Optical fiber dislocation ammonia gas sensor based on self-assembled film
-
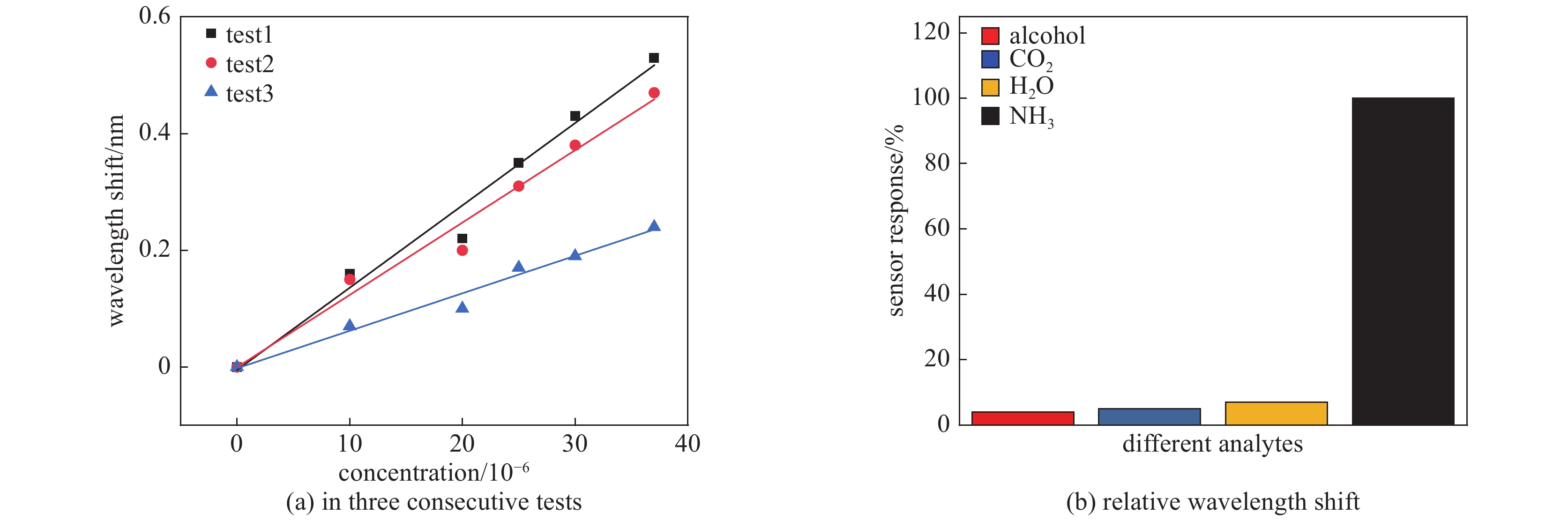
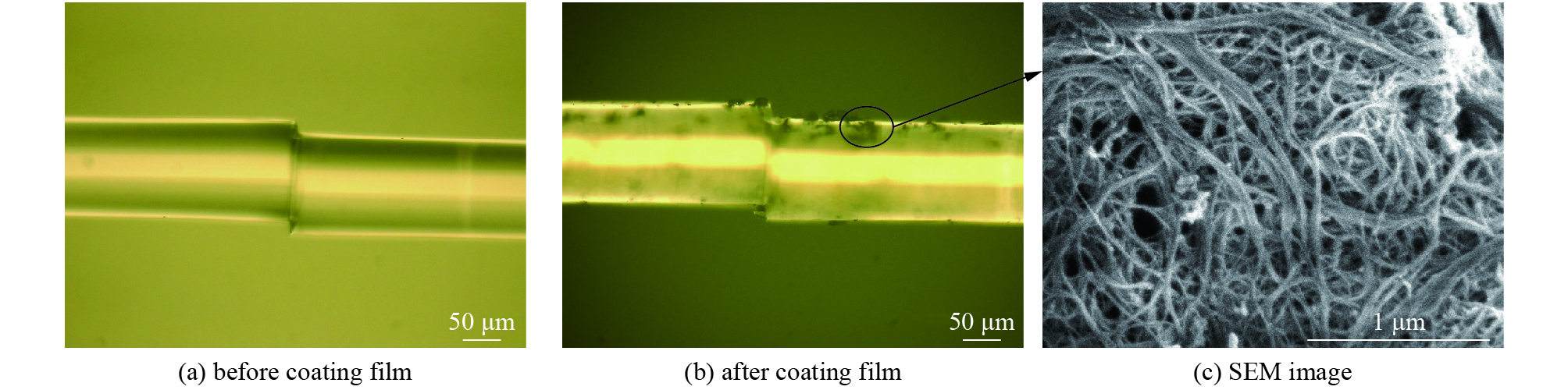
摘要: 演示了一种基于单壁碳纳米管(SWCNTs)-聚合物自组装复合膜的光纤错位型氨气传感器。通过层层自组装技术在高Q谐振器上涂覆薄膜,薄膜上存在大量的游离羧基以及较大的比表面积,这提供了光与薄膜之间的强相互作用,以及对氨气的高吸附性和选择性。光谱随氨气浓度影响的有效折射率而变化。在(10~37) ×10−6的低浓度范围内,光谱变化与氨气浓度差之比即灵敏度为13.25 pm/10−6,检测极限为3.77 ×10−6并且具有良好的线性。这项工作研制为低浓度和高选择性氨气传感器提供了一种有效的方法。Abstract: This paper presents the ammonia gas sensor of optical fiber dislocation type based on single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs)-polymer self-assembled composite film. Alone with high-Q resonator, the film has a large number of free carboxyl groups and a large specific surface area, which provides strong interaction between light and the film, as well as high adsorption and selectivity to ammonia. The spectrum from the sensor varies with the effective refractive index affected by the ammonia concentration. In the low concentration range of (10−37)×10−6, the ratio of the spectral change to the ammonia concentration difference (i.e. the sensitivity) is of 13.25 pm/10−6, a detection limit is 3.77×10−6 with good linearity. This work provides an effective method for developing low-concentration and high-selectivity ammonia sensors.
-
Key words:
- fiber /
- dislocation welding /
- ammonia sensor /
- self-assembled film /
- carbon nanotubes
-
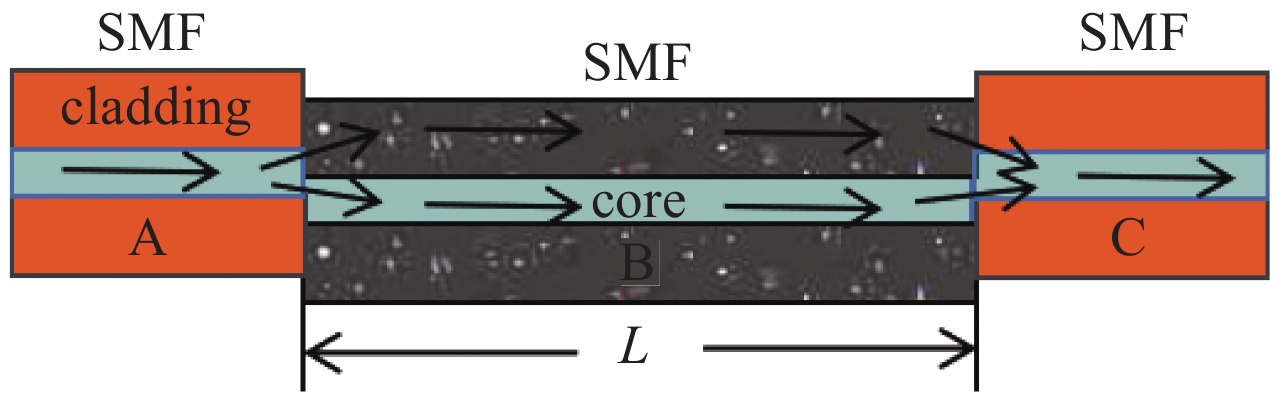
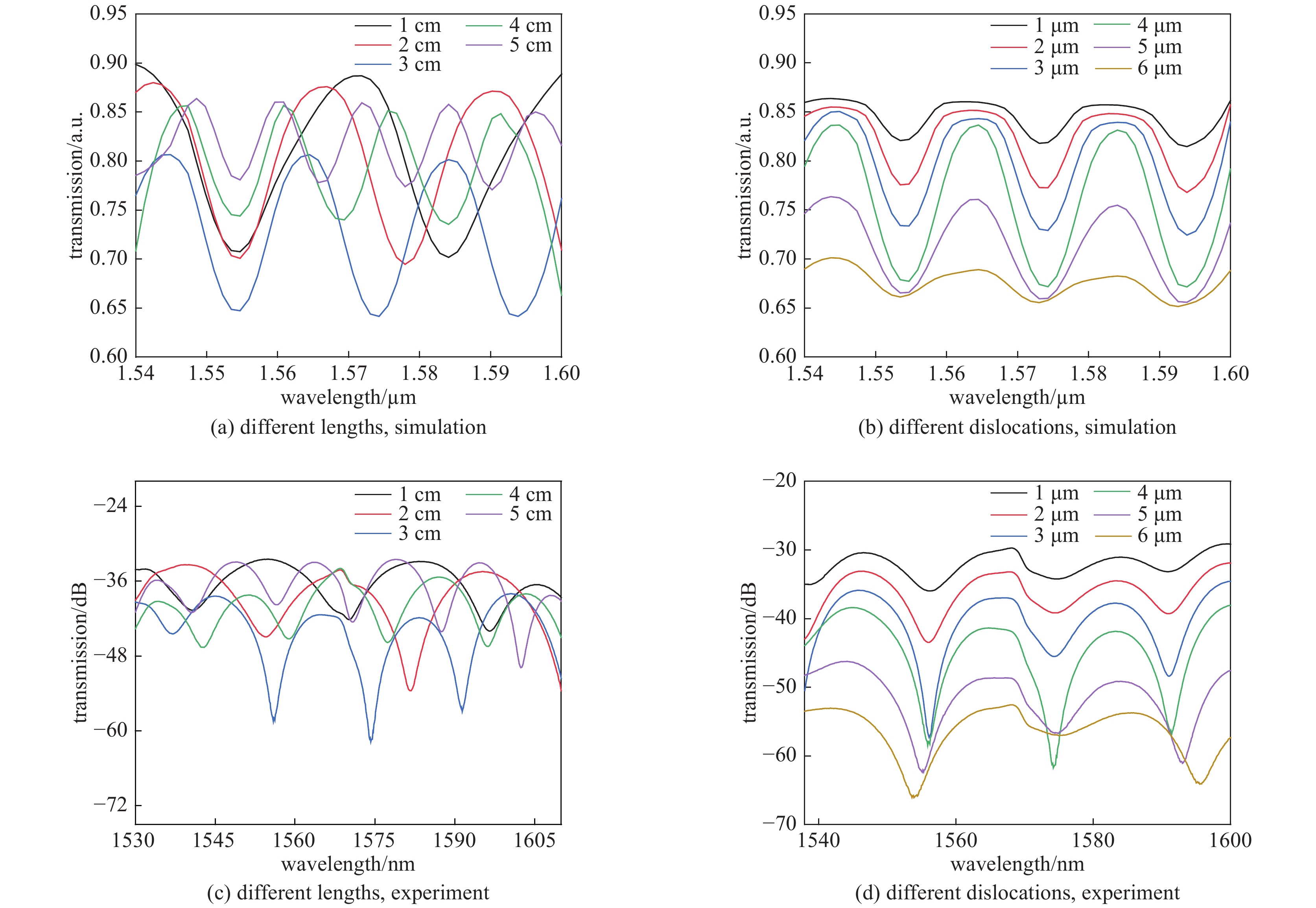
图 4 仿真不同长度对应的干涉谱和不同错位量对应的干涉谱以及实验不同长度对应的干涉谱不同错位量对应的干涉谱
Figure 4. Simulated interference spectra corresponding to different lengths and interference spectra corresponding to different dislocations,experimental interference spectra corresponding to different lengths and interference spectras corresponding to different dislocations
表 1 误差分析
Table 1. Repetitive experimental data
x1/nm x2/nm x3/nm x4/nm x5/nm x6/nm x7/nm x8/nm $\overline x $/nm D/nm σ/% 0.050 0.041 0.030 0.035 0.037 0.050 0.047 0.042 0.041 0.006 15.4 -
[1] Malins C, Doyle A, MacCraith B D, et al. Personal ammonia sensor for industrial environments[J]. Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 1999, 1(5): 417-222. doi: 10.1039/a904846d [2] Liu Xu, Chen Nan, Han Bingqian, et al. Nanoparticle cluster gas sensor: Pt activated SnO2 nanoparticles for NH3 detection with ultrahigh sensitivity[J]. Nanoscale, 2015, 7(36): 14872-14880. doi: 10.1039/C5NR03585F [3] Schmidt F M, Vaittinen O, Metsälä M, et al. Ammonia in breath and emitted from skin[J]. Journal of Breath Research, 2013, 7: 017109. doi: 10.1088/1752-7155/7/1/017109 [4] Timmer B, Olthuis W, van den Berg A. Ammonia sensors and their applications—a review[J]. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2005, 107(2): 666-677. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2004.11.054 [5] Renganathan B, Sastikumar D, Gobi G, et al. Nanocrystalline ZnO coated fiber optic sensor for ammonia gas detection[J]. Optics & Laser Technology, 2011, 43(8): 1398-1404. [6] Sharma A L, Kumar K, Deep A. Nanostructured polyaniline films on silicon for sensitive sensing of ammonia[J]. Sensors and Actuators A: Physical, 2013, 198: 107-112. doi: 10.1016/j.sna.2013.04.026 [7] Turner C, Španěl P, Smith D. A longitudinal study of ammonia, acetone and propanol in the exhaled breath of 30 subjects using selected ion flow tube mass spectrometry, SIFT-MS[J]. Physiological Measurement, 2006, 27(4): 321-337. doi: 10.1088/0967-3334/27/4/001 [8] Cao Wenqing, Duan Yixiang. Optical fiber-based evanescent ammonia sensor[J]. Sensors andActuators B: Chemical, 2005, 110(2): 252-259. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2005.02.015 [9] Khalaf A L, Mohamad F S, Abdul Rahman N, et al. Room temperature ammonia sensor using side-polished optical fiber coated with graphene/polyaniline nanocomposite[J]. Optical Materials Express, 2017, 7(6): 1858-1870. doi: 10.1364/OME.7.001858 [10] Zhao Na, Fu Haiwei, Shao Min, et al. High temperature probe sensor with high sensitivity based on Michelson interferometer[J]. Optics Communications, 2015, 343: 131-134. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2014.12.012 [11] Huang Ran, Ni Kai, Ma Qifei, et al. Refractometer based on a tapered Mach–Zehnder interferometer with Peanut-Shape structure[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2016, 83: 80-82. doi: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2016.03.011 [12] Liao C R, Hu T Y, Wang D N. Optical fiber Fabry-Perot interferometer cavity fabricated by femtosecond laser micromachining and fusion splicing for refractive index sensing[J]. Optics Express, 2012, 20(20): 22813-22818. doi: 10.1364/OE.20.022813 [13] Feng Weiqiang, Liu Zhengyong, Tam H Y, et al. The pore water pressure sensor based on Sagnac interferometer with polarization-maintaining photonic crystal fiber for the geotechnical engineering[J]. Measurement, 2016, 90: 208-214. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2016.04.067 [14] Liao C R, Chen HF, Wang D N. Ultracompact optical fiber sensor for refractive index and high-temperature measurement[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2014, 32(14): 2531-2535. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2014.2328356 [15] Hu Pengbing, Chen Zhemin, Yang Mei, et al. Highly sensitive liquid-sealed multimode fiber interferometric temperature sensor[J]. Sensors and Actuators A: Physical, 2015, 223: 114-118. doi: 10.1016/j.sna.2015.01.009 [16] Hao Ting, Chiang K S. Graphene-based ammonia-gas sensor using in-fiber Mach–Zehnder interferometer[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2017, 29(23): 2035-2038. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2017.2761981 [17] Fu Haiwei, Wang Qiqi, Ding Jijun, et al. Fe2O3 nanotube coating micro-fiber interferometer for ammonia detection[J]. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2020, 303: 127186. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2019.127186 [18] Yu Caibin, Wu Yu, Liu Xiaolei, et al. Miniature fiber-optic NH3 gas sensor based on Pt nanoparticle-incorporated graphene oxide[J]. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2017, 244: 107-113. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2016.12.126 [19] Yao Baicheng, Wu Y U, Cheng Yang, et al. All-optical Mach–Zehnder interferometric NH3 gas sensor based on graphene/microfiber hybrid waveguide[J]. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2014, 194: 142-148. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2013.12.085 [20] Gouveia C, Jorge P A S, Baptista J M, et al. Temperature-independent curvature sensor using FBG cladding modes based on a core misaligned splice[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2011, 23(12): 804-806. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2011.2138125 [21] Yao Qiqi, Meng Hongyun, Wang Wei, et al. Simultaneous measurement of refractive index and temperature based on a core-offset Mach–Zehnder interferometer combined with a fiber Bragg grating[J]. Sensors and Actuators A: Physical, 2014, 209: 73-77. doi: 10.1016/j.sna.2014.01.017 [22] Shen Liguo, Cui Xia, Yu Genying, et al. Thermodynamic assessment of adsorptive fouling with the membranes modified via layer-by-layer self-assembly technique[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2017, 494: 194-203. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2017.01.051 [23] Richardson J J, Cui Jiwei, Björnmalm M, et al. Innovation in layer-by-layer assembly[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2016, 116(23): 14828-14867. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.6b00627 [24] Tan Y C, Ji W B, Mamidala V, et al. Carbon-nanotube-deposited long period fiber grating for continuous refractive index sensor applications[J]. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2014, 196: 260-264. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2014.01.063 [25] Wang S G, Zhang Qing, Yang D J, et al. Multi-walled carbon nanotube-based gas sensors for NH3 detection[J]. Diamond and Related Materials, 2004, 13(4/8): 1327-1332. [26] Huang Xinyue, Li Xueming, Yang Jianchun, et al. An in-line Mach–Zehnder interferometer using thin-core fiber for ammonia gas sensing with high sensitivity[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7: 44994. doi: 10.1038/srep44994 [27] Sun Xiaoyan, Chu Dongkai, Dong Xinran, et al. Highly sensitive refractive index fiber inline Mach–Zehnder interferometer fabricated by femtosecond laser micromachining and chemical etching[J]. Optics & Laser Technology, 2016, 77: 11-15. [28] Kalita A, Hussain S, Hussain Malik A, et al. Vapor phase sensing of ammonia at the sub-ppm level using a perylene diimide thin film device[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2015, 3(41): 10767-10774. doi: 10.1039/C5TC02521D [29] White I M, Fan Xudong. On the performance quantification of resonant refractive index sensors[J]. Optics Express, 2008, 16(2): 1020-1028. doi: 10.1364/OE.16.001020 -




 下载:
下载: