Intelligent assembly scheduling for large laser devices
-
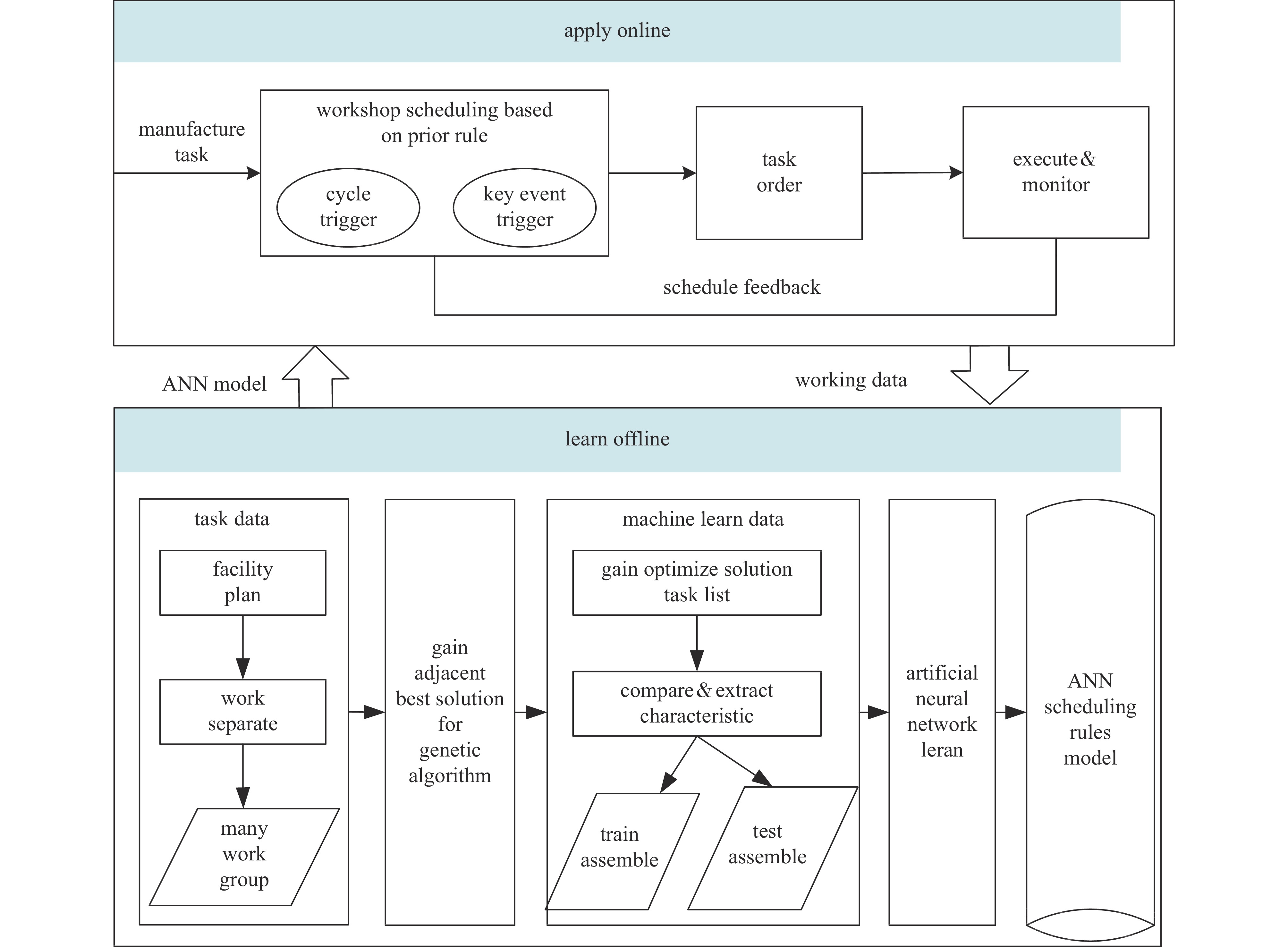
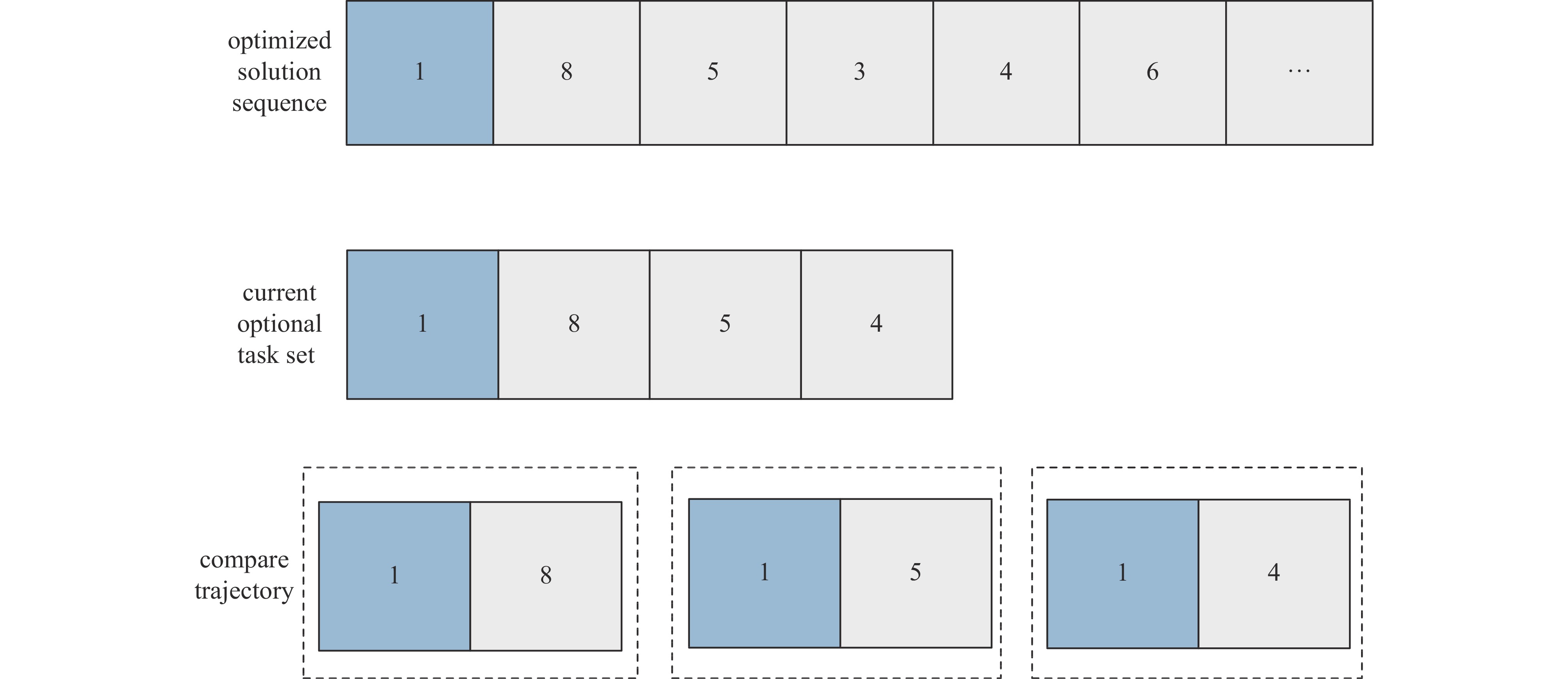
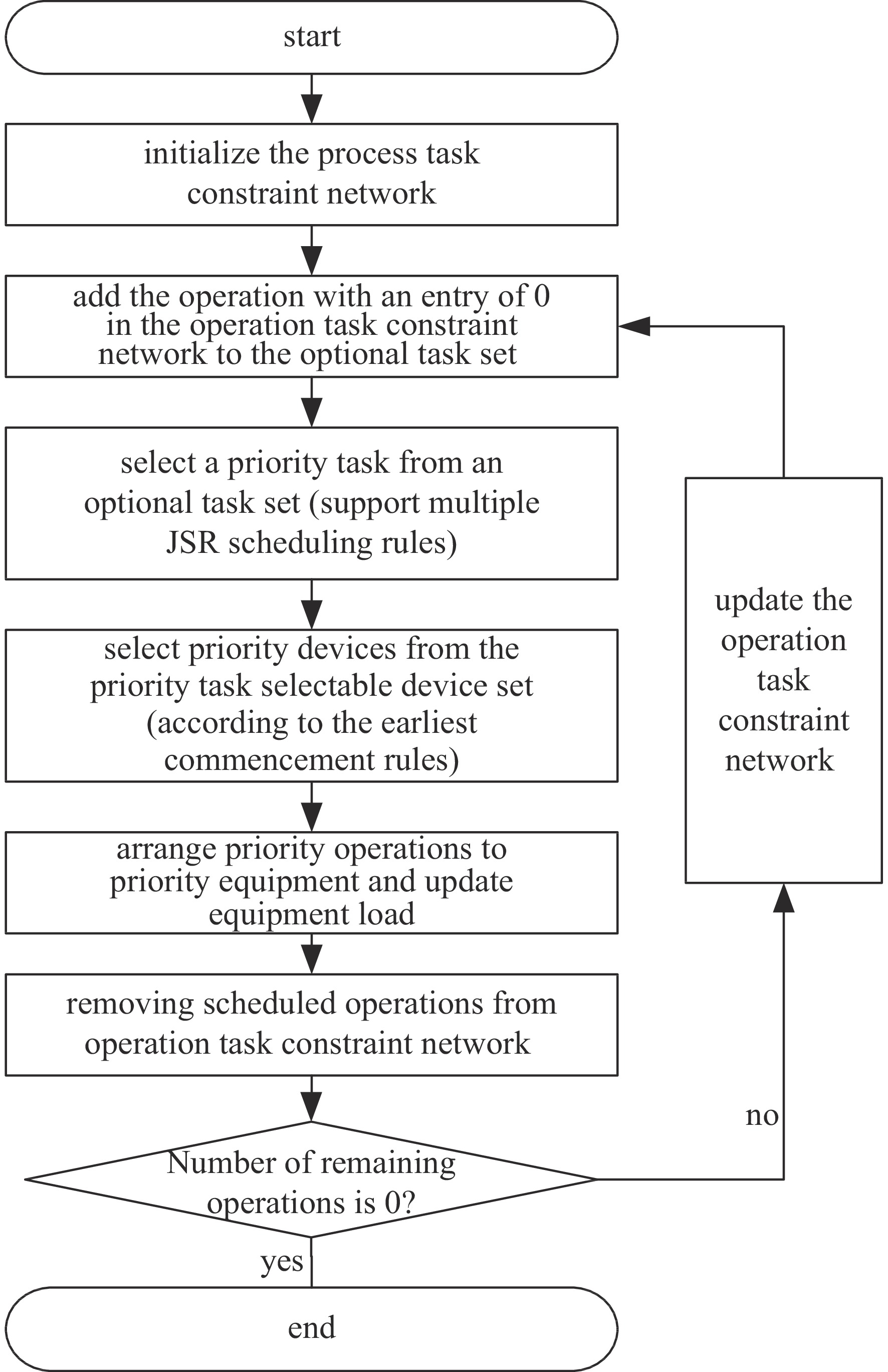
摘要: 针对大型激光装置精密装校过程中的智能装配调度问题,提出一种基于人工神经网络的调度优先规则获取方法。该方法离线阶段通过遗传算法对典型算例进行优化求解,从优化解中抽取任务比较轨迹及特征数据,采用人工神经网络学习生成任务优先模型;在线阶段基于该模型构建闭环调度决策模式,实现动态不确定生产环境下的快速响应与精准决策。数据实验和实际应用案例验证了该方法的有效性,随着光机模块数量增加,ANN调度算法的优势更加明显,ANN调度算法和GA算法二者优化结果小于6%时,前者的计算效率是后者的400倍以上。Abstract: Aiming at the assembly scheduling problem of optical and mechanical modules for large laser devices, a scheduling priority rule acquisition method based on artificial neural networks (ANNs) is proposed. In the offline phase, this method optimizes the scheduling data through genetic algorithms, extracts task comparison trajectories and feature data from the optimization solution, and uses ANNs to learn the task priority comparison model. In the online phase, a closed-loop decision scheduling mode is constructed based on this model to achieve rapid response and accurate decision-making in dynamic uncertain production environments. Data experiments and practical application cases verify the effectiveness of this method. With the increase of the number of optical-mechanical modules, the advantages of ANN scheduling algorithm become more obvious. When the optimization results of ANN scheduling algorithm and GA algorithm are less than 6%, the computational efficiency of the former is more than 400 times that of the latter.
-
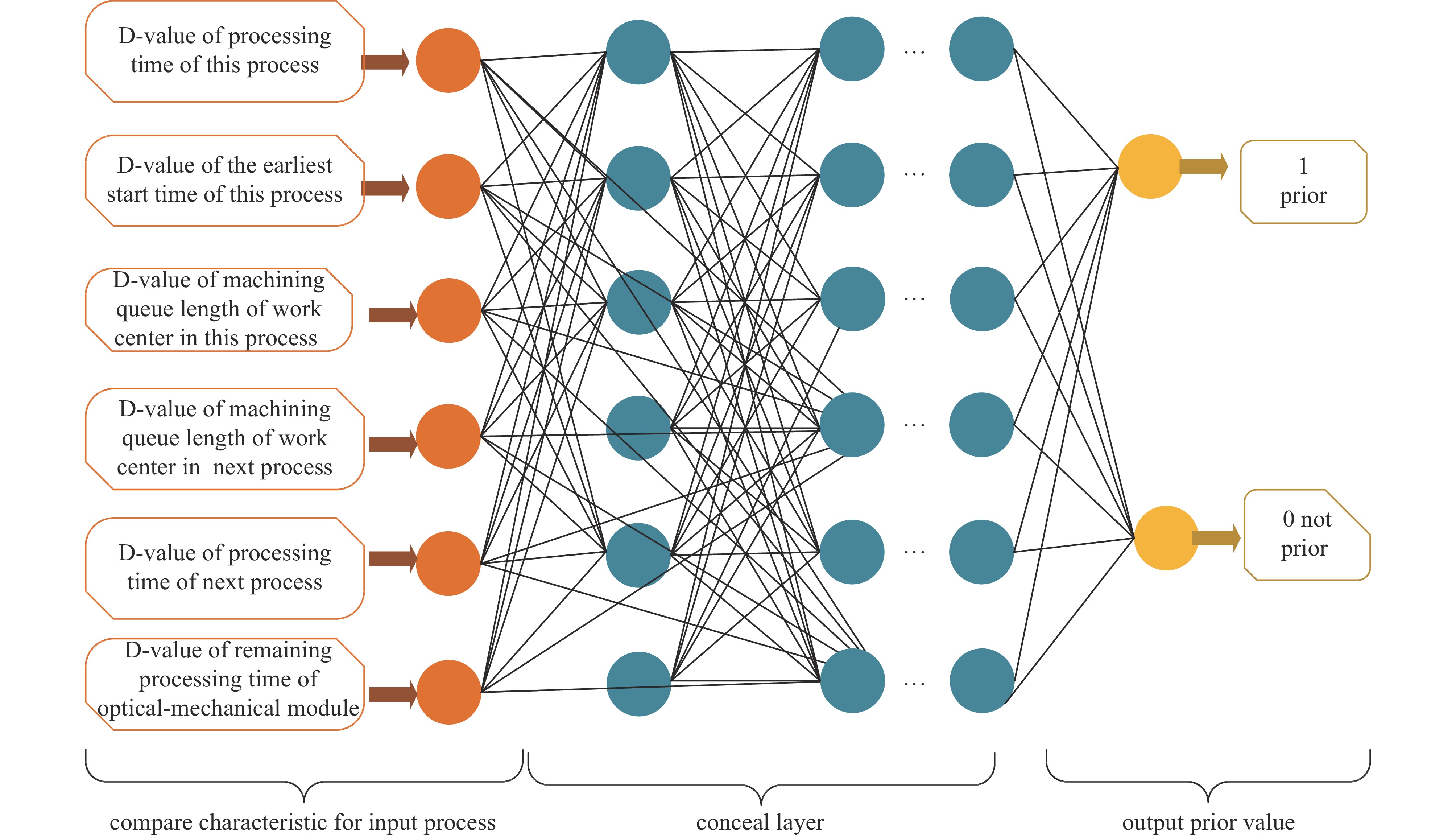
表 1 人工神经网络的输入特征
Table 1. Input characteristics of artificial neural network
No. characteristics remark 1 t(PT) processing time of this process 2 t(ES) the earliest start time of this process 3 l(WIQ) machining queue length of work center in this process 4 l(WINQ) machining queue length of work center in next process 5 t(NPT) processing time of next process 6 t(WKR) remaining processing time of optical-mechanical module 表 2 典型光机模块工艺路线及工时
Table 2. Process route and working hours of typical optical-mechanical modules
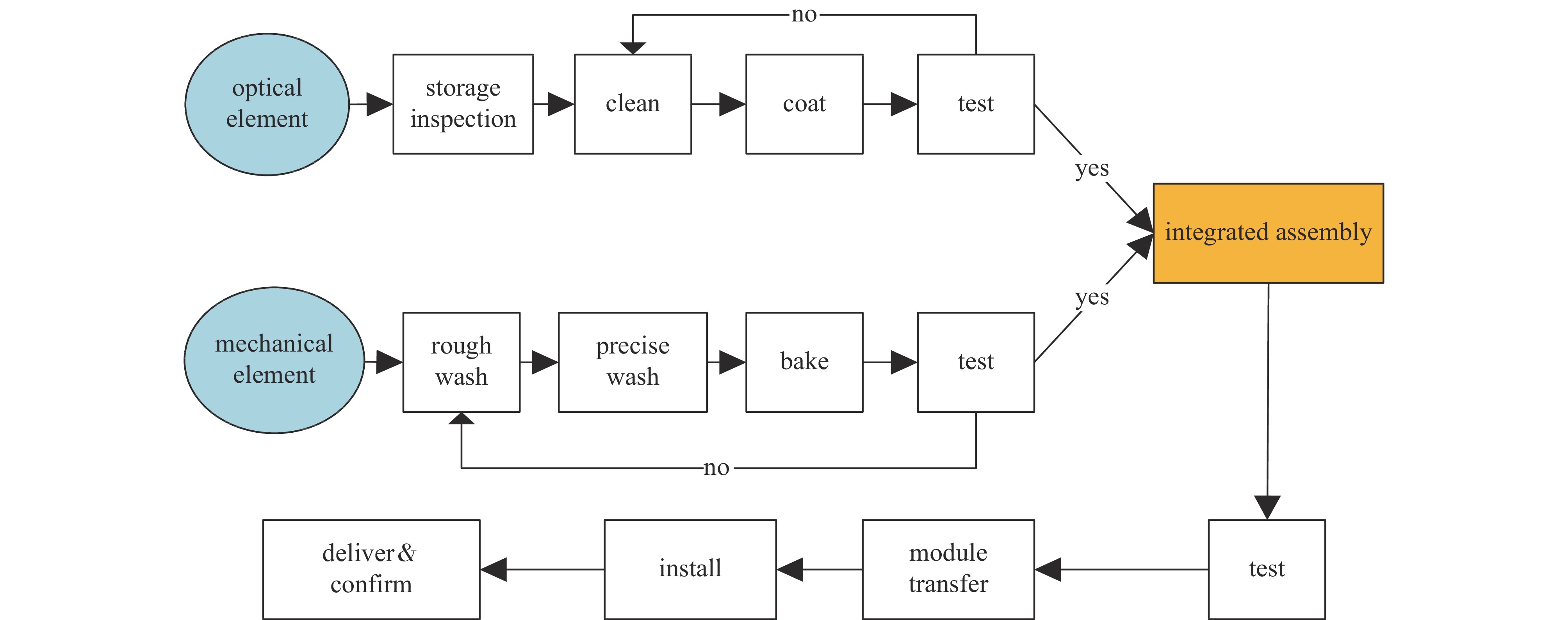
process process name processing time/min 10 storage inspection of optical elements 120 20 cleaning of optical elements 540 30 optical element coating 162 40 optical element detection 120 50 mechanical frame warehousing inspection 12 60 rough washing of mechanical frame 15 70 fine washing of mechanical frame 30 80 high temperature baking of mechanical frame 67 90 cleanliness detection of mechanical frame 120 100 mechanical assembly 720 110 optical-mechanical assembly and test 360 120 transfer and storage 288 表 3 五种调度算法运算结果
Table 3. Operational results of five scheduling algorithms
No. m C T/s FIFO SPT LWKR ANN GA FIFO SPT LWKR ANN GA 1 5 2322 2202 2 036 2 047 1 998 0.19 0.19 0.21 0.63 280 2 5 2434 2193 2276 2149 2047 0.20 0.20 0.23 0.69 295 3 10 3111 3490 3070 2631 2582 0.39 0.41 0.46 0.88 510 4 10 3790 3361 3792 3007 2894 0.41 0.42 0.52 0.87 555 5 15 3931 3987 4478 3635 3428 0.61 0.62 0.77 1.21 613 6 15 4008 3965 3729 3321 3168 0.63 0.63 0.81 1.17 679 7 20 7284 7312 6953 6202 5997 0.91 0.92 1.09 1.53 1011 8 20 7220 7023 6897 6228 6082 0.97 0.95 1.19 1.48 997 -
[1] 郑万国, 邓颖, 周维, 等. 激光聚变研究中心激光技术研究进展[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2013, 25(12):3082-3090 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20132512.3082Zheng Wanguo, Deng Ying, ZhouWei, et al. Development of laser technology in research center of laser fusion[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2013, 25(12): 3082-3090 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20132512.3082 [2] Panwalkar SS, Iskander W. A survey of scheduling rules[J]. Operations Research, 1977, 25(1): 45-61. doi: 10.1287/opre.25.1.45 [3] 张泽群, 唐敦兵, 金永乔, 等. 信息物联驱动下的离散车间自组织生产调度技术[J]. 机械工程学报, 2018, 54(16):34-44 doi: 10.3901/JME.2018.16.034Zhang Zequn, Tang Dunbing, JinYongqiao, et al. Self-organizing production technology for discrete workshop scheduling driven by internet of things[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2018, 54(16): 34-44 doi: 10.3901/JME.2018.16.034 [4] 龙田, 石宇强, 王俊佳. 柔性作业车间在线调度问题的仿真建模与分析[J]. 机械设计与制造, 2015(12):27-30 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3997.2015.12.008Long Tian, Shi Yuqiang, Wang Junjia. Simulation modeling and analysis for online flexible job-shop scheduling problem[J]. Machinery Design & Manufacture, 2015(12): 27-30 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3997.2015.12.008 [5] Burke E K, Hyde M, Kendall G, et al. A survey of hyper-heuristics[R]. Nottingham: University of Nottingham, 2009. [6] 范华丽, 熊禾根, 蒋国璋, 等. 动态车间作业调度问题中调度规则算法研究综述[J]. 计算机应用研究, 2016, 33(3):648-653 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3695.2016.03.002Fan Huali, Xiong Hegen, Jiang Guozhang, et al. Survey of dispatching rulesfor dynamic job-shop scheduling problem[J]. Application Research of Computers, 2016, 33(3): 648-653 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3695.2016.03.002 [7] Mouelhi-Chibani W, Pierreval H. Training a neural network to select dispatching rules in real time[J]. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 2010, 58(2): 249-256. [8] Golmohammadi D. A neural network decision-making model for job-shop scheduling[J]. International Journal of Production Research, 2013, 51(17): 5142-5157. doi: 10.1080/00207543.2013.793476 [9] Zhang Liping, Hu Yifan, Wang Chuangjian, et al. Effective dispatching rules mining based on near-optimal schedules in intelligent job shop environment[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Systems, 2022, 63: 424-438. doi: 10.1016/j.jmsy.2022.04.019 [10] Holland JH. Adaptation in natural and artificial systems: an introductory analysis with applications to biology, control, and artificial intelligence[M]. Cambridge: The MIT Press, 1992. -




 下载:
下载: