Sub-microsecond high voltage pulse power supply based on magnetic isolated driving
-
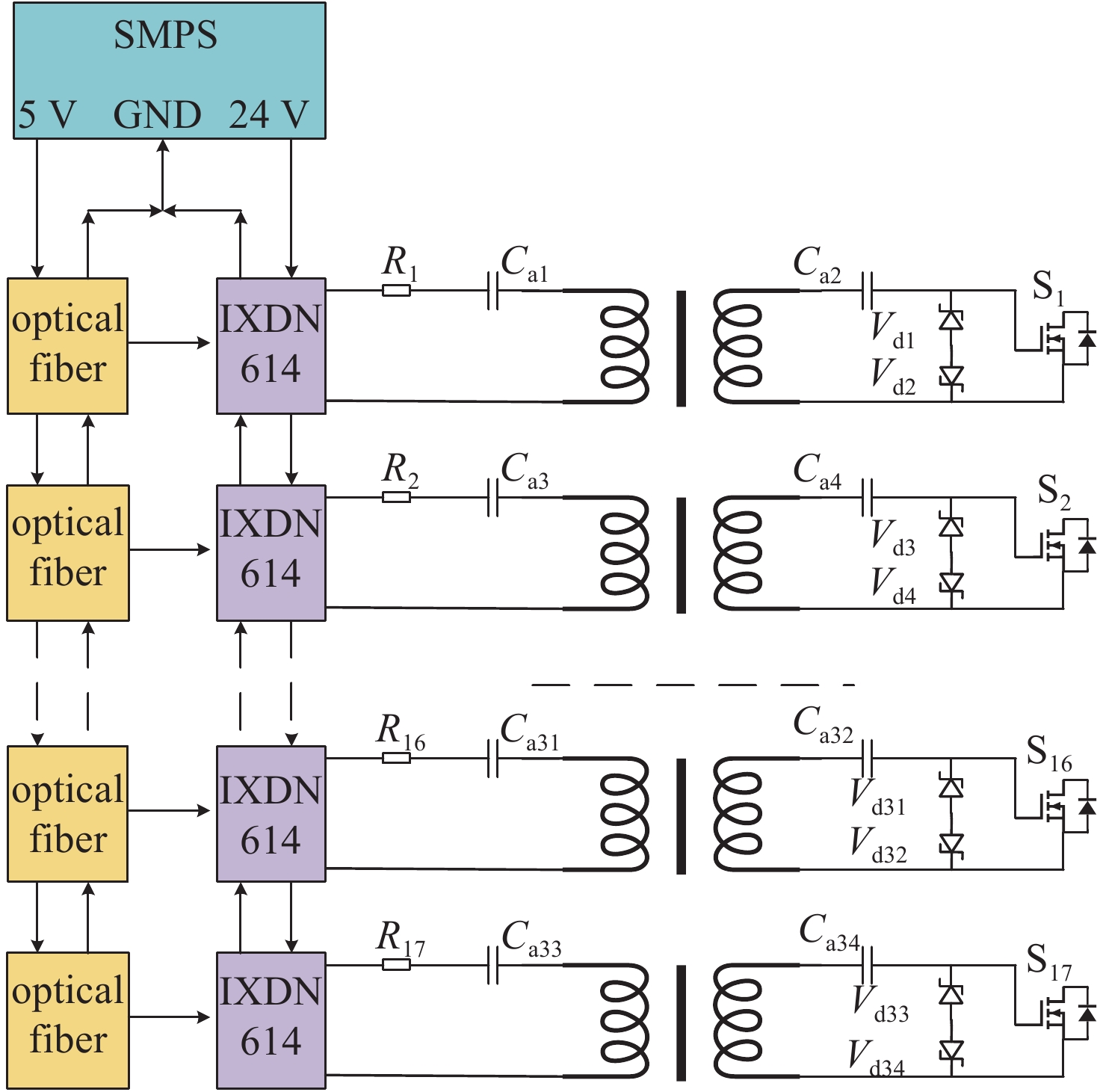
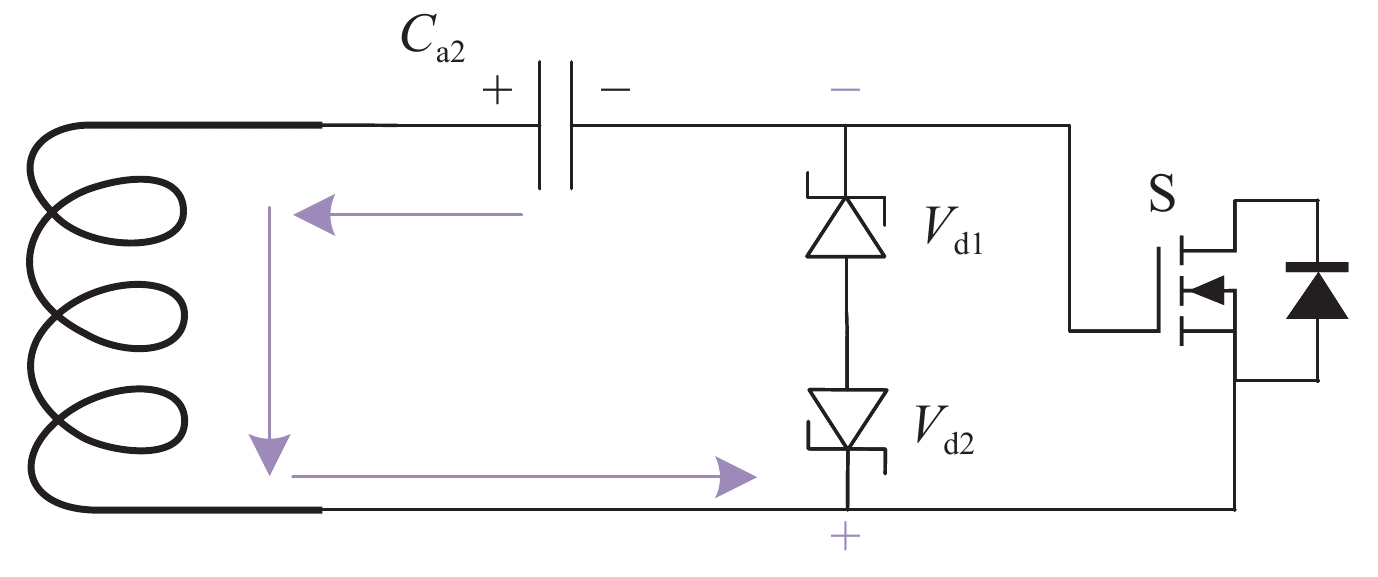
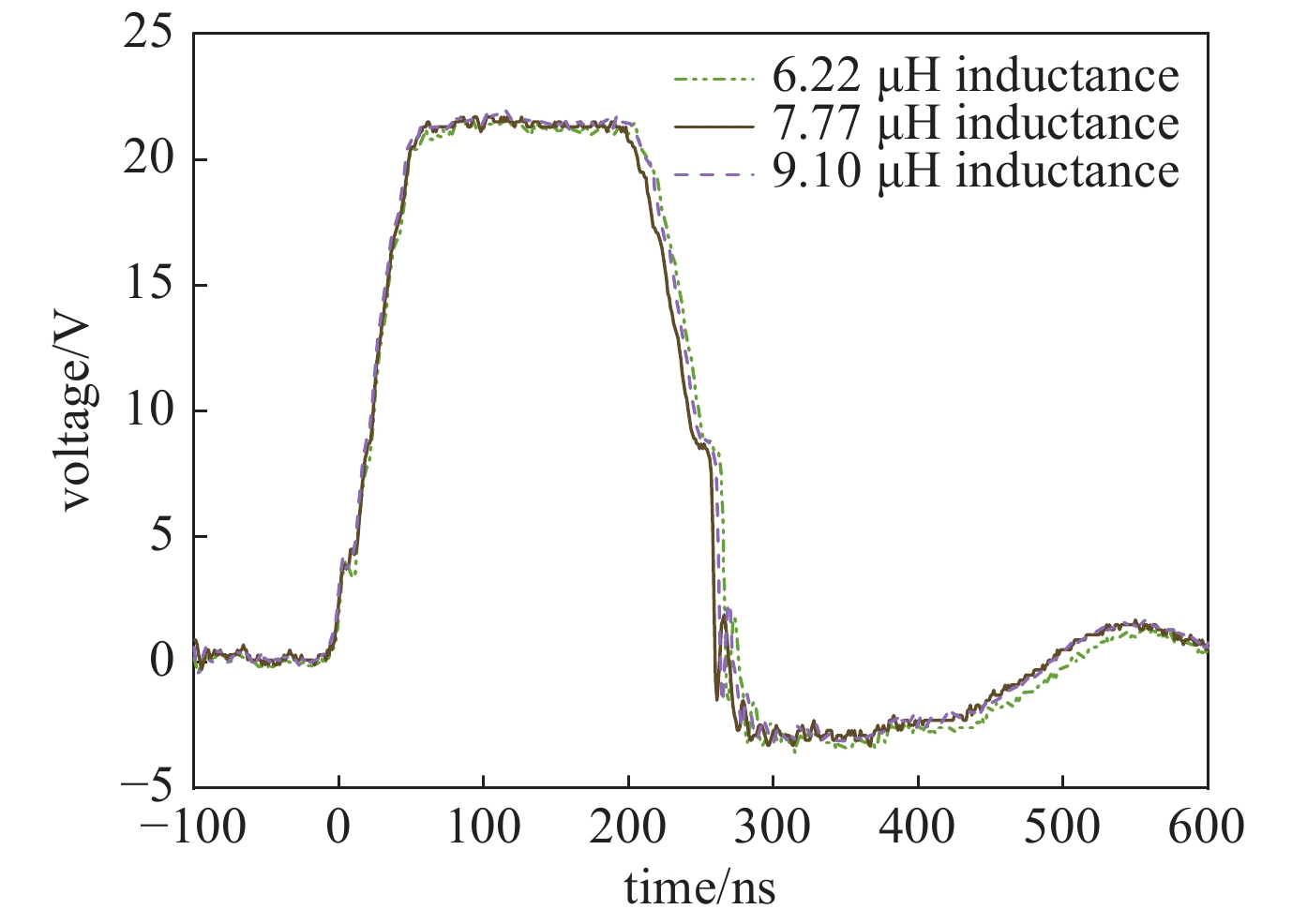
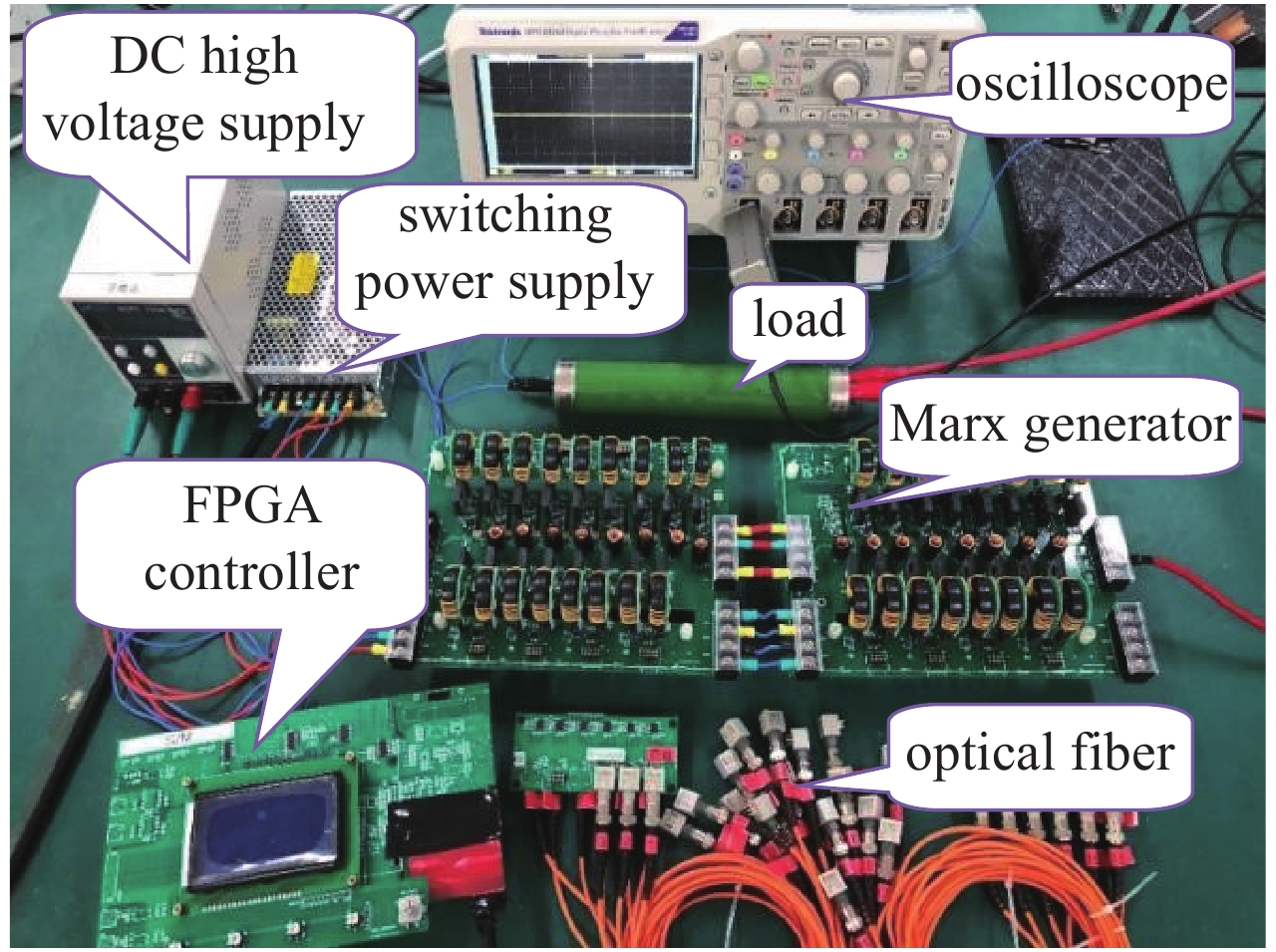
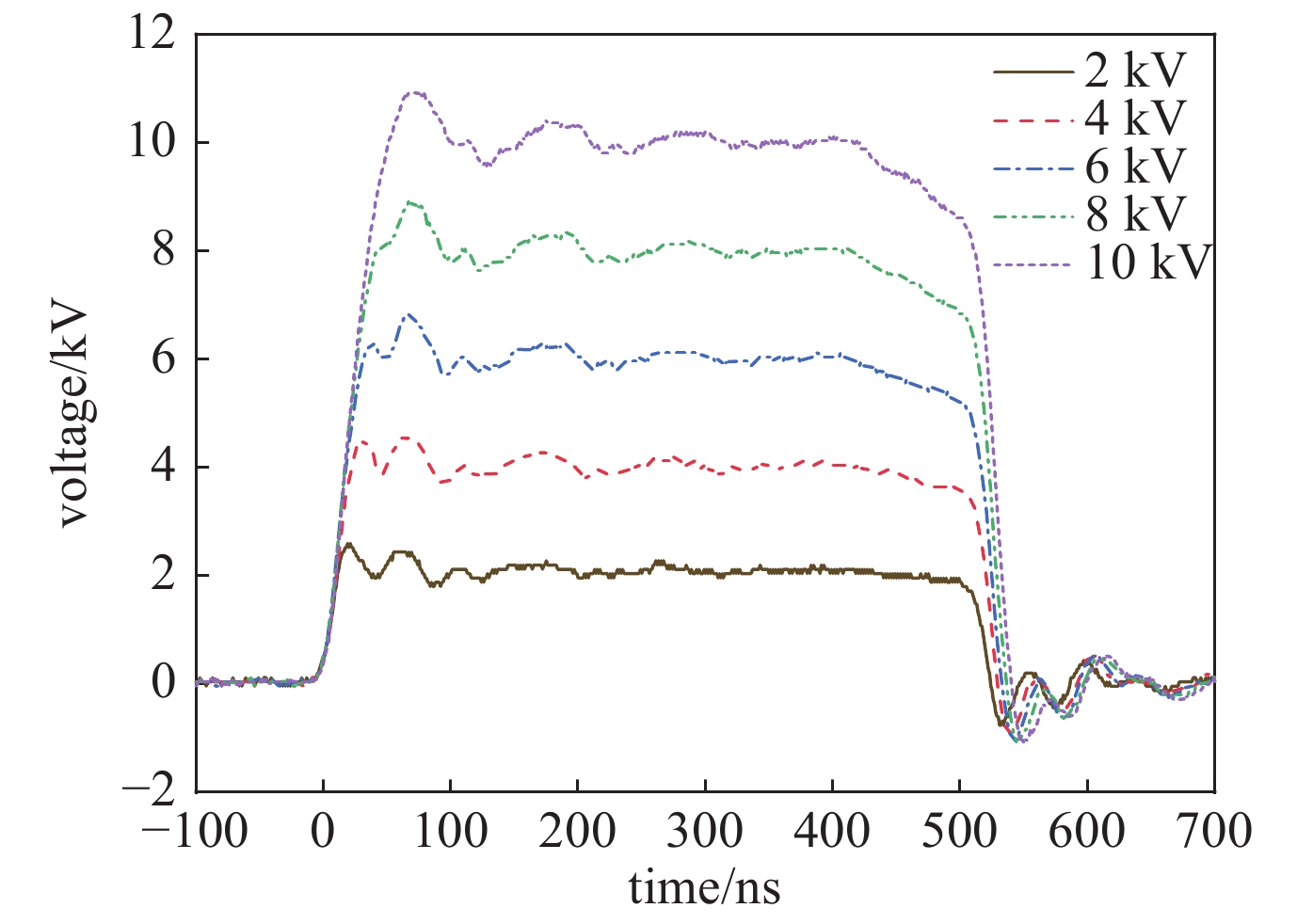
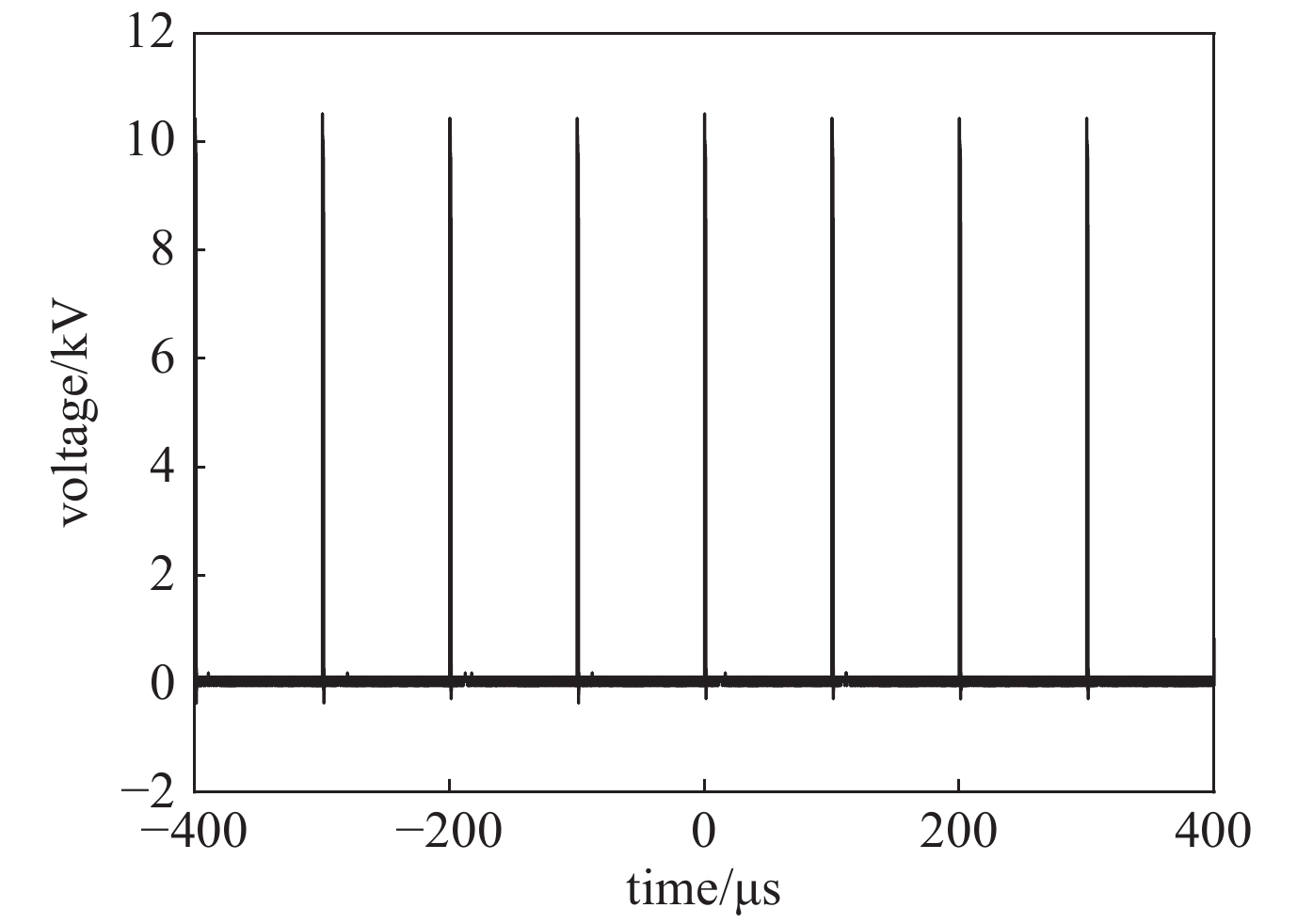
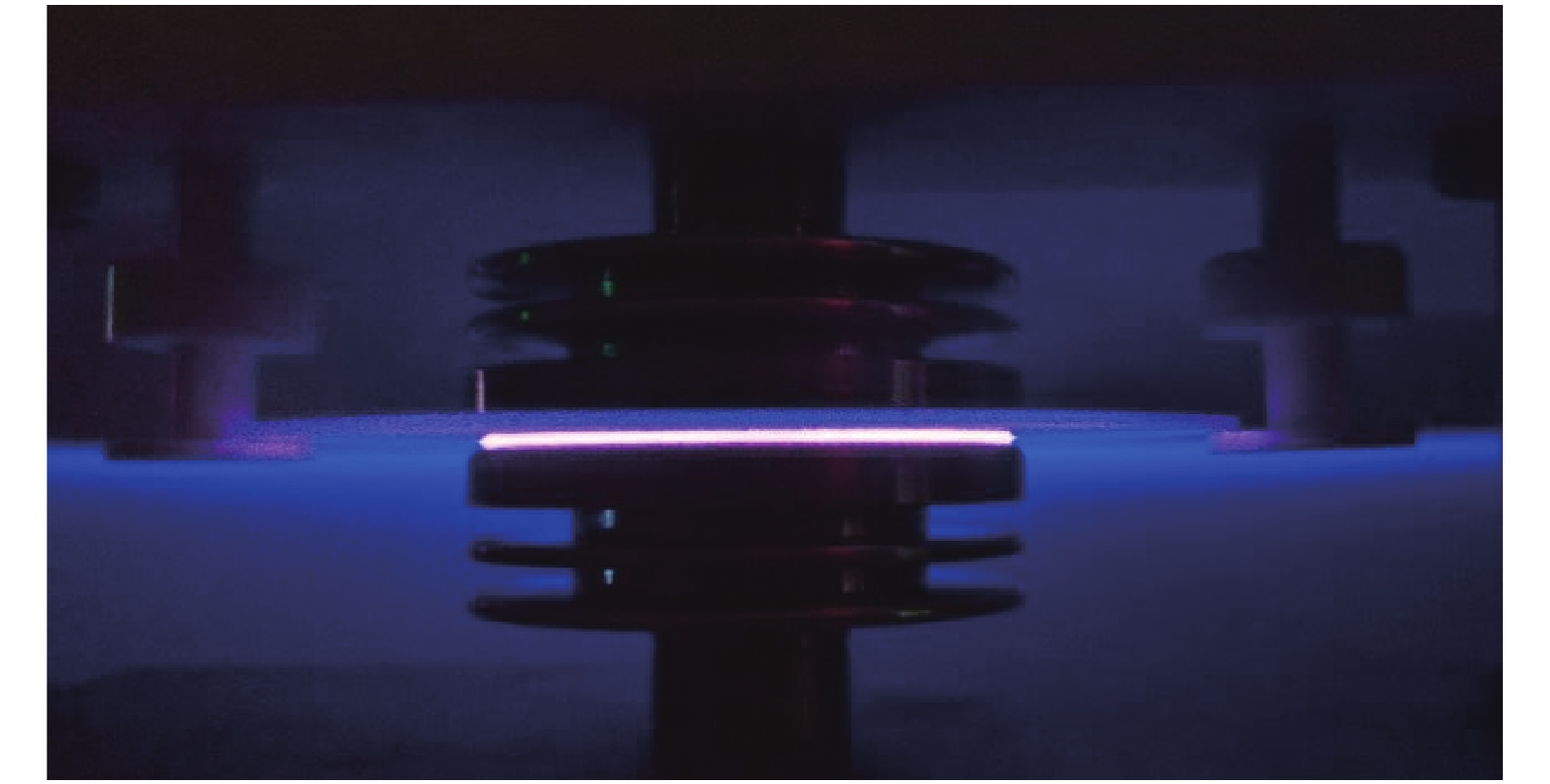
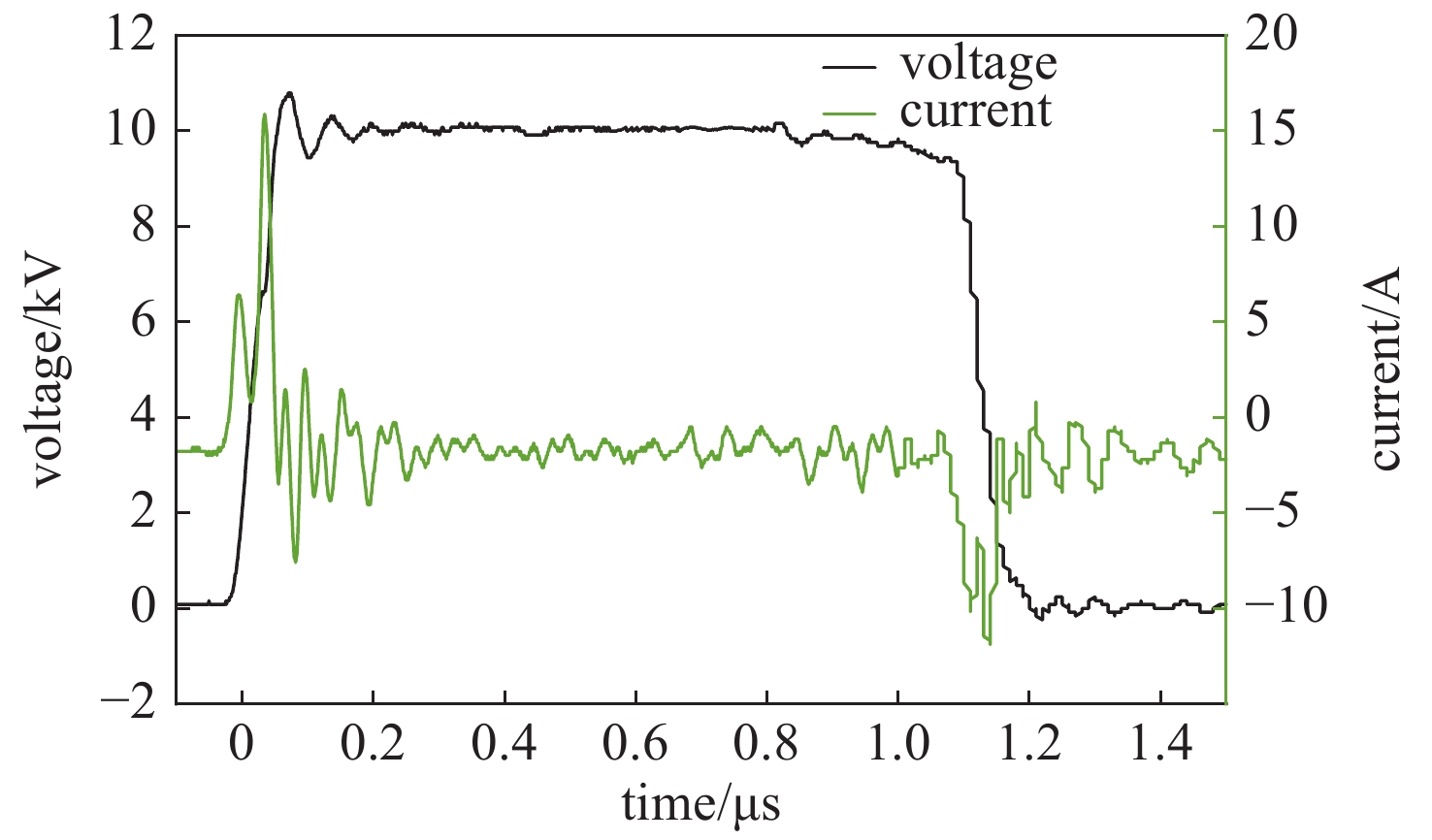
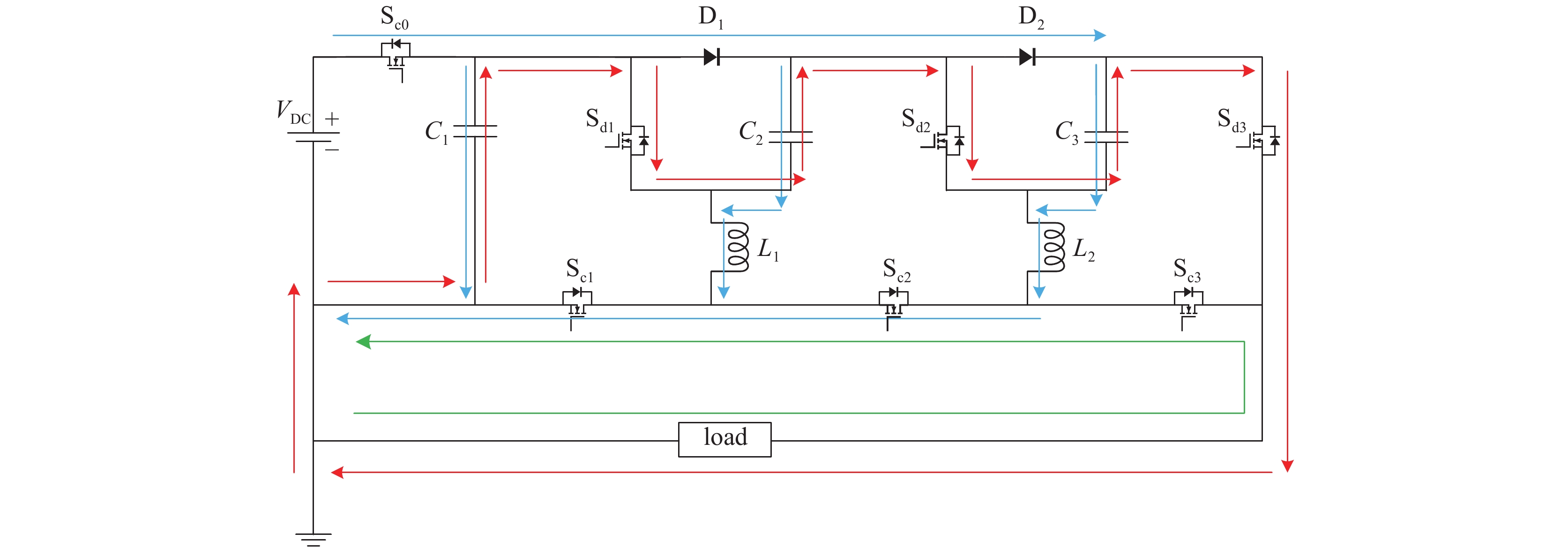
摘要: 为满足不可逆电穿孔对高压纳秒脉冲电源的需求,并且突破电源模块耐压的限制,提出了一款以正极性Marx为主电路、具有ns级前沿的高重复频率的亚微秒高压脉冲电源。该脉冲电源使用光纤传输信号,经过驱动芯片放大信号后,利用磁芯变压器传递驱动信号给MOSFET。磁芯变压器给电路提供了磁隔离,使驱动电路不会受高压输出的影响,提高了电路的耐压水平。驱动电路设计简单,所需元器件较少,可提供负压偏置,使开关管可靠关断,提高电路的抗电磁干扰能力,保障电路稳定运行。此电源由16级电路构成,实验表明:在10 kΩ纯阻性负载上,当输入电压为630 V时,即可得到10 kV的高压输出。其最小脉宽为300 ns,频率1 Hz~10 kHz可调。该脉冲电源结构紧凑,能够做到输出电压、脉宽、频率可调。研究了磁芯材料和匝数对驱动脉宽的影响。结果表明:匝比的增加会影响信号脉宽,在一定的条件下,单匝电感量的差异和磁芯材料的不同对信号脉宽的影响较小。Abstract: To meet the demand of irreversible electroporation for nanosecond pulse power supply, this paper proposes a sub-microsecond high voltage pulse power supply with high repetition frequency, which is based on positive Marx circuit and has ns rising time. The pulse power supply uses optical fiber to transmit signals. After the driver chip amplifies the signal, the magnetic core transformer is used to transmit the drive signal to the MOSFET. The magnetic core transformer provides magnetic isolation to the circuit, so that the drive circuit will not be affected by the high voltage output and the withstand voltage level of the circuit is improved. The design of drive circuit is simple, and it requires fewer components. It provides negative bias voltage so that the switch can be reliably turned off and can effectively improve the electromagnetic compatibility. A 16-stage prototype has been built. The experiment showed that 10 kV square pulses were obtained over 10 kΩ resistive load when the input voltage was 630 V. Its minimum pulse width is 300 ns, and the frequency is adjustable from 1 Hz to 10 kHz. The pulse power supply is compact, and can flexibly adjust the voltage amplitude, pulse width and frequency. The influence of the magnetic material and number of turns of the windings of the magnetic core are also studied. The increase of turns ratio will affect the signal pulse width. Under certain conditions, the difference of single turn inductance and magnetic core material have little effect on signal pulse width.
-
Key words:
- sub-microsecond pulse /
- magnetic isolation /
- pulsed power supply /
- pulsed transformer
-
表 1 三款磁芯型号
Table 1. Three core models
No. of core material of core size of core I Fe-based amorphous alloy 16 mm×
26 mm×5 mmII Fe-based amorphous alloy 12 mm×
20 mm×8 mmIII ferrite 12 mm×
20 mm×8 mm表 2 实验中磁芯参数表
Table 2. Table of magnetic core parameters in the experiment
No. of
experimenttype of
coresingle turn inductance
of core/μHturns
ratio1 I 7.77 7∶7 2 I 7.77 5∶5 3 I 7.77 3∶3 4 I 7.77 1∶1 5 I 6.22 3∶3 6 I 9.10 3∶3 7 II 7.77 7∶7 8 II 7.77 5∶5 9 II 7.77 3∶3 10 II 7.77 1∶1 11 III 7.37 7∶7 12 III 7.37 5∶5 13 III 7.37 3∶3 14 III 7.37 1∶1 -
[1] 卢新培, 严萍, 任春生, 等. 大气压脉冲放电等离子体的研究现状与展望[J]. 中国科学:物理学、力学、天文学, 2011, 41(7):801-815. (Lu Xinpei, Yan Ping, Ren Chunsheng, et al. Review on atmospheric pressure pulsed DC discharge[J]. SCIENTIA SINICA Phys, Mech & Astron, 2011, 41(7): 801-815 [2] Miklavčič D, Sersa G, Brecelj E, et al. Electrochemotherapy: technological advancements for efficient electroporation-based treatment of internal tumors[J]. Medical & Biological Engineering & Computing, 2012, 50(12): 1213-1225. [3] Magori Y, Ohta S, Kagetama T, et al. In vivo experiment of applying nanosecond pulsed electric fields on solid tumor[C]//IEEE Pulsed Power Conference. 2011: 1253-1257. [4] 姚陈果, 宁郡怡, 刘红梅, 等. 微/纳秒脉冲电场靶向不同尺寸肿瘤细胞内外膜电穿孔效应研究[J]. 电工技术学报, 2020, 35(1):115-124. (Yao Chenguo, Ning Junyi, Liu Hongmei, et al. Study of electroporation effect of different size tumor cells targeted by micro-nanosecond pulsed electric field[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2020, 35(1): 115-124 [5] Beebe S J, Fox P M, Rec L J, et al. Nanosecond, high intensity pulsed electric fields induce apoptosis in human cells[J]. Faseb Journal, 2003, 17(9): 1493-1495. [6] Schoenbach K H, Katsuki S, Stark R H, et al. Bioelectrics—New applications for pulsed power technology[J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2002, 30(1): 293-300. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2002.1003873 [7] Schoenbach K H, Joshi R P. Ultrashort electrical pulses open a new gateway into biological cells[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2004, 92(7): 1122-1137. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2004.829009 [8] Schoenbach K H, Nuccitelli R, Beebe S J. ZAP: Extreme voltage could be a surprisingly delicate tool in the fight against cancer[J]. IEEE Spectrum, 2006, 43(8): 20-26. [9] 唐靖超, 殷海荣, 马佳路, 等. 纳秒电脉冲作用下KcsA-膜蛋白体系电穿孔的分子动力学模拟[J]. 真空电子技术, 2019, 4(1):14-20. (Tang Jingchao, Yin Hairong, Ma Jialu, et al. Electroporation of KcsA membrane protein system under nanosecond pulsed electric field: A molecular dynamics simulation[J]. Vacuum Electronics, 2019, 4(1): 14-20 [10] 赵君科, 夏连胜, 任先文, 等. 陡前沿纳秒脉冲电源的研制[J]. 高电压技术, 1999(2):44-46. (Zhao Junke, Xia Liansheng, Ren Xianwen, et al. Research on pulsed power source with nanoseconds risetime[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 1999(2): 44-46 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6520.1999.02.016 [11] 周启明, 孙庚晨, 罗学金, 等. 100kV高压ns陡脉冲源的研制[J]. 高电压技术, 2002, 28(6):37-39. (Zhou Qiming, Sun Gengchen, Luo Xuejin, et al. Development of a nanosecond high voltage pulse power of 100kV and 50Ω loading[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2002, 28(6): 37-39 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6520.2002.06.017 [12] 李玺钦, 丁明军, 吴红光, 等. 低抖动快前沿重复频率高压脉冲触发源研制[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2014, 26:095001. (Li Xiqin, Ding Mingjun, Wu Hongguang, et al. Development of low jitter fast fall time and repetitive high voltage pulsed trigger[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2014, 26: 095001 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201426.095001 [13] Liu Y, Fan R, Zhang X, et al. Bipolar high voltage pulse generator without H-bridge based on cascade of positive and negative Marx generators[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dielectrics and Electrical Insulation, 2019, 26(2): 476-483. doi: 10.1109/TDEI.2018.007861 [14] 嵇保健, 王若冰, 洪峰, 等. 基于Marx电路的纳秒级高压脉冲电源设计[J]. 高电压技术, 2016, 42(12):3758-3762. (Ji Baojian, Wang Ruobing, Hong Feng, et al. Design of nanosecond high-voltage pulsed power source based on Marx generator[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2016, 42(12): 3758-3762 [15] Richard L C, Palo A. High voltage pulsed power supply using solid state switches with voltage cell isolation: United States, US7550876B2[P]. 2009-06-30. [16] Wang Jianjing, Chung S H. Impact of parasitic elements on the spurious triggering pulse in synchronous buck converter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2014, 29(12): 6672-6685. [17] 纪圣儒, 朱志明, 周雪珍, 等. MOSFET隔离型高速驱动电路[J]. 电焊机, 2007, 37(5):6-9,77. (Ji Shengru, Zhu Zhiming, Zhou Xuezhen, et al. Electrical-isolated high-speed MOSFET driver circuit[J]. Electric Welding Machine, 2007, 37(5): 6-9,77 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2303.2007.05.002 [18] 徐建清, 高勇, 杨媛, 等. SiC MOSFET驱动电路设计及特性分析[J]. 半导体技术, 2020, 45(5):352-358,408. (Xu Jianqing, Gao Yong, Yang Yuan, et al. Driving circuit design and performance analysis for SiC MOSFET[J]. Semiconductor Devices, 2020, 45(5): 352-358,408 -




 下载:
下载: