Statistical characteristics of S-band microwave pulse breakdown time in free space
-
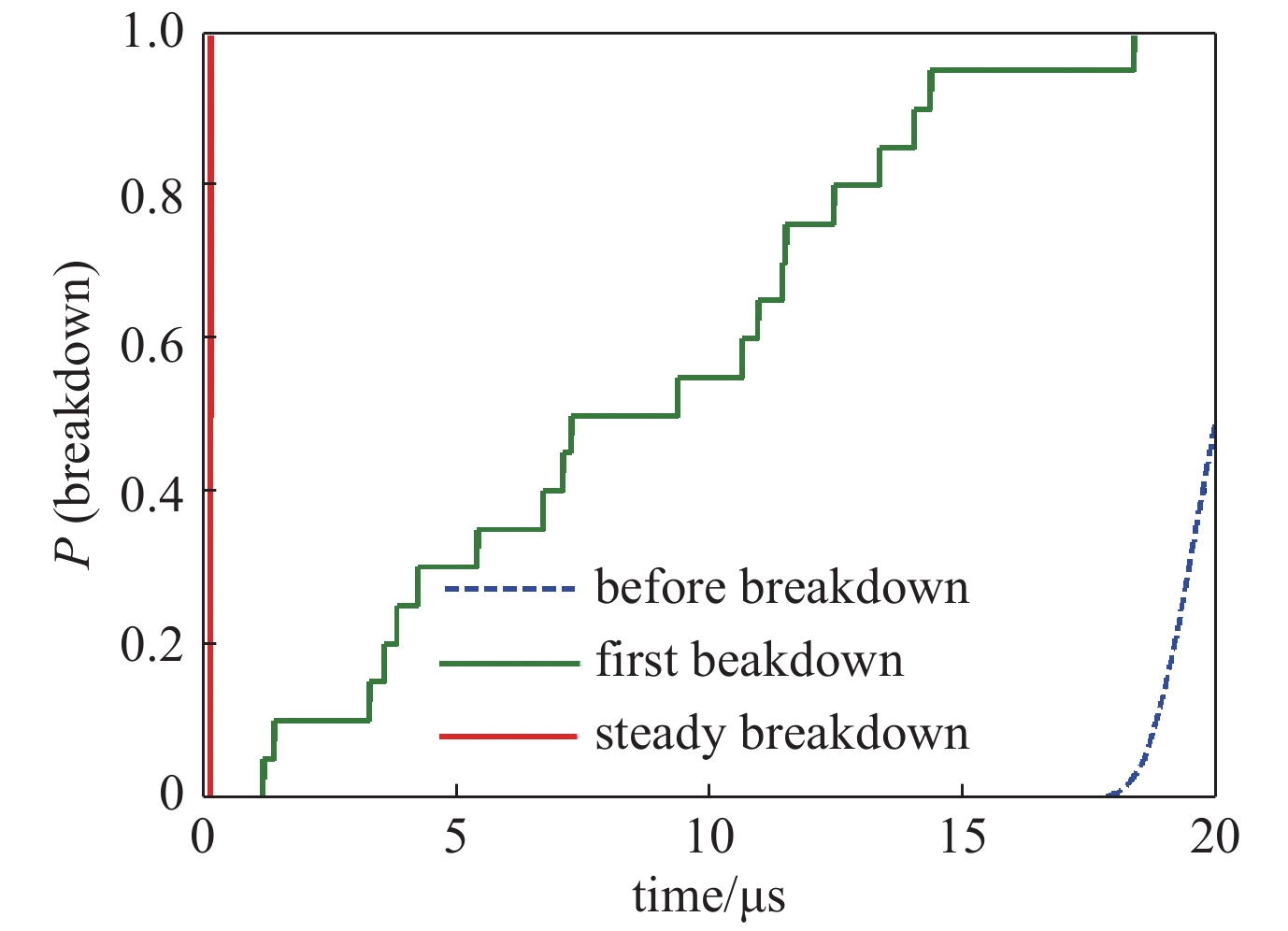
摘要: 综合考虑有效初始电子产生理论、雪崩电子击穿理论等过程中的击穿延迟时间,探讨了开放空间微波脉冲的击穿延时概率分布,提出了重复频率微波脉冲击穿概率模型,定义了基于概率模型的微波脉冲击穿阈值。利用S波段微波准光学反射聚焦系统对一定气压大气击穿过程进行了模拟,监测击穿放电发光时刻作为击穿时间,分别在铯137放射源存在与否情况下开展了系列实验。研究结果表明,提高种子电子产生率相较于提高电离率是增大脉冲击穿概率更有效的方法;重复频率过程中,若存在累积效应,击穿延时概率分布曲线将左移并趋于稳定,击穿后的气体在短时间内容易再次击穿。Abstract: In the vicinity of atmospheric breakdown threshold, microwave pulse breakdown discharge becomes a probabilistic problem, which is closely related to breakdown time. When atmospheric breakdown occurs, the transmission pulse width and peak power will be shortened. The development of high power microwave technology is severely restricted by the hazards. To study the breakdown problem in high power microwave atmospheric transmission, the probability distribution curves of breakdown time in different processes are compared, and the effects of ionization rate and seed electron generation rate on breakdown time are discussed. The breakdown process of free space microwave was experimentally studied using S-band high power microwave pulse source. The breakdown time of plasma was monitored by photomultiplier tube, and a series of experiments were carried out in the presence or absence of cesium 137 seed electron source. The results show that increasing the seed electron generation rate is a more effective method to increase the pulse breakdown probability. In the process of repetition frequency, if there is cumulative effect, the breakdown delay time probability distribution curve will move to the left and tend to be stable. And the gas after breakdown will be easy to breakdown again in a short time.
-
Key words:
- high power microwave /
- seed electron /
- breakdown time /
- statistical characteristics
-
表 1 实验参数
Table 1. Parameters of experiments
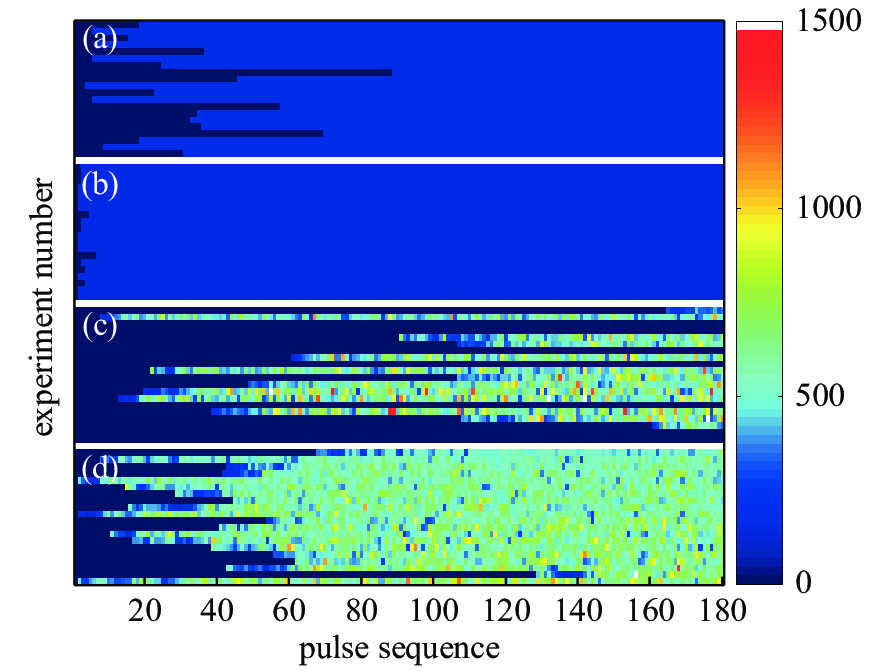
No. pressure/Pa E/(kV·cm−1) ionization rate/MHz seed electron production rate A 1000 0.92 52.5 − B 1000 1.29 188.2 − C 8000 1.87 \ low D 8000 1.87 \ high -
[1] Barker R, Edi S. High power microwave source and technology[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2005: 154-158. [2] 杨浩, 闫二艳, 郑强林, 等. 临近空间高功率微波辐照放电试验技术[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2019, 31:103216. (Yang Hao, Yan Eryan, Zheng Qianglin, et al. Examination research of high power microwave irradiation discharge in near space[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2019, 31: 103216 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201931.190151 [3] Sprangle P, Hafizi B, Milchberg H, et al. Active remote detection of radioactivity based on electromagnetic signatures[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2014, 21: 013103. doi: 10.1063/1.4861633 [4] Isaacs J, Miao Chenlong, Sprangle P. Remote monostatic detection of radioactive material by laser-induced breakdown[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2016, 23: 033507. doi: 10.1063/1.4943404 [5] Nusinovich G S, Pu Ruifeng, Antonsen Jr T M, et al. Development of THz-range gyrotrons for detection of concealed radioactive materials[J]. Journal of Infrared, Millimeter, and Terahertz Waves, 2011, 32(3): 380-402. doi: 10.1007/s10762-010-9708-y [6] Nusinovich G S, Sprangle P, Semenov V E, et al. On the sensitivity of terahertz gyrotron based systems for remote detection of concealed radioactive materials[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2012, 111: 124912. doi: 10.1063/1.4730959 [7] Dorozhkina D, Semenov V, Olsson T, et al. Investigations of time delays in microwave breakdown initiation[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2006, 13: 013506. doi: 10.1063/1.2158696 [8] Foster J, Krompholz H, Neuber A. Investigation of the delay time distribution of high power microwave surface flashover[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2011, 18: 013502. doi: 10.1063/1.3534823 [9] Kim D, Yu D, Sawant A, et al. Remote detection of radioactive material using high-power pulsed electromagnetic radiation[J]. Nature Communications, 2017, 8: 15394. doi: 10.1038/ncomms15394 [10] 魏进进, 周东方, 余道杰, 等. 高功率微波作用下O–离子解吸附产生种子电子过程[J]. 物理学报, 2016, 65:055202. (Wei Jinjin, Zhou Dongfang, Yu Daojie, et al. Seed electron production from O– detachment in high power microwave air breakdown[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2016, 65: 055202 doi: 10.7498/aps.65.055202 [11] Cook A M, Hummelt J S, Shapiro M A, et al. Measurements of electron avalanche formation time in W-band microwave air breakdown[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2011, 18: 080707. doi: 10.1063/1.3626383 [12] Edmiston G, Krile J, Neuber A, et al. High-power microwave surface flashover of a gas–dielectric interface at 90–760 torr[J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2006, 34(5): 1782-1788. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2006.883392 [13] 魏进进, 周东方. 高功率微波脉冲大气击穿概率研究[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2014, 26:063003. (Wei Jinjin, Zhou Dongfang. Probability distribution of high power microwave pulse breakdown in air[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2014, 26: 063003 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201426.063003 [14] 杨浩, 闫二艳, 郑强林, 等. 一种准光反射聚焦微波放电大气等离子体装置[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2019, 31:053002. (Yang Hao, Yan Eryan, Zheng Qianglin, et al. A microwave plasma system with quasi optical focusing reflector[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2019, 31: 053002 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201931.180350 [15] 赵刚, 闫二艳, 陈朝阳, 等. 高功率微波大气击穿阈值分析及实验[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2013, 25(s1):111-114. (Zhao Gang, Yan Eryan, Chen Chaoyang, et al. Analysis and experimental study on threshold of air breakdown by high power microwave[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2013, 25(s1): 111-114 [16] Hidaka Y, Choi E M, Mastovsky I, et al. Imaging of atmospheric air breakdown caused by a high-power 110-GHz pulsed Gaussian beam[J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2008, 36(4): 936-937. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2008.924612 [17] Zhou Qianhong, Dong Zhiwei. Modeling study on pressure dependence of plasma structure and formation in 110 GHz microwave air breakdown[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2011, 98: 161504. doi: 10.1063/1.3583452 [18] Cook A, Shapiro M, Temkin R. Pressure dependence of plasma structure in microwave gas breakdown at 110 GHz[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2010, 97: 011504. doi: 10.1063/1.3462320 [19] Hagelaar G J M, Pitchford L C. Solving the Boltzmann equation to obtain electron transport coefficients and rate coefficients for fluid models[J]. Plasma Sources Science and Technology, 2005, 14(4): 722-733. doi: 10.1088/0963-0252/14/4/011 [20] Phelps A V, Pitchford L C. Anisotropic scattering of electrons by N2 and its effect on electron transport[J]. Physical Review A, 1985, 31(5): 2932-2949. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.31.2932 [21] SIGLO database[EB/OL]. [2013-06-04]. http://www.lxcat.laplace.univ-tlse.fr. [22] Lawton S A, Phelps A V. Excitation of the b 1Σ+g state of O2 by low energy electrons[J]. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 1978, 69(3): 1055-1068. doi: 10.1063/1.436700 [23] PHELPS database[EB/OL]. http://www.lxcat.laplace.univ-tlse.fr, retrieved June 4, 2013NOTE: 3 body attachment cross section are normalized to gas density in units of cm. -





 下载:
下载: