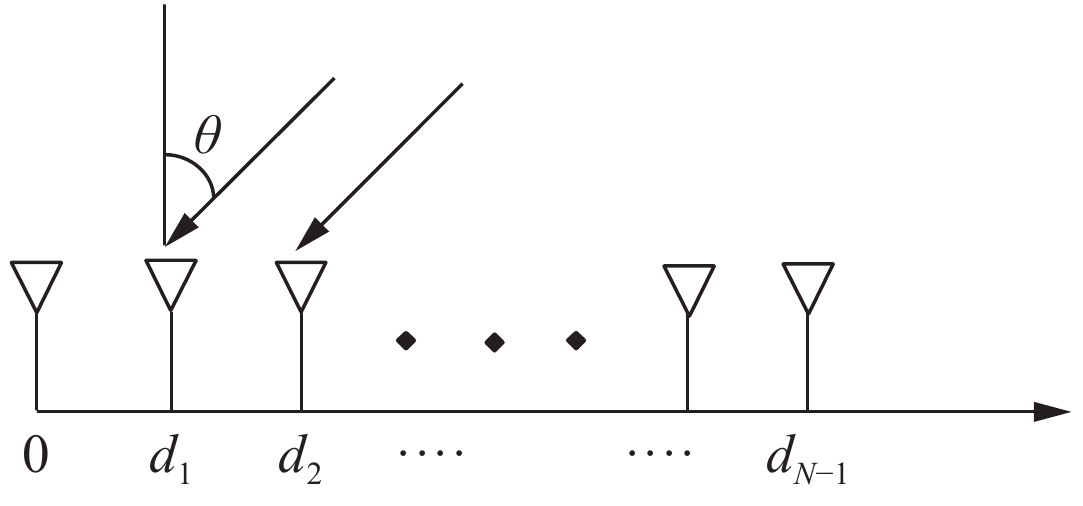
Thinned array optimization based on genetic model improved artificial bee colony algorithm
-
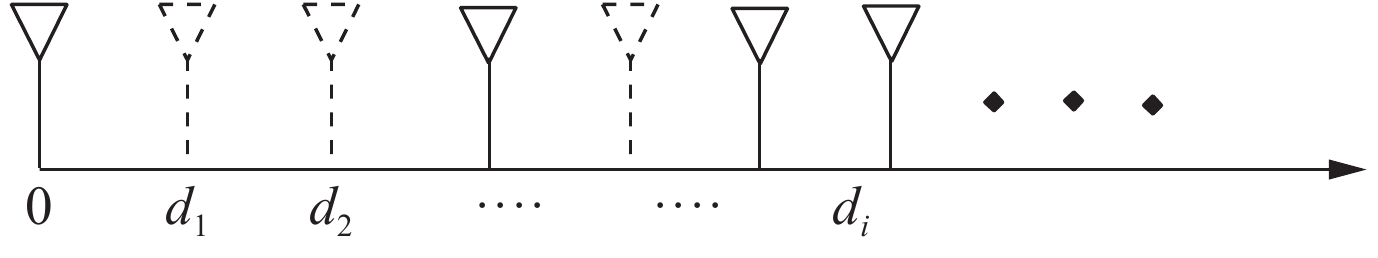
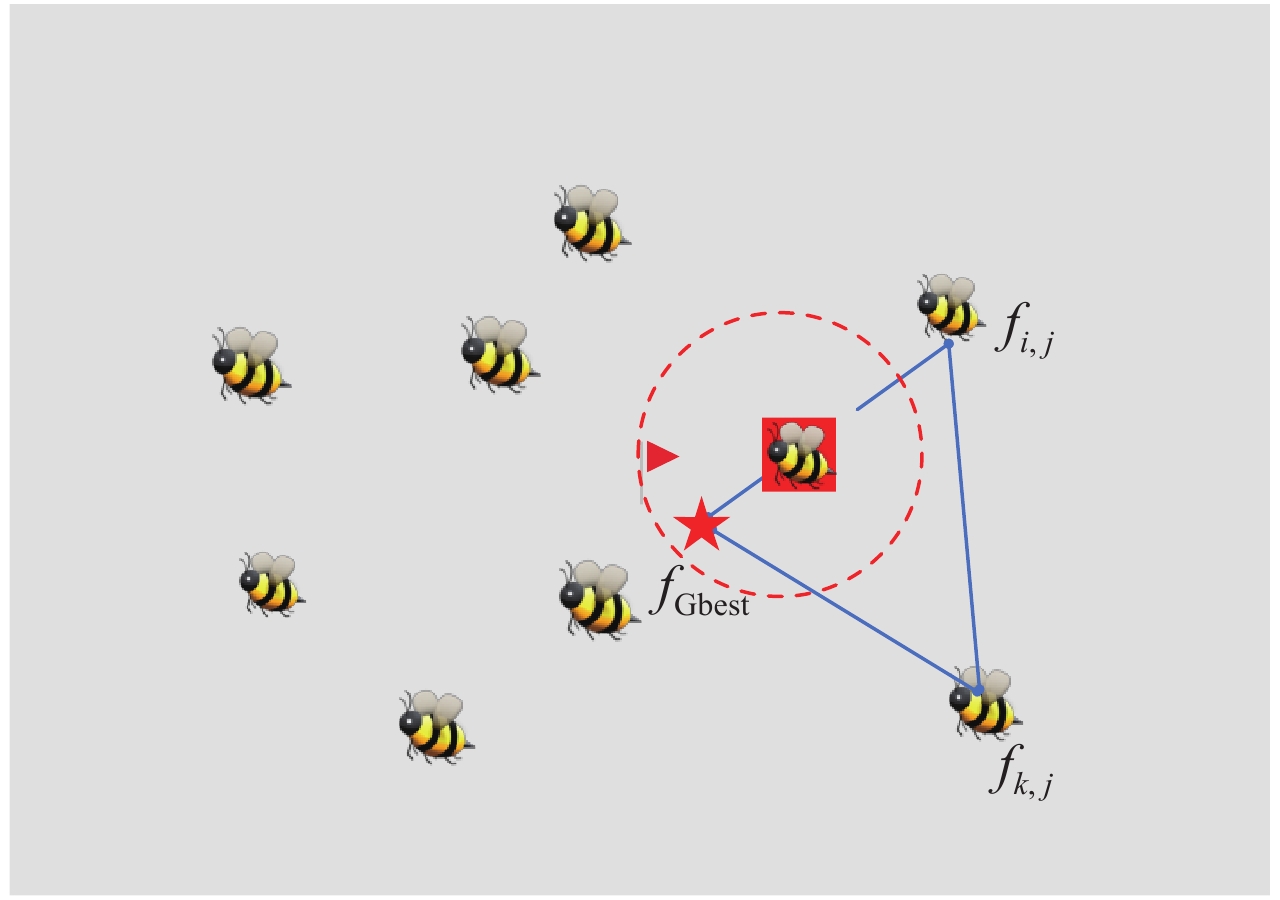
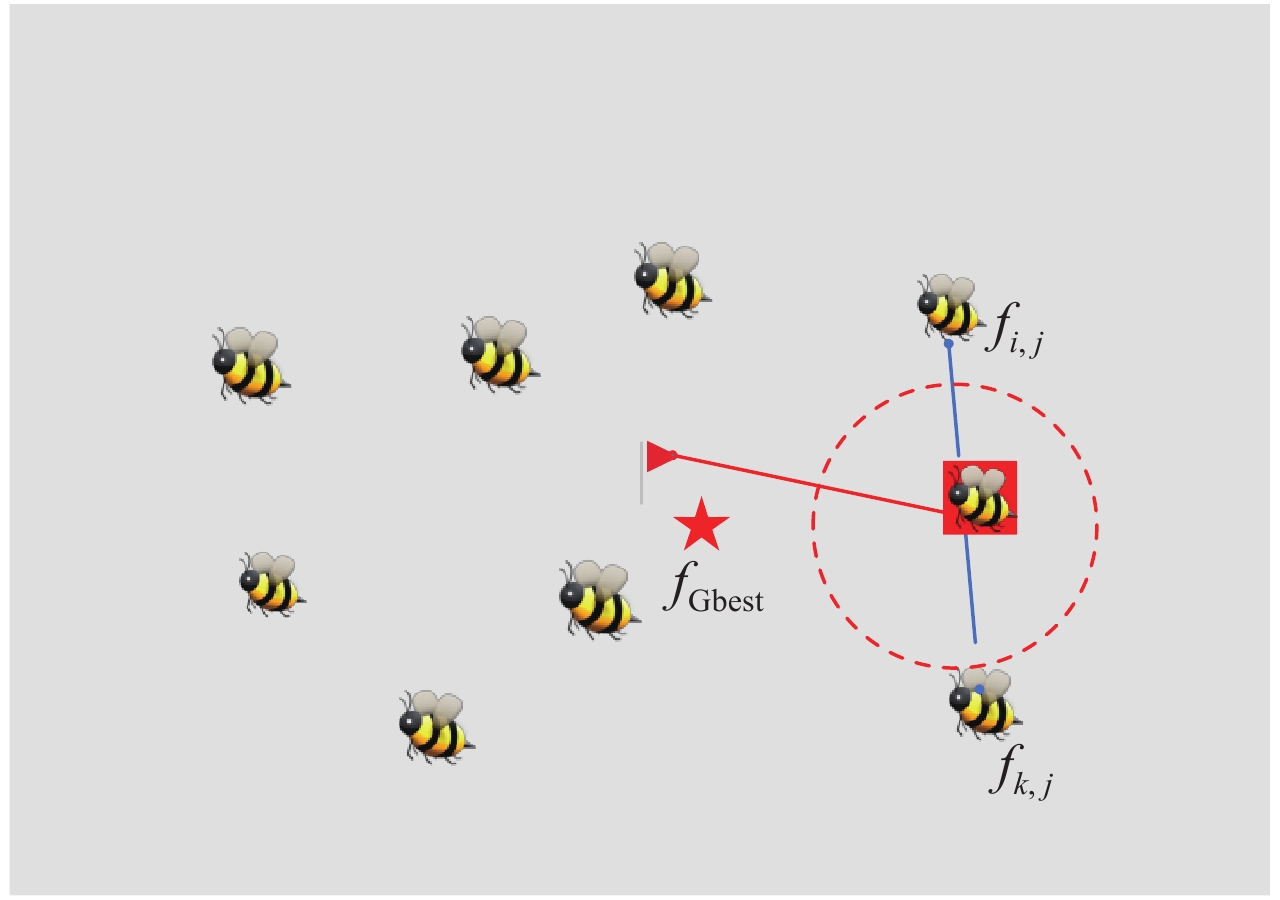
摘要: 人工蜂群算法作为一种新兴的群体智能算法,在解决复杂连续问题时表现突出。但是由于算法本身内在运行机制的原因,算法在搜索上表现出优异的性能,却疏于开发。为了平衡搜索和开发二者之间的矛盾,提出了一种基于遗传模型改进的人工蜂群算法,并成功运用到了阵列综合领域。算法先将全局最优解引入邻域搜索过程,指导蜂群寻找最佳蜜源,加速算法收敛。为了避免人工蜂群算法陷入局部最优,需要提高其开发能力,通过借鉴遗传算法中的进化机制,建立了遗传模型,对采取最佳保留后的蜜源进行遗传操作,丰富蜜源的多样性。在一组广泛使用的数值函数上对改进人工蜂群算法进行了测试,实验数据表明,该算法相较于其他算法具有很强的竞争力。将该算法运用于线性阵列的稀疏优化,旨在降低阵列的峰值旁瓣电平,在同样的阵列约束下与其他算法进行了优化对比,仿真结果进一步证明了算法的有效性。Abstract: To solve the problem that artificial bee colony algorithm is good at exploration and neglect exploitation, this paper proposes an improved artificial bee colony algorithm based on genetic model, which has been successfully applied to array synthesis. Firstly, the global optimal solution is introduced into the neighborhood search process to guide the bees to find the best nectar source thus to accelerate the convergence of the algorithm. Secondly, to avoid the local optimization of the algorithm, the exploitation ability of artificial bee colony algorithm must be improved. The evolutionary mechanism of genetic algorithm is used for reference, and a genetic model is established to carry out genetic operation on the honey source after adopting the optimal retention, to enrich the diversity of honey source. The improved artificial bee colony algorithm is tested on a set of widely used numerical functions, and the experimental data show that the proposed algorithm has strong competitiveness compared with other algorithms. Then, the algorithm is applied to the sparse optimization of the linear array to reduce the peak sidelobe level of the array. The optimization is compared with other algorithms under the same array constraints. The simulation results further prove the effectiveness of the algorithm.
-
表 1 基准数值函数
Table 1. Benchmark numerical functions
function expression range minimum value Sphere $ {f}_{1}\left(x\right)={\displaystyle\sum }_{i=1}^{D}{x}_{i}^{2} $ $ {\left[-\mathrm{100,100}\right]}^{D} $ 0 Elliptic $ {f}_{2}\left(x\right)={\displaystyle\sum }_{i=1}^{D}{{\left({10}^{6}\right)}^{\tfrac{i-1}{D-1}}}x_{i}^{2} $ $ {\left[-\mathrm{100,100}\right]}^{D} $ 0 SumSquare $ {f}_{3}\left(x\right)={\displaystyle\sum }_{i=1}^{D}{ix}_{i}^{2} $ $ {\left[-\mathrm{10,10}\right]}^{D} $ 0 Exponential ${f}_{4}\left(x\right)=\mathrm{e}\mathrm{x}\mathrm{p}\left(0.5 {\displaystyle\sum }_{i=1}^{D}{x}_{i}\right)$ $ {\left[-\mathrm{10,10}\right]}^{D} $ 0 Rosenbrock $ {f}_{5}\left(x\right)={\displaystyle\sum }_{i}^{D-1}\left[{100\left({x}_{i+1}-{x}_{i}^{2}\right)}^{2}-{\left({x}_{i}-1\right)}^{2}\right] $ $ {\left[-\mathrm{5,10}\right]}^{D} $ 0 Rastrigin $ {f}_{6}\left(x\right)={\displaystyle\sum }_{i}^{D}\left[{x}_{i}^{2}-10\mathrm{cos}\left(2\pi {x}_{i}\right)+10\right] $ $ {\left[-\mathrm{5.12,5.12}\right]}^{D} $ 0 Himmelblau $ {f}_{7}\left(x\right)=1/\mathrm{D}{\displaystyle\sum }_{i}^{D}\left[{x}_{i}^{4}-16{x}_{i}^{2}+5{x}_{i}\right] $ $ {\left[-\mathrm{5,5}\right]}^{D} $ −78.33236 表 2 GMIABC与ABC,GABC算法比较
Table 2. Comparison of GMIABC, ABC and GABC algorithms
algorithm $ {f}_{1}\left(x\right) $ $ {f}_{2}\left(x\right) $ $ {f}_{3}\left(x\right) $ $ {f}_{4}\left(x\right) $ $ {f}_{5}\left(x\right) $ $ {f}_{6}\left(x\right) $ $ {f}_{7}\left(x\right) $ ABC mean 2.42e−15 4.52e−8 7.32e–15 7.18e−21 4.75e−01 1.34e−13 −78.332 std 3.20e−15 4.83e−8 8.18e−15 7.21e−21 5.81e−01 1.97e−13 0 GABC mean 5.12e−16 4.19e−16 5.25e–15 7.18e−23 9.71e−02 0 −78.332 std 4.35e−17 4.25e−16 6.18e−15 7.07e−23 1.01e−01 0 3.13e−15 GA mean 1.23e−13 4.47e−12 8.10e−11 0 4.1675e−05 0 −78.332 std 1.63e−13 5.77e−12 7.82e−11 0 5.0100e−05 0 1.0974e−14 GMIABC mean 3.73e−23 4.99e−21 3.57e−20 0 1.910158e−07 0 −78.33233 std 4.16e−23 1.21e−20 6.93e−20 0 2.110158e−07 0 0 表 3 GMIABC与GA, ABC,ABCSIM算法阵列稀疏优化比较
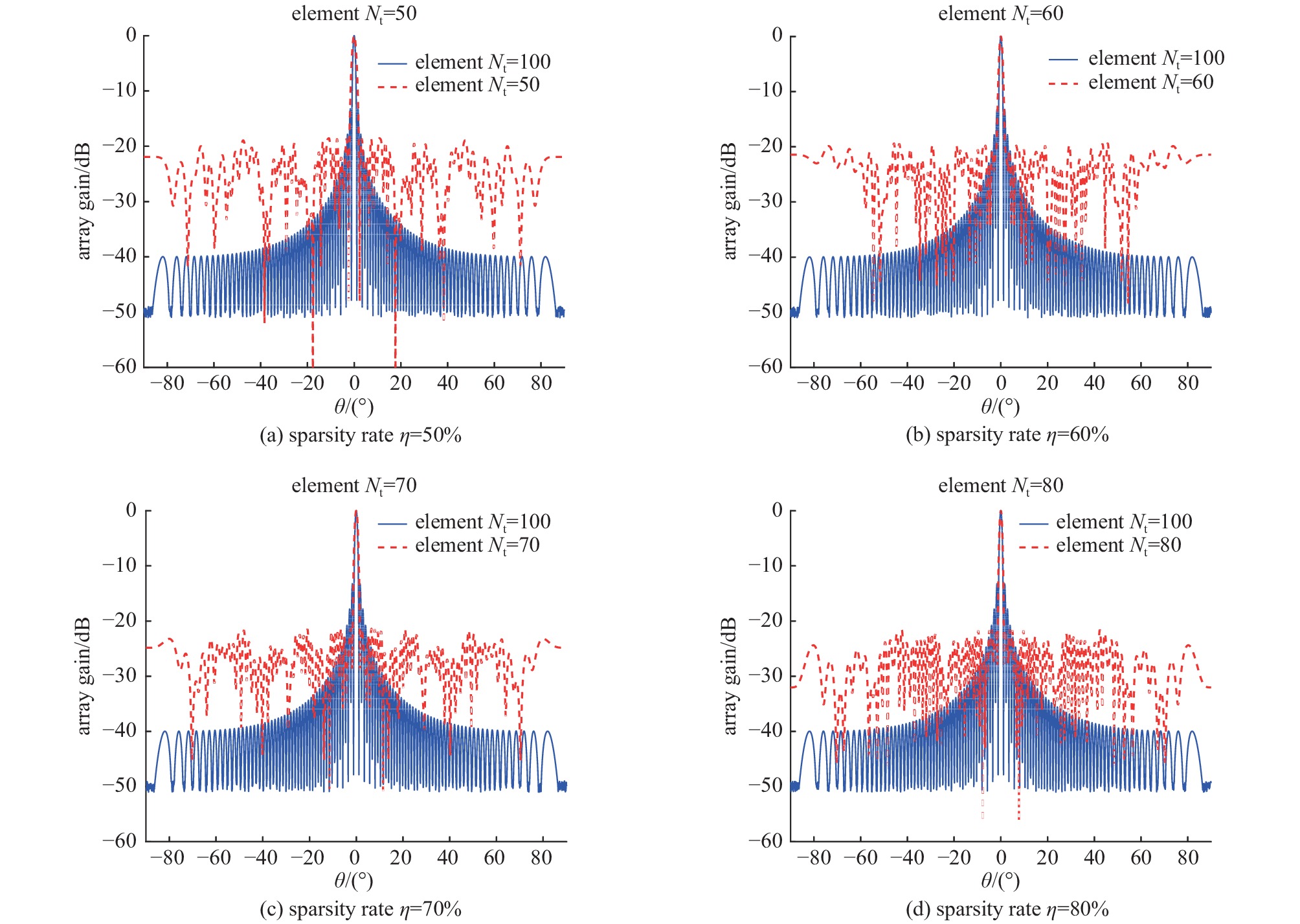
Table 3. Comparison of sparsity optimization between GMIABC and GA, ABC and ABCSIM algorithms
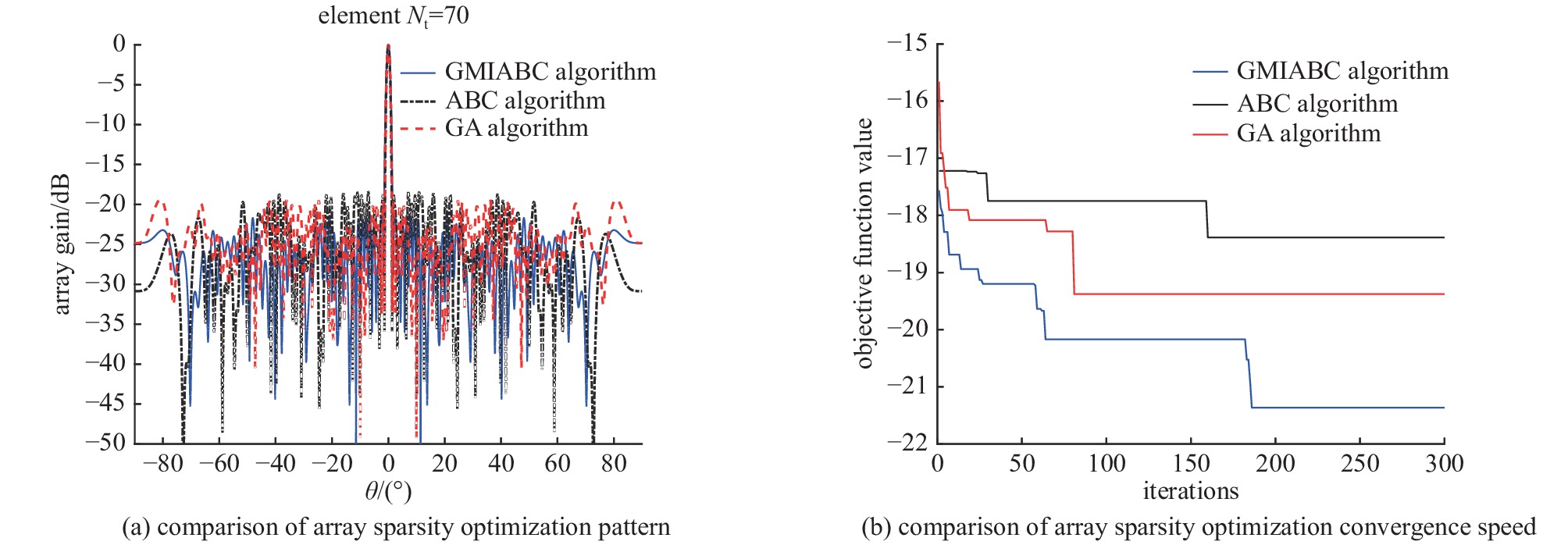
algorithm min/dB mean/dB std min/dB mean/dB std min/dB mean/dB std min/dB mean/dB std η=50%(Nt= 50) η=60%(Nt =60) η=70%(Nt =70) η=80%(Nt =80) GA −15.935 −15.677 0.189 −18.121 −17.521 0.353 −19.378 −19.110 0.187 −20.941 −20.752 0.178 ABC −15.330 −15.061 0.237 −16.806 −16.563 0.207 −18.386 −17.722 0.423 −19.836 −18.430 0.967 ABCSIM −17.211 −16.863 0.262 −17.426 −17.158 0.217 −18.202 −17.588 0.429 −18.172 −17.764 0.331 GMIABC min/dB −18.541 −18.281 0.227 −19.368 −19.200 0.135 −21.365 −20.892 0.171 −21.338 −21.573 0.175 -
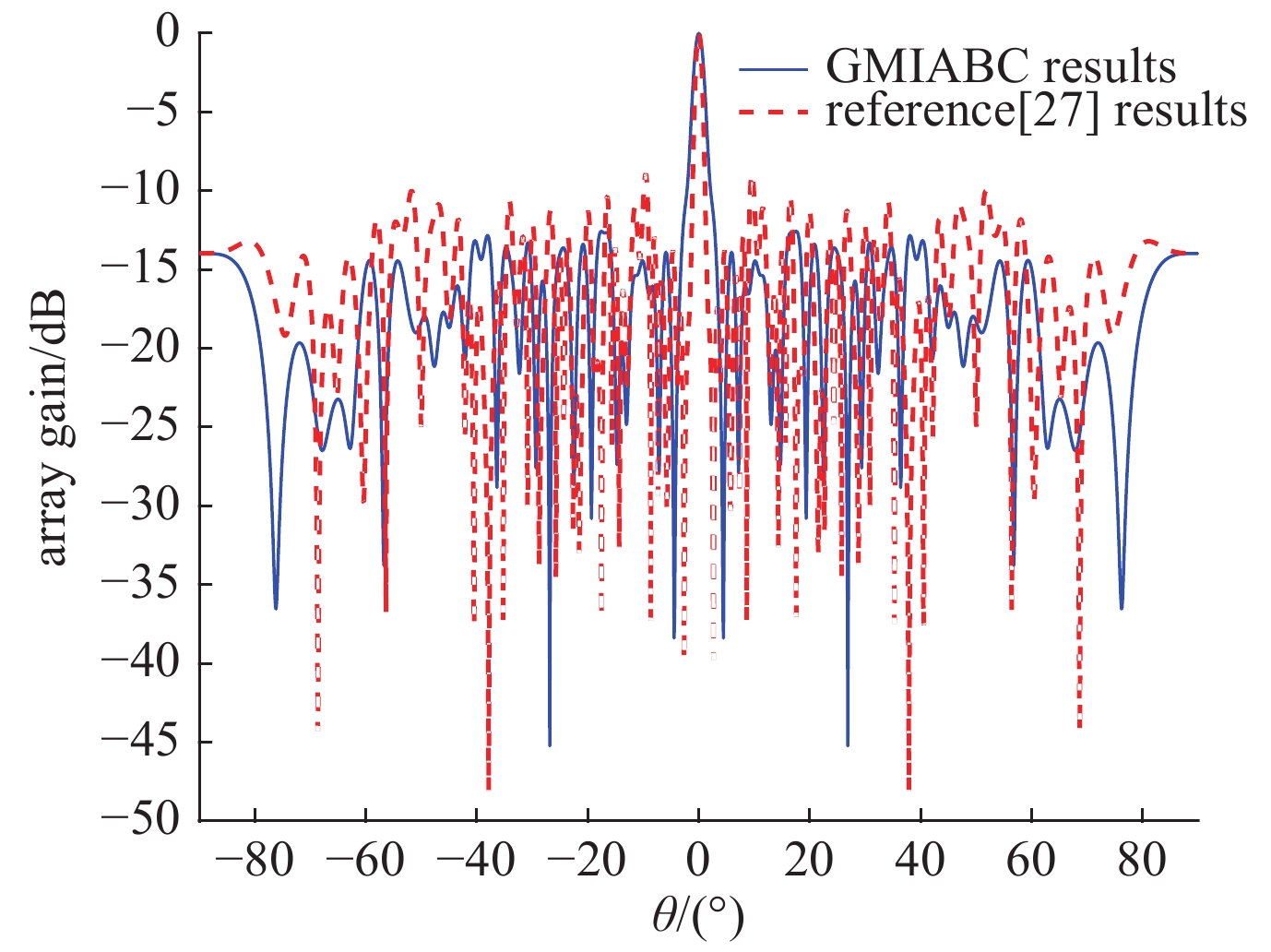
[1] Wang Lei, Zhang Xin, Zhang Xiu. Antenna array design by artificial bee colony algorithm with similarity induced search method[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 2019, 55: 7201904. [2] Xiao Songyi, Wang Hui, Wang Wenjun, et al. Artificial bee colony algorithm based on adaptive neighborhood search and Gaussian perturbation[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2021, 100: 106955. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2020.106955 [3] 庞育才, 刘松. 基于改进人工蜂群算法的MIMO雷达稀疏阵列优化[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2018, 40(5):1026-1030. (Pang Yucai, Liu Song. Optimization of MIMO radar sparse array based on modified artificial bee colony[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2018, 40(5): 1026-1030 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2018.05.10 [4] Reddy K Y, Kumar R B, Jijenth M, et al. Synthesis of randomly spaced planar antenna array with low peak side lobe level (PSLL) using Modified Genetic Algorithm[C]//2017 IEEE International Conference on Antenna Innovations & Modern Technologies for Ground, Aircraft and Satellite Applications (iAIM). IEEE, 2017: 524-527. [5] Sallam T, Attiya A. Low sidelobe cosecant-squared pattern synthesis for large planar array using genetic algorithm[J]. Progress in Electromagnetics Research M, 2020, 93: 23-34. doi: 10.2528/PIERM20042005 [6] Laseetha T S J, Sukanesh R. Synthesis of linear antenna array using genetic algorithm to maximize sidelobe level reduction[J]. International Journal of Computer Applications, 2011, 20(7): 27-33. doi: 10.5120/2445-3302 [7] Goudos S K, Moysiadou V, Samaras T, et al. Application of a comprehensive learning particle swarm optimizer to unequally spaced linear array synthesis with sidelobe level suppression and null control[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2010, 9: 125-129. doi: 10.1109/LAWP.2010.2044552 [8] Gangwar V S, Singh A K, Thomas E, et al. Side lobe level suppression in a thinned linear antenna array using particle swarm optimization[C]//2015 International Conference on Applied and Theoretical Computing and Communication Technology (iCATccT). IEEE, 2015: 787-790. [9] Recioui A. Sidelobe level reduction in linear array pattern synthesis using particle swarm optimization[J]. Journal of Optimization Theory and Applications, 2012, 153(2): 497-512. doi: 10.1007/s10957-011-9953-9 [10] Behera A K, Ahmad A, Mandal S K, et al. Synthesis of cosecant squared pattern in linear antenna arrays using differential evolution[C]//Proceedings of 2013 IEEE Conference on Information & Communication Technologies. IEEE, 2013: 1025-1028. [11] Cui Chaoyi, Jiao Yongchang, Zhang Li, et al. Synthesis of Subarrayed Monopluse arrays with contiguous elements using a DE algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2017, 65(8): 4340-4345. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2017.2714021 [12] Zhang Ze, Su Wentao, Zhou Kaifu. Airborne radar sub array partitioning method based on artificial bee colony algorithm[C]//2019 IEEE 3rd Information Technology, Networking, Electronic and Automation Control Conference (ITNEC). IEEE, 2019: 484-489. [13] Zhang Xin, Zhang Xiu, Wang Lei. Antenna design by an adaptive variable differential artificial bee colony algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 2018, 54: 7201704. [14] Goudos S K, Siakavara K, Sahalos J N. Novel spiral antenna design using artificial bee colony optimization for UHF RFID applications[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2014, 13: 528-531. doi: 10.1109/LAWP.2014.2311653 [15] Chatterjee A, Mandal D. Synthesis of hexagonal planar array using swarm-based optimization algorithms[J]. International Journal of Microwave and Wireless Technologies, 2015, 7(2): 151-160. doi: 10.1017/S1759078714000683 [16] 崔佩璋, 全厚德, 乔成林. 基于改进蜂群算法的非均匀阵列综合[J]. 火力与指挥控制, 2016, 41(12):87-90. (Cui Peizhang, Quan Houde, Qiao Chenglin. Synthesis of non-uniform arrays using modified bees algorithm[J]. Fire Control & Command Control, 2016, 41(12): 87-90 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0640.2016.12.019 [17] 杨群, 曹祥玉, 高军, 等. 基于改进的人工蜂群算法的阵列综合研究[J]. 微波学报, 2014, 30(s1):37-40. (Yang Qun, Cao Xiangyu, Gao Jun, et al. Array synthesis on the basis of an improved artificial bee colony algorithm[J]. Journal of Microwaves, 2014, 30(s1): 37-40 [18] Wang Hui, Wang Wenjun, Xiao Songyi, et al. Improving artificial Bee colony algorithm using a new neighborhood selection mechanism[J]. Information Sciences, 2020, 527: 227-240. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2020.03.064 [19] Karaboga D. An idea based on honey bee swarm for numerical optimization[R]. Kayseri, Türkey: Erciyes University, 2005. [20] Karaboga D, Basturk B. A powerful and efficient algorithm for numerical function optimization: artificial bee colony (ABC) algorithm[J]. Journal of Global Optimization, 2007, 39(3): 459-471. doi: 10.1007/s10898-007-9149-x [21] Banharnsakun A, Achalakul T, Sirinaovakul B. The best-so-far selection in Artificial Bee Colony algorithm[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2011, 11(2): 2888-2901. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2010.11.025 [22] Črepinšek M, Liu S H, Mernik M. Exploration and exploitation in evolutionary algorithms[J]. ACM Computing Surveys, 2013, 45: 35. [23] Peng Hu, Deng Changshou, Wu Zhijian. Best neighbor-guided artificial bee colony algorithm for continuous optimization problems[J]. Soft Computing, 2019, 23(18): 8723-8740. doi: 10.1007/s00500-018-3473-6 [24] Li Genghui, Cui Laizhong, Fu Xianghua, et al. Artificial bee colony algorithm with gene recombination for numerical function optimization[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2017, 52: 146-159. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2016.12.017 [25] Frisch K V. The dance language and orientation of bees[M]. Cambridge: Harvard University Press, 1967: 181-182. [26] Zhu Guopu, Kwong S. Gbest-guided artificial bee colony algorithm for numerical function optimization[J]. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 2010, 217(7): 3166-3173. doi: 10.1016/j.amc.2010.08.049 [27] 陈客松, 何子述, 韩春林. 最佳稀疏直线阵列的分区穷举综合法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2006, 28(11):2030-2032. (Chen Kesong, He Zishu, Han Chunlin. Divisional exhaustive method applied to optimum thinning of linear arrays[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2006, 28(11): 2030-2032 -




 下载:
下载: