Numerical simulation on spacecraft chargingdue to electron beam emission
-
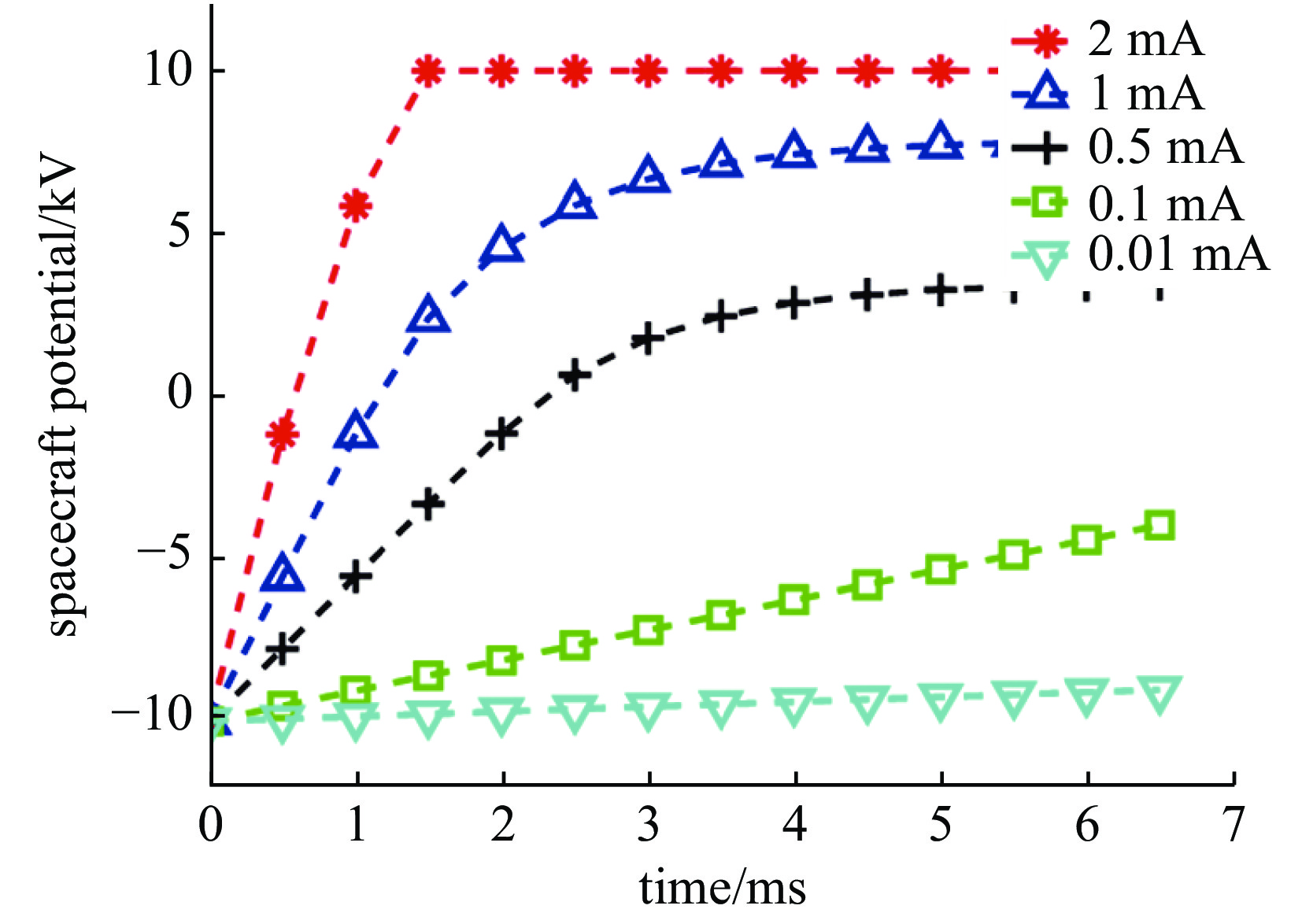
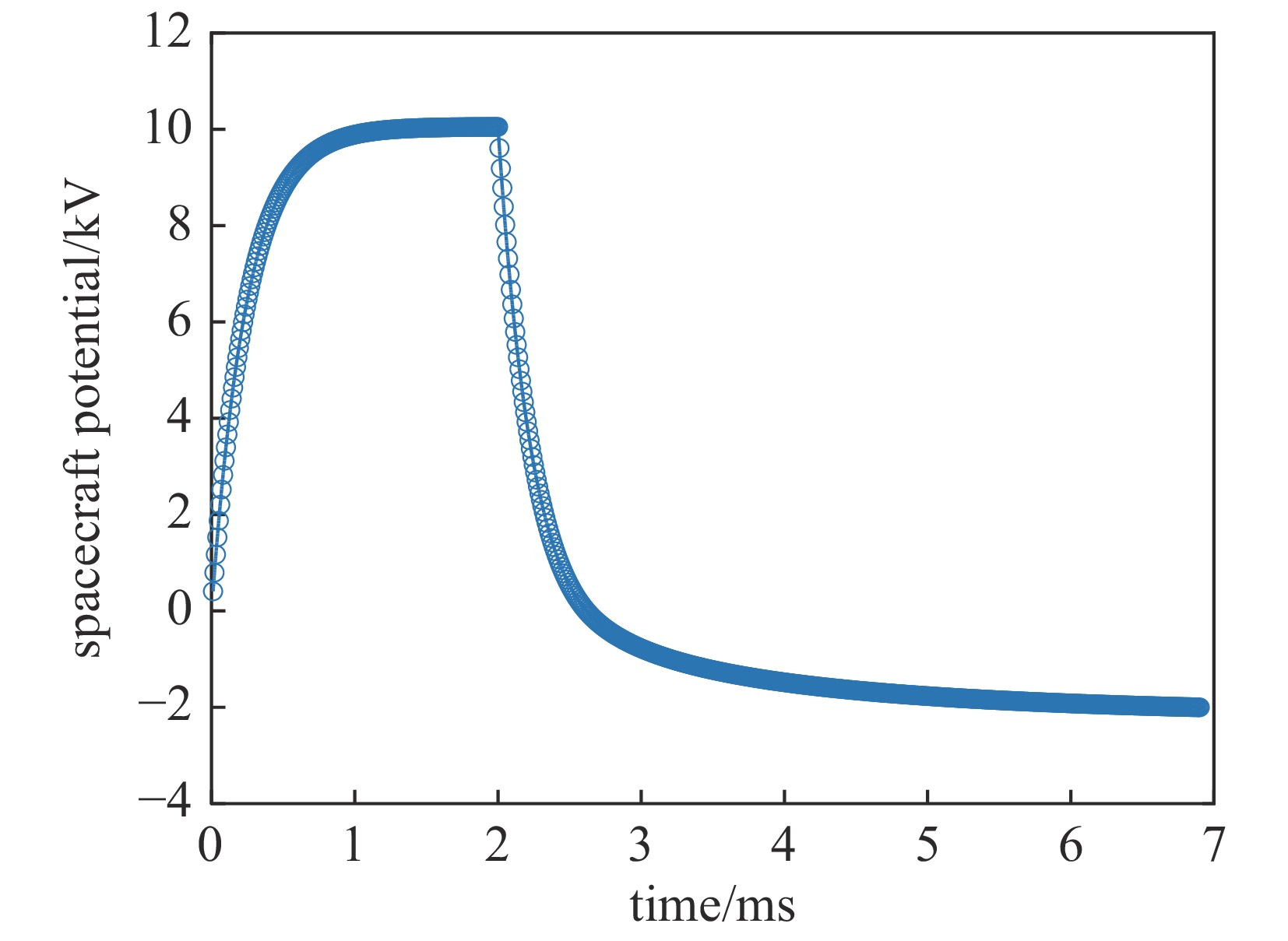
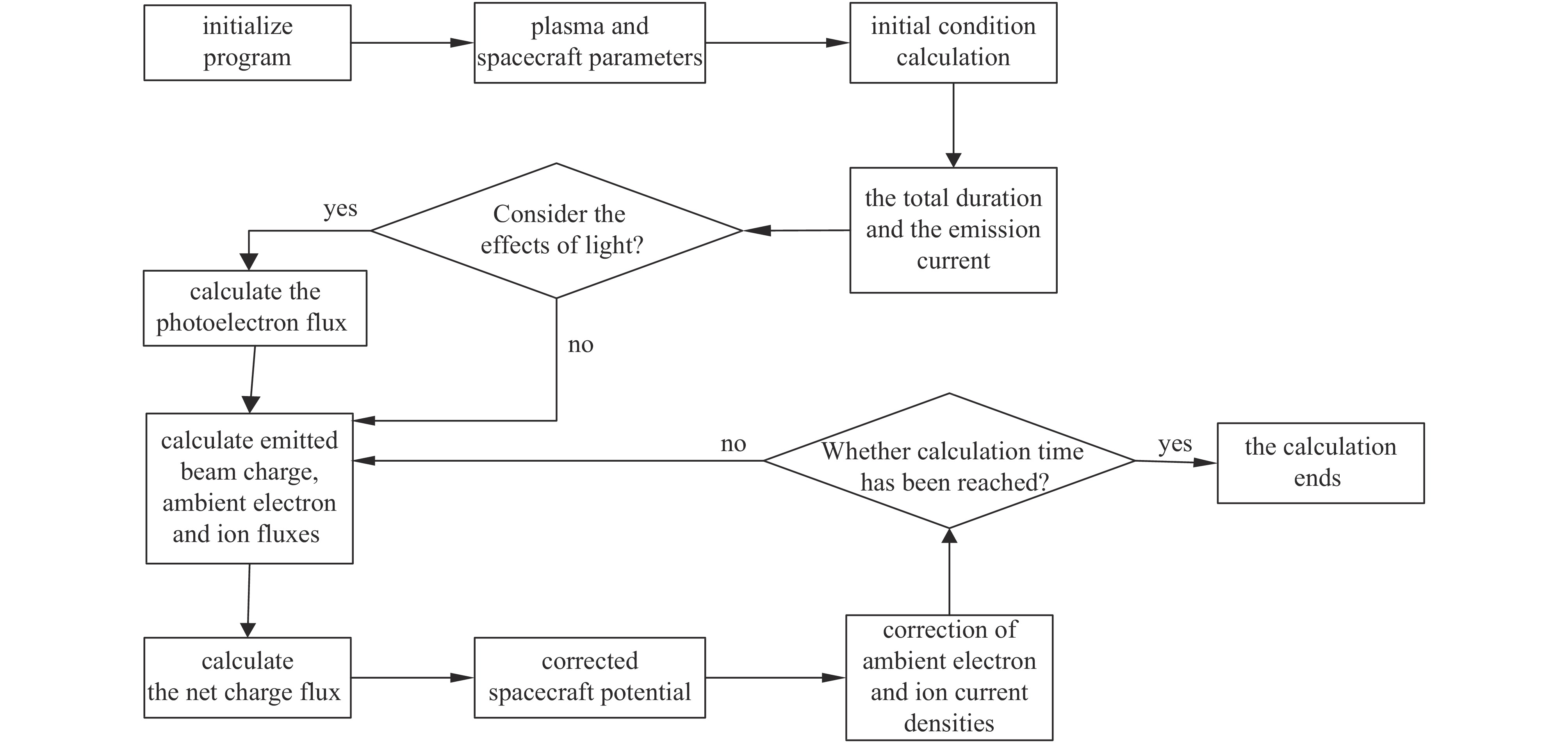
摘要: 通过发射电子束测量空间地磁场是一种新的有效的地磁场高精度测量方法,但电子束发射对在轨航天器自身状态和安全存在影响。为了研究这一影响,从同步轨道充电机制出发,基于轨道限制机制和朗缪尔方程研究了航天器发射高能电子束时的诱发充电模型,推导了不同初始电位情况下束流发射的平衡电位公式,并编制程序研究了这一过程中粒子束电流、能量、光照等因素对航天器充电电位的影响,得到了航天器对外发射高能电子束时诱发航天器自身或平台的充电电位随时间变化规律,并通过部分解析解对比验证了模拟结果的正确性。Abstract: Measuring the geomagnetic field in space by emitting electron beams is a new and effective high-precision measurement method of the geomagnetic field, but the emission of electron beams has an impact on the state and safety of the spacecraft. To study the influence, based on the orbit-limited mechanism, the model of spacecraft charging due to high-energy electron beam emission was studied, and the potential balance formula under different initial potentials was derived , and a program was compiled to study the impact of particle beam current, energy, light electron and other factors affecting the spacecraft charging potential. The time-varying law of the charging potential induced by the spacecraft itself or the platform when the spacecraft emits high-energy electron beams is obtained, and the correctness of the simulation results is verified by the partial analytical solution comparison.
-
表 1 半径为1 m球形航天器的环境粒子流随电位变化表 (假定环境离子为质子)
Table 1. Environmental particle flow of a spherical spacecraft with a radius of 1m vs spacecraft potential (assuming that the ion is proton)
spacecraft
potential/kVenvironmental electron
current density/(A·m−2)environmental
electron current/µAenvironmental ion
current density/(A·m−2)environmental
ion current/µA− 1000 ~0 0 $ {\text{2}}{\text{.1}} \times {\text{1}}{{\text{0}}^{ - 4}} $ 670.00 −100 ~0 0 $ {\text{2}}{\text{.1}} \times {\text{1}}{{\text{0}}^{ - {\text{5}}}} $ 67.60 −10 $ {\text{7}}{\text{.2}} \times {\text{1}}{{\text{0}}^{ - {\text{11}}}} $ 0 $ {\text{2}}{\text{.3}} \times {\text{1}}{{\text{0}}^{ - {\text{6}}}} $ 7.30 −1 $ {\text{2}}{\text{.5}} \times {\text{1}}{{\text{0}}^{ - {\text{6}}}} $ 31 $ {\text{4}}{\text{.0}} \times {\text{1}}{{\text{0}}^{ - {\text{7}}}} $ 1.20 0 $ {\text{7}}{\text{.9}} \times {\text{1}}{{\text{0}}^{ - {\text{6}}}} $ 100 $ {\text{1}}{\text{.8}} \times {\text{1}}{{\text{0}}^{ - {\text{7}}}} $ 0.58 1 $ {\text{1}}{\text{.7}} \times {\text{1}}{{\text{0}}^{ - {\text{5}}}} $ 210 $ {\text{5}}{\text{.8}} \times {\text{1}}{{\text{0}}^{ - {\text{8}}}} $ 0.18 10 $ {\text{1}}{\text{.0}} \times {\text{1}}{{\text{0}}^{ - {\text{4}}}} $ 1200 $ {\text{1}}{\text{.7}} \times {\text{1}}{{\text{0}}^{ - {\text{12}}}} $ ~0 100 $ {\text{9}}{\text{.2}} \times {\text{1}}{{\text{0}}^{ - {\text{4}}}} $ 1160 ~0 ~0 1000 $ {\text{9}}{\text{.1}} \times {\text{1}}{{\text{0}}^{ - {\text{3}}}} $ 11000 ~0 ~0 -
[1] 刘慧, 刘战捷. 空间无损检测技术评述[J]. 航天器环境工程, 2015, 32(1):108-113 doi: 10.12126/see.2015.01.021Liu Hui, Liu Zhanjie. Review of nondestructive evaluation in space[J]. Spacecraft Environment Engineering, 2015, 32(1): 108-113 doi: 10.12126/see.2015.01.021 [2] 马淑英, 颜伟男, 黄莹, 等. 空间环境CT探测技术-环电流ENA成像及其CT反演的模拟研究[C]//中国空间科学学会空间探测专业委员会第二十二次学术会议论文集. 2009Ma Shuying, Yan Weinan, Huang Ying, et al. CT detection technology in space environment-simulation research of ring current ENA imaging and CT inversion[C]// Proceedings of the 22nd National Symposium on Space Exploration Dalian. 2009 [3] Robb R A, Hoffman E A, Sinak L J, et al. High-speed three-dimensional X-ray computed tomography: the dynamic spatial reconstructor[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1983, 71(3): 308-319. doi: 10.1109/PROC.1983.12589 [4] Tan Chengjun, Tang Chuanxiang, Huang Wenhui, et al. Beam and image experiment of beam deflection electron gun for distributed X-ray sources[J]. Nuclear Science and Techniques, 2019, 30: 50. doi: 10.1007/s41365-019-0561-y [5] Powis A T, Porazik P, Greklek-Mckeon M, et al. Evolution of a relativistic electron beam for tracing magnetospheric field lines[J]. Frontiers in Astronomy and Space Sciences, 2019, 6: 69. doi: 10.3389/fspas.2019.00069 [6] Sanchez E R, Powis A T, Kaganovich I D, et al. Relativistic particle beams as a resource to solve outstanding problems in space physics[J]. Frontiers in Astronomy and Space Sciences, 2019, 6: 71. doi: 10.3389/fspas.2019.00071 [7] Xue Bixi, Hao Jianhong, Zhao Qiang, et al. Influence of geomagnetic field on the long-range propagation of relativistic electron beam in the atmosphere[J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2020, 48(11): 3871-3876. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2020.3026088 [8] 郝建红, 王希, 张芳, 等. 随移动窗推进的带电粒子束团长程传输模拟分析[J]. 国防科技大学学报, 2021, 43(5):168-174 doi: 10.11887/j.cn.202105020Hao Jianhong, Wang Xi, Zhang Fang, et al. Simulation analysis of long-range propagation of charged particle beams propelled by moving window[J]. Journal of National University of Defense Technology, 2021, 43(5): 168-174 doi: 10.11887/j.cn.202105020 [9] 周昊澄, 张天平. LEO大型载人航天器主动电位控制技术进展[J]. 真空与低温, 2014, 20(4):243-247 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7086.2014.04.011Zhou Haocheng, Zhang Tianping. Active LEO large scale manned spacecraft potential control evolve[J]. Vacuum & Cryogenics, 2014, 20(4): 243-247 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7086.2014.04.011 [10] 毛根旺, 唐金兰. 航天器推进系统及其应用[M]. 西安: 西北工业大学出版社, 2009Mao Genwang, Tang Jinlan. Propulsion system of spacecraft and its application[M]. Xi’an: Northwestern Polytechnical University Press, 2009 [11] 夏广庆, 王冬雪, 薛伟华, 等. 螺旋波等离子体推进研究进展[J]. 推进技术, 2011, 32(6):857-863 doi: 10.13675/j.cnki.tjjs.2011.06.022Xia Guangqing, Wang Dongxue, Xue Weihua, et al. Progress on the research of helicon plasma thruster[J]. Journal of Propulsion Technology, 2011, 32(6): 857-863 doi: 10.13675/j.cnki.tjjs.2011.06.022 [12] Lai S T. An improved Langmuir probe formula for modeling satellite interactions with near-geostationary environment[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Space Physics, 1994, 99(A1): 459-467. doi: 10.1029/93JA02728 [13] Lai S T. Fundamentals of spacecraft charging: spacecraft interactions with space plasmas[M]. Princeton: Princeton University Press, 2012. [14] Lai S T. A critical overview on spacecraft charging mitigation methods[J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2003, 31(6): 1118-1124. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2003.820969 [15] Lai S T. Some novel ideas of spacecraft charging mitigation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2012, 40(2): 402-409. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2011.2176755 [16] Pisacane V L. The space environment and its effects on space systems[M]. Reston: American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2008. [17] Lai S T, Cahoy K. Trapped photoelectrons during spacecraft charging in sunlight[J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2015, 43(9): 2856-2860. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2015.2453370 [18] Lai S T. Importance of surface conditions for spacecraft charging[J]. Journal of Spacecraft and Rockets, 2010, 47(4): 634-638. doi: 10.2514/1.48824 [19] Reeves G D, Delzanno G L, Fernandes P A, et al. The beam plasma interactions experiment: an active experiment using pulsed electron beams[J]. Frontiers in Astronomy and Space Sciences, 2020, 7: 23. doi: 10.3389/fspas.2020.00023 [20] Neubert T, Gilchrist B E. Particle simulations of relativistic electron beam injection from spacecraft[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2002, 107: 1167. [21] Neubert T, Gilchrist B E. 3D electromagnetic PIC simulations of relativistic electron pulse injections from spacecraft[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2002, 29(9): 1385-1390. doi: 10.1016/S0273-1177(02)00185-0 [22] Neubert T, Gilchrist B E. Relativistic electron beam injection from spacecraft: performance and applications[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2004, 34(11): 2409-2412. doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2003.08.081 [23] Hoshi K, Muranaka T, Kojima H, et al. Numerical analysis of active spacecraft charging in the geostationary environment[J]. Journal of Spacecraft and Rockets, 2016, 53(4): 589-598. doi: 10.2514/1.A33270 [24] 刘继奎, 张可墨, 柳青, 等. 航天器大功率传输介质深层充放电试验研究[J]. 高电压技术, 2018, 44(3):864-869 doi: 10.13336/j.1003-6520.hve.20180301025Liu Jikui, Zhang Kemo, Liu Qing, et al. Internal charging and discharging tests of large power transfer dielectric on spacecraft[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2018, 44(3): 864-869 doi: 10.13336/j.1003-6520.hve.20180301025 [25] Wang Song, Wu Zhancheng, Tang Xiaojin, et al. A new charging model for spacecraft exposed dielectric (SICCE)[J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2016, 44(3): 289-295. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2016.2521867 [26] 郑汉生. 典型结构的深层充放电规律及放电干扰影响研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学, 2017Zheng Hansheng. Research on internal charging discharging of typical structures and discharging interference[D]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2017 [27] 刘尚合, 胡小锋, 原青云, 等. 航天器充放电效应与防护研究进展[J]. 高电压技术, 2019, 45(7):2108-2118 doi: 10.13336/j.1003-6520.hve.20190628007Liu Shanghe, Hu Xiaofeng, Yuan Qingyun, et al. Research progress in charging-discharging effects and protection of spacecraft[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2019, 45(7): 2108-2118 doi: 10.13336/j.1003-6520.hve.20190628007 -




 下载:
下载: