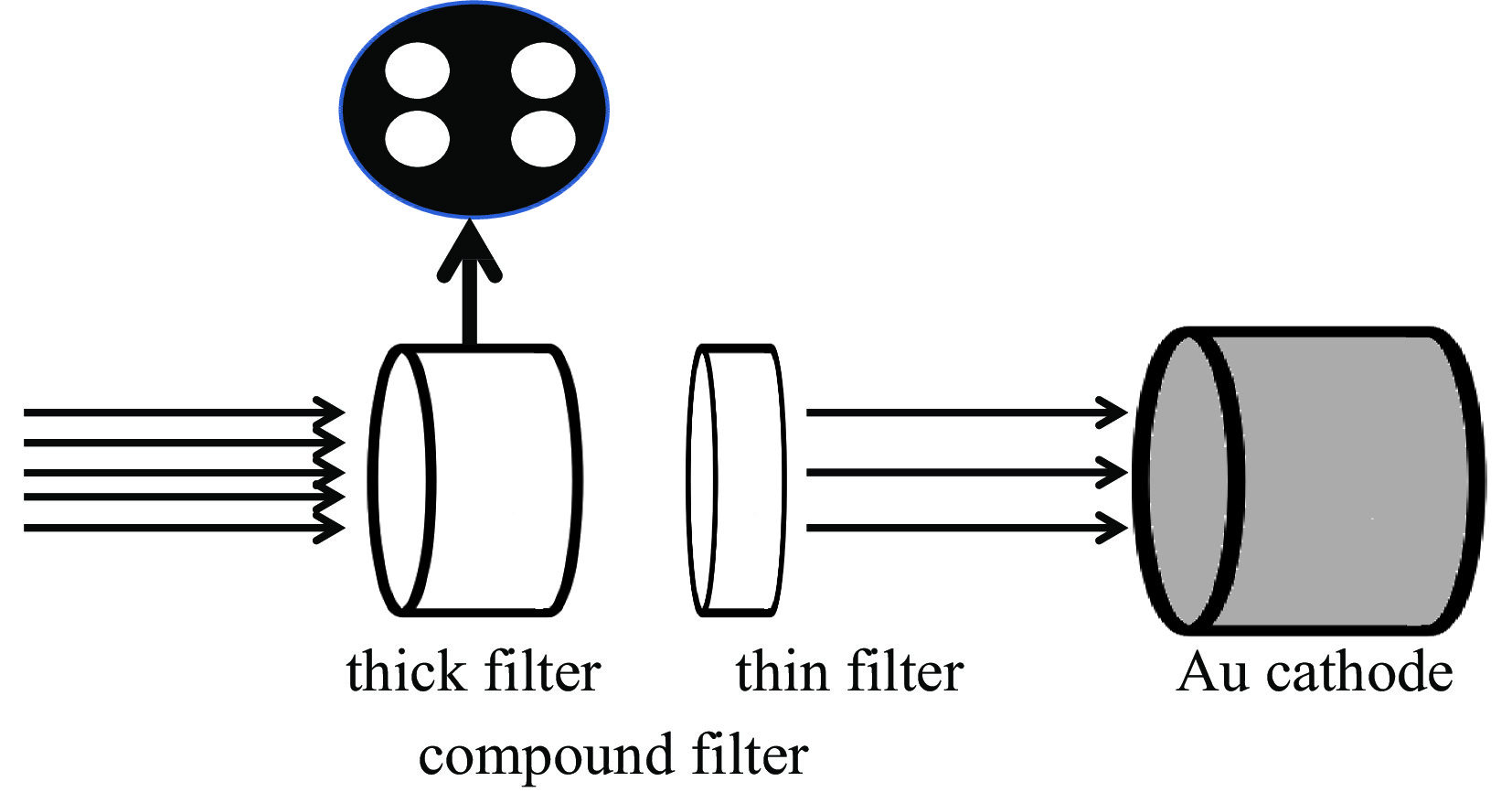
Optimization algorithm for compound filter parameters of flat response X-ray diode
-
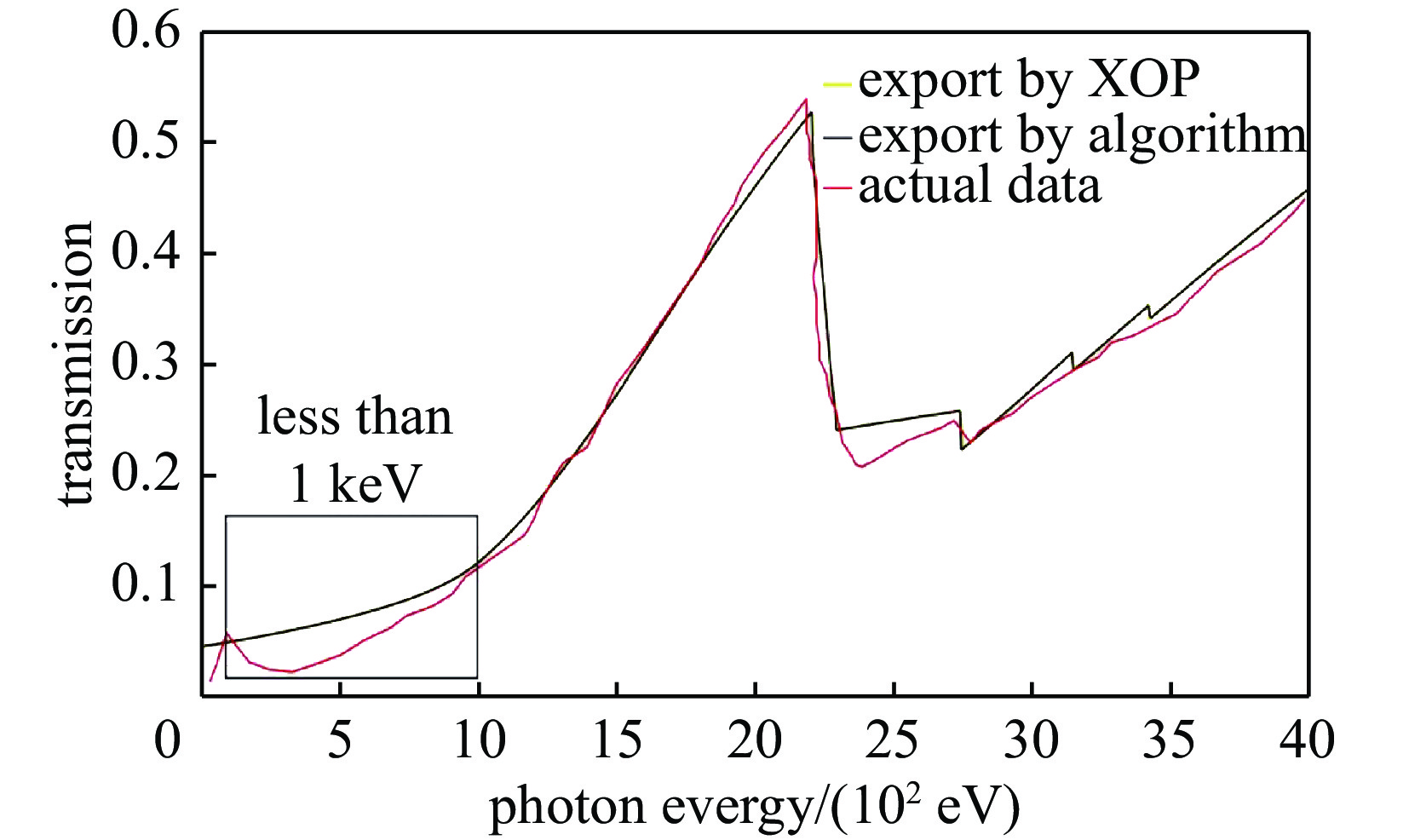
摘要: 在间接驱动激光聚变研究中,平响应X射线二极管是X射线辐射能流测量的主要探测器。为了获得理想的平响应效果,采用传统方法需要花费大量时间优化二极管的复合滤片参数,为此引入了粒子群优化算法,将之用于平响应X射线二极管复合滤片参数的优化,该方法可更快捷、更准确地得到复合滤片的优化参数。提出了新的滤片组合方式,并优化其平响应特性,得到了比传统滤片组合更优的参数配比。该项工作为平响应X射线二极管复合滤片参数的寻优提供了一种更高效的方法。Abstract: In the study of indirectly driven laser fusion, the flat response X-ray diode is the main detector for the measurement of X-ray radiation energy flux. To obtain ideal flat response effect, it usually costs a lot of time to optimize the composite filter parameters of the detector. In this paper, the particle swarm optimization algorithm is developed and applied to optimize the parameters of compound filter of flat response X-ray diode. Compared with the previous work, the method developed in this paper can get the optimized parameters of composite filter more quickly and accurately. On this basis, this paper proposes a new filter combination mode, optimizes its flat response characteristics, and obtains a better parameter ratio than the traditional filter combination. The work in this paper provides a more efficient method for searching the parameters of the composite filter of the response X-ray diode
-
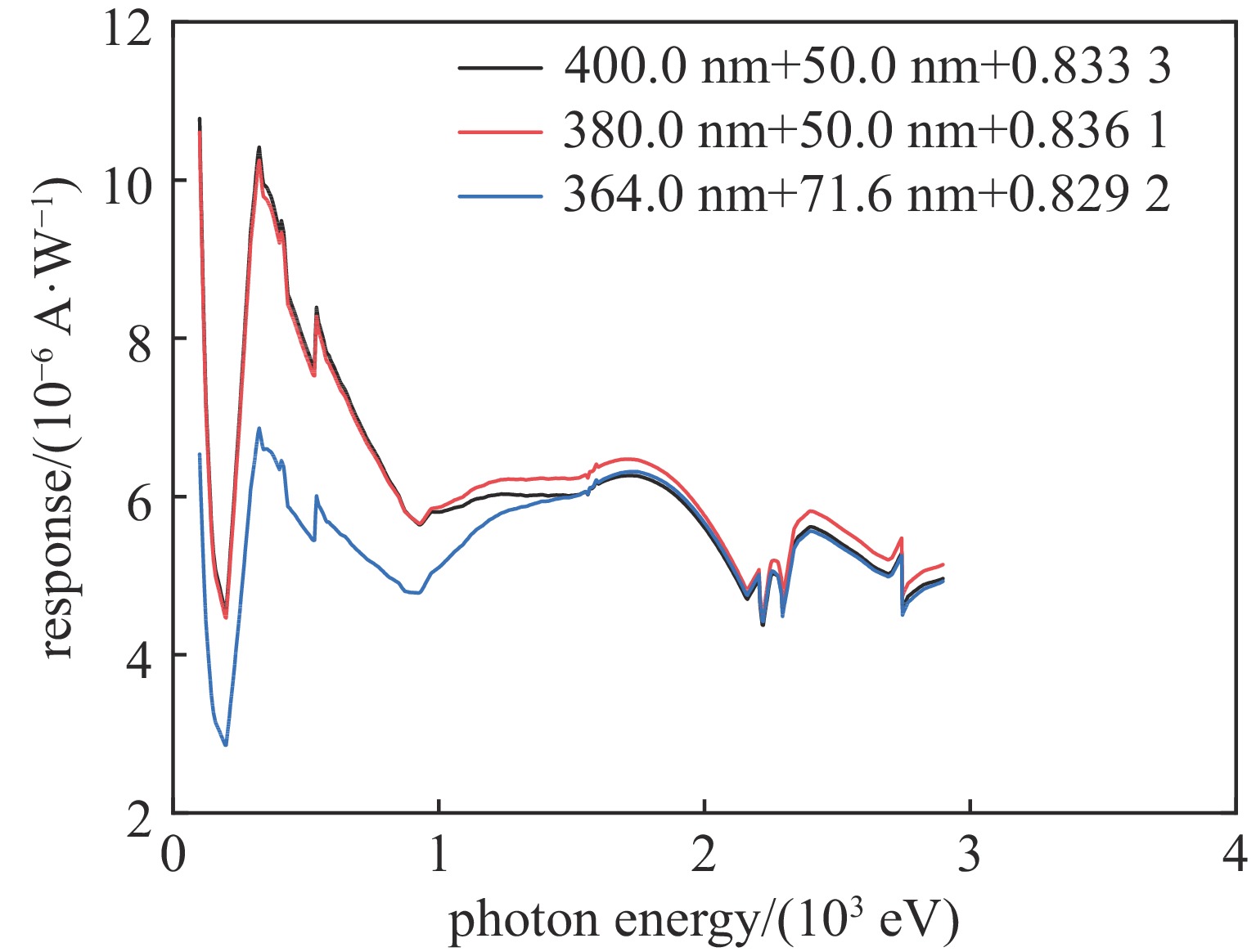
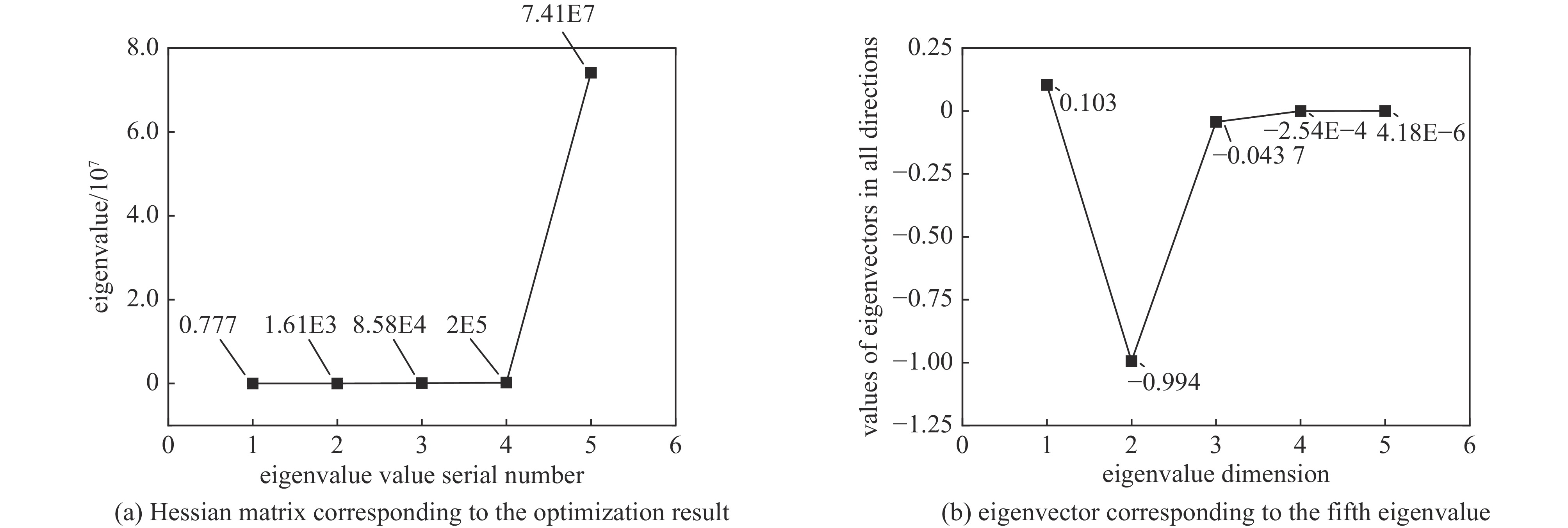
表 1 双层金复合滤片组合算法优化结果
Table 1. Optimization results of combination algorithm of double gold composite filter
flat thick filter thickness/nm thin filter thickness/nm weight (thick filter) weight (thin filter) 0.01213 360.2 71.0 0.829 3 1 0.01219 363.1 72.2 0.828 4 1 0.01218 364.0 71.6 0.829 2 1 表 2 双层金滤片与单层铝滤片组成的复合滤片参数优化结果
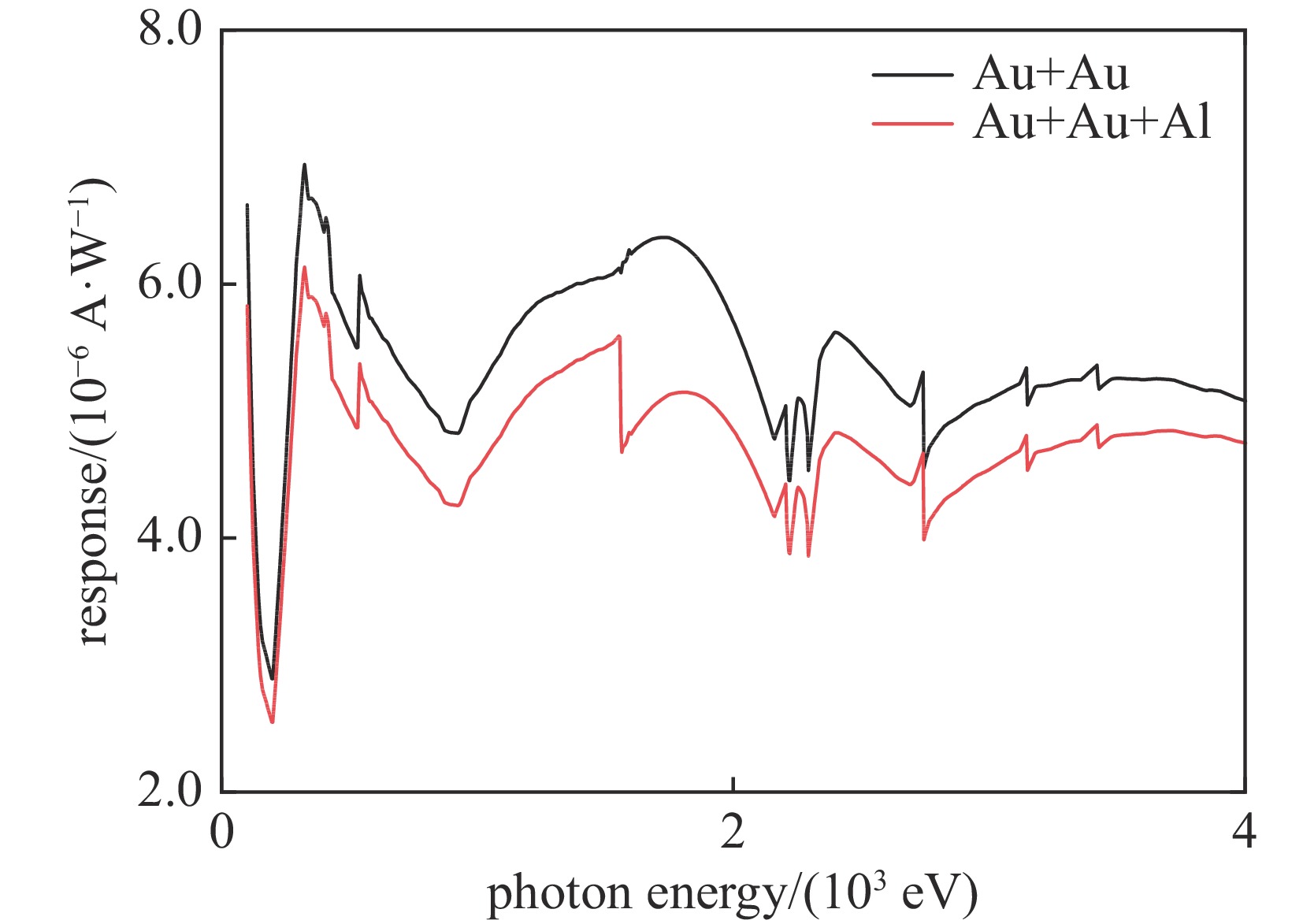
Table 2. Parameter optimization results of composite filter composed of double-layer gold filter and single-layer aluminum filter
flat thick filter 1 (Au)
thickness/nmthin filter 2 (Au)
thickness/nmfilter 3 (Al)
thickness/nmweight
(thick filter 1)weight
(thin filter 2)weight
(filter 3)0.01052 399.1 63.6 186.0 0.8486 0.8880 1 0.01052 406.8 64.1 185.9 0.8496 0.8472 1 0.01053 412.3 63.6 189.2 0.8515 0.8516 1 -
[1] Lindl J D, Amendt P, Berger R L, et al. The physics basis for ignition using indirect-drive targets on the National Ignition Facility[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2004, 11(2): 339-491. doi: 10.1063/1.1578638 [2] Dewald E L, Glenzer S H, Landen O L, et al. First laser–plasma interaction and hohlraum experiments on the National Ignition Facility[J]. Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 2005, 47: B405. doi: 10.1088/0741-3335/47/12B/S29 [3] Glenzer S H, MacGowan B J, Meezan N B, et al. Demonstration of ignition radiation temperatures in indirect-drive inertial confinement fusion hohlraums[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2011, 106: 085004. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.106.085004 [4] 汪志诚. 热力学·统计物理[M]. 5版. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2013Wang Zhicheng. Thermodynamics·statistical physics[M]. 5th ed. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2013 [5] Meezan N B, Atherton L J, Callahan D A, et al. National Ignition Campaign Hohlraum energetics[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2010, 17: 056304. doi: 10.1063/1.3354110 [6] Betti R, Chang Poyu, Spears B K, et al. Thermonuclear ignition in inertial confinement fusion and comparison with magnetic confinement[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2010, 17: 058102. doi: 10.1063/1.3380857 [7] Dewald E L, Suter L J, Landen O L, et al. Radiation-driven hydrodynamics of high-Z hohlraums on the National Ignition Facility[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2005, 95: 215004. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.95.215004 [8] Li Zhichao, Jiang Xiaohua, Liu Shenye, et al. A novel flat-response X-ray detector in the photon energy range of 0.1-4 keV[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2010, 81: 073504. doi: 10.1063/1.3460269 [9] Kornblum H N, Slivinsky V W. Flat-response, subkiloelectronvolt X-ray detector with a subnanosecond time response[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 1978, 49(8): 1204-1205. doi: 10.1063/1.1135548 [10] Clery D. Fusion's great bright hope. Science, 2009, 324(5925): 326-330. [11] Li Zhichao, Zhu Xiaoli, Jiang Xiaohua, et al. Note: Continuing improvements on the novel flat-response X-ray detector[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2011, 82: 106106. doi: 10.1063/1.3657158 [12] 车兴森, 侯立飞, 杨轶濛, 等. 用于平响应X光探测器的复合滤片参数优化[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2017, 46:1017008 doi: 10.3788/IRLA201746.1017008Che Xingsen, Hou Lifei, Yang Yimeng, et al. Parameter optimization of compound filters applied for flat-response X-ray detectors[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2017, 46: 1017008 doi: 10.3788/IRLA201746.1017008 [13] Guo Liang, Li Sanwei, Zheng Jian, et al. A compact flat-response X-ray detector for the radiation flux in the range from 1.6 keV to 4.4 keV[J]. Measurement Science and Technology, 2012, 23: 065902. doi: 10.1088/0957-0233/23/6/065902 [14] 郭亮. 空腔M带X光辐射能流研究[D]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学, 2012Guo Liang. The precise measurement and modeling of M-band radiation flux from void hohlraums[D]. Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China, 2012 [15] Bentley C D, Simmons A C. Spectral response calibrations of X-ray diode photocathodes in the 50-5900 eV photon energy region[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2001, 72(1): 1202-1204. doi: 10.1063/1.1322622 [16] 郑志坚, 丁永坤, 丁耀南, 等. 激光惯性约束聚变综合诊断系统[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2003, 15(11):1073-1078Zheng Zhijian, Ding Yongkun, Ding Yaonan, et al. Recent progress and application of diagnostic technique in laser fusion[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2003, 15(11): 1073-1078 [17] Henke B L, Knauer J P, Premaratne K. The characterization of X-ray photocathodes in the 0.1-10-keV photon energy region[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1981, 52(3): 1509-1520. doi: 10.1063/1.329789 [18] Henke B L, Smith J A, Attwood D T. 0.1-10-keV X-ray-induced electron emissions from solids—Models and secondary electron measurements[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1977, 48(5): 1852-1866. doi: 10.1063/1.323938 [19] Henke B L, Lee P, Tanaka T J, et al. Low-energy X-ray interaction coefficients: Photoabsorption, scattering, and reflection: E= 100-2000 eV Z= 1-94[J]. Atomic Data and Nuclear Data Tables, 1982, 27(1): 1-144. doi: 10.1016/0092-640X(82)90002-X [20] Shi Yuhui, Eberhart R. A modified particle swarm optimizer[C]//1998 IEEE International Conference on Evolutionary Computation Proceedings. IEEE World Congress on Computational Intelligence (Cat. No. 98TH8360). Anchorage: IEEE, 1998: 69-73. [21] 王传珂, 李晋, 杨鸣, 等. 平响应X射线光阴极的理论设计与计算模拟[J]. 光子学报, 2017, 46:0523001 doi: 10.3788/gzxb20174605.0523001Wang Chuanke, Li Jin, Yang Ming, et al. Theoretical design and numerical simulation of flat response X-ray photocathode[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica, 2017, 46: 0523001 doi: 10.3788/gzxb20174605.0523001 [22] Del Río M S, Dejus R J. XOP v2.4: recent developments of the X-ray optics software toolkit[C]//Proceedings of SPIE 8141, Advances in Computational Methods for X-Ray Optics II. 2011: 814115. [23] Del Rio M S. Advances in computational methods for X-ray and neutron optics[C]//Proceedings of SPIE 8141, Advances in Computational Methods for X-Ray Optics II. 2004: 814101. [24] 张贤达. 矩阵分析与应用[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2004Zhang Xianda. Matrix analysis and application[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2004 -




 下载:
下载: