Research on physical mechanism of mode-locked free-electron laser based on electron beam phase space beating
-
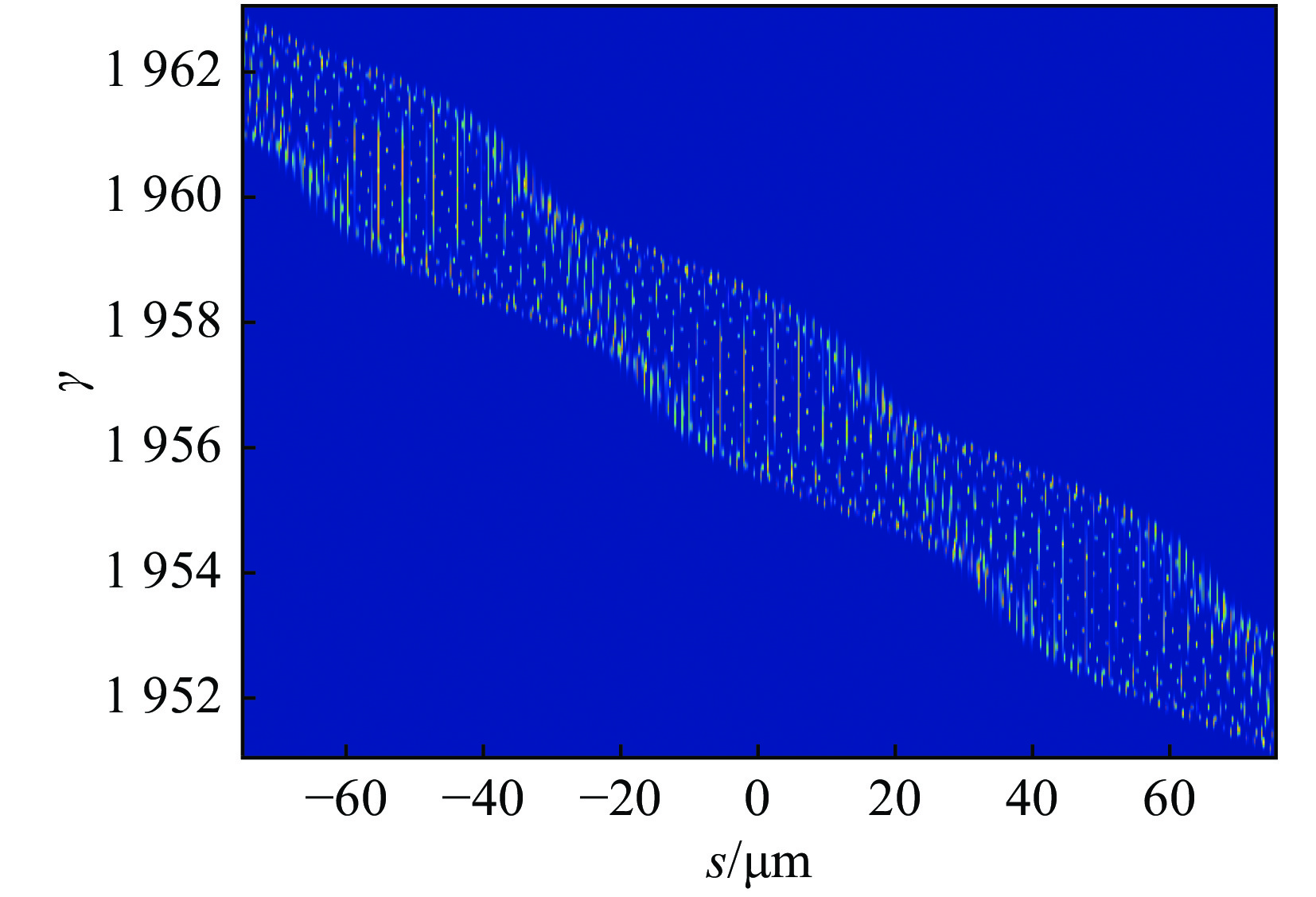
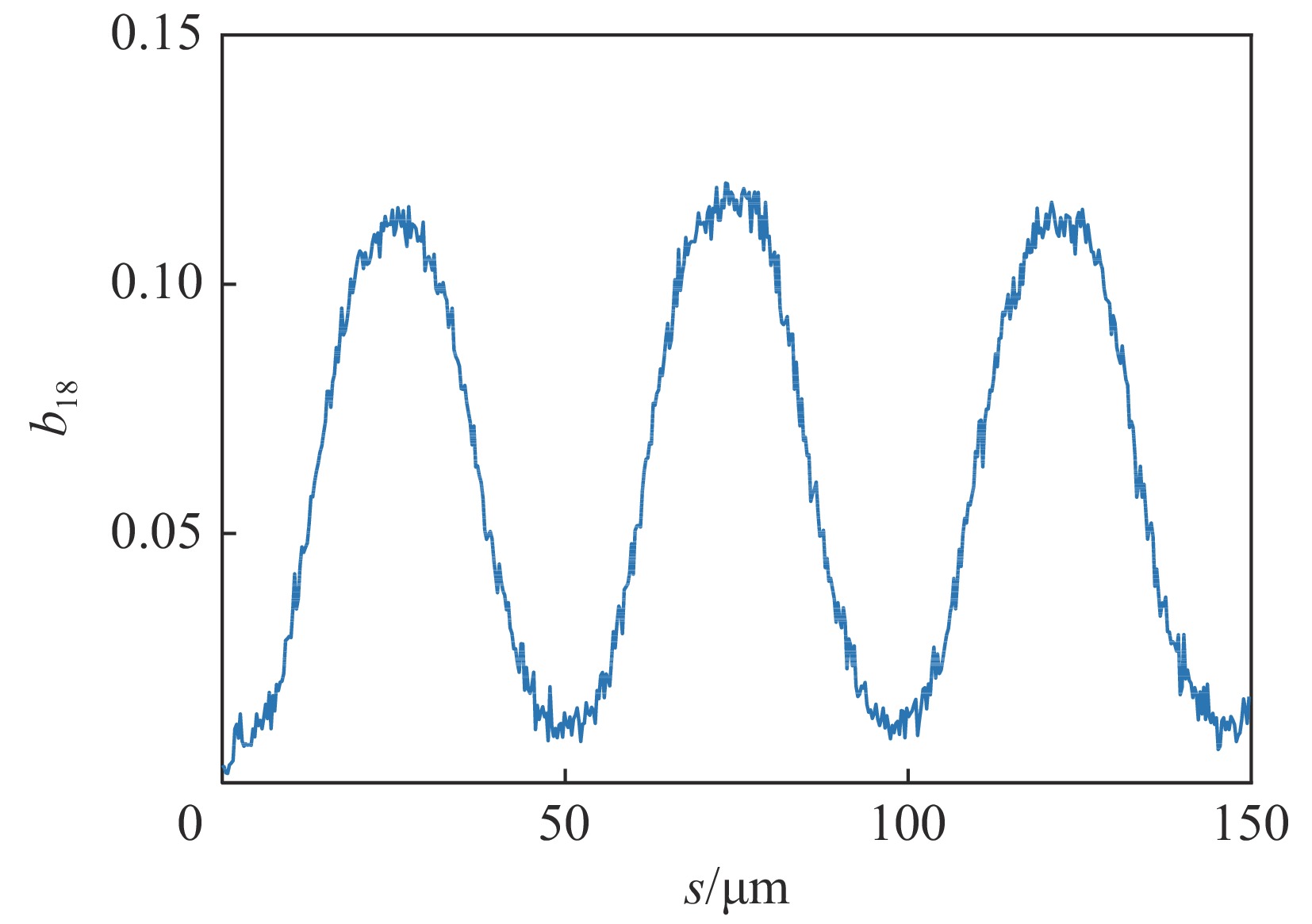
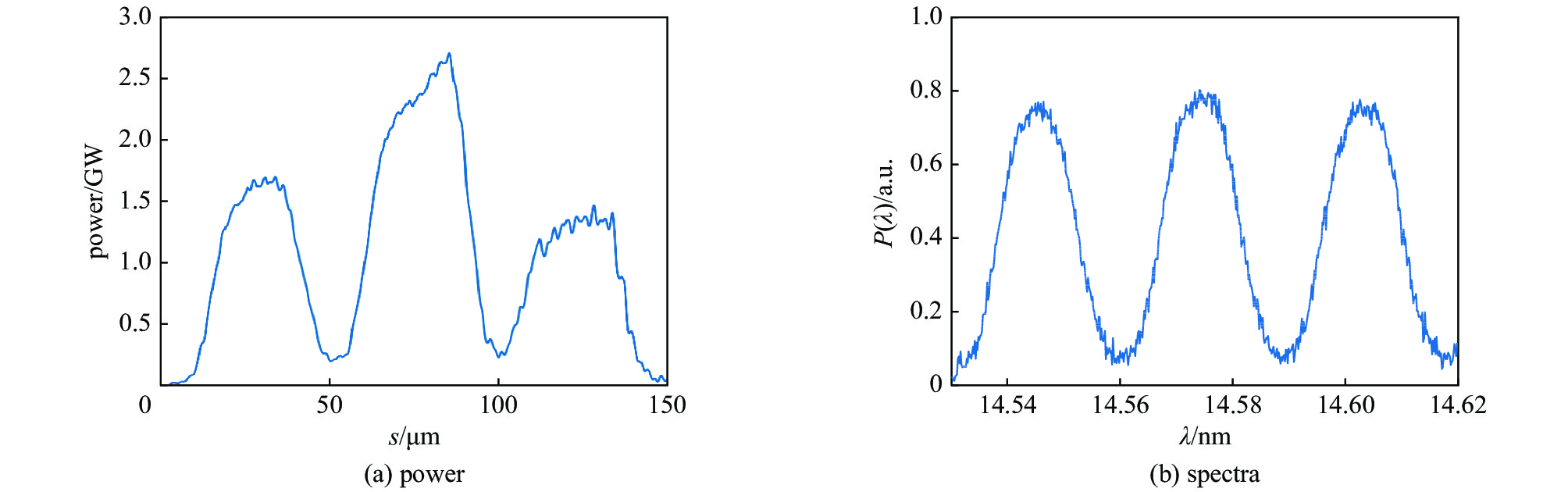
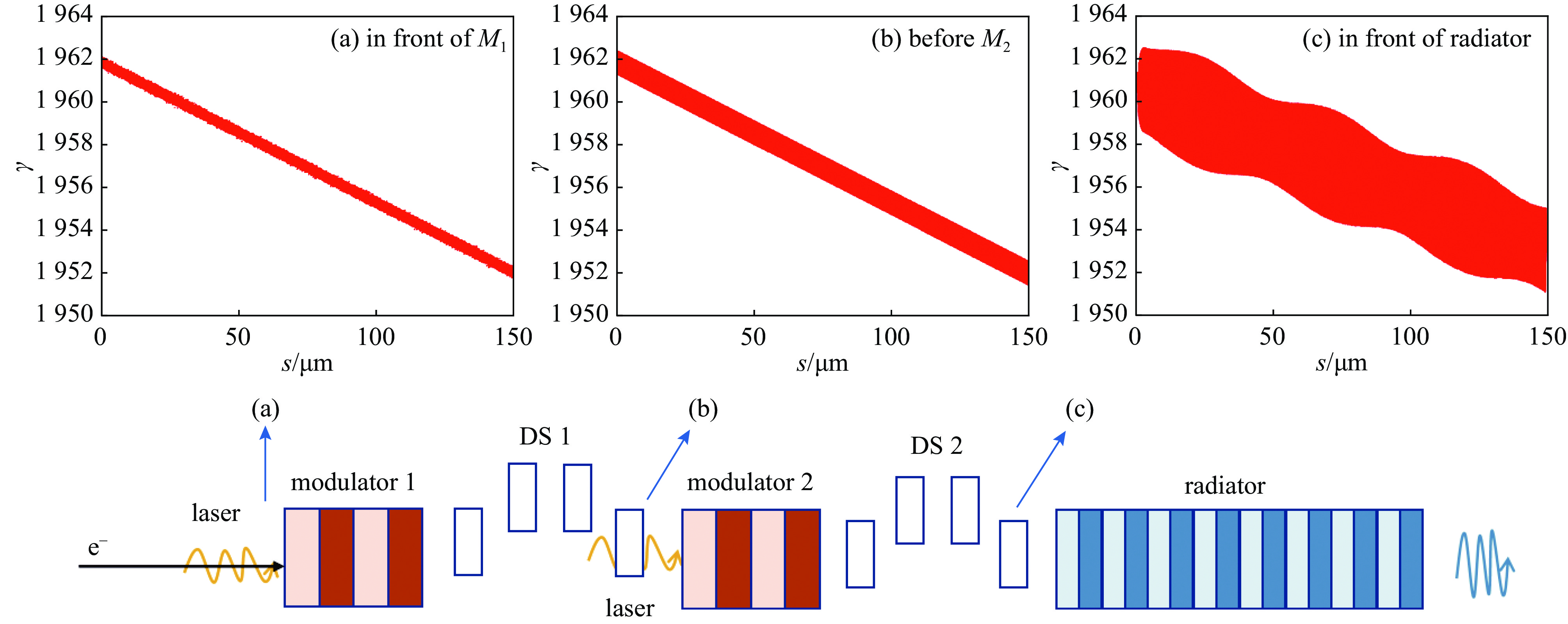
摘要: 提出基于束流相空间拍频产生锁模多色自由电子激光的方案,利用带有能量啁啾的电子束流和上海软X射线自由电子激光装置(SXFEL)上的两个调制段-色散段结构,在束流中通过拍频形成多个流强脉冲串,并在此基础上进行高次谐波辐射,产生锁模多色自由电子激光辐射脉冲。模拟结果表明,利用264 nm的种子激光,可在束流中形成18次谐波的群聚分量,并能最终产生中心波长约14.58 nm 的锁模多色FEL辐射。Abstract: The theory, method, and experimental studies on mode-locked free-electron laser (FEL) have been of great interests in the world. In this paper, we propose a method to generate mode-locked multi-color free-electron laser radiation pulses based on the electron beam phase space beating. Utilizing an electron beam with head-tail energy chirp and the two modulator-chicane setups in the Shanghai Soft X-ray free-electron laser facility (SXFEL), multiple current pulse trains can be formed and mode-locked multi-color free electron laser pulses can be generated. The simulation results indicate that, with the help the 264 nm seed laser, bunching factor at the 18th harmonic of the seed laser can be formed and ultimately mode-locked multi-color FEL radiation pulse with a central wavelength of approximately 14.58 nm can be generated. This study is of great significance for the development of the mode-locked FEL in China and the performance improvement of the SXFEL facility.
-
Key words:
- free electron laser /
- mode-locking /
- frequency beating /
- beam manipulation
-
表 1 主要参数
Table 1. Main Parameters
beam
energy/GeVenergy
spreadpeak
current/Aemittance
(RMS)/(μm·rad)wavelength/nm peak power
of seed1/MWpeak power
of seed2/MW${R}_{56,1}$/µm ${R}_{56,2}$/µm 1 0.4 × 10−5 1500 1.0 264 52 100 160 30 -
[1] Emma P, Akre R, Arthur J, et al. First lasing and operation of an ångstrom-wavelength free-electron laser[J]. Nature Photonics, 2010, 4(9): 641-647. doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2010.176 [2] Allaria E, Appio R, Badano L, et al. Highly coherent and stable pulses from the FERMI seeded free-electron laser in the extreme ultraviolet[J]. Nature Photonics, 2012, 6(10): 699-704. doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2012.233 [3] Huang Nanshun, Deng Haixiao, Liu Bo, et al. Features and futures of X-ray free-electron lasers[J]. The Innovation, 2021, 2: 100097. [4] Chapman H N. X-ray free-electron lasers for the structure and dynamics of macromolecules[J]. Annual Review of Biochemistry, 2019, 88: 35-58. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biochem-013118-110744 [5] Bostedt C, Boutet S, Fritz D M, et al. Linac coherent light source: the first five years[J]. Reviews of Modern Physics, 2016, 88: 015007. doi: 10.1103/RevModPhys.88.015007 [6] Thompson N R, McNeil B W J. Mode locking in a free-electron laser amplifier[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2008, 100: 203901. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.100.203901 [7] Kur E, Dunning D J, McNeil B W J, et al. A wide bandwidth free-electron laser with mode locking using current modulation[J]. New Journal of Physics, 2011, 13: 063012. doi: 10.1088/1367-2630/13/6/063012 [8] Xiang Dao, Ding Yuantao, Raubenheimer T, et al. Mode-locked multichromatic X rays in a seeded free-electron laser for single-shot X-ray spectroscopy[J]. Physical Review Special Topics-Accelerators and Beams, 2012, 15: 050707. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevSTAB.15.050707 [9] Feng Chao, Chen Jianhui, Zhao Zhentang. Generating stable attosecond X-ray pulse trains with a mode-locked seeded free-electron laser[J]. Physical Review Special Topics-Accelerators and Beams, 2012, 15: 080703. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevSTAB.15.080703 [10] Henderson J R, McNeil B W J. Echo enabled harmonic generation free electron laser in a mode-locked configuration[J]. Europhysics Letters, 2012, 100: 64001. doi: 10.1209/0295-5075/100/64001 [11] Dunning D J, McNeil B W J, Thompson N R. Few-cycle pulse generation in an X-ray free-electron laser[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2013, 110: 104801. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.110.104801 [12] Maroju P K, Grazioli C, Di Fraia M, et al. Attosecond pulse shaping using a seeded free-electron laser[J]. Nature, 2020, 578(7795): 386-391. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2005-6 [13] Maroju P K, Grazioli C, Di Fraia M, et al. Complex attosecond waveform synthesis at FEL FERMI[J]. Applied Sciences, 2021, 11: 9791. doi: 10.3390/app11219791 [14] Reiche S. GENESIS 1.3: a fully 3D time-dependent FEL simulation code[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 1999, 429(1/3): 243-248. -




 下载:
下载: