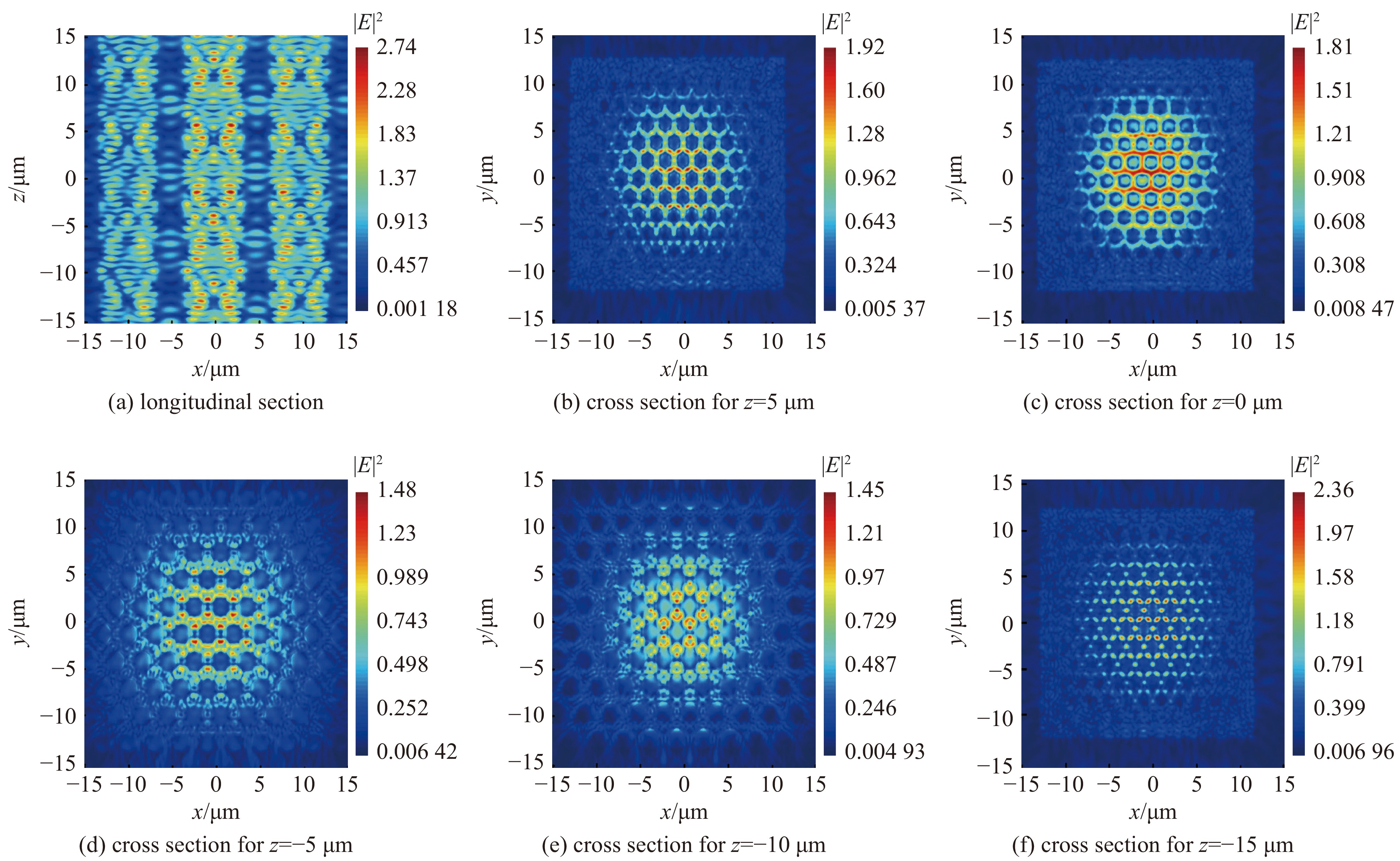
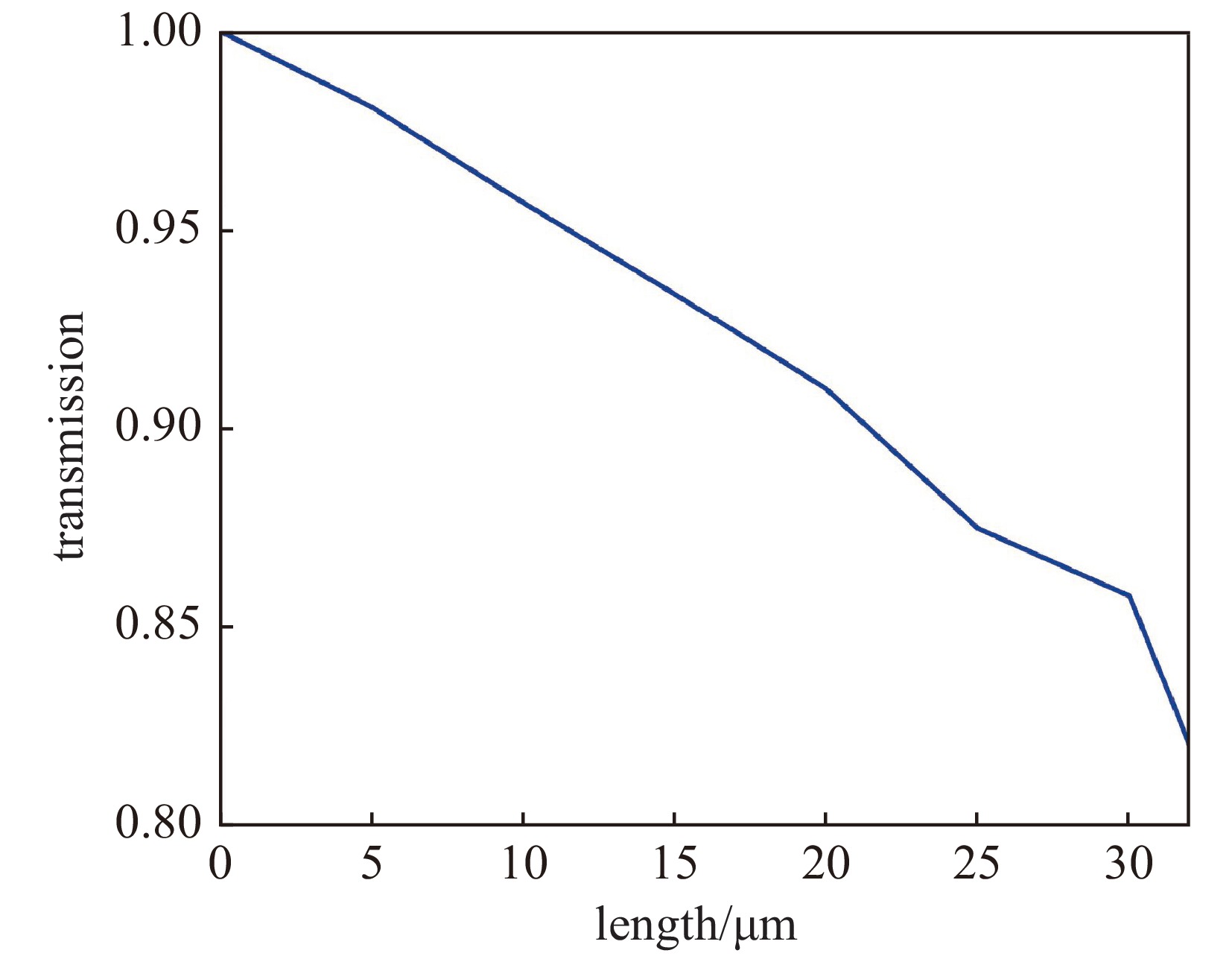
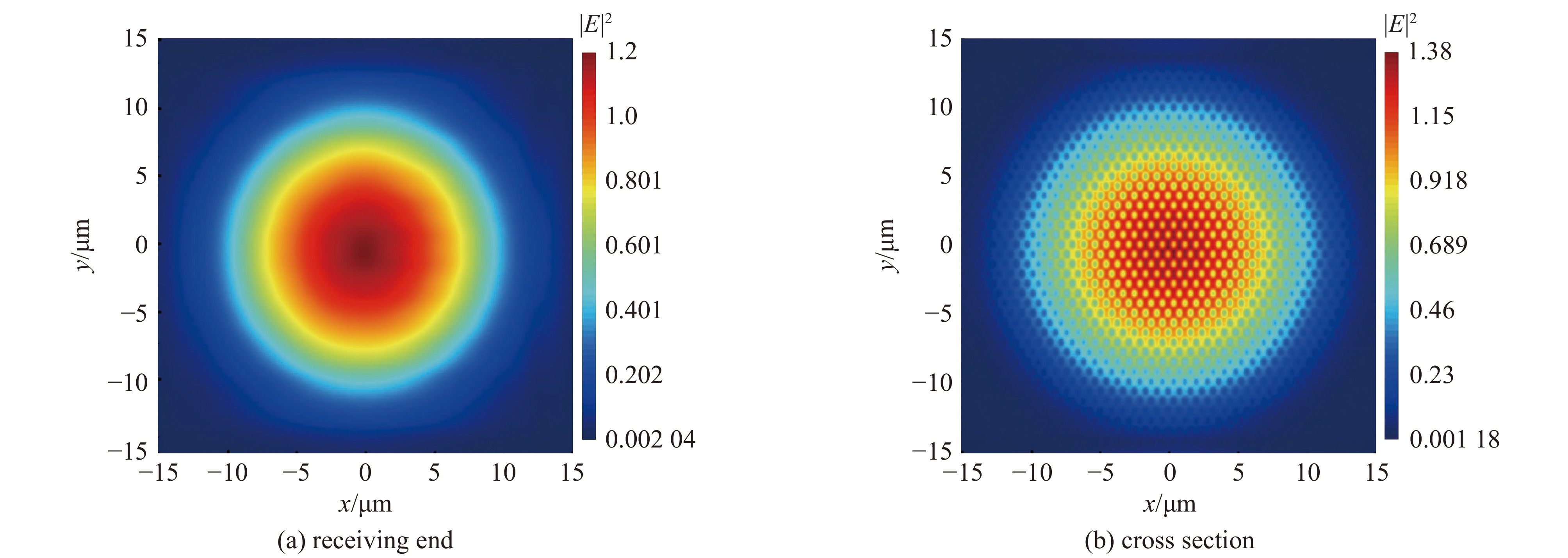
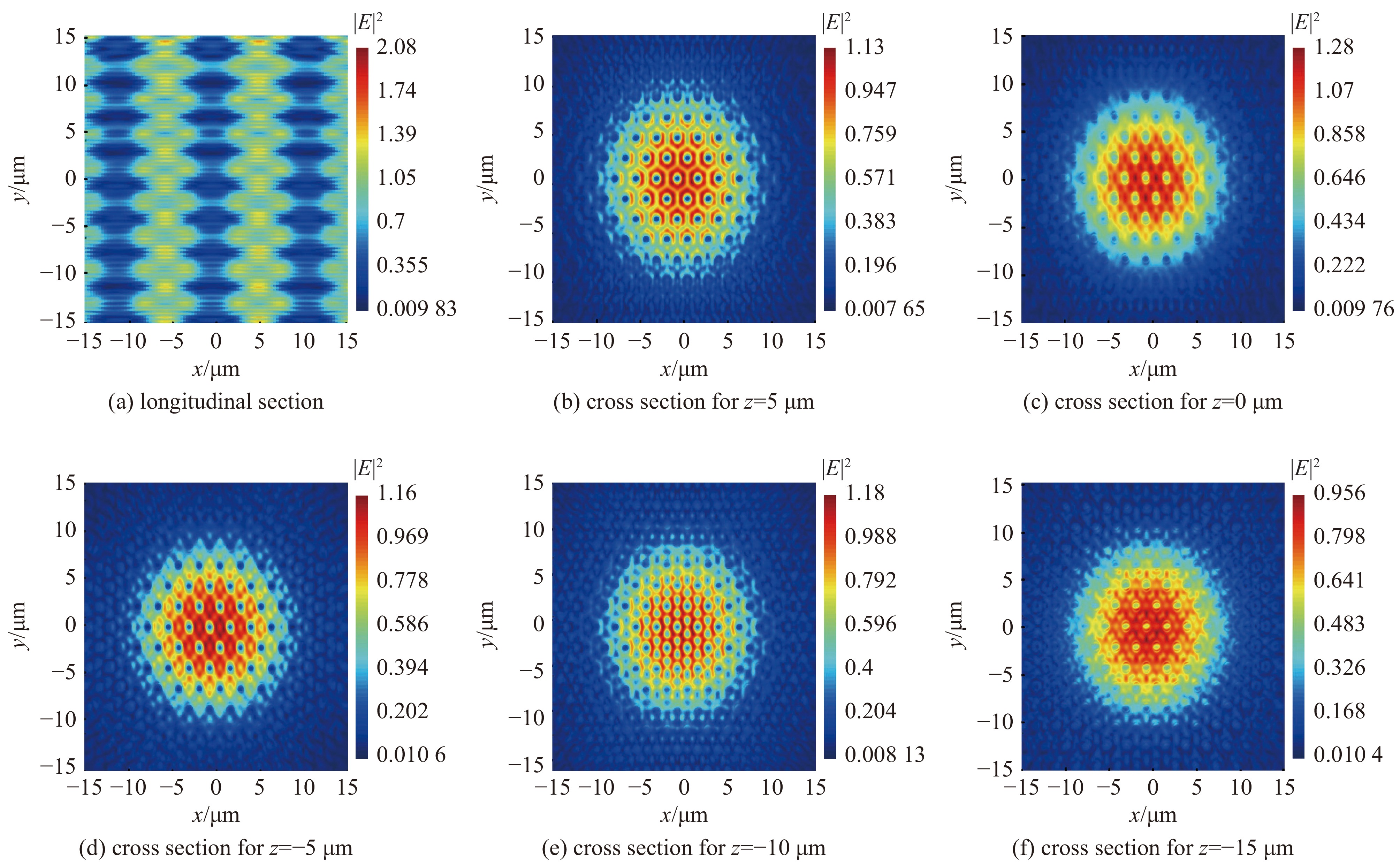
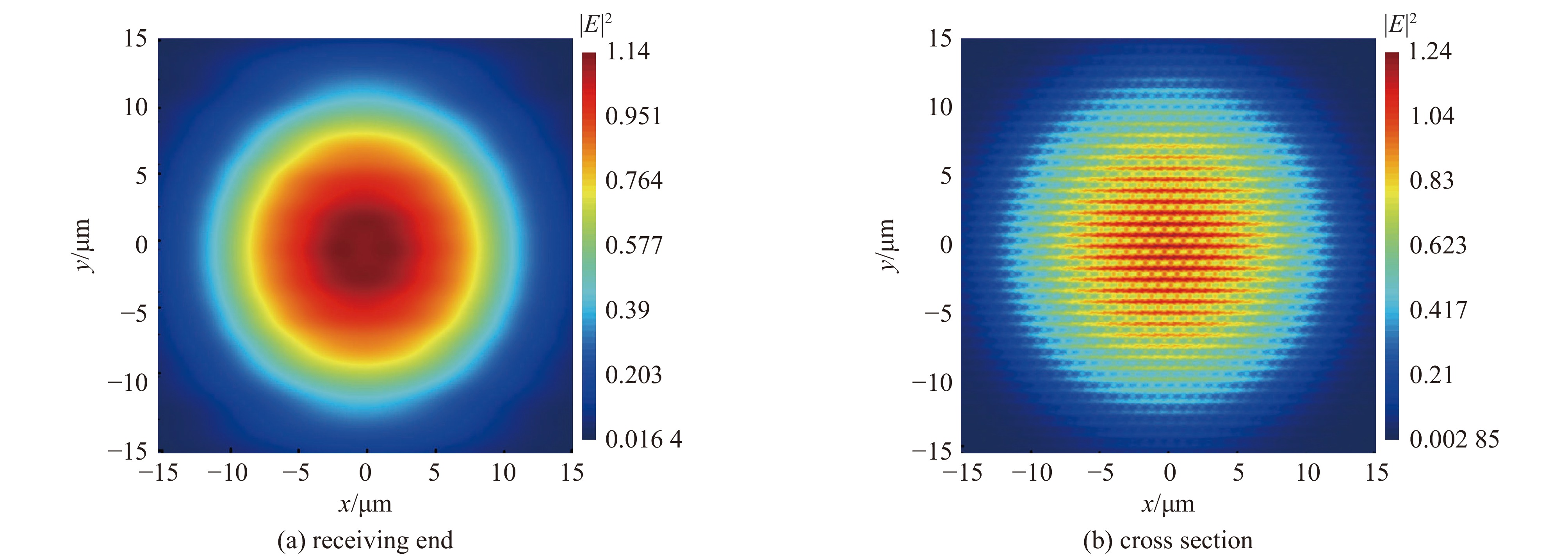
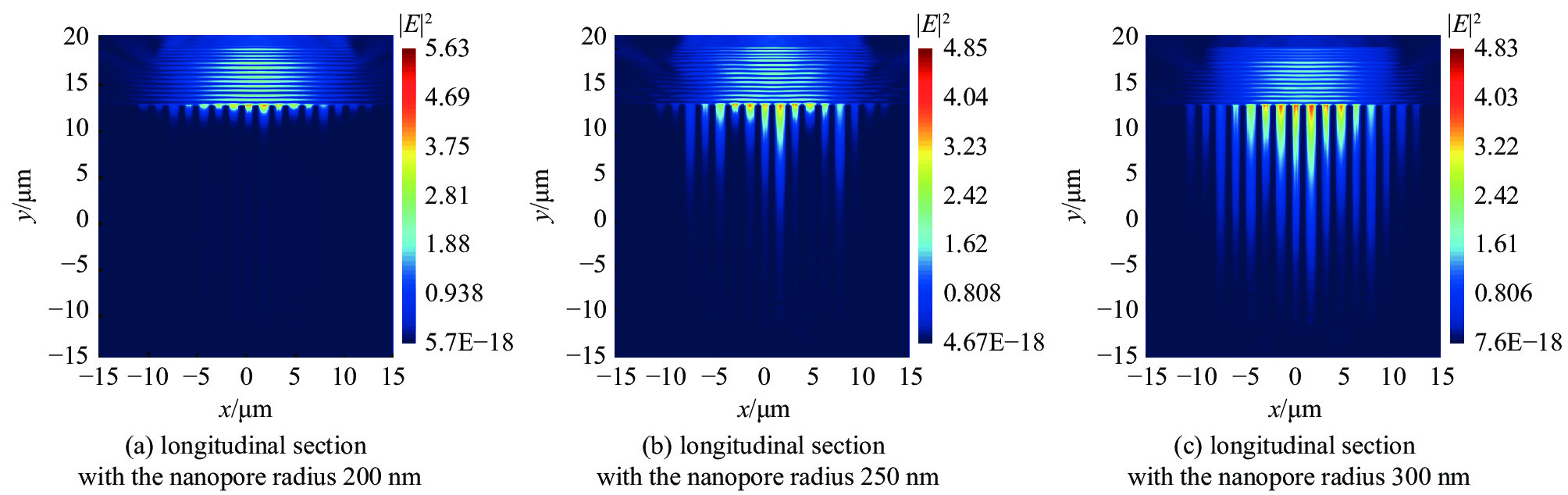
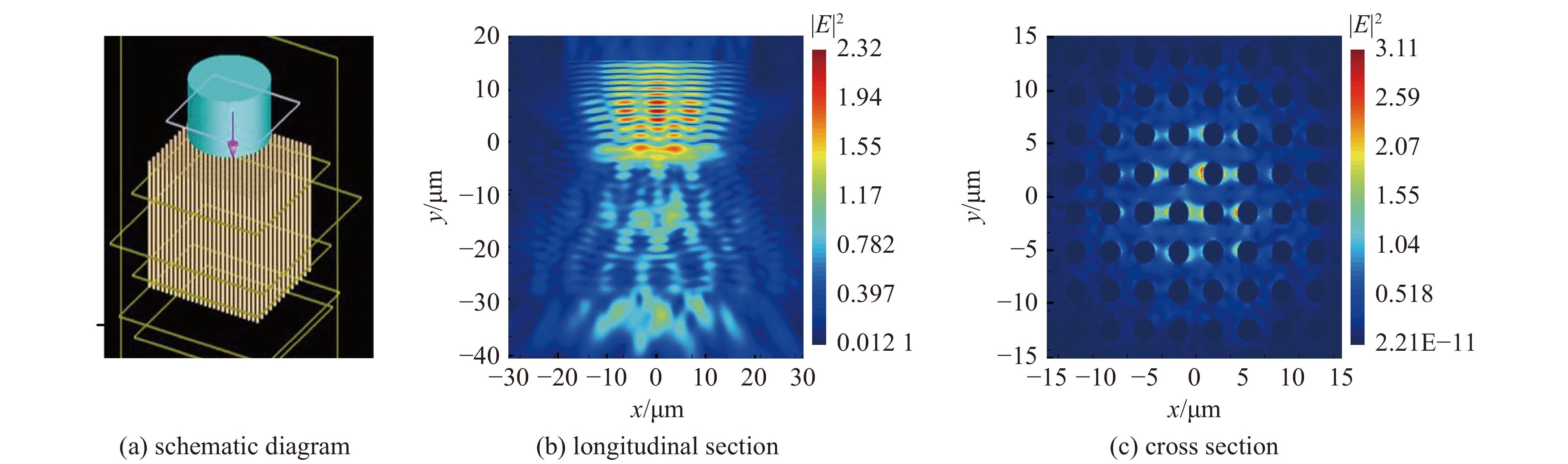
| [1] |
Tabak M, Hammer J, Glinsky M E, et al. Ignition and high gain with ultrapowerful lasers[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 1994, 1(5): 1626-1634. doi: 10.1063/1.870664
|
| [2] |
邓建军, 王勐, 谢卫平, 等. 面向Z箍缩驱动聚变能源需求的超高功率重复频率驱动器技术[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2014, 26:100201 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20142610.100201Deng Jianjun, Wang Meng, Xie Weiping, et al. Super-power repetitive Z-pinch driver for fusion-fission reactor[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2014, 26: 100201 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20142610.100201
|
| [3] |
丁永坤, 江少恩, 刘慎业, 等. 激光聚变研究中心聚变靶物理实验和诊断技术研究进展[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2013, 25(12):3077-3081 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20132512.3077Ding Yongkun, Jiang Shaoen, Liu Shenye, et al. Recent progress on physical experiment and target diagnostics in research center of laser fusion[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2013, 25(12): 3077-3081 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20132512.3077
|
| [4] |
Patel P K, Mackinnon A J, Key M H, et al. Isochoric heating of solid-density matter with an ultrafast proton beam[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2003, 91: 125004. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.91.125004
|
| [5] |
Hu H Y, Müller C, Keitel C H. Complete QED theory of multiphoton trident pair production in strong laser fields[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2010, 105: 080401. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.105.080401
|
| [6] |
Li Boyuan, Zhang Zhimeng, Wang Jian, et al. Transport of fast electrons in a nanowire array with collisional effects included[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2015, 22: 123118. doi: 10.1063/1.4938515
|
| [7] |
Yang Yue, Li Boyuan, Wu Yuchi, et al. Manipulation and optimization of electron transport by nanopore array targets[J]. Plasma Science and Technology, 2021, 23: 15001. doi: 10.1088/2058-6272/abbd37
|
| [8] |
Jiang S, Krygier A G, Schumacher D W, et al. Effects of front-surface target structures on properties of relativistic laser-plasma electrons[J]. Physical Review E, 2014, 89: 013106. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.89.013106
|
| [9] |
Snyder J, Ji Liangliang, George K M, et al. Relativistic laser driven electron accelerator using micro-channel plasma targets[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2019, 26: 033110. doi: 10.1063/1.5087409
|
| [10] |
Kong Defeng, Zhang Guoqiang, Shou Yinren, et al. High-energy-density plasma in femtosecond-laser-irradiated nanowire-array targets for nuclear reactions[J]. Matter and Radiation at Extremes, 2022, 7: 064403. doi: 10.1063/5.0120845
|
| [11] |
Shou Yinren, Kong Defeng, Wang Pengjie, et al. High-efficiency water-window X-ray generation from nanowire array targets irradiated with femtosecond laser pulses[J]. Optics Express, 2021, 29(4): 5427-5436. doi: 10.1364/OE.417512
|
| [12] |
Demaria A J, Stetser D A, Heynau H. Self mode-locking of lasers with saturable absorbers[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 1966, 8(7): 174-176. doi: 10.1063/1.1754541
|
| [13] |
Poyé A, Hulin S, Bailly-Grandvaux M, et al. Physics of giant electromagnetic pulse generation in short-pulse laser experiments[J]. Physical Review E, 2015, 91: 043106. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.91.043106
|
| [14] |
De Marco M, Cikhardt J, Krása J, et al. Electromagnetic pulses produced by expanding laser produced Au plasma[J]. Nukleonika, 2015, 60(2): 239-243. doi: 10.1515/nuka-2015-0043
|
| [15] |
Mead M J, Neely D, Gauoin J, et al. Electromagnetic pulse generation within a petawatt laser target chamber[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2004, 75(10): 4225-4227. doi: 10.1063/1.1787606
|
| [16] |
Xu Zhiqian, Meng Cui. Numerical simulation of EMP environment radiated by X-rays inside a high-power laser facility[C]//2018 International Applied Computational Electromagnetics Society Symposium (ACES). 2018: 1-2.
|
| [17] |
Yee K. Numerical solution of initial boundary value problems involving Maxwell’s equations in isotropic media[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1966, 14(3): 302-307. doi: 10.1109/TAP.1966.1138693
|




 下载:
下载: