Comparison and analysis of the electromagnetic radiation, ionizing radiation and other physical technologies for disinfection and sterilization
-
摘要:
消毒灭菌技术广泛应用于食品工业、医疗领域、水处理等方面。相对于传统化学和热效应的消毒灭菌方法,γ射线、X射线、电子束、微波、低温等离子体、紫外线、高压脉冲电场等物理手段具有不污染环境、消毒灭菌温度低、没有化学残留物等优点而日益受到重视。但这些物理技术手段各有不同,本文首先介绍了γ射线、X射线、电子束、微波、低温等离子体、紫外线、高压脉冲电场等消毒灭菌的技术原理,然后对比了各自优缺点和应用领域。每种方法都有优势和不足,应针对不同的消毒灭菌对象而选择不同的方式。最后,展望了消毒灭菌的发展方向,提出了消毒灭菌在家庭日常消毒、医疗垃圾处理、有人状态下的室内空气消毒等方面的迫切需求。
Abstract:Disinfection and sterilization technologies are of great significance in the food industry, medical field and water treatment, et al. Compared with traditional chemical and thermal methods, physical disinfection and sterilization approaches such as γ-rays, X-rays, electron beams, microwaves, low-temperature plasmas, ultraviolet rays and high-voltage pulsed electric fields have the advantages of no environmental pollution, low sterilization temperatures, no chemical residues, and so on. These physical disinfection and sterilization approaches are getting increasing concerns because of unique advantages. In this paper, the mechanisms of present physical disinfection and sterilization technics were summarized. The advantages and disadvantages of these physical means as well as their application areas are reviewed. Based on the superiorities and drawbacks of each method, different approaches should be adopted for the disinfection and sterilization of specific objects. Moreover, this paper highlights the trends on development of physical disinfection and sterilization approaches and proposes the extensive demands of the physical approaches on various aspects of our life.
-
图 1 用于辐照的集成电子束源[14]
Figure 1. Source of e-beam. Beams are extracted into a chamber for irradiation
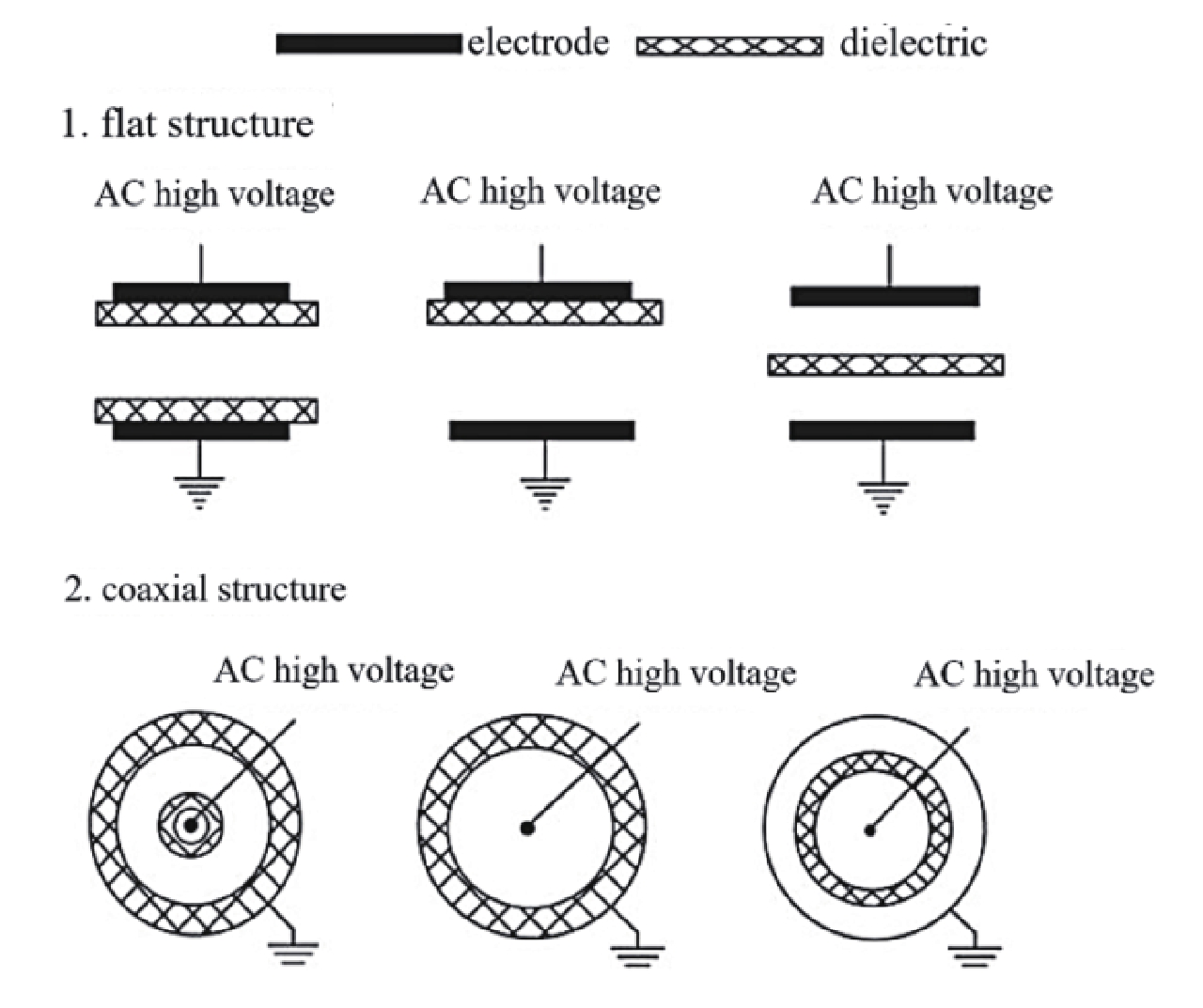
图 2 常见介质阻挡放电的电极结构[24]
Figure 2. Configurations of dielectric barrier electrodes
图 3 细胞膜崩解过程[48]
Figure 3. Schematic diagram of reversible and irreversible breakdown
表 1 各种物理消毒灭菌方法性能比较
Table 1. Performance comparison of various irradiation sterilization methods
γ射线 X射线 高能电子束 重频低能电子束 微波 低温等离子体 紫外线 高压脉冲电场 产生方式 放射性核素60Co或137Cs源(以60Co源为主) X光机或在电子加速器上安装转换靶 高能电子加速器 高重频低能电子发生器(如SINUS-320) 微波电子管(常用磁控管和速调管) 介质阻挡放电或大气压下的等离子体射流 一般采用紫外线灯 高压脉冲电源(矩形波、指数衰减波、振荡波) 成本 建造和废料处理成本高 成本较高 成本较高 成本相对较低,可移动或集成到生
产线较低 较低 低廉 操作维护成本低 穿透能力 强 强 较弱 较弱 较强,但可能存在冷热点 弱 弱 能穿透两电极之间区域 对人体危害及防护 连续产生γ射线,对人体有危害,防护要求高 X射线的产生可控,设备在运行时防护要求高 可以通过开关控制电子束的产生,设备在运行时防护要求较高 对人体有一定危害,需要进行防护 需进行适当防护,切断电源后活性粒子很快消失 对皮肤有损害,空气消毒应在无人状态进行 对人体危害较小 其他 若废料处理不当容易造成泄漏;需要不断补充
新源会对高分子材料造成损坏,对高分子材料消毒前需考察材料的抗辐照老化性能 热效应和非热效应共同作用 主要是紫外线和活性粒子的灭菌作用 处理时间很短;需控制工作场强,防止介质击穿 表 2 各种物理消毒灭菌方法适用领域
Table 2. Applications of various irradiation sterilization methods
γ射线、X射线 电子束 微波 低温等离子体 紫外线 高压脉冲电场 食品消毒灭菌 √(用于大包装物品) √ √ √(食品表面、液体食品) √ 水净化处理 √ √ √(新兴) √(常用) √(新兴) 医疗器械消毒灭菌 √ √ 医疗垃圾处理 √ √ 药物消毒灭菌 √ √ 物品表面处理 √ √ 空气消毒 √(新兴) √(常用) -
[1] Wholesomeness of irradiated foods: Report of a joint FAO/IAEA/WHO Expert Committee[R]. World Health Organization Technical Report, 1981, 659: 1-34. [2] Organization W H. High-dose irradiation: Wholesomeness of food irradiated with doses above 10 kGy[R]. Report of a Joint FAO/IAEA/WHO Study Group. World Health Organization Technical Report, 1999, 890: i-vi, 1-197. [3] 王晶晶. 电子束与γ射线辐照对象拔蚌微生物和品质影响的异同性[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2016: 1-2.Wang Jingjing. Effects of electron beam and gamma ray irradiation on the microbial diversity and quality of commercial fresh geoduck clam (Panopea abrupta)[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2016: 1-2 [4] 段鑫. X射线对生鲜牛肉的杀菌效果[D]. 上海: 上海海洋大学, 2011: 3-8.Duan Xin. Effect of X-ray irradiation on the sterilization of fresh beef[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Ocean University, 2011: 3-8 [5] 陈倩, 陈昭斌. 高能电子束辐照技术在消毒领域的应用[J]. 中国消毒学杂志, 2017, 34(10):966-969. (Chen Qian, Chen Zhaobin. Application of high energy electron beam irradiation in disinfection field[J]. Chinese Journal of Disinfection, 2017, 34(10): 966-969 [6] 夏文水, 钟秋平. 食品冷杀菌技术研究进展[J]. 中国食品卫生杂志, 2003, 15(6):539-544. (Xia Wenshui, Zhong Qiuping. Research progress in cold sterilization of foods[J]. Chinese Journal of Food Hygiene, 2003, 15(6): 539-544 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-8456.2003.06.022 [7] 宋卫东, 张宏娜, 陈海军, 等. 辐照在食品加工中的作用及应用[J]. 食品工业科技, 2011, 32(9):454-457. (Song Weidong, Zhang Hongna, Chen Haijun, et al. Quality assurance and case study of food irradiation by γ-ray[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2011, 32(9): 454-457 [8] 邓文敏, 陈浩, 裴颖, 等. 高能电子加速器在食品辐照加工中的应用分析[J]. 核农学报, 2012, 26(6):919-923. (Deng Wenmin, Chen Hao, Pei Ying, et al. The application analysis of high energy electron accelerator in food irradiation processing[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2012, 26(6): 919-923 doi: 10.11869/hnxb.2012.06.0919 [9] 王斐. 辐射加工用电子直线加速器控制系统的研究[D]. 北京: 机械科学研究总院, 2018: 6-10.Wang Fei. Research of electron linear accelerator control system for radiation processing[D]. Beijing: China Academy of Machinery Science and Technology Group Co., Ltd, 2018: 6-10. [10] 史戎坚. 电子加速器工业应用导论[M]. 北京: 中国质检出版社, 2012.Shi Rongjian. An introduction to electron accelerators and industrial applications[M]. Beijing: China Quality and Standards Press, 2012 [11] 邓桥, 陈昭斌. 高能电子束在医疗卫生用品消毒中的应用[J]. 中国消毒学杂志, 2018, 35(12):943-945. (Deng Qiao, Chen Zhaobin. Application of high energy electron beam in disinfection of medical and sanitary products[J]. Chinese Journal of Disinfection, 2018, 35(12): 943-945 doi: 10.11726/j.issn.1001-7658.2018.12.019 [12] 单张生. NBL-1010型电子加速器的辐照应用[J]. 核农学报, 2000, 14(6):353-358. (Shan Zhangsheng. Irradiation application of NBL-1010 electron accelerator[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2000, 14(6): 353-358 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8551.2000.06.007 [13] 王梁燕, 洪奇华, 孙志明, 等. 电子束辐照技术在生命科学中的应用[J]. 核农学报, 2018, 32(2):283-290. (Wang Liangyan, Hong Qihua, Sun Zhiming, et al. Application of electron beam irradiation technology in life sciences[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 32(2): 283-290 doi: 10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2018.02.0283 [14] Rostov V V, Barmin V V, Landl V F, et al. High-current pulsed-repetitive electron accelerator “SINUS-320”: Formation and diagnostics of a wide-aperture beam[J]. Russian Physics Journal, 2019, 62(7): 1253-1259. doi: 10.1007/s11182-019-01842-5 [15] 孙俊. 微波消毒技术在医疗废物集中处理工程中的应用[J]. 环境保护科学, 2007, 33(4):84-86. (Sun Jun. Application of microwave disinfection technique in medical waste centralized treatment engineering[J]. Environmental Protection Science, 2007, 33(4): 84-86 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-6216.2007.04.027 [16] 杨国峰, 周建新. 食品微波杀菌有关问题的探讨[J]. 食品科学, 2006, 27(10):593-596. (Yang Guofeng, Zhou Jianxin. Some discussions on microwave disinfect in food processing[J]. Food Science, 2006, 27(10): 593-596 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-6630.2006.10.152 [17] Bohr H, Bohr J. Microwave-enhanced folding and denaturation of globular proteins[J]. Physical Review E, 2000, 61(4): 4310-4314. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.61.4310 [18] Velizarov S, Raskmark P, Kwee S. The effects of radiofrequency fields on cell proliferation are non-thermal[J]. Bioelectrochemistry and Bioenergetics, 1999, 48(1): 177-180. doi: 10.1016/S0302-4598(98)00238-4 [19] Kozempel M F, Annous B A, Cook R D, et al. Inactivation of microorganisms with microwaves at reduced temperatures[J]. Journal of Food Protection, 1998, 61(5): 582-585. doi: 10.4315/0362-028X-61.5.582 [20] 史亚歌. 冷烟熏三文鱼热处理动力学及微波杀菌技术研究[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2015: 7-8.SHI Yage. Thermal treatment kinetics and microwave pasteurization technique of cold smoked salmon[D]. Yangling: Northwest A&F University, 2015: 7-8 [21] 樊伟伟, 黄慧华. 微波杀菌技术在食品工业中的应用[J]. 食品与机械, 2007, 23(1):143-147. (Fan Weiwei, Huang Huihua. Application of microwave sterilization in food industry[J]. Food & Machinery, 2007, 23(1): 143-147 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-5788.2007.01.042 [22] 贾建平, 刘克富, 朱业湘, 等. 大气压下低温等离子体灭菌消毒技术的研究[J]. 高电压技术, 2007, 33(2):116-119. (Jia Jianping, Liu Kefu, Zhu Yexiang, et al. Sterilization by non-thermal plasma at an atmospheric pressure[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2007, 33(2): 116-119 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6520.2007.02.028 [23] 李和平, 于达仁, 孙文廷, 等. 大气压放电等离子体研究进展综述[J]. 高电压技术, 2016, 42(12):3697-3727. (Li Heping, Yu Daren, Sun Wenting, et al. State-of-the-art of atmospheric discharge plasmas[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2016, 42(12): 3697-3727 [24] 王新新. 介质阻挡放电及其应用[J]. 高电压技术, 2009, 35(1):1-11. (Wang Xinxin. Dielectric barrier discharge and its applications[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2009, 35(1): 1-11 [25] 金杞糠. 脉冲低温等离子体射流用于灭菌和凝血的实验研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2018: 3-9.Jin Qikang. Experimental study on microorganism disinfection and blood coagulation using a pulsed cold plasma jet[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2018: 3-9. [26] 郑超. 低温等离子体和脉冲电场灭菌技术[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2013: 26-29.Zheng Chao. Non-thermal plasma and pulsed electric field induced disinfection[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2013: 26-29 [27] Moisan M, Barbeau J, Moreau S, et al. Low-temperature sterilization using gas plasmas: A review of the experiments and an analysis of the inactivation mechanisms[J]. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 2001, 226(1/2): 1-21. [28] 赵会超, 低温等离子体技术应用研究[D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2013: 28-29.ZHAO Huichao. Research on application of low temperature plasma technology[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2013: 28-29. [29] Halfmann H, Denis B, Bibinov N, et al. Identification of the most efficient VUV/UV radiation for plasma based inactivation of Bacillus atrophaeus spores[J]. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 2007, 40(19): 5907-5911. doi: 10.1088/0022-3727/40/19/019 [30] Kong M G, Kroesen G, Morfill G, et al. Plasma medicine: an introductory review[J]. New Journal of Physics, 2009, 11: 115012. doi: 10.1088/1367-2630/11/11/115012 [31] Laroussi M, Leipold F. Evaluation of the roles of reactive species, heat, and UV radiation in the inactivation of bacterial cells by air plasmas at atmospheric pressure[J]. International Journal of Mass Spectrometry, 2004, 233(1-3): 81-86. doi: 10.1016/j.ijms.2003.11.016 [32] 贾建平. 介质阻挡放电等离子体灭菌消毒实验研究[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2007: 51-52.Jia Jianping. Sterilization by non-thermal plasma with the dielectric barrier discharge[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science & Technology, 2007: 51-52. [33] Fridman G, Brooks A D, Balasubramanian M, et al. Comparison of direct and indirect effects of non-thermal atmospheric-pressure plasma on bacteria[J]. Plasma Processes and Polymers, 2007, 4(4): 370-375. doi: 10.1002/ppap.200600217 [34] Guo J, Huang K, Wang J. Bactericidal effect of various non-thermal plasma agents and the influence of experimental conditions in microbial inactivation: A review[J]. Food Control, 2015, 50(4): 482-490. [35] 张晔, 刘志伟, 谭兴和, 等. 冷等离子体食品杀菌应用研究进展[J]. 中国酿造, 2019, 38(1):20-24. (Zhang Ye, Liu Zhiwei, Tan Xinghe, et al. Research progress of cold plasma application in food sterilization[J]. China Brewing, 2019, 38(1): 20-24 doi: 10.11882/j.issn.0254-5071.2019.01.005 [36] 王莹莹. 电机系举办首期“云上论电”线上学术报告会[EB/OL]. https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/6b9rHlps5pnB63TVwr1PTw. [37] 周明, 彭楠, 代强, 等. 高强度紫外线对临床常见致病菌的杀灭效果观察[J]. 中国消毒学杂志, 2015, 32(3):219-221. (Zhou Ming, Peng Nan, Dai Qiang, et al. Observation on disinfection effect of clinical common pathogens by high strength UV irradiation[J]. China Journal of Disinfection, 2015, 32(3): 219-221 [38] Lee C H, Wu S B, Hong C H, et al. Molecular mechanisms of UV-induced apoptosis and its effects on skin residential cells: The implication in UV-based phototherapy[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2013, 14(3): 6414-6435. doi: 10.3390/ijms14036414 [39] 孙文俊. 饮用水紫外线消毒生物安全性研究[D]. 北京: 清华大学, 2010: 4-6.Sun Wenjun. Study on the biological safety of drinking water following UV disinfection[D]. Beijing: Tsinghua University, 2010: 4-6 [40] Pfeifer G P. Formation and processing of UV photoproducts: Effects of DNA sequence and chromatin environment[J]. Photochemistry and Photobiology, 1997, 65(2): 270-283. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1997.tb08560.x [41] Knudson G B. Photoreactivation of UV-irradiated legionella pneumophila and other legionella species[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 1985, 49(4): 975-980. doi: 10.1128/AEM.49.4.975-980.1985 [42] 王俊娇, 吕鑑, 张英, 等. 紫外线持续消毒能力的研究[J]. 工业用水与废水, 2006, 37(4):44-46. (Wang Junjiao, Lü Jian, Zhang Ying, et al. Persistent disinfection ability of ultraviolet radiation[J]. Industrial Water and Wastewater, 2006, 37(4): 44-46 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2455.2006.04.012 [43] 陈大华, 杨澄学. 紫外线汞灯及其在消毒中的应用[J]. 中国照明电器, 2009(9):19-22. (Chen Dahua, Yang Chengxue. The disinfectant ultraviolet mercury lamps and its applications in the sterilization[J]. China Light and Lighting, 2009(9): 19-22 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6150.2009.09.005 [44] 何志明, 廖辉, 晏波元. 低压高强紫外线灯温度特性及在水处理中的应用[J]. 中国照明电器, 2015(2):18-20. (He Zhiming, Liao Hui, Yan Boyuan, et al. Temperature property of low pressure high output ultraviolet lamp and the application in water treatment[J]. China Light and Lighting, 2015(2): 18-20 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6150.2015.02.005 [45] 李江. 紫外线消毒技术的研究[D]. 天津: 天津大学, 2003: 11-13.Li Jiang. Study on ultraviolet germicidal irradiation(UVGI)[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University, 2003: 11-13 [46] 张艳. 紫外消毒模型开发与设备优化研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2010: 2-3.Zhang Yan. Development of UV disinfection model and equipment optimization[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2010: 2-3 [47] Sale A, Hamilton W. Effects of high electric fields on microorganisms: I. Killing of bacteria and yeasts[J]. Biochemical and Biophysical, 1967, 148(3): 781-788. [48] Zimmermann U. Electrical breakdown electropermeabilization and electrofusion[J]. Reviews of Physiology, Biochemistry and Pharmacology, 1986, 105(6): 176-256. [49] Tsong T. Electroporation of cell membranes[J]. Biophysical Journal, 1991, 60(2): 297-306. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82054-9 [50] 丁宏伟. 高压脉冲电场对牛乳的杀菌灭酶研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2006: 8-9.Ding Hongwei. Study on sterilization and killing enzyme of milk by high intensity pulsed electric fields (PEF)[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2006: 8-9 [51] 邵帅. 医疗垃圾预处理器具设计研究[D]. 武汉: 湖北工业大学, 2019: 17-18.Shao Shuai. Design and research of medical waste preprocessor[D]. Wuhan: Hubei University of Technology, 2019: 17-18 -




 下载:
下载: