| [1] |
Foster Jr J S, Gjelde E, Graham W R, et al. Report of the commission to assess the threat to the United States from electromagnetic pulse (EMP) attack. Volume 1: Executive report[R]. Washington DC: Committee on Electromagnetic Pulse Environment, 2004.
|
| [2] |
Foster Jr J S, Gjelde E, Graham W R, et al. Report of the commission to assess the threat to the United States from electromagnetic pulse (EMP) attack: Critical national infrastructures[R]. Electromagnetic Pulse (EMP) Commission MCLEAN VA, 2008.
|
| [3] |
U. S. Department of Energy. U. S. Department of Energy electromagnetic pulse resilience action plan[M]. New York: CreateSpace Independent Publishing Platform, 2017.
|
| [4] |
U. S. Department of Energy and the Electric Power Research Institute. Joint electromagnetic pulse resilience strategy[R]. Electric Power Research Institute, 2016.
|
| [5] |
董宁, 谢彦召. 考虑参数不确定性的高空电磁脉冲E1分量环境计算及分析[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2019, 31:070002. (Dong Ning, Xie Yanzhao. Early-time high-altitude electromagnetic pulse simulation and analysis considering parameter uncertainty[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2019, 31: 070002 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201931.190140
|
| [6] |
Cui Meng. Numerical simulation of the HEMP environment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electromagnetic Compatibility, 2013, 55(3): 440-445. doi: 10.1109/TEMC.2013.2258024
|
| [7] |
RackwitzR. Reliability analysis—a review and some perspectives[J]. Structural Safety, 2001, 23(4): 365-395. doi: 10.1016/S0167-4730(02)00009-7
|
| [8] |
Sharp D H, Wood-SchultzMM. QMU and nuclear weapons certification: what’s under the hood[J]. Los Alamos Science, 2003, 28: 47-53.
|
| [9] |
Marcy P W, Williams B J, Tippetts T B. Quantification of margins and uncertainty for multicomponent systems[R]. Los Alamos: Los Alamos National Lab, 2019.
|
| [10] |
彭忠明, 梁天锡, 魏发远. QMU与概率可靠性: 区别与联系[C]//技术融合创新·可靠服务企业·安全产品制胜——2013年全国机械行业可靠性技术学术交流会暨第四届可靠性工程分会第五次全体委员大会论文集. 2013Peng Zhongming, Liang Tianxi, Wei Fayuan. QMU and probabilistic reliability: difference and connection[C]//Proceedings of the 2013 National Reliability Technology Academic Conference of Machinery Industry and the Fifth Plenary Meeting of the Fourth Reliability Engineering Branch. 2013
|
| [11] |
梁天锡, 彭忠明, 沈展鹏, 等. 基于裕量与不确定性量化的系统可靠性评估[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2017, 17(3):121-129. (Liang Tianxi, Peng Zhongming, Shen Zhanpeng, et al. System reliability assessment based on QMU[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2017, 17(3): 121-129 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2017.03.018
|
| [12] |
刘振中. 基于QMU的卫星电源系统抗辐射性能评估[D]. 长沙: 国防科学技术大学Liu Zhenzhong. Radiation effects evaluation of satellite electric power system based on quantifications of margins and uncertainties[D]. Changsha: National University of Defense Technology
|
| [13] |
范如玉, 韩峰, 郭红霞. 电源系统抗伽玛总剂量辐射能力评估方法[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2011, 23(2):536-540. (Fan Ruyu, Han Feng, Guo Hongxia. Assessment method of gamma-dose radiation hardness of power supply system[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2011, 23(2): 536-540 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20112302.0536
|
| [14] |
Ianoz M, Nicoara B I C, Radasky W A. Modeling of an EMP conducted environment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electromagnetic Compatibility, 1996, 38(3): 400-413. doi: 10.1109/15.536070
|
| [15] |
杜子韦华, 谢彦召. 架空及埋地多导体线缆对HEMP辐照的瞬态响应[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2019, 31:070003. (Du Ziweihua, Xie Yan zhao. Transient response of overhead and buried multiconductor lines to HEMP[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2019, 31: 070003 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201931.190142
|
| [16] |
李湛宇, 董宁, 纪锋, 等. 基于多项式混沌方法的场线耦合响应不确定度量化[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2017, 29:113203. (Li Zhanyu, Dong Ning, Ji Feng, et al. Uncertainty quantification analysis of random field coupling to transmission lines based on polynomial chaos expansion method[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2017, 29: 113203 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201729.170135
|
| [17] |
束国刚, 杜子韦华, 黄玮, 等. 核电站最小安全系统电磁脉冲效应试验研究[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2018, 30:103203. (Shu Guogang, Du Ziweihua, Huang Wei, et al. Experiment research on electromagnetic effects of minimum safety system in nuclear power plant[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2018, 30: 103203 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201830.180115
|
| [18] |
Zhou Yi, Xie Yanzhao, Zhang Daozhong, et al. Modeling and performance evaluation of inductive couplers for pulsed current injection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electromagnetic Compatibility, 2021, 63(3): 710-719. doi: 10.1109/TEMC.2020.3023042
|
| [19] |
黄忠胜, 陈宇浩, 杨明, 等. 基于贝叶斯方法的设备级电磁脉冲效应评估[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2015, 27:125002. (Huang Zhongsheng, Chen Yuhao, Yang Ming, et al. Effect assessment of electromagnetic pulse at equipment level based on Bayesian method[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2015, 27: 125002 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201527.125002
|
| [20] |
An Z W, Huang H Z, Liu Y. A discrete stress–strength interference model based on universal generating function[J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2008, 93(10): 1485-1490.
|




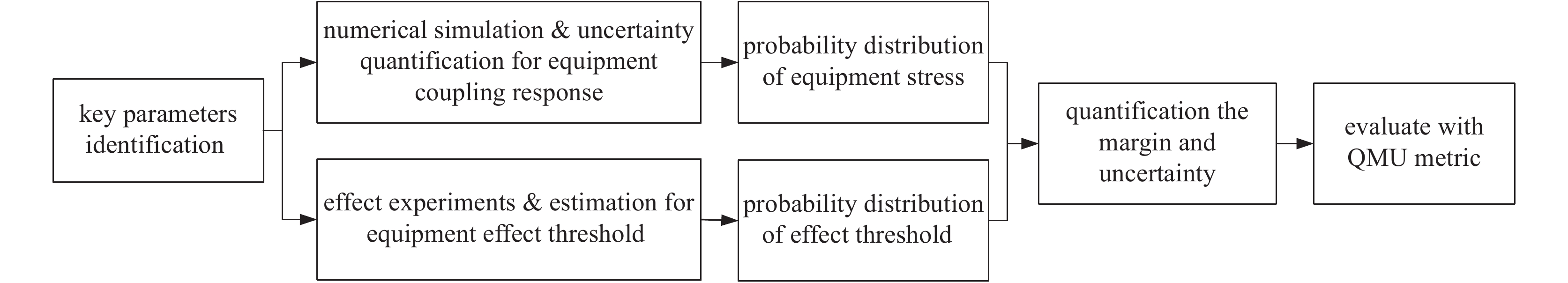
 下载:
下载: