A novel metamaterial absorber based on double magnetic media and mortise structure
-
摘要: 针对薄型化微波吸波材料在低频段带宽受限的技术瓶颈,本研究提出一种基于双层磁性介质与榫眼结构的新型吸波体设计方案,重点突破材料厚度与吸收带宽间的制约关系,实现L/S频段电磁波的高效吸收。研究采用磁性介质基板构建双层异质结构,结合表面周期排布的榫眼式金属谐振单元,利用磁损耗与结构谐振的协同效应增强电磁能量耗散。仿真结果表明,该吸波体在1.16~2.82 GHz频段内吸收率超过90%,有效覆盖L波段并延伸至S波段部分频段,在薄层条件下实现了1.66 GHz的宽频吸收,解决了低频段吸波材料厚度与带宽的固有矛盾,可为新一代薄型宽带吸波体的工程应用提供可行方案。Abstract:
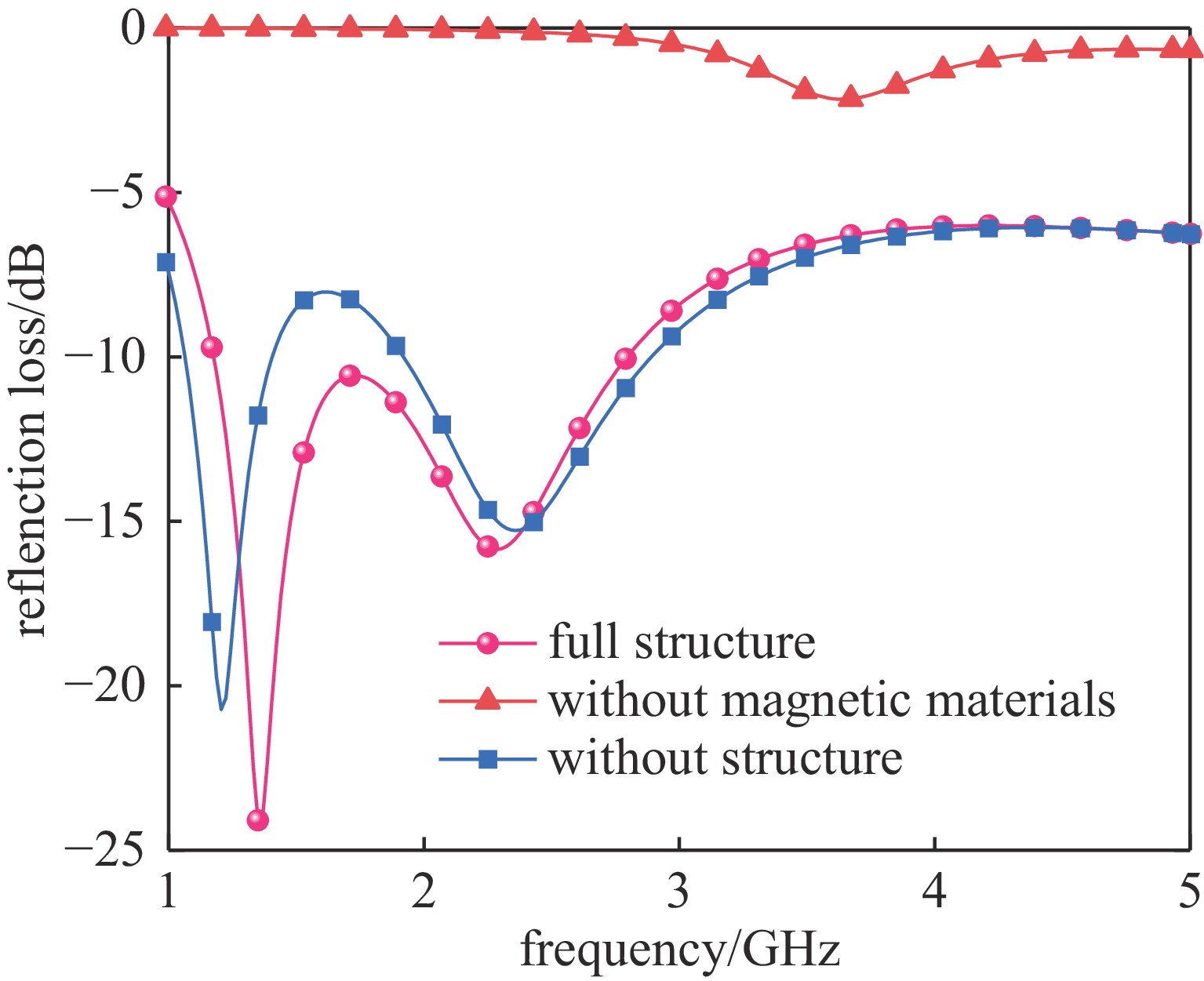
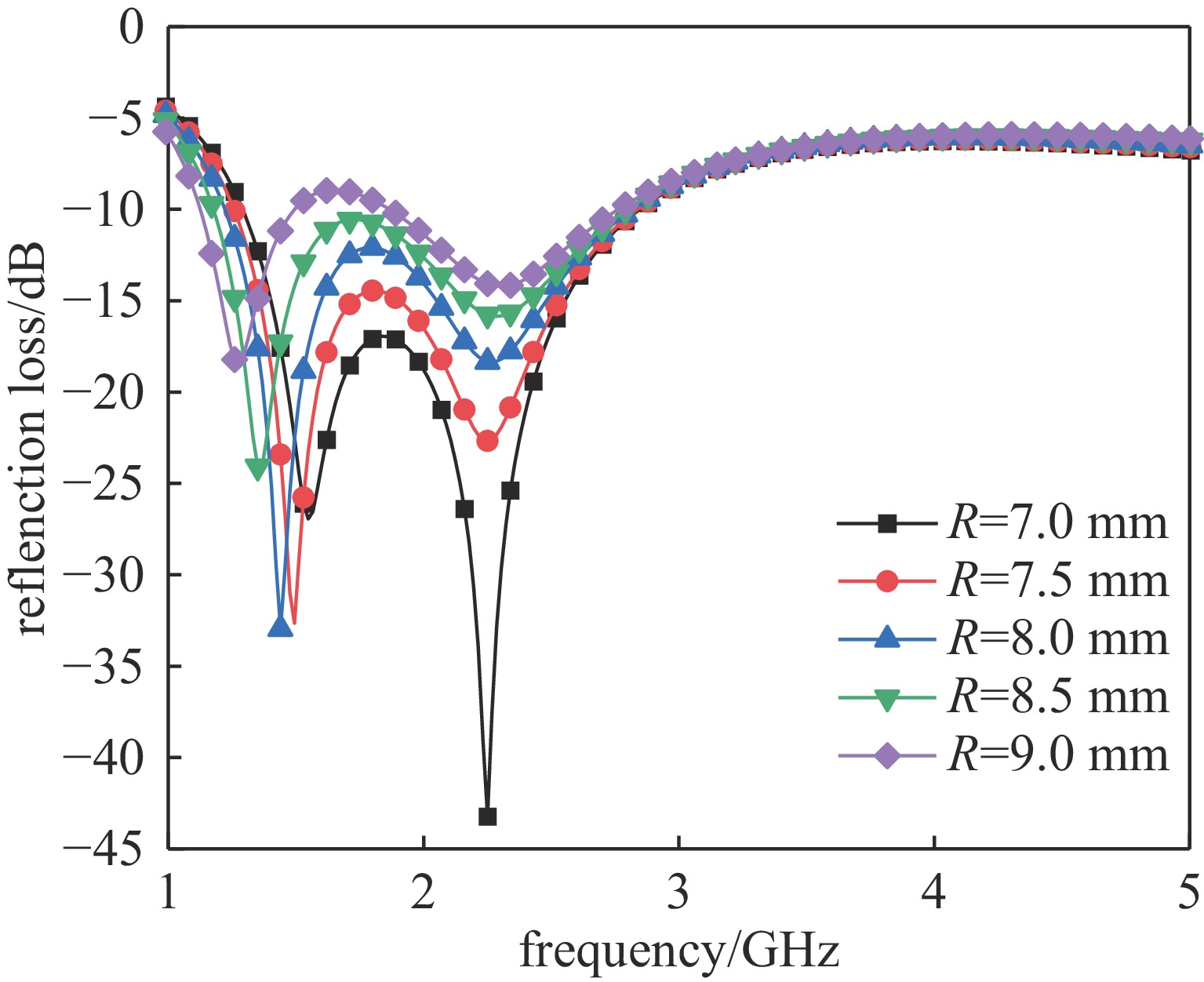
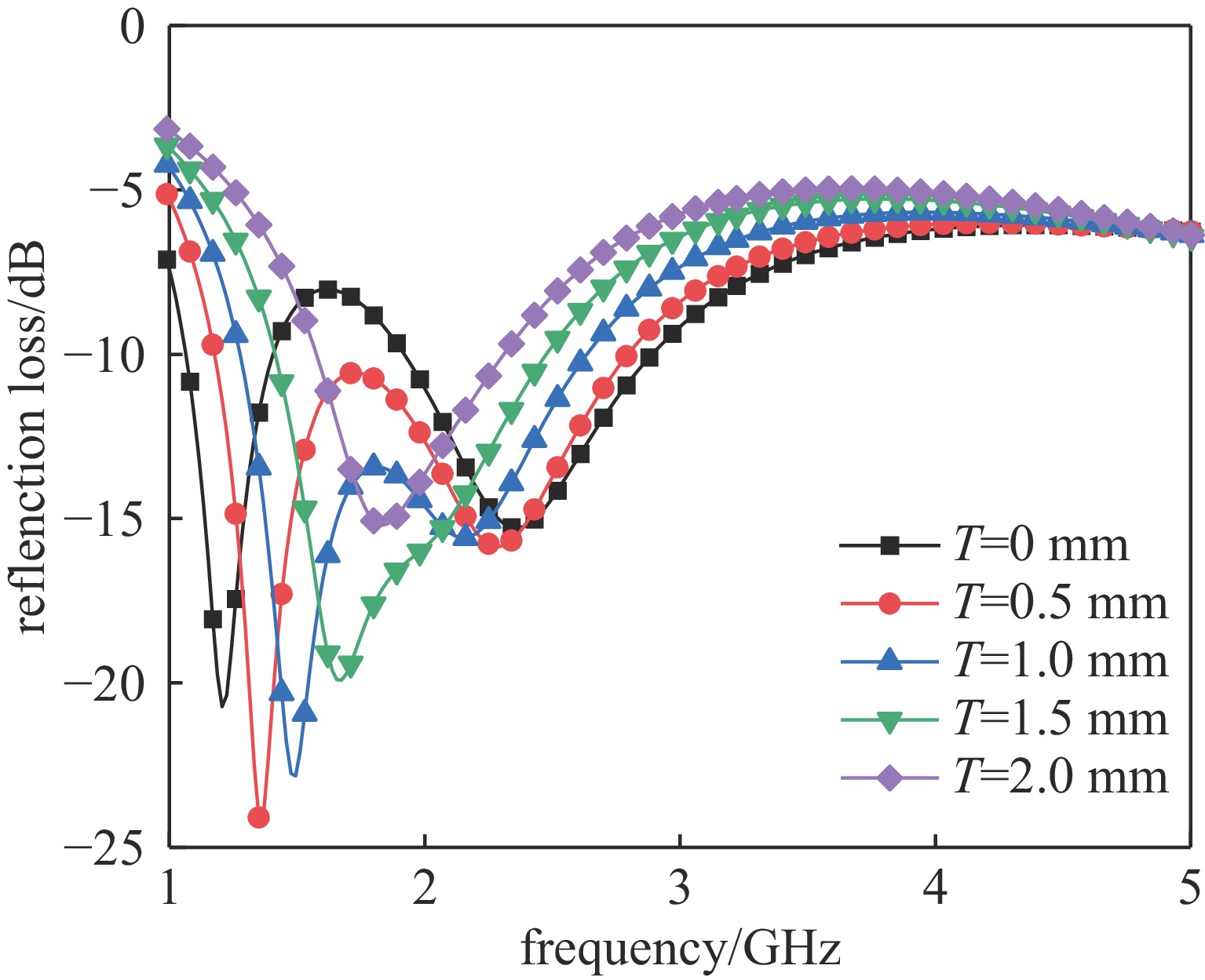
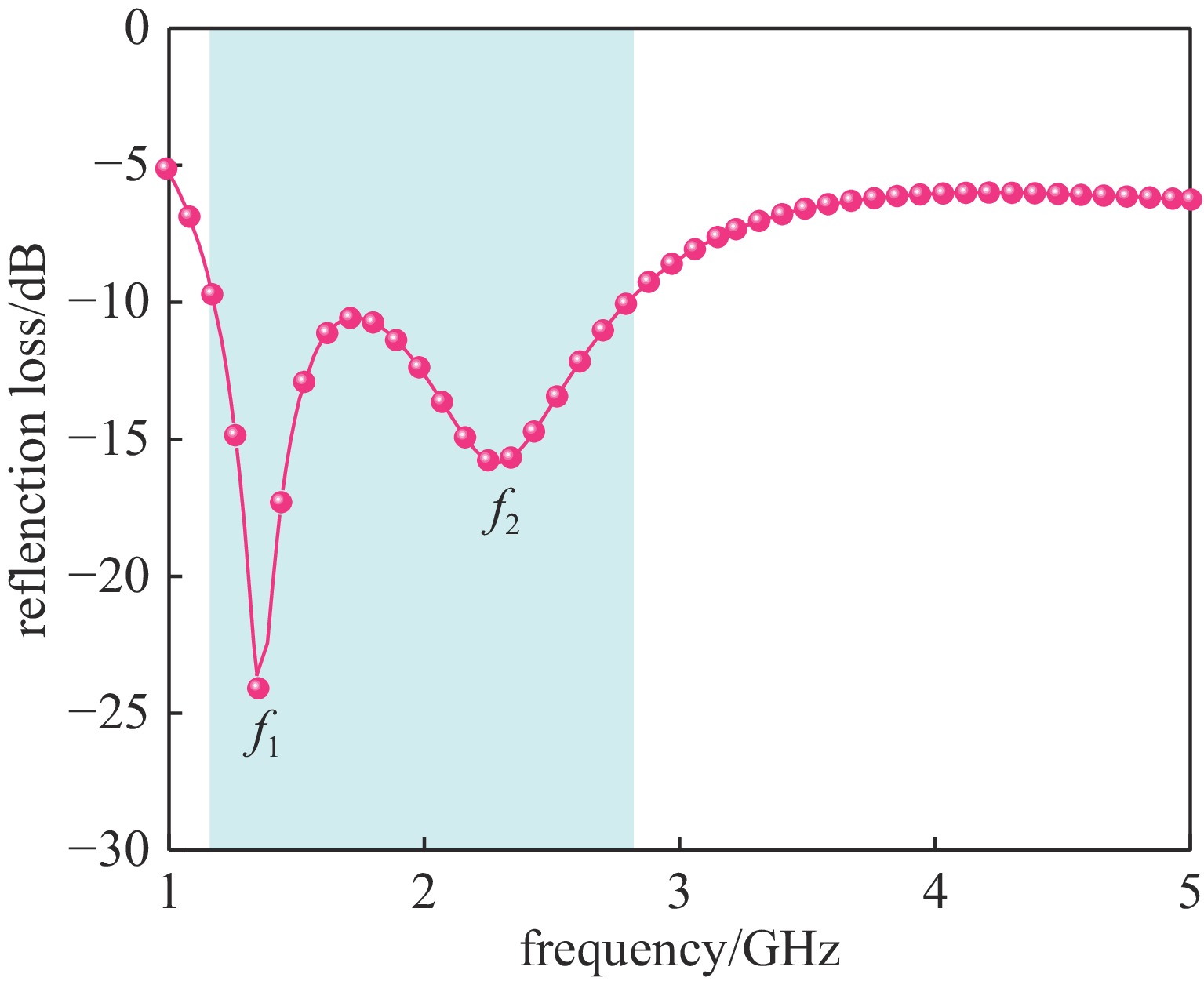
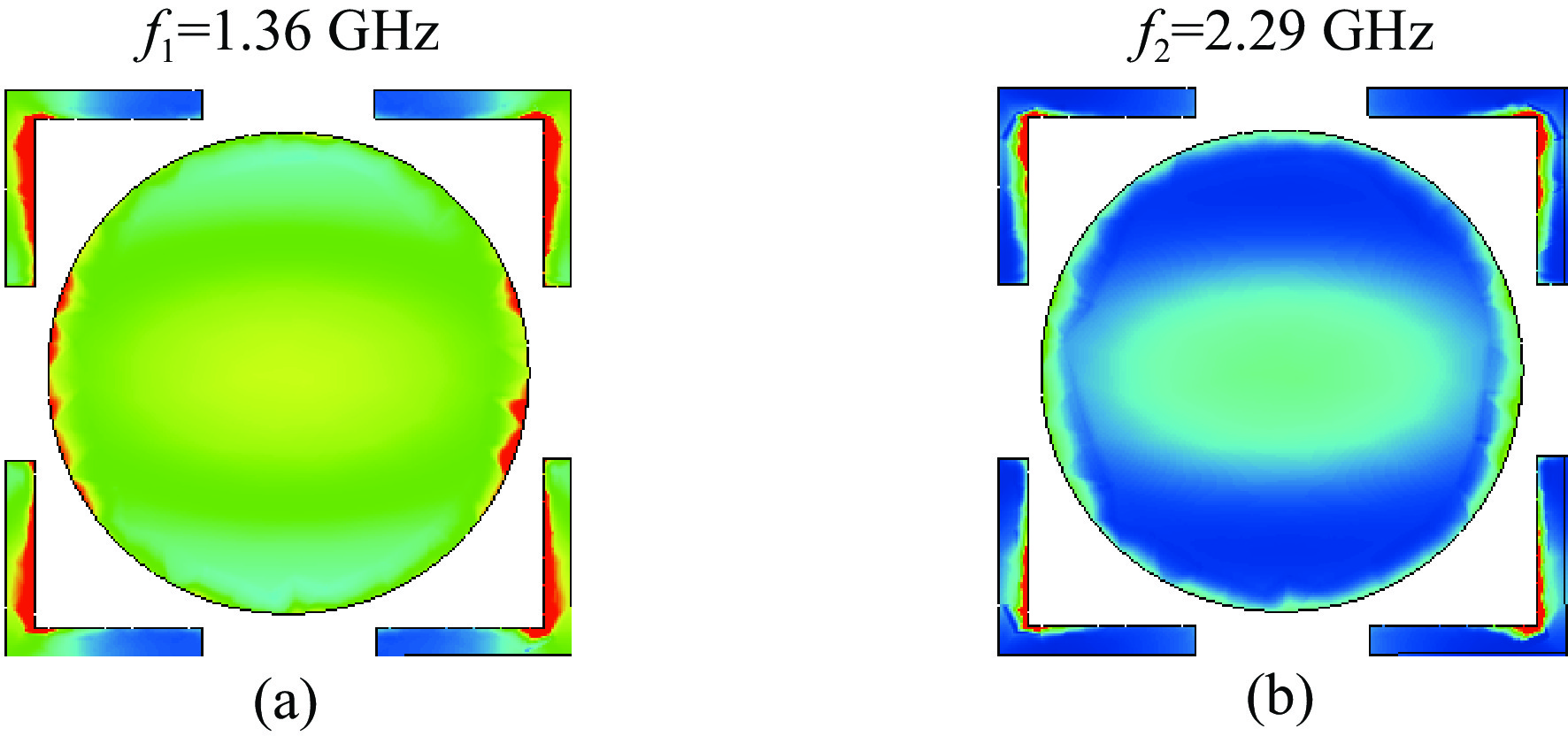
Background In the design process of microwave absorbing structures, due to the larger wavelength of low-frequency electromagnetic waves, the thickness of the corresponding absorbing body will also increase. Therefore, achieving low-frequency broadband absorption in the microwave band with a thin thickness is a challenge.Purpose To address the technical bottleneck of limited bandwidth in thin microwave absorbing materials at low frequenciesthis study proposes a new absorbing body design scheme based on a double-layer magnetic medium and mortise structure, focusing on breaking through the constraint relationship between material thickness and absorption bandwidth to achieve efficient absorption of electromagnetic waves in the L/S frequency bands.Methods The metamaterial is constructed with a double-layer structure using magnetic material, combined with surface periodically arranged mortise-type metal resonant units, and utilizes the synergistic effect of magnetic loss and structural resonance to enhance electromagnetic energy dissipation.Results Simulation results show that within the working frequency band, there are two absorption peaks at f1=1.36 GHz and f2=2.29 GHz, and the absorption rate exceeds 90% in the 1.16-2.82 GHz frequency band, effectively covering the L band and extending to part of the S band. Under thin-layer conditions, it achieves a wideband absorption of 1.66 GHz, resolving the inherent contradiction between thickness and bandwidth of low-frequency absorbing materials.Conclusions The novel metamaterial absorber based on double magnetic media and mortise structure can provide a feasible solution for the engineering application of the next-generation thin broadband absorbing bodies.-
Key words:
- L/S band /
- microwave absorbing materials /
- metamaterials /
- magnetic materials
-
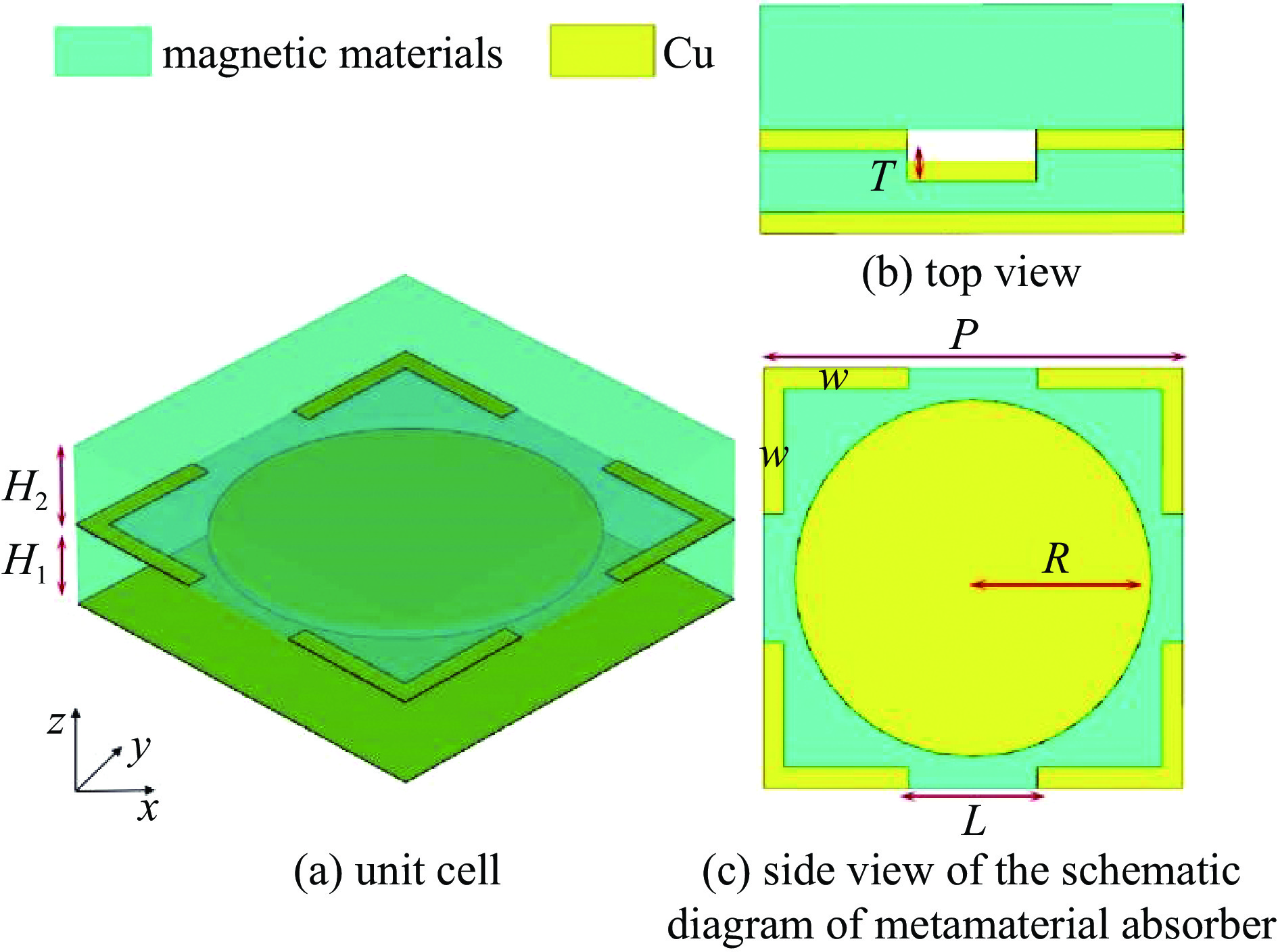
表 1 单元结构的尺寸参数
Table 1. Dimensional parameters of unit structure
Structure
ParametersParameter
Value/mmP 20 H1 1.9 H2 6 R 8.5 w 1 L 6.1 T 0.5 -
[1] 徐锐敏, 唐璞, 薛正辉, 等. 微波技术基础[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2009Xu Ruimin, Tang Pu, Xue Zhenghui, et al. Fundamentals of microwave technology[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2009 [2] Li Changzhi, Peng Zhengyu, Huang T Y, et al. A review on recent progress of portable short-range noncontact microwave radar systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2017, 65(5): 1692-1706. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2017.2650911 [3] Skolnik M. Role of radar in microwaves[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2002, 50(3): 625-632. doi: 10.1109/22.989947 [4] Anderson D A, Sapiro R E, Raithel G. An atomic receiver for AM and FM radio communication[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2021, 69(5): 2455-2462. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2020.2987112 [5] Jones D A, Lelyveld T P, Mavrofidis S D, et al. Microwave heating applications in environmental engineering—a review[J]. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 2002, 34(2): 75-90. doi: 10.1016/S0921-3449(01)00088-X [6] Warwick J W, Pearce J B, Evans D R, et al. Planetary radio astronomy observations from voyager 1 near Saturn[J]. Science, 1981, 212(4491): 239-243. doi: 10.1126/science.212.4491.239 [7] 李希, 王东俊, 张袁, 等. 超宽带薄型频率选择表面吸波体设计[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2024, 36:063001 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202436.230443Li Xi, Wang Dongjun, Zhang Yuan, et al. Design of an ultra-wideband thin frequency selective surface absorber[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2024, 36: 063001 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202436.230443 [8] Sambhav S, Ghosh J. Low profile polarization-insensitive wideband rasorber with in-band transmission[J]. International Journal of RF and Microwave Computer-Aided Engineering, 2022, 32: e23444. [9] Liao Kun, Liu Shaobin, Shao Xianxian, et al. An ultra-wideband dual-band hybrid frequency-selective rasorber[J]. International Journal of RF and Microwave Computer-Aided Engineering, 2022, 32: e23197. [10] Cheng Yongzhi, He Bo, Zhao Jingcheng, et al. Ultra-thin low-frequency broadband microwave absorber based on magnetic medium and metamaterial[J]. Journal of Electronic Materials, 2017, 46(2): 1293-1299. doi: 10.1007/s11664-016-5115-z [11] Wang Zhenxu, Wang Jiafu, Han Yajuan, et al. Wideband absorption at low microwave frequencies assisted by magnetic squeezing in metamaterials[J]. Frontiers in Physics, 2020, 8: 595642. doi: 10.3389/fphy.2020.595642 [12] Zhang Zilong, Zhang Lei, Chen Xiqiao, et al. Broadband metamaterial absorber for low-frequency microwave absorption in the S-band and C-band[J]. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 2020, 497: 166075. doi: 10.1016/j.jmmm.2019.166075 [13] Ni Xiaomin, Zheng Zhong, Xiao Xiukun, et al. Silica-coated iron nanoparticles: shape-controlled synthesis, magnetism and microwave absorption properties[J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2010, 120(1): 206-212. doi: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2009.10.047 [14] Wei Guoke, Wang Tao, Zhang Hang, et al. Enhanced microwave absorption of barium cobalt hexaferrite composite with improved bandwidth via c-plane alignment[J]. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 2019, 471: 267-273. doi: 10.1016/j.jmmm.2018.09.063 [15] Huang Wanqiao, Zhu Zhenghou. Broadband metamaterial absorbers based on magnetic composites[J]. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 2023, 576: 170792. doi: 10.1016/j.jmmm.2023.170792 -




 下载:
下载: