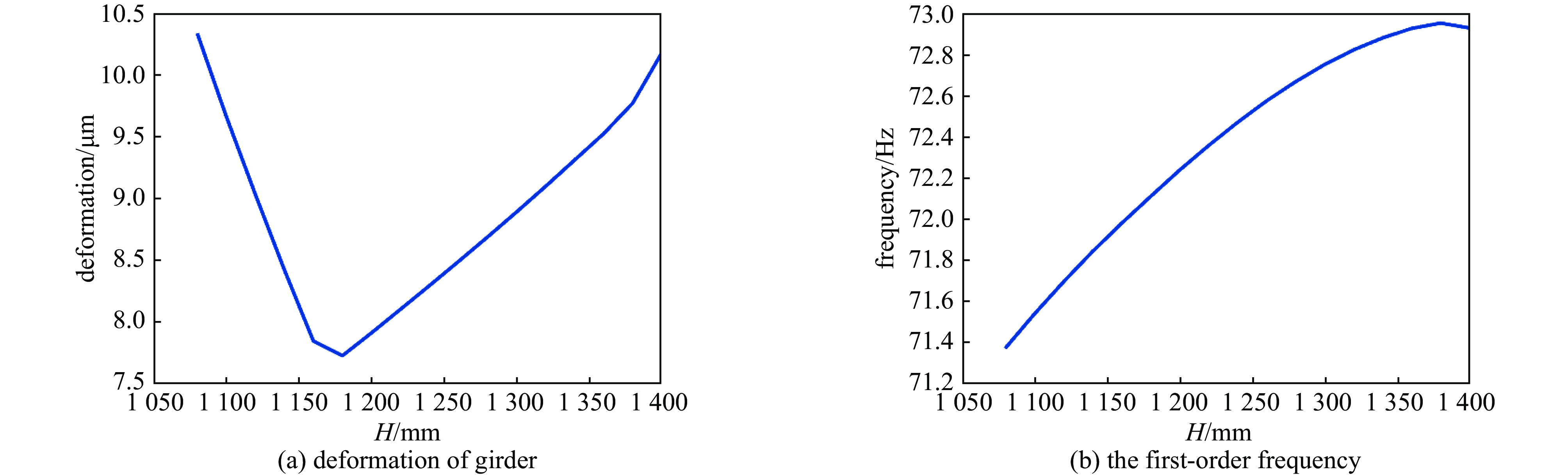
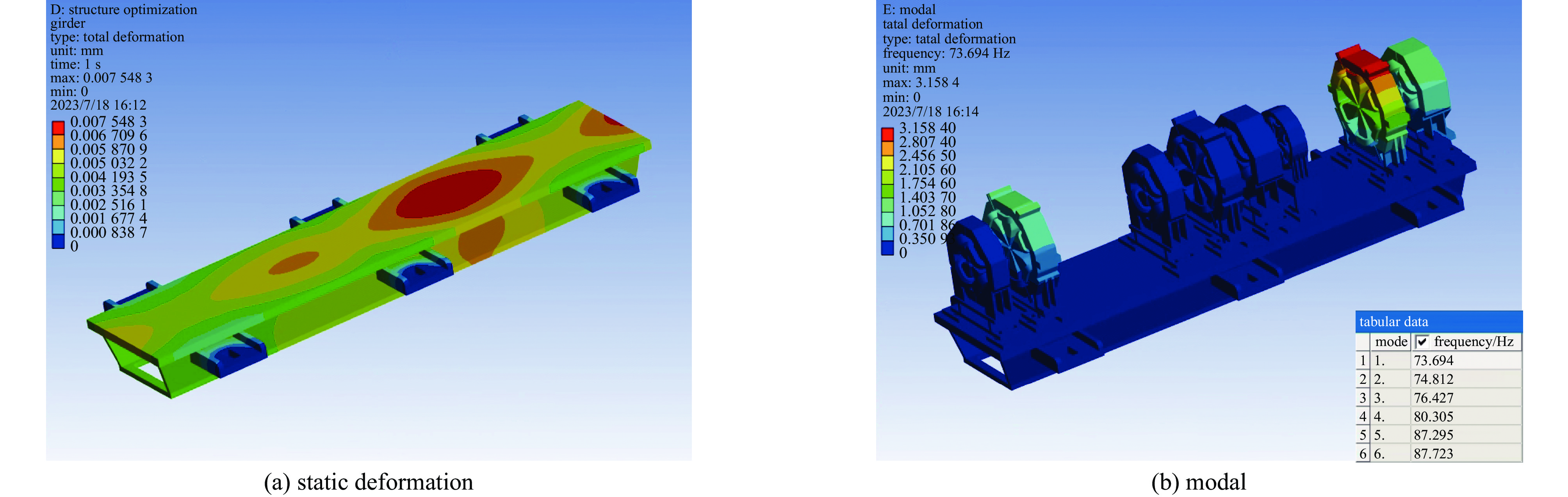
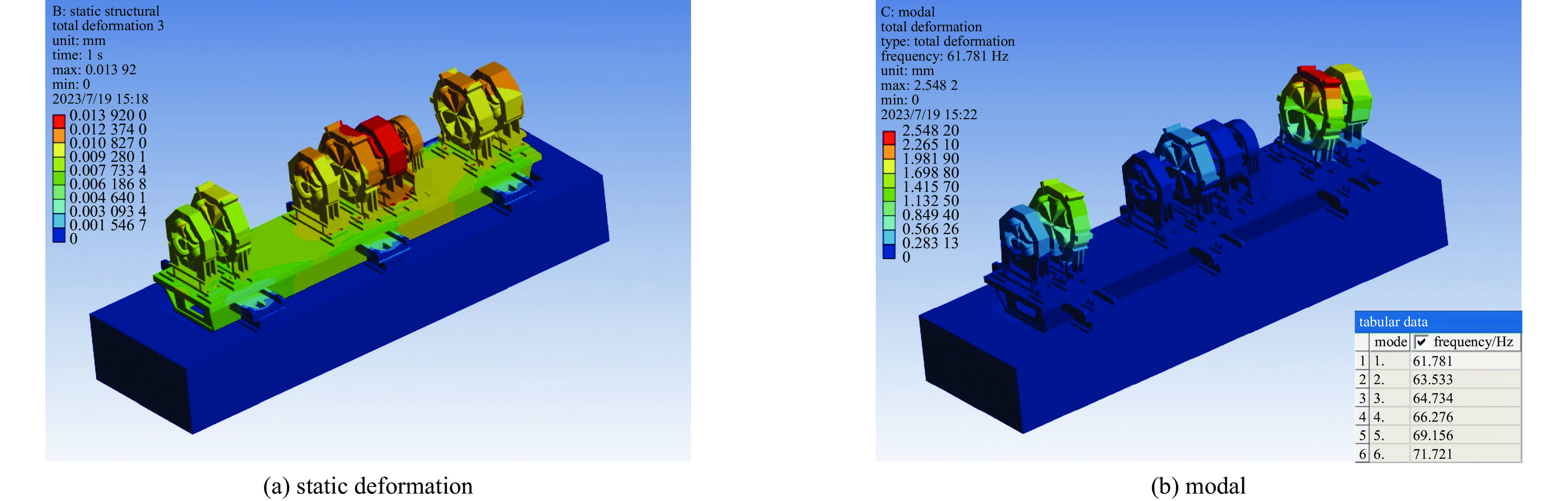
case the first-order frequency/Hz total deformation/mm case the first-order frequency/Hz total deformation/mm 1 311.3 0.01443 22 315.3 0.01358 2 309.3 0.01465 23 250.1 0.01377 3 288.1 0.01485 24 198.9 0.01397 4 260.1 0.01504 25 163.6 0.01417 5 241.9 0.01521 26 138.2 0.01436 6 230.0 0.01537 27 118.9 0.01453 7 222.8 0.01551 28 104.1 0.01470 8 313.9 0.01415 29 311.6 0.01328 9 298.1 0.01436 30 231.9 0.01347 10 250.4 0.01456 31 181.1 0.01367 11 217.3 0.01476 32 146.2 0.01386 12 193.9 0.01494 33 121.3 0.01405 13 177.4 0.0151 34 102.6 0.01422 14 165.6 0.01526 35 88.2 0.01439 15 315.4 0.01387 36 296.2 0.01297 16 272.3 0.01407 37 216.5 0.01316 17 221.2 0.01427 38 166.5 0.01335 18 186.2 0.01447 39 132.5 0.01354 19 161.0 0.01465 40 108.3 0.01372 20 142.3 0.01483 41 90.5 0.01389 21 127.8 0.01499 42 76.8 0.01406 表 5 不同D值对应的横梁形变量和整体一阶模态值
Table 5. Deformation and the first-order frequency of the girder with different D values
case D/mm deformation/mm the first-order frequency/Hz 1 1080 0.010332647 71.37528032 2 1100 0.009657498 71.54180391 3 1120 0.009025472 71.69795512 4 1140 0.008412724 71.84591134 5 1160 0.007834575 71.98321915 6 1180 0.007714708 72.11422153 7 1200 0.007899744 72.24277478 8 1220 0.008091512 72.36269286 9 1240 0.008284279 72.47581847 10 1260 0.008479983 72.58074762 11 1280 0.00867867 72.67432685 12 1300 0.008881759 72.75808202 13 1320 0.009089703 72.82974036 14 1340 0.009303582 72.88817963 15 1360 0.009517383 72.93432918 16 1380 0.009765245 72.96061067 17 1400 0.010172279 72.93668228 -
[1] 焦毅, 白正贺. 第四代同步辐射光源物理设计与优化[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2022, 34:104004 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202234.220136Jiao Yi, Bai Zhenghe. Physics design and optimization of the fourth-generation synchrotron light sources[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2022, 34: 104004 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202234.220136 [2] 张令翊, 庄杰佳, 赵夔, 等. 第四代光源[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2001, 13(1):51-55Zhang Lingyi, Zhuang Jiejia, Zhao Kui, et al. Fourth-generation light source[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2001, 13(1): 51-55 [3] Hettel R. DLSR design and plans: an international overview[J]. Journal of Synchrotron Radiation, 2014, 21(5): 843-855. doi: 10.1107/S1600577514011515 [4] 殷立新. 光源加速器机械工程设计与实施[R]. 上海: 上海光源, 2008Yin Lixin. Mechanical engineering design and implementation of SSR[R]. 2008 [5] Jiao Yi, Xu Gang, Cui Xiaohao, et al. The HEPS project[J]. Journal of Synchrotron Radiation, 2018, 25(Pt 6): 1611-1618. [6] Cianciosi F, Brochard T, Marion P, et al. The girder system for the new ESRF storage ring[C]//Proceedings of MEDSI 2016. 2016: 147-151. [7] Martensson N, Eriksson M. The saga of MAX IV, the first multi-bend achromat synchrotron light source[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 2018, 907: 97-104. [8] 王梓豪. HEPS-TF磁铁支架稳定性研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学, 2019: 16-18Wang Zihao. Study on the stability of HEPS-TF magnet girder[D]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2019: 16-18 [9] 何兴, 申雨, 马俊达, 等. 超高层建筑的巨型异形钢柱柱底灌浆施工技术[J]. 建筑施工, 2017, 39(1):40-41 doi: 10.14144/j.cnki.jzsg.2017.01.014He Xing, Shen Yu, Ma Junda, et al. Construction technology of column bottom grouting for huge special-shaped steel column of super tall building[J]. Building Construction, 2017, 39(1): 40-41 doi: 10.14144/j.cnki.jzsg.2017.01.014 [10] 杜开福. 用高强无收缩灌浆料替代型钢柱底二次砼浇灌施工应用[J]. 建筑工程技术与设计, 2017(19):1755-1756Du Kaifu. Construction of two times concrete pouring with high-strength non-shrinkage grouting instead of steel column bottom[J]. Architecture Engineering Technology and Design, 2017(19): 1755-1756 [11] 李春华, 王梓豪, 周宁闯, 等. 先进光源磁铁支撑基座稳定性的实验研究[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2021, 33:034003 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202133.200201Li Chunhua, Wang Zihao, Zhou Ningchuang, et al. Experimental study on magnet support plinths of advanced light source[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2021, 33: 034003 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202133.200201 [12] 苗玉刚, 赵峰, 何斌. 基于SolidWorks Simulation的工装压板有限元分析及优化设计[J]. 煤矿机械, 2015, 36(11):192-194Miao Yugang, Zhao Feng, He Bin. Finite element analysis and optimization design of tooling plate based on SolidWorks simulation[J]. Coal Mine Machinery, 2015, 36(11): 192-194 [13] DS SolidWorks公司, 陈超祥, 胡其登. SolidWorks® Simulation高级教程[M]. 杭州新迪数字工程系统有限公司, 译. 5版. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 2018: 160-174DS SolidWorks, Chen Chaoxiang, Hu Qideng. SolidWorks professional[M]. Hangzhou Xindi Digital Engineering System Co. , Ltd, trans. 5th ed. Beijing: China Machine Press, 2018: 160-174 [14] 张海艇, 何晓业, 王巍, 等. 基于合肥先进光源的准直参考网络机械系统设计及其仿真分析[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2020, 32:084003 doi: 基于合肥先进光源的准直参考网络机械系统设计及其仿真分析Zhang Haiting, He Xiaoye, Wang Wei, et al. Design and simulation analysis of mechanical system of reference network for alignment based on Hefei Advanced Lightsource Facility[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2020, 32: 084003 doi: 基于合肥先进光源的准直参考网络机械系统设计及其仿真分析 [15] Jankovics D, Gohari H, Tayefeh M, et al. Developing topology optimization with additive manufacturing constraints in ANSYS®[J]. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 2018, 51(11): 1359-1364. doi: 10.1016/j.ifacol.2018.08.340 -





 下载:
下载: