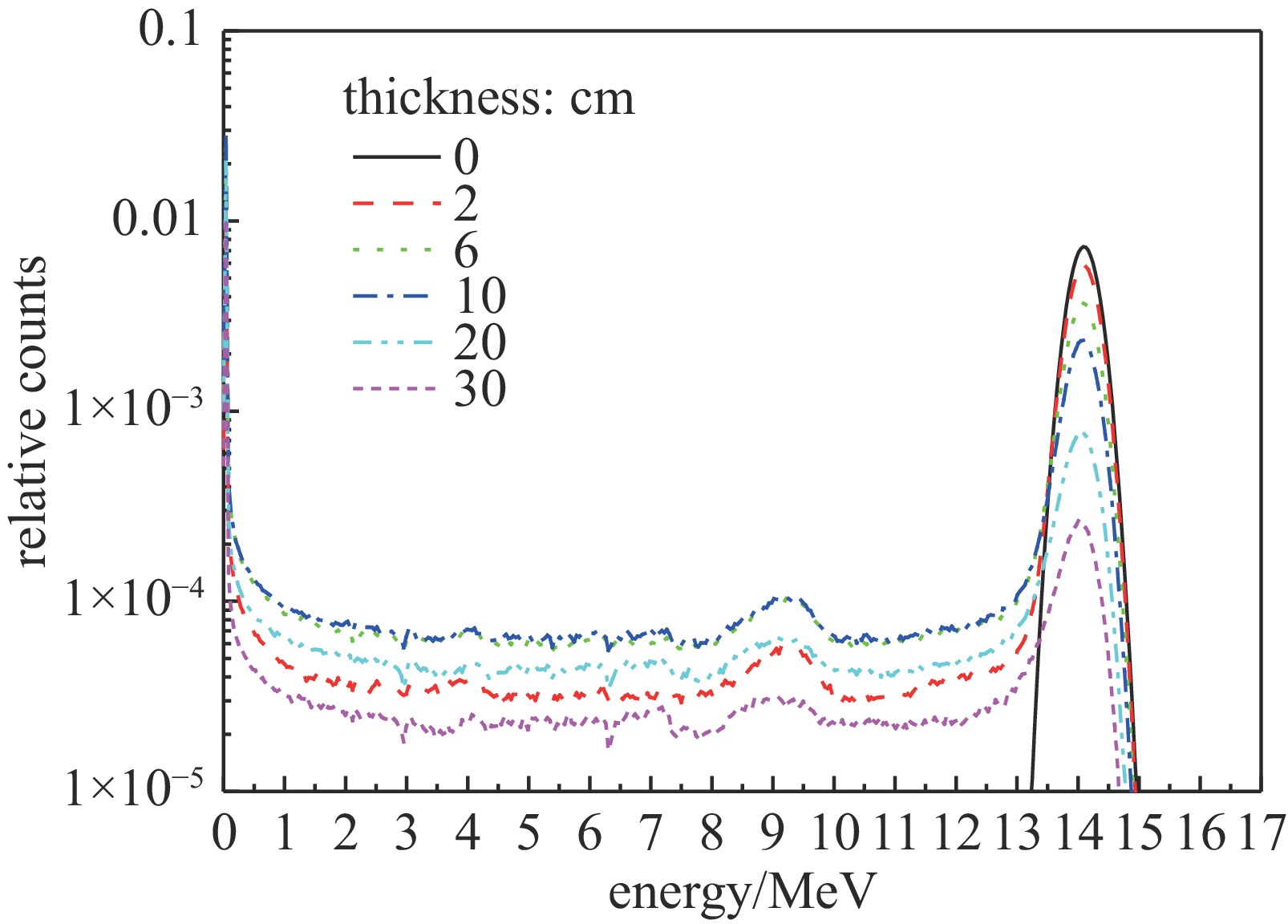
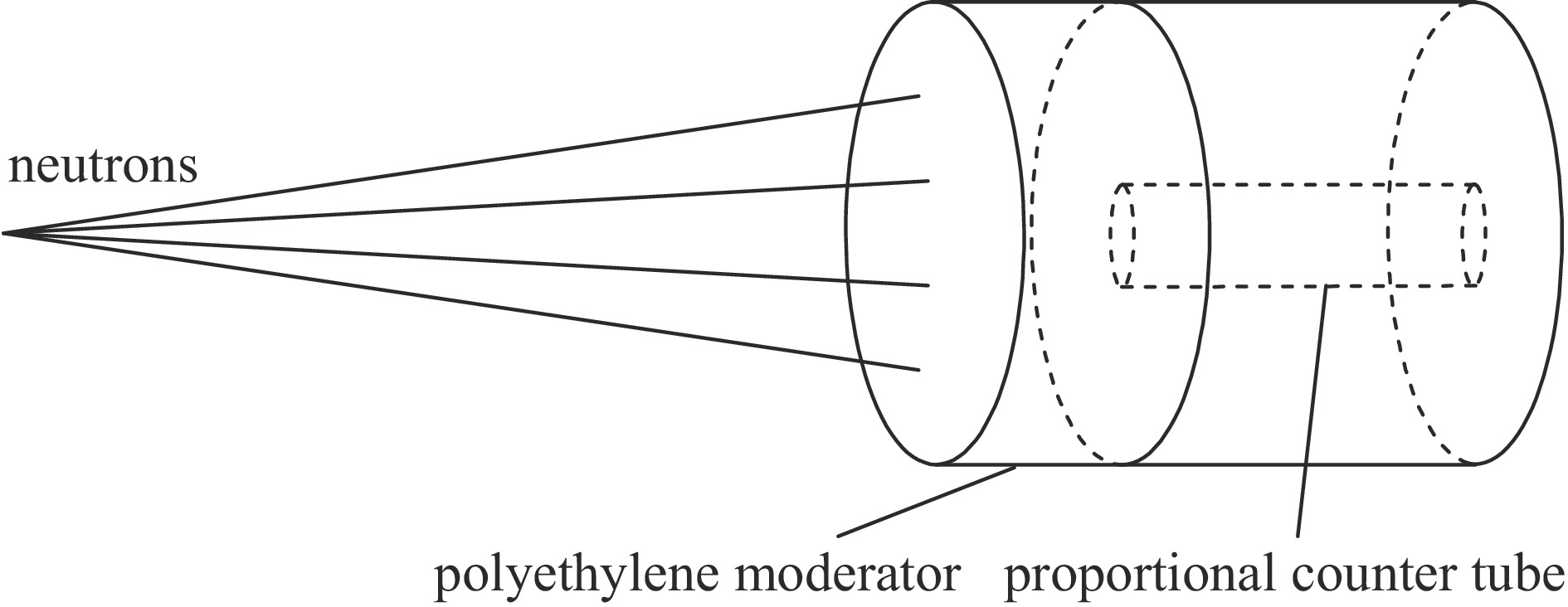
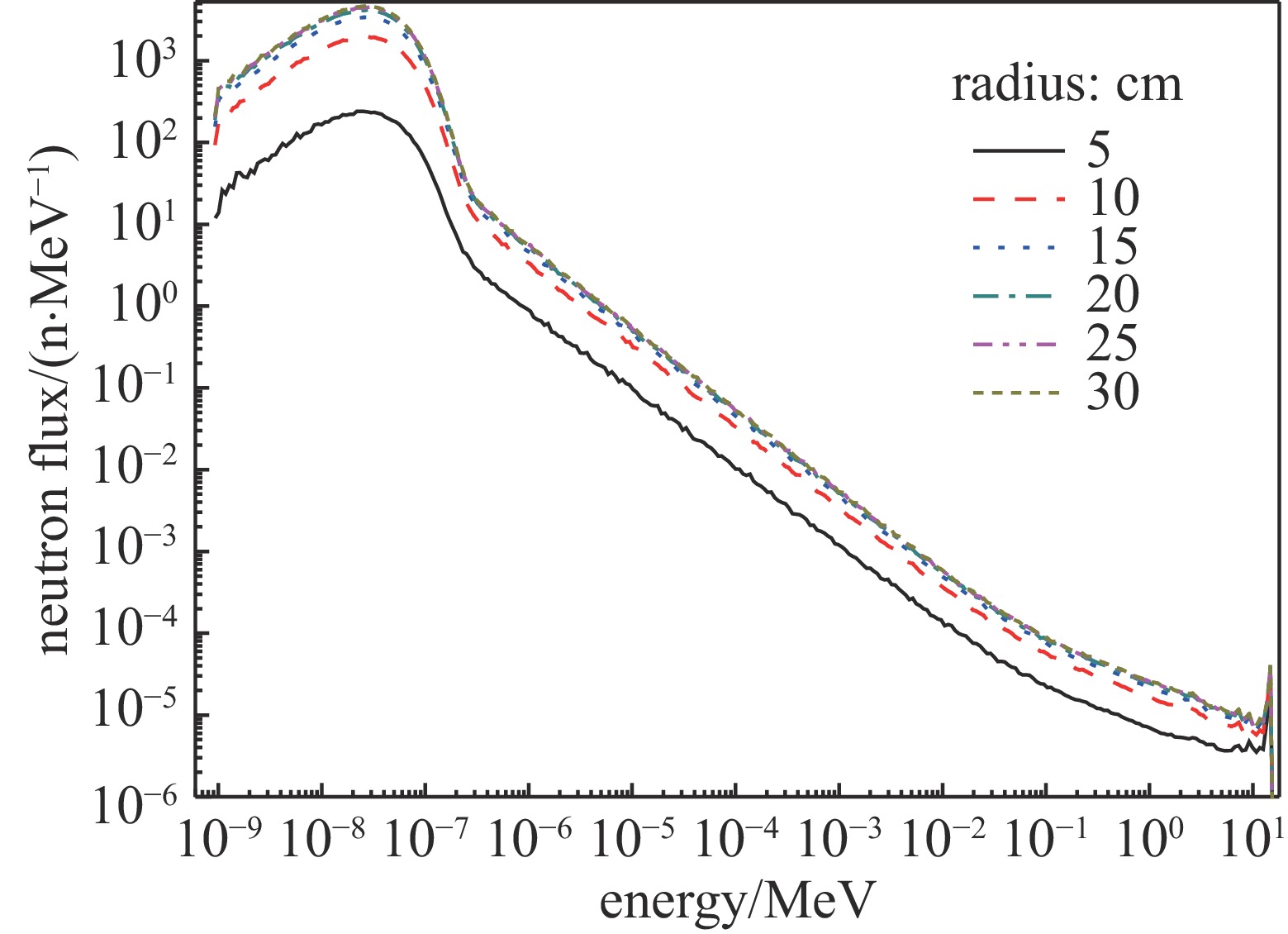
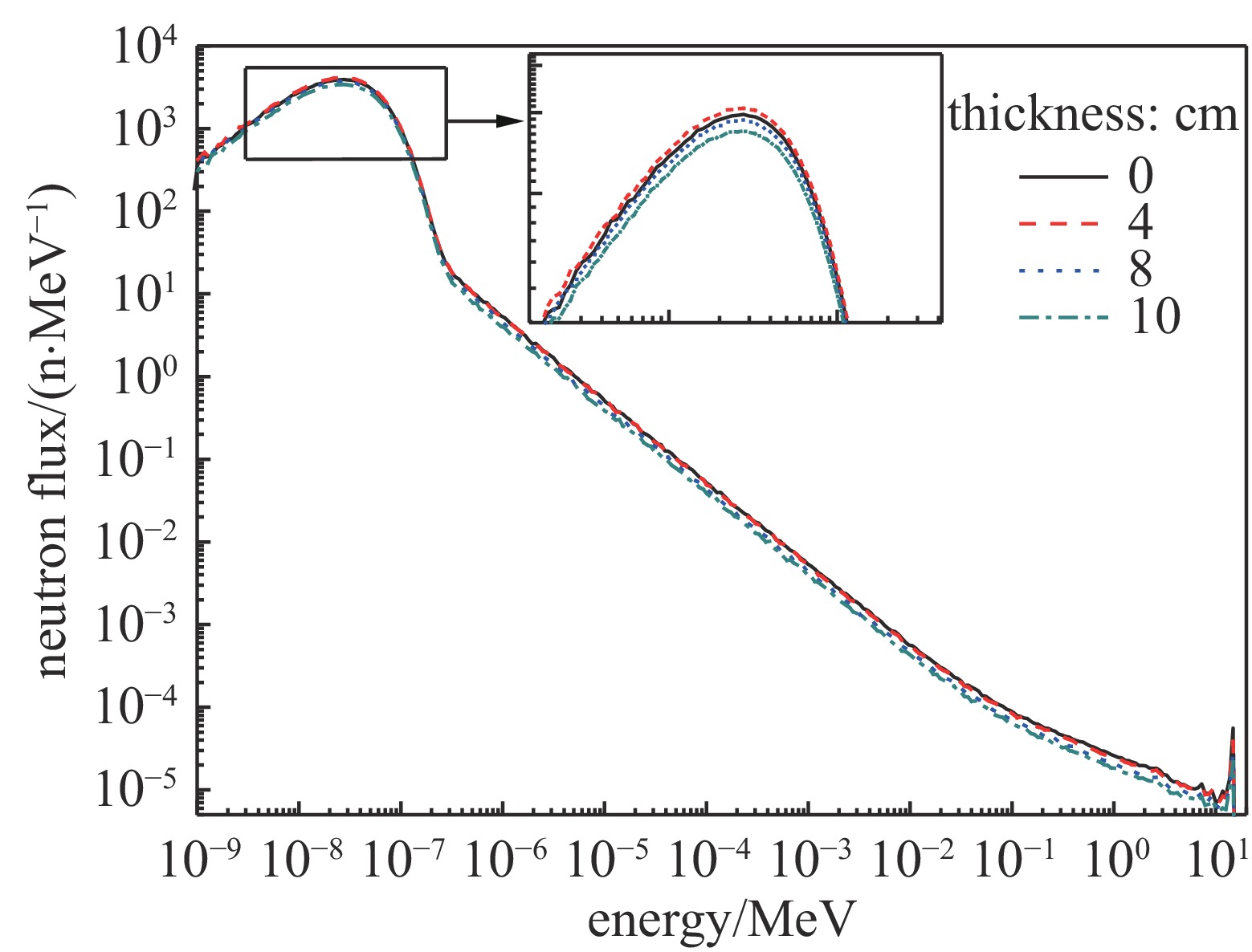
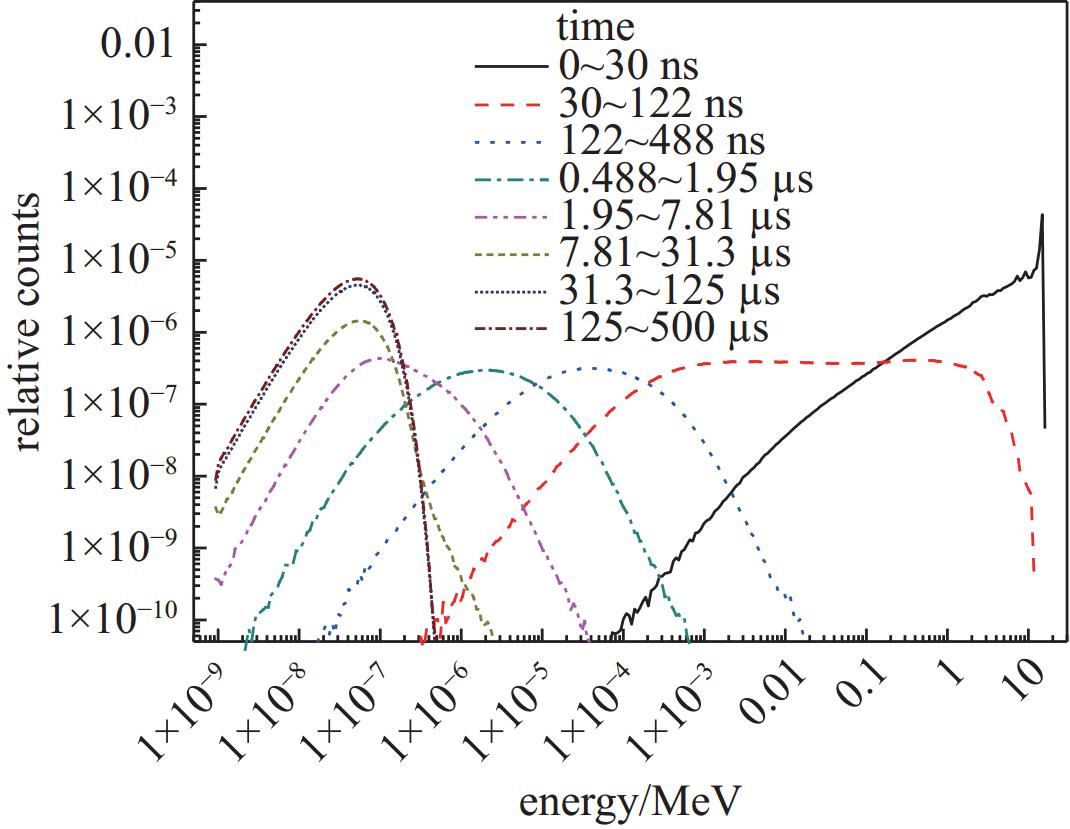
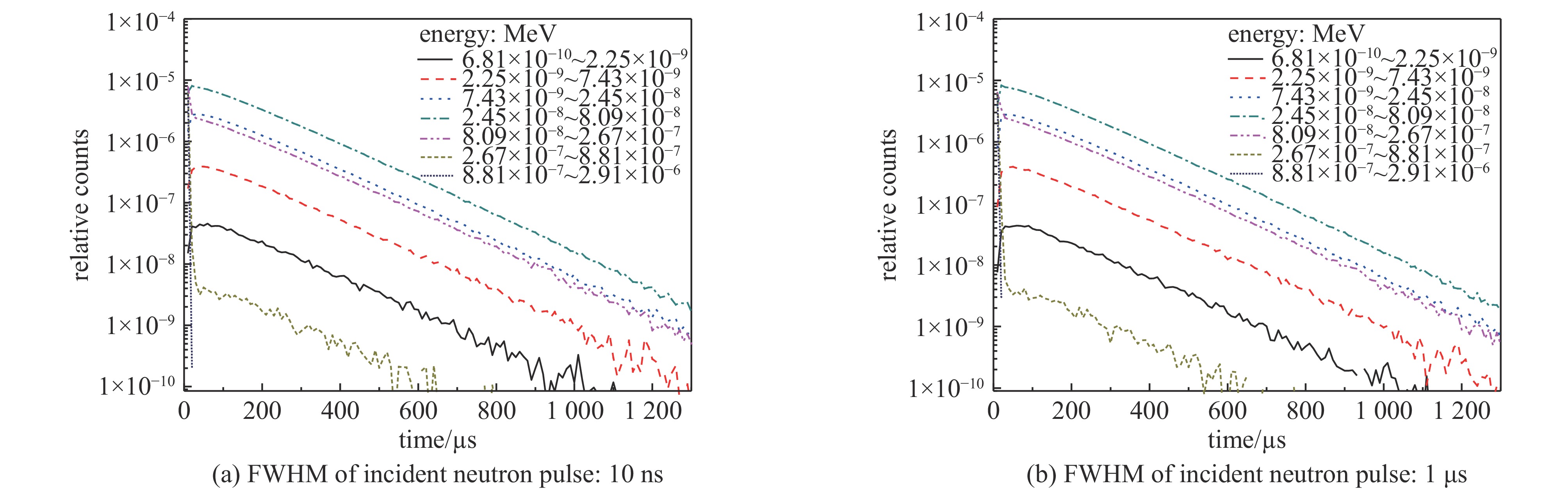
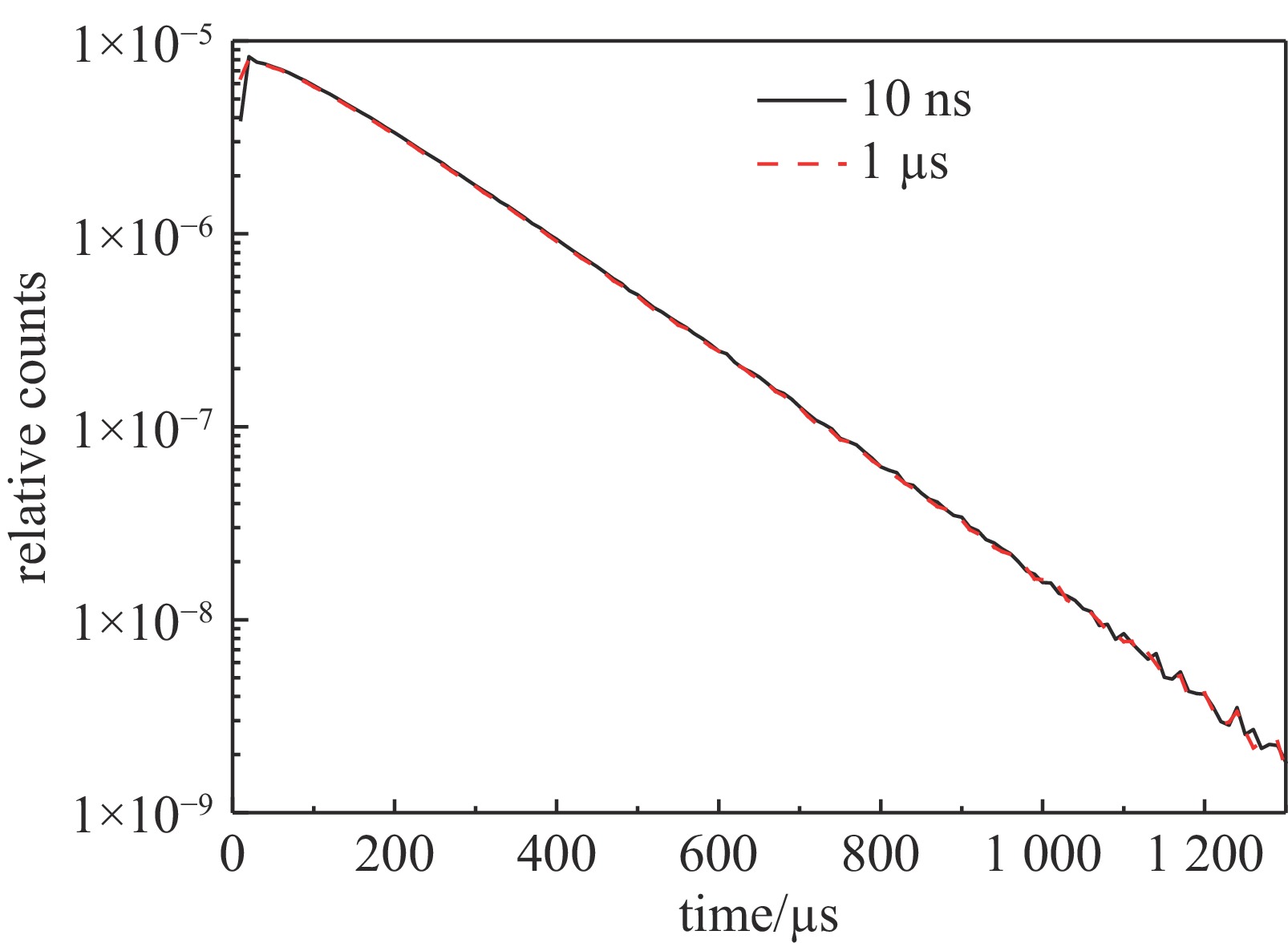
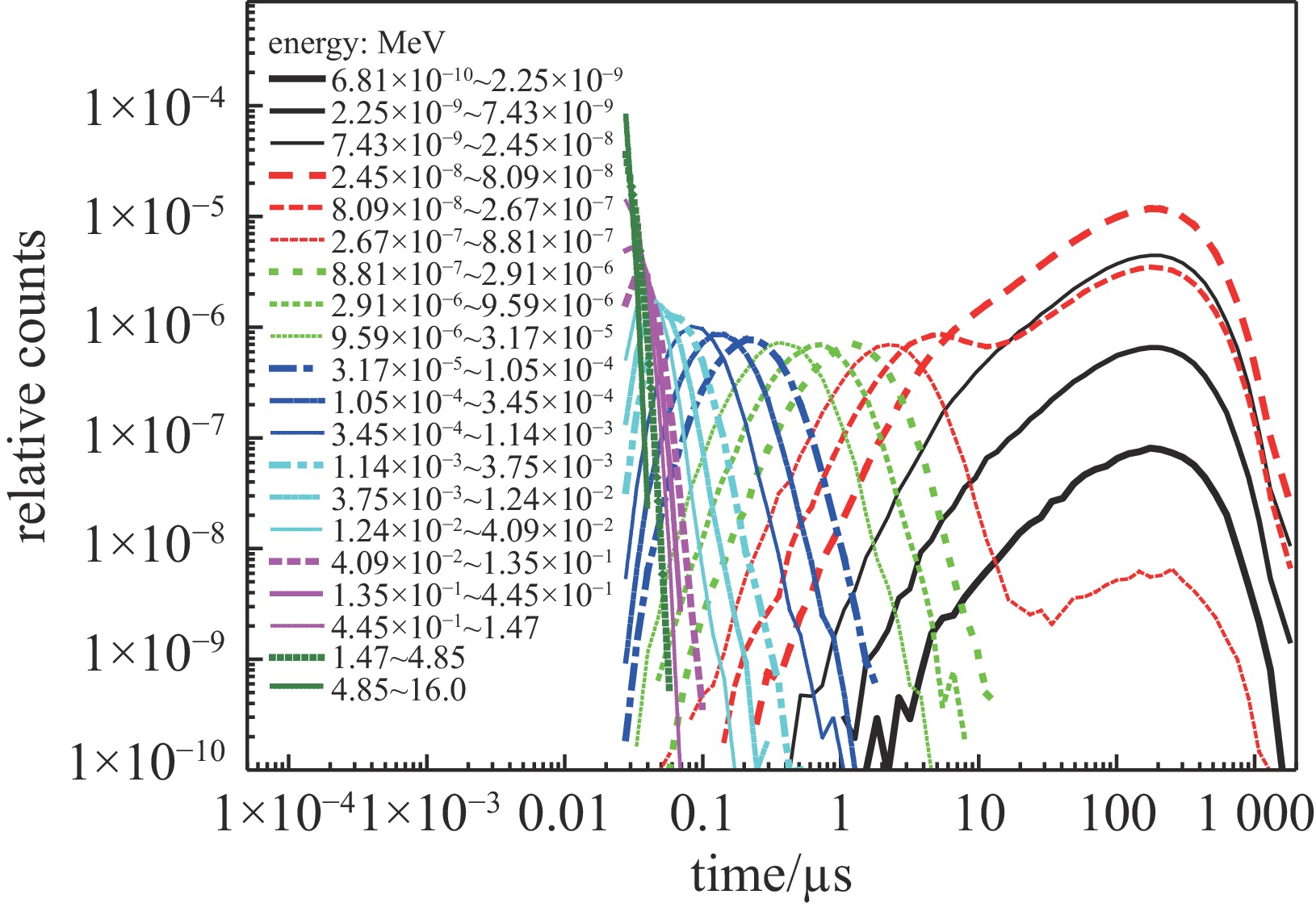
| [1] |
Hanson A O, Mckibben J L. A neutron detector having uniform sensitivity from 10 KeV to 3 MeV[J]. Physical Review, 1947, 72(8): 673-677.
|
| [2] |
Nobles R A, Day R B, Henkel R L, et al. Response of the long counter[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 1954, 25(4): 334-335.
|
| [3] |
East L V, Walton R B. Polyethylene moderated 3He neutron detectors[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods, 1969, 72(2): 161-166. doi: 10.1016/0029-554X(69)90152-9
|
| [4] |
Slaughter D R, Rueppel D W. Calibration of a depangher long counter from 2 keV to 19 MeV[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods, 1977, 145(2): 315-320. doi: 10.1016/0029-554X(77)90427-X
|
| [5] |
Hu Q Y, Li B J, Zhang D, et al. Optimizing the design of a moderator-based neutron detector for a flat response curve in the 2-14MeV energy range[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 2009, 609(2/3): 213-216.
|
| [6] |
Lacoste V, Gressier V. Experimental characterization of the IRSN long counter for the determination of the neutron fluence reference values at the AMANDE facility[J]. Radiation Measurements, 2010, 45(10): 1254-1257. doi: 10.1016/j.radmeas.2010.07.004
|
| [7] |
Lacoste V. Design of a new long counter for the determination of the neutron fluence reference values at the IRSN AMANDE facility[J]. Radiation Measurements, 2010, 45(10): 1250-1253. doi: 10.1016/j.radmeas.2010.06.026
|
| [8] |
Roberts N J, Thomas D J, Lacoste V, et al. Comparison of long counter measurements of monoenergetic and radionuclide source-based neutron fluence[J]. Radiation Measurements, 2010, 45(10): 1151-1153.
|
| [9] |
Pereira J, Hosmer P, Lorusso G, et al. The neutron long counter NERO for studies of β-delayed neutron emission in the r-process[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 2010, 618(1/3): 275-283.
|
| [10] |
Lawrence D J, Goldsten J O, Peplowski P N, et al. The psyche Gamma-Ray and neutron spectrometer[J]. Space Science Reviews, 2025, 221: 78. doi: 10.1007/s11214-025-01201-6
|
| [11] |
Leconte P, Belverge D, Bernard D, et al. Accurate measurements of delayed neutron data for reactor applications: methodology and application to 235U(nth, f)[J]. The European Physical Journal A, 2024, 60: 197. doi: 10.1140/epja/s10050-024-01402-7
|
| [12] |
Hu Q Y, Zhang J H, Zhang D, et al. An improved long counter for neutron fluence measurement with a flat response over a wide energy range from 1 keV to 15 MeV[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 2014, 768: 43-45.
|
| [13] |
Wang Guanbo, Qian Dazhi, Li Junjie, et al. Experimental and theoretical study of long counters on the departure of “point” assumption and scattering background influence[J]. Radiation Measurements, 2015, 82: 146-153. doi: 10.1016/j.radmeas.2015.07.007
|
| [14] |
Park R J, Byun S H. Optimization of a neutron long counter design by Monte Carlo simulation[J]. Health Physics, 2019, 117(3): 300-305.
|
| [15] |
Tagziria H, Thomas D J. Calibration and Monte Carlo modelling of neutron Long Counters[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 2000, 452(3): 470-483.
|
| [16] |
Li Yannan, Li Taosheng, Wang Ying, et al. Determination method of high Fluence rate for D-T neutron source with long counter[J]. Radiation Measurements, 2021, 148: 106662. doi: 10.1016/j.radmeas.2021.106662
|
| [17] |
Smolyar V P, Tarasov V A, Mileva A O, et al. Geant4 simulation of the moderating neutrons spectrum[J]. Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 2023, 212: 111151.
|
| [18] |
Marshall T O. Attenuation of 14 MeV neutrons in water[J]. Health Physics, 1970, 19: 571-574.
|
| [19] |
Deiev O S. GEANT 4 simulation of neutron transport and scattering in media[J]. Problems of Atomic Science and Technology, 2013, 85: 236-241.
|
| [20] |
Lisovska V, Malykhina T, Shpagina V, et al. GEANT4 modeling of energy spectrum of fast neutrons source for the development of research technique of heavy scintillators[J]. East European Journal of Physics, 2019(2): 58-63.
|
| [21] |
Shin J W, Hong S W, Bak S I, et al. GEANT4 and PHITS simulations of the shielding of neutrons from the 252Cf source[J]. Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 2014, 65(5): 591-598.
|
| [22] |
Robinson A E. New libraries for simulating neutron scattering in dark matter detector calibrations[J]. Physical Review C, 2014, 89: 032801.
|
| [23] |
Lemrani R, Robinson M, Kudryavtsev V A, et al. Low-energy neutron propagation in MCNPX and GEANT4[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 2006, 560(2): 454-459. doi: 10.1016/j.nima.2005.12.238
|
| [24] |
Ali F, Surette J, Atanackovic J, et al. Calculation of response parameters for a neutron long counter instrument[J]. Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 2024, 214: 111502. doi: 10.1016/j.apradiso.2024.111502
|




 下载:
下载: