Trapezoidal double ridge waveguide slow wave structure for 340 GHz backward wave oscillator
-
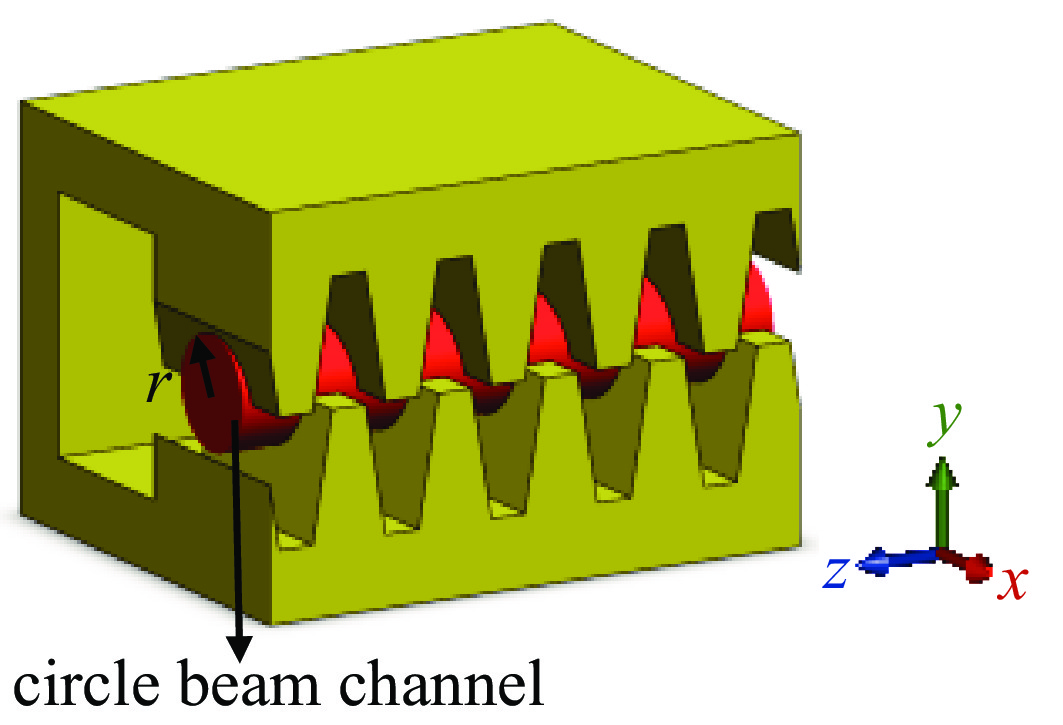
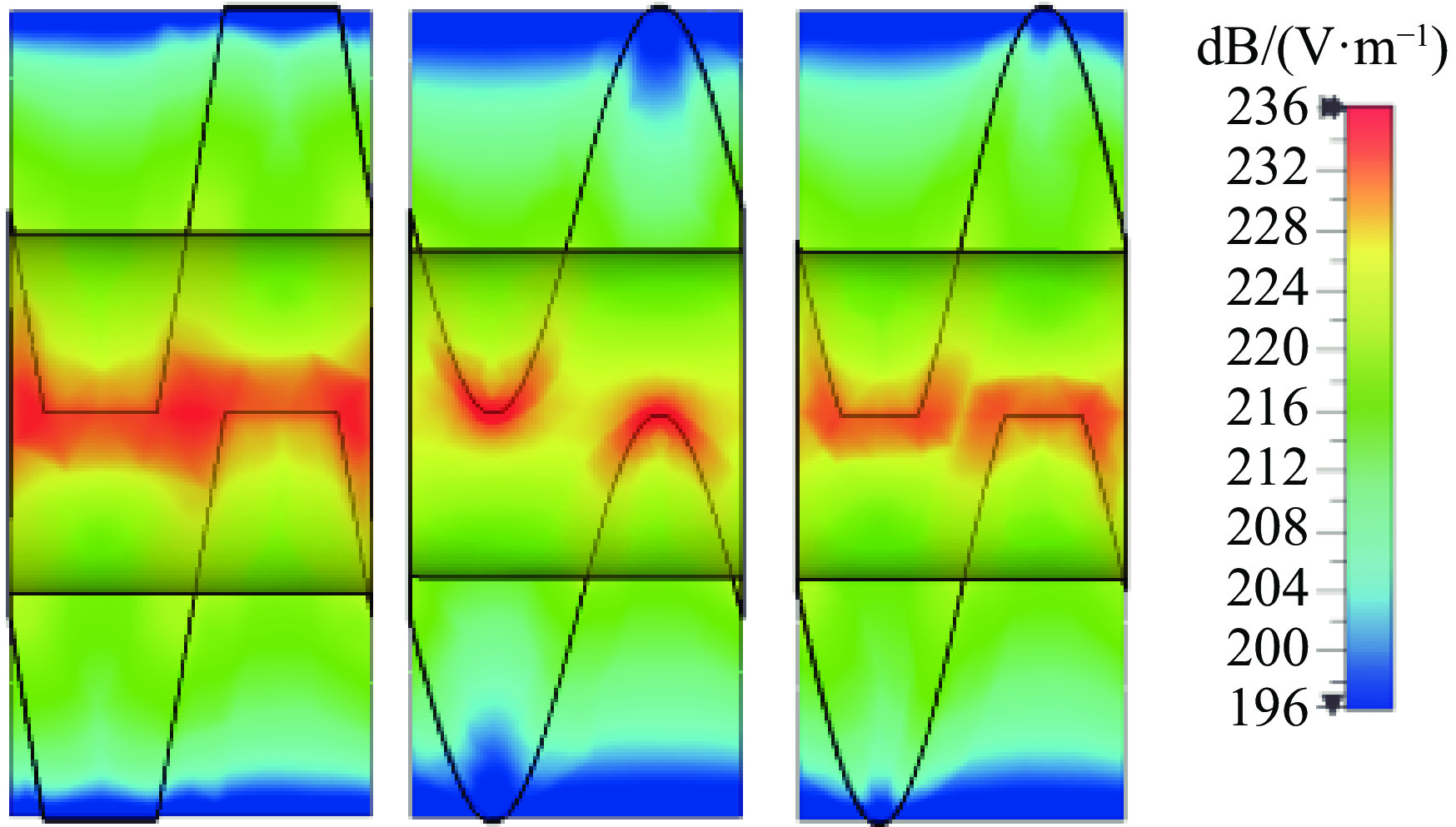
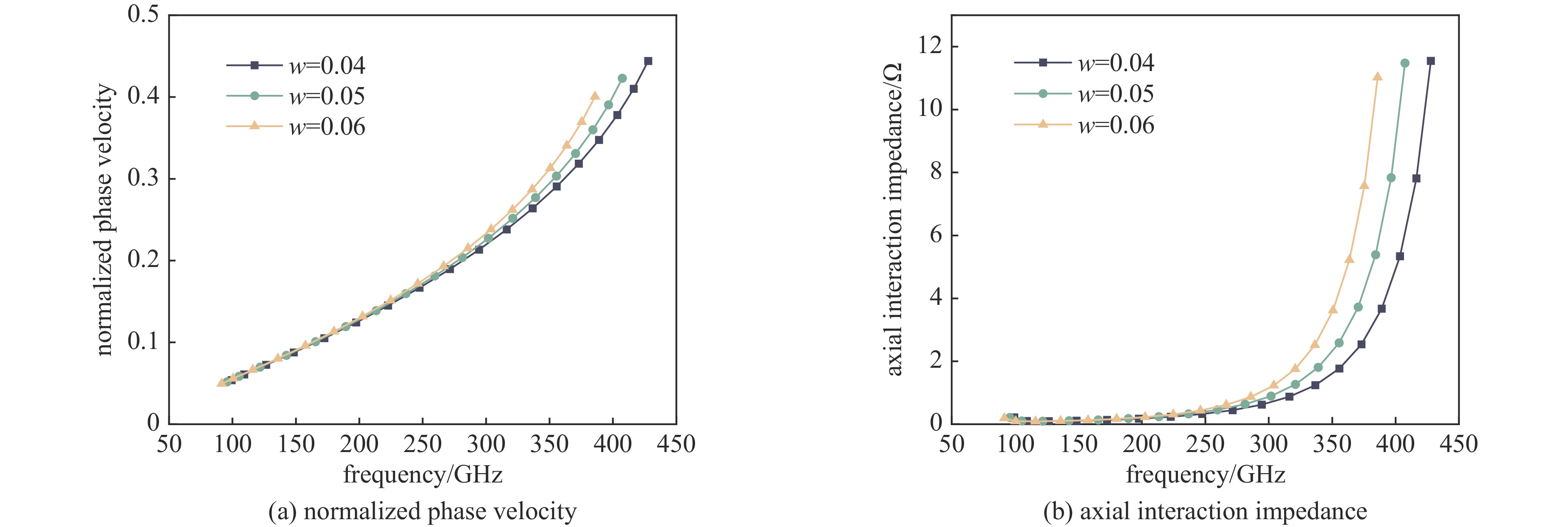
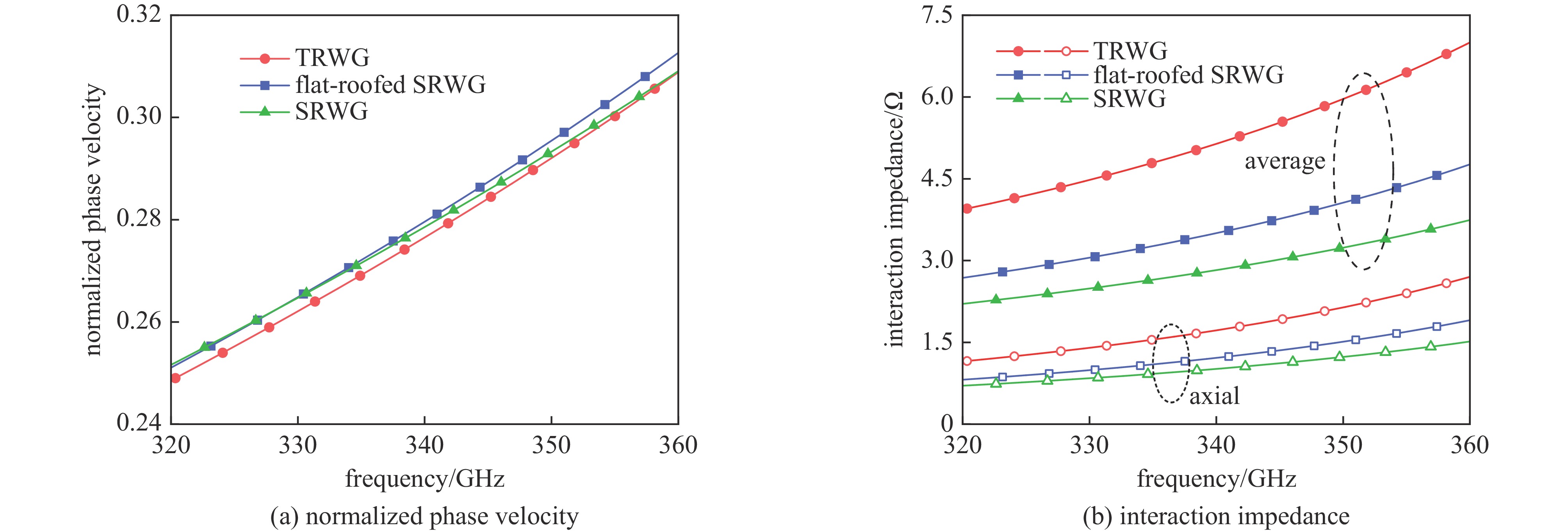
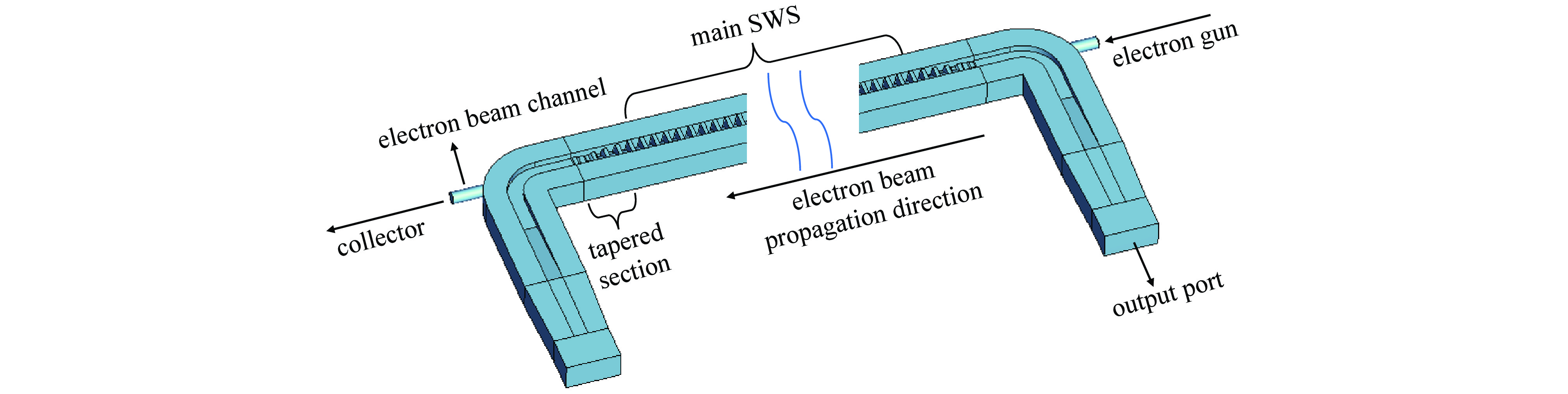
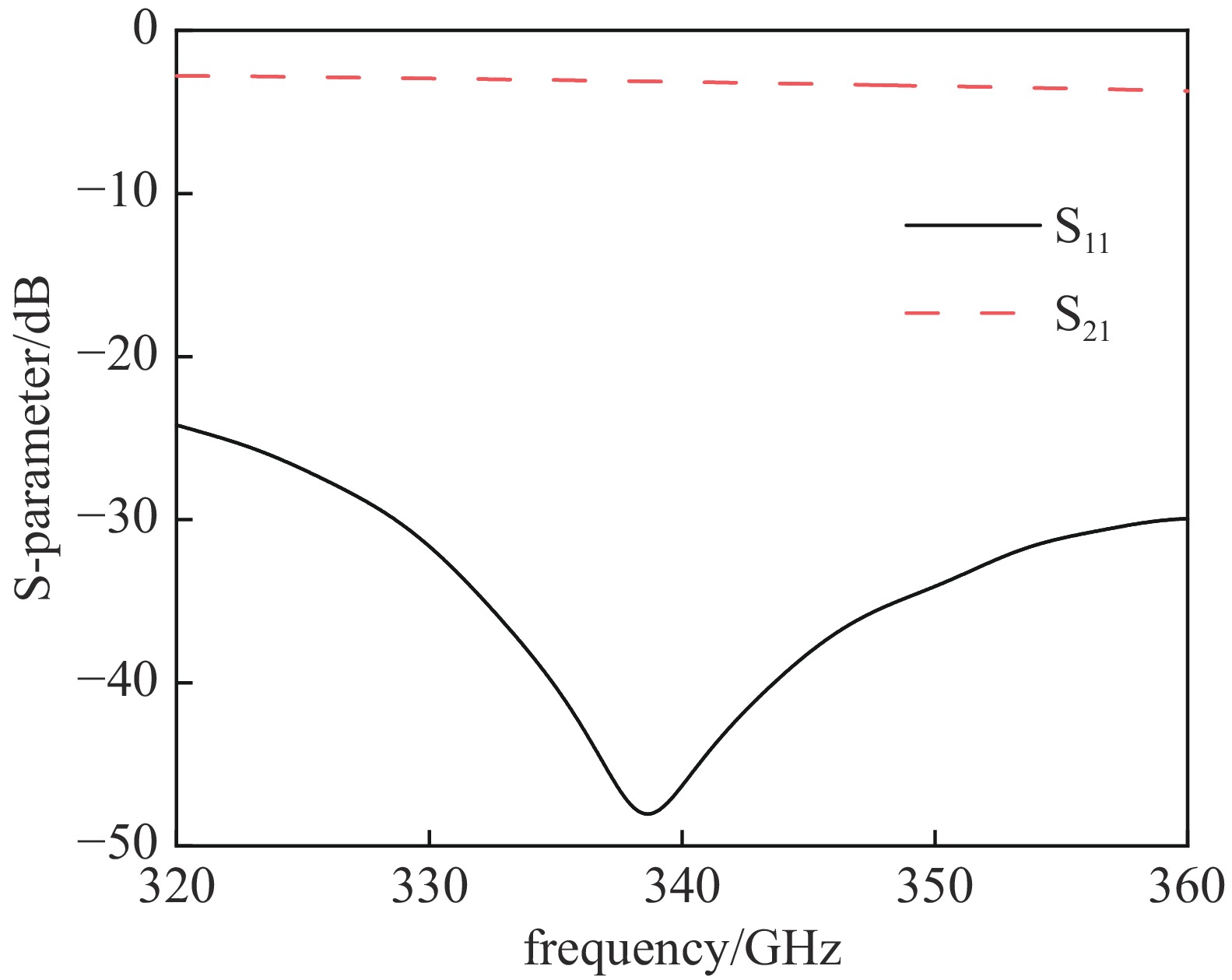
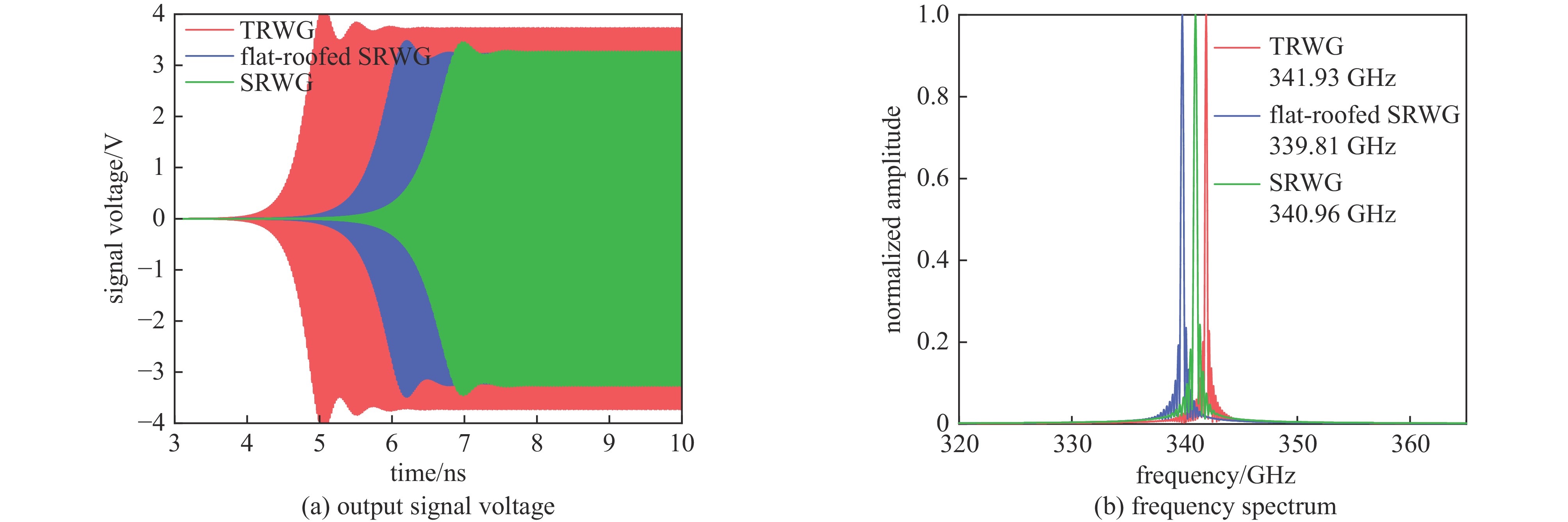
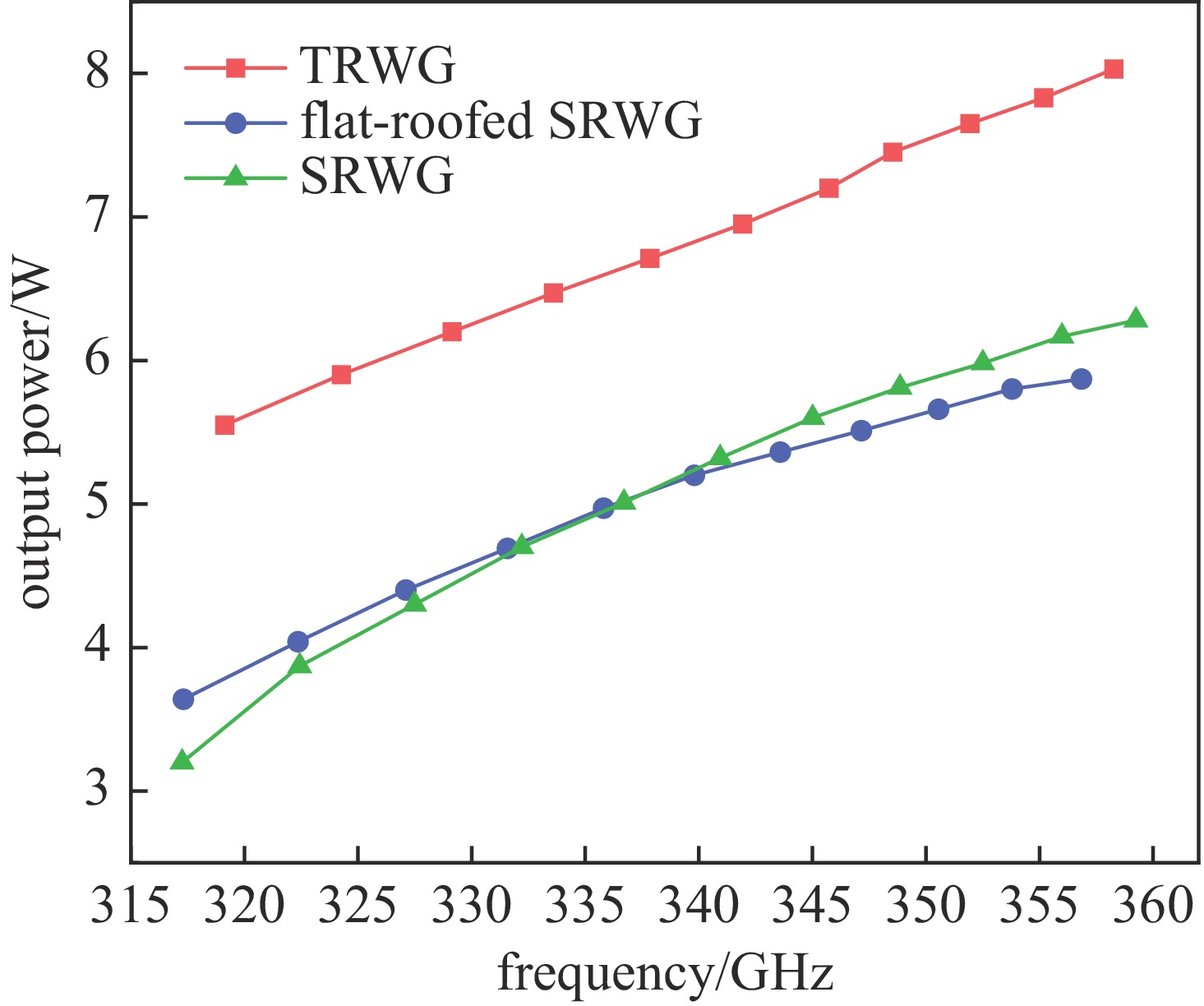
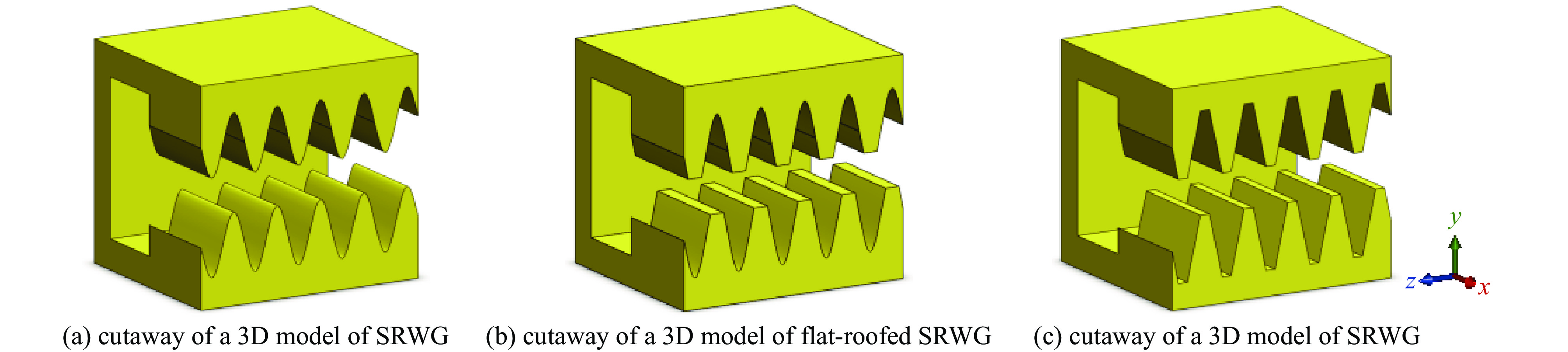
摘要: 为进一步提高返波管的耦合阻抗和输出功率,提出了一种梯形双脊波导慢波结构。与正弦双脊波导和平顶型正弦双脊波导相比,在归一化相速度基本一致时,梯形双脊波导的电子注通道中心轴线耦合阻抗和截面平均耦合阻抗都得到了显著提升。仿真结果显示,在320~360 GHz频带范围内,其平均耦合阻抗较正弦双脊波导提升78.33%~86.97%,较平顶型正弦双脊波导提升至少46.65%。在相同工作条件及频带范围内,梯形双脊波导返波管在340 GHz频段的输出功率为5.55~8.03 W,比正弦双脊波导返波管提升26.97%~73.44%,比平顶型正弦双脊波导返波管提升33.65%~52.47%。此时三种返波管均为最佳管长,梯形双脊波导返波管可比另两种结构缩短至少16.5%。Abstract: A trapezoidal double ridge waveguide slow wave structure has been proposed to further enhance the interaction impedance and output power of backward wave oscillators. Compared to conventional sine double ridge waveguide and flat-roofed sine double ridge waveguide, significant improvements in both the axial interaction impedance at the center of the electron beam channel and the average interaction impedance across the cross-section are observed, while maintaining a similar normalized phase velocity. Simulation results indicate that within the frequency range of 320~360 GHz, the average interaction impedance of the trapezoidal double ridge waveguide is increased by 78.33% to 86.97% compared to the sine double ridge waveguide, and by at least 46.65% compared to the flat-roofed sine double ridge waveguide. Under the same operating conditions and frequency range, the output power of the trapezoidal double ridge waveguide backward wave oscillator in the 340 GHz band is measured to be 5.55~8.03 W, representing an increase of 26.97% to 73.44% compared to the sine double ridge waveguide and an enhancement of 33.65% to 52.47% over the flat-roofed sine double ridge waveguide. At this point, all three types of backward wave oscillators are optimized for tube length, with the trapezoidal double ridge waveguide backward wave oscillator being at least 16.5% shorter than the other two structures.
-
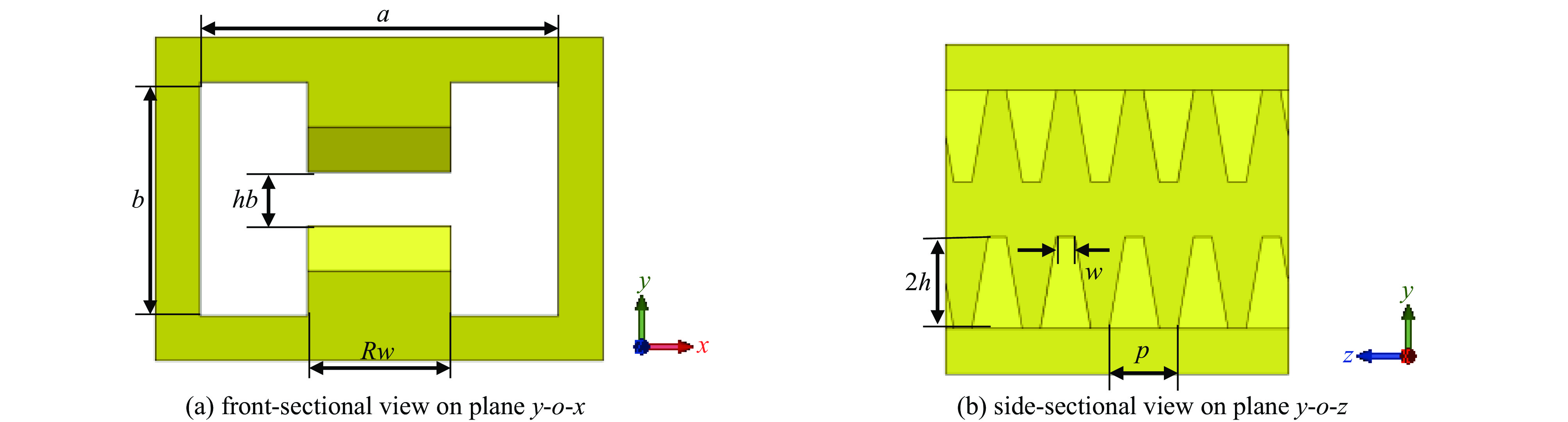
表 1 梯形双脊波导尺寸参数
Table 1. Parameters of TRWG
parameter value/mm width of TRWG a 0.80 height of TRWG b 0.36 width of ridge Rw 0.20 width of trapezoidal upper base w 0.05 height of trapezoid h 0.09 period length p 0.16 radius of circle beam channel r 0.08 height of sheet beam channel hb 0 -
[1] 王文祥. 微波工程技术[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2009: 1-677Wang Wenxiang. Microwave engineering technology[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2009: 1-677 [2] Abrams R H, Levush B, Mondelli A A, et al. Vacuum electronics for the 21st century[J]. IEEE Microwave Magazine, 2001, 2(3): 61-72. doi: 10.1109/6668.951550 [3] Qiu J X, Levush B, Pasour J, et al. Vacuum tube amplifiers[J]. IEEE Microwave Magazine, 2009, 10(7): 38-51. doi: 10.1109/MMM.2009.934517 [4] Chong C K, Menninger W L. Latest advancements in high-power millimeter-wave helix TWTs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2010, 38(6): 1227-1238. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2010.2041940 [5] Hu Linlin, Cai Jinchi, Chen Hongbin. Applications and development of terahertz backward wave oscillators[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2016, 44(4): 974-982. [6] Tucek J C, Basten M A, Gallagher D A, et al. 220 GHz power amplifier development at Northrop Grumman[C]//Proceedings of the IVEC 2012. 2012: 553-554. [7] Tucek J, Kreischer K, Gallagher D, et al. Development and operation of a 650 GHz folded waveguide source[C]//Proceedings of 2007 IEEE International Vacuum Electronics Conference. 2007: 1-2. [8] Zhou Quanfeng, Song Rui, Lei Wenqiang, et al. Development of a 0.22THz folded waveguide travelling wave tube[C]//Proceedings of 2015 IEEE International Vacuum Electronics Conference. 2015: 1-2. [9] Wang Zhanliang, Zhou Qing, Gong Huarong, et al. Development of a 140-GHz folded-waveguide traveling-wave tube in a relatively larger circular electron beam tunnel[J]. Journal of Electromagnetic Waves and Applications, 2017, 31(17): 1914-1923. doi: 10.1080/09205071.2017.1341346 [10] Tian Yanyan, Yue Lingna, Xu Jin, et al. A novel slow-wave structure—Folded rectangular groove waveguide for millimeter-wave TWT[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 2012, 59(2): 510-515. doi: 10.1109/TED.2011.2175929 [11] Field M, Kimura T, Atkinson J, et al. Development of a 100-W 200-GHz high bandwidth mm-wave amplifier[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 2018, 65(6): 2122-2128. doi: 10.1109/TED.2018.2790411 [12] Zhang Changqing, Pan Pan, Cai Jun, et al. Demonstration of a PCM-focused sheet beam TWT amplifier at G-band[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 2023, 70(6): 2798-2803. doi: 10.1109/TED.2022.3233291 [13] 赖剑强. 交错双栅慢波结构的应用研究[D]. 成都: 电子科技大学, 2012: 69-90Lai Jianqiang. Research on applications of staggered double vane slow-wave structure[D]. Chengdu: University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2012: 69-90 [14] 赖剑强, 魏彦玉, 黄民智, 等. W波段交错双栅返波振荡器高频系统[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2012, 24(9):2164-2168 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20122409.2164Lai Jianqiang, Wei Yanyu, Huang Minzhi, et al. RF circuit for W-band staggered double vane backward wave oscillator[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2012, 24(9): 2164-2168 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20122409.2164 [15] 冯霖琦, 岳玲娜, 徐进, 等. 一种宽带瓦量级交错双栅脊波导返波振荡器的研究[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2023, 35:123001Feng Linqi, Yue Lingna, Xu Jin, et al. Investigation of a wide band watt level backward wave oscillator based on ridged double staggered grating waveguide[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2023, 35: 123001 [16] Xu Xiong, Wei Yanyu, Shen Fei, et al. Sine waveguide for 0.22-THz traveling-wave tube[J]. IEEE Electron Device Letters, 2011, 32(8): 1152-1154. doi: 10.1109/LED.2011.2158060 [17] Zhang Luqi, Wei Yanyu, Jiang Xuebing, et al. A truncated sine waveguide for G-band TWT[C]//Proceedings of 2017 Eighteenth International Vacuum Electronics Conference. 2017: 1-2. [18] Lu Zhigang, Zhu Meiling, Ding Kesen, et al. Investigation of double tunnel sine waveguide slow-wave structure for terahertz dual-beam TWT[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 2020, 67(5): 2176-2181. doi: 10.1109/TED.2020.2981992 [19] Zhang Luqi, Wei Yanyu, Guo Guo, et al. A ridge-loaded sine waveguide for G-band traveling-wave tube[J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2016, 44(11): 2832-2837. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2016.2605161 [20] Zhang Luqi, Wei Yanyu, Guo Guo, et al. An ultra-broadband watt-level terahertz BWO based upon novel sine shape ridge waveguide[J]. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 2016, 49: 235102. doi: 10.1088/0022-3727/49/23/235102 [21] Yue Lingna, Bai Ziqing, Feng Linqi, et al. Investigation of a 300–350 GHz BWO with flat-roofed sine double ridge waveguide and Brewster window[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 2024, 71(11): 7049-7055. doi: 10.1109/TED.2024.3453784 -




 下载:
下载: