Study on slow wave structure and interaction of 2−18 GHz ultra-wide band traveling-wave tube
-
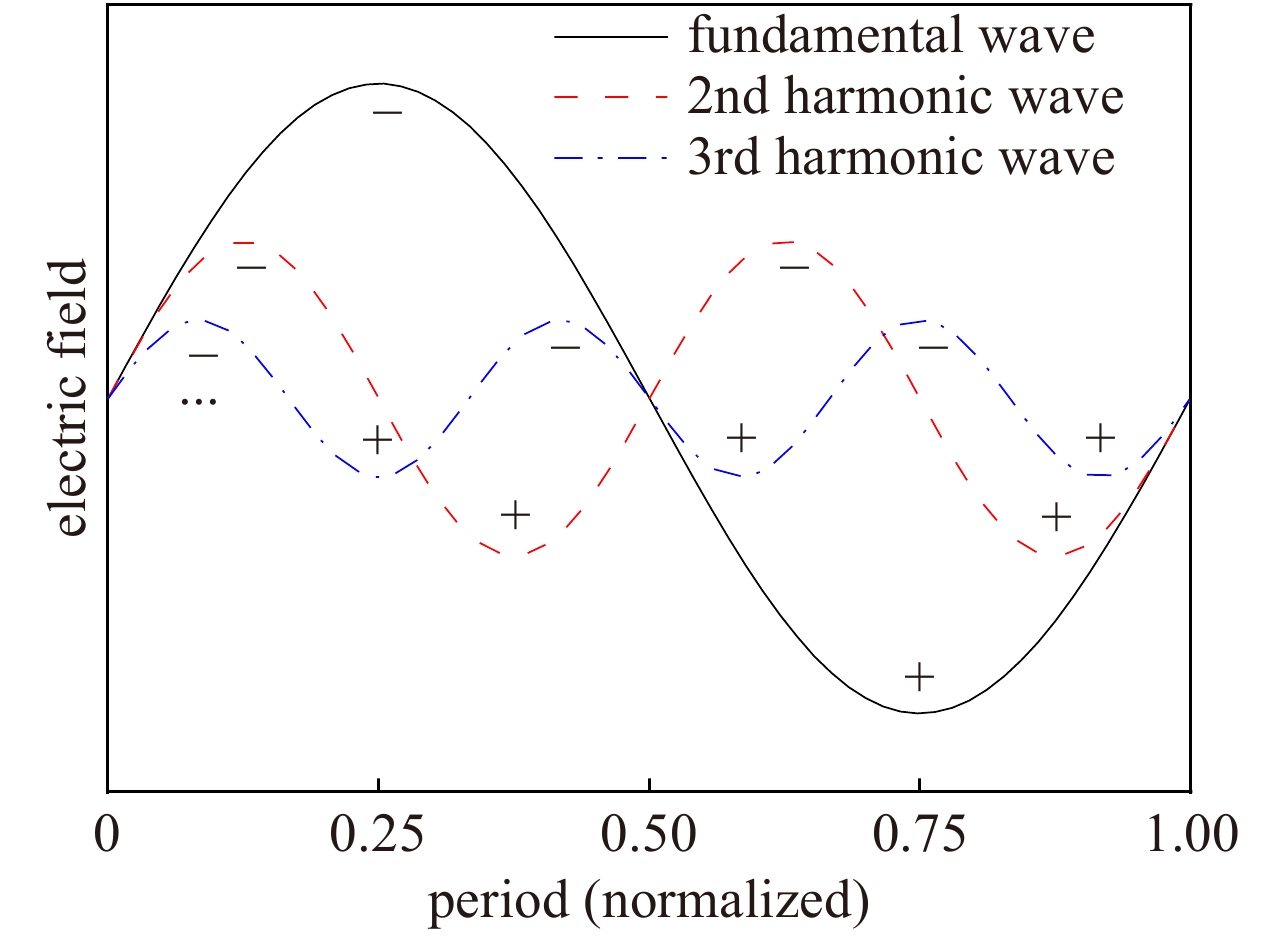
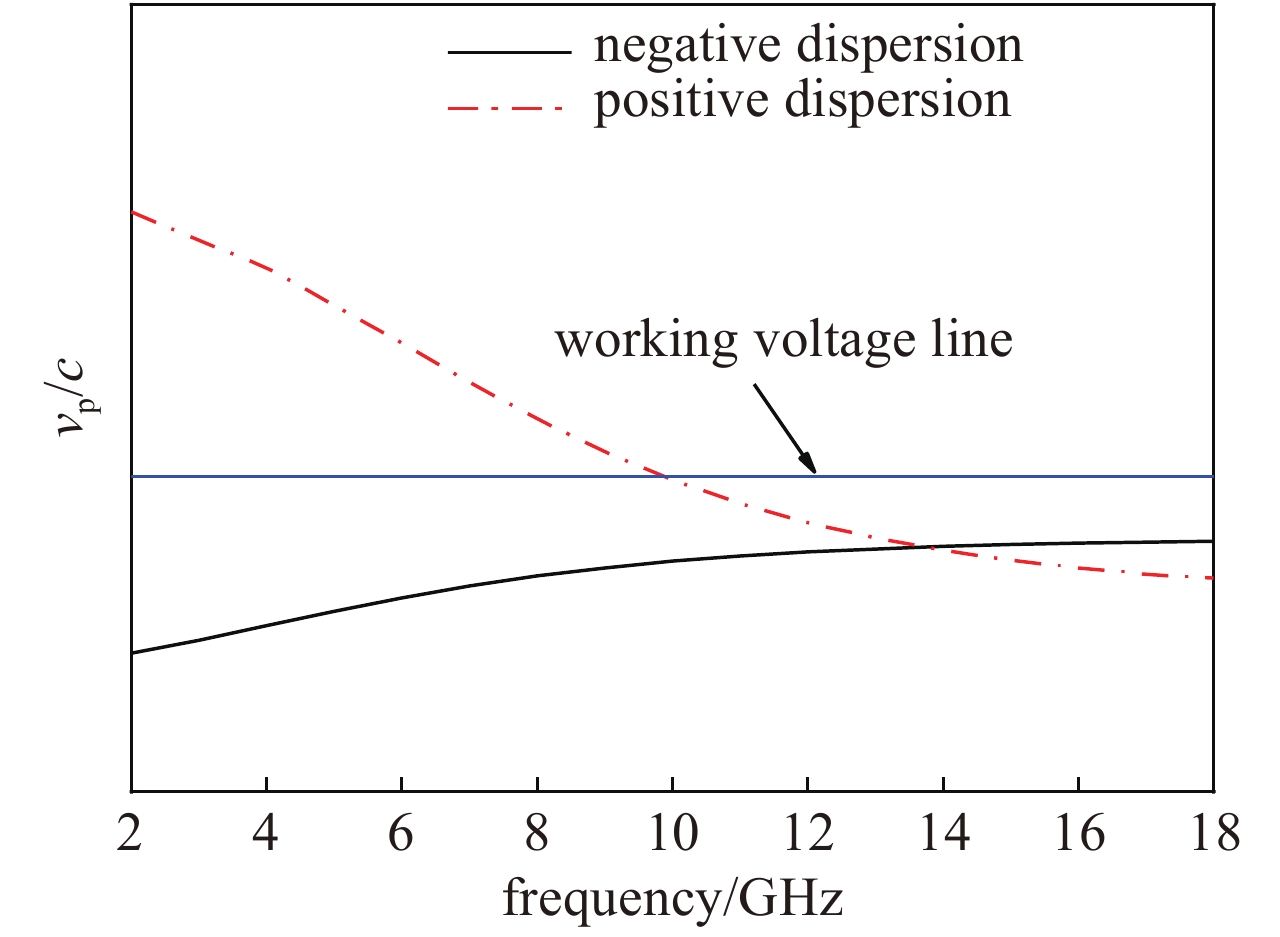
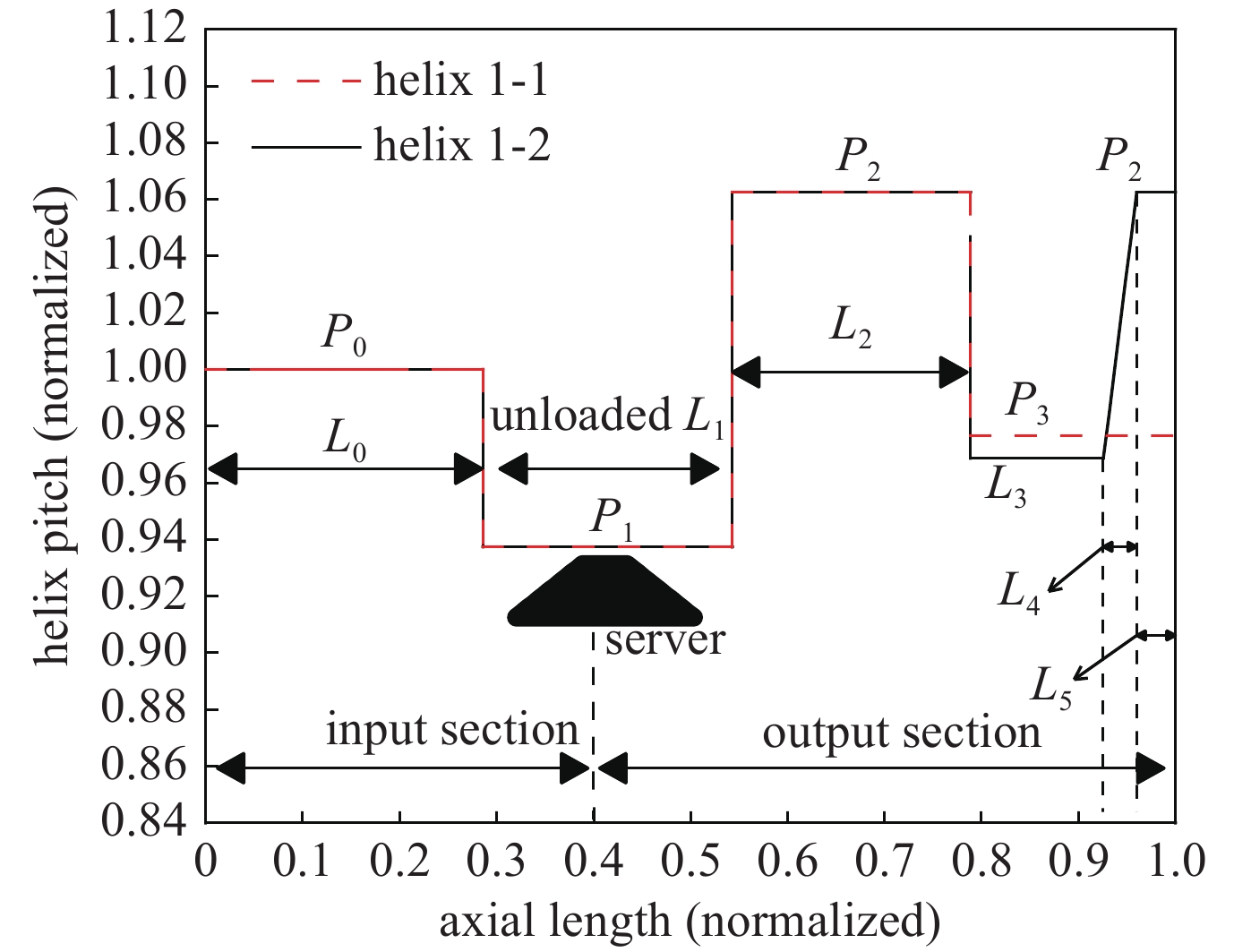
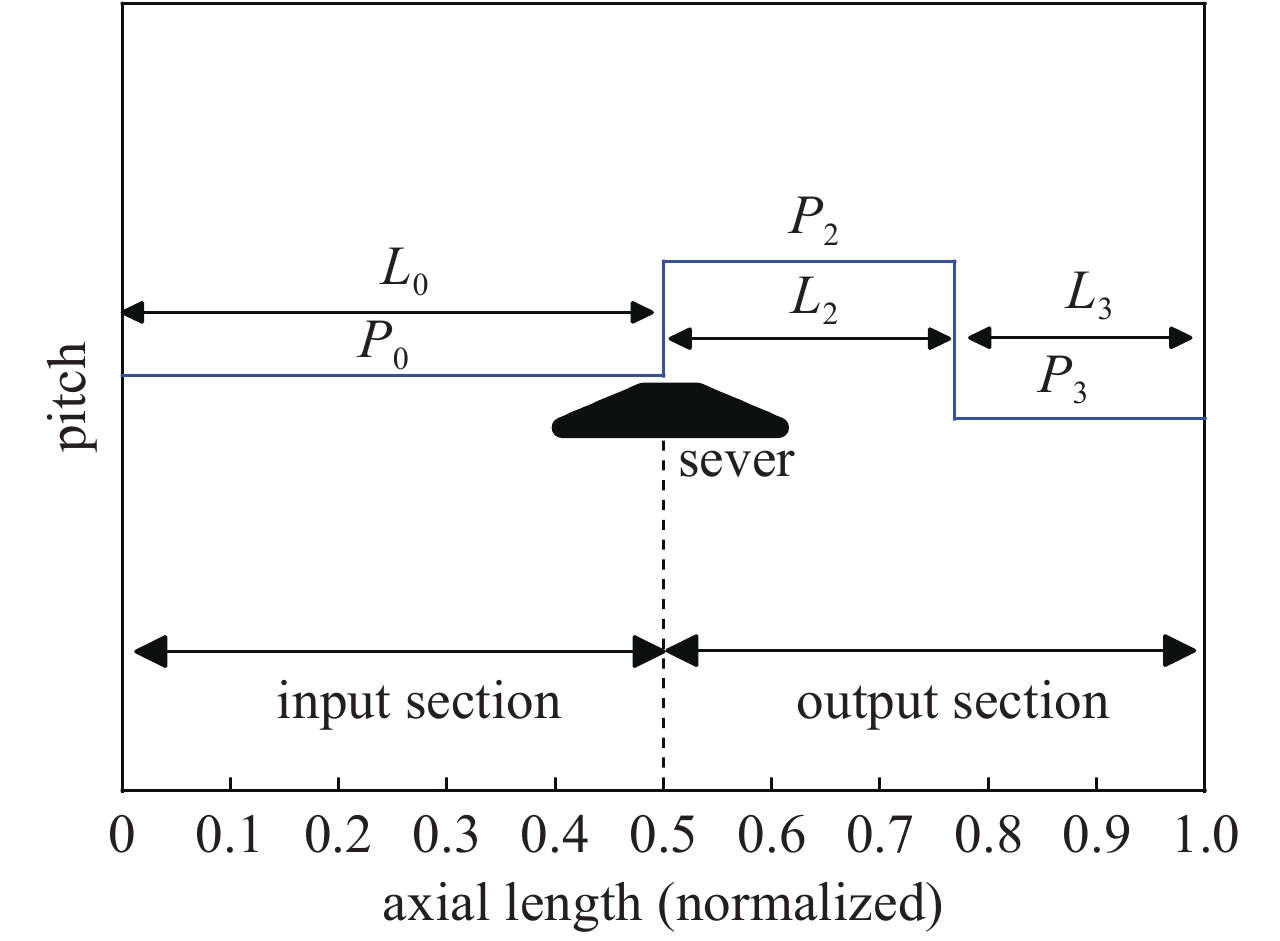
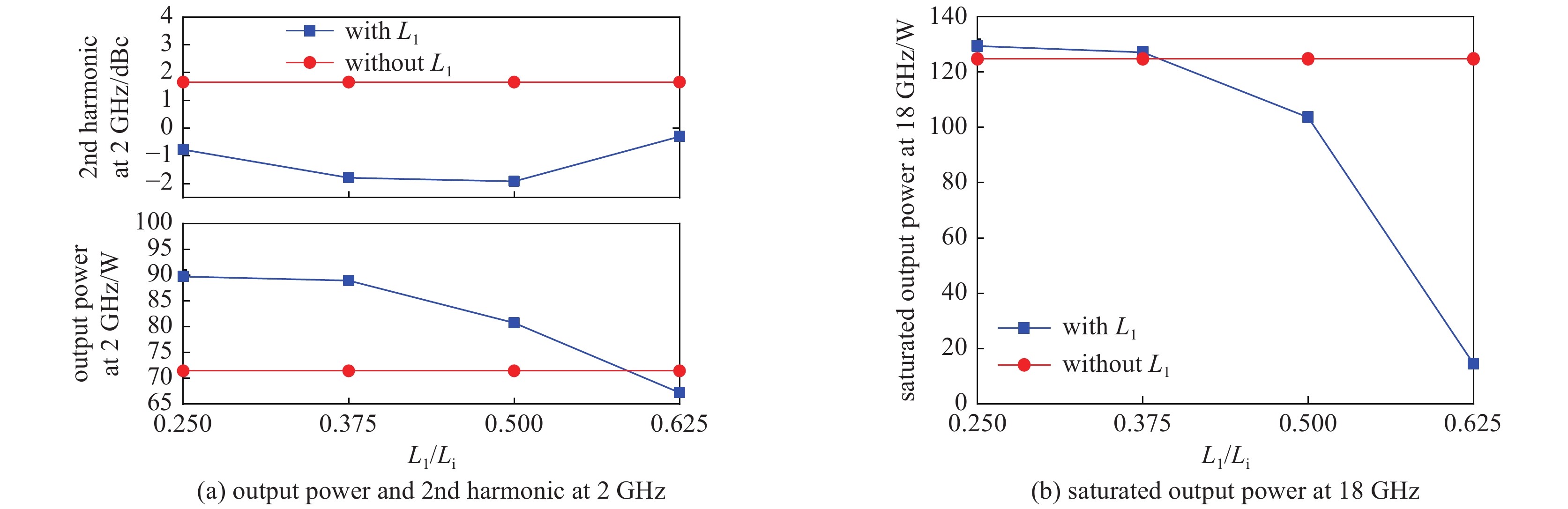
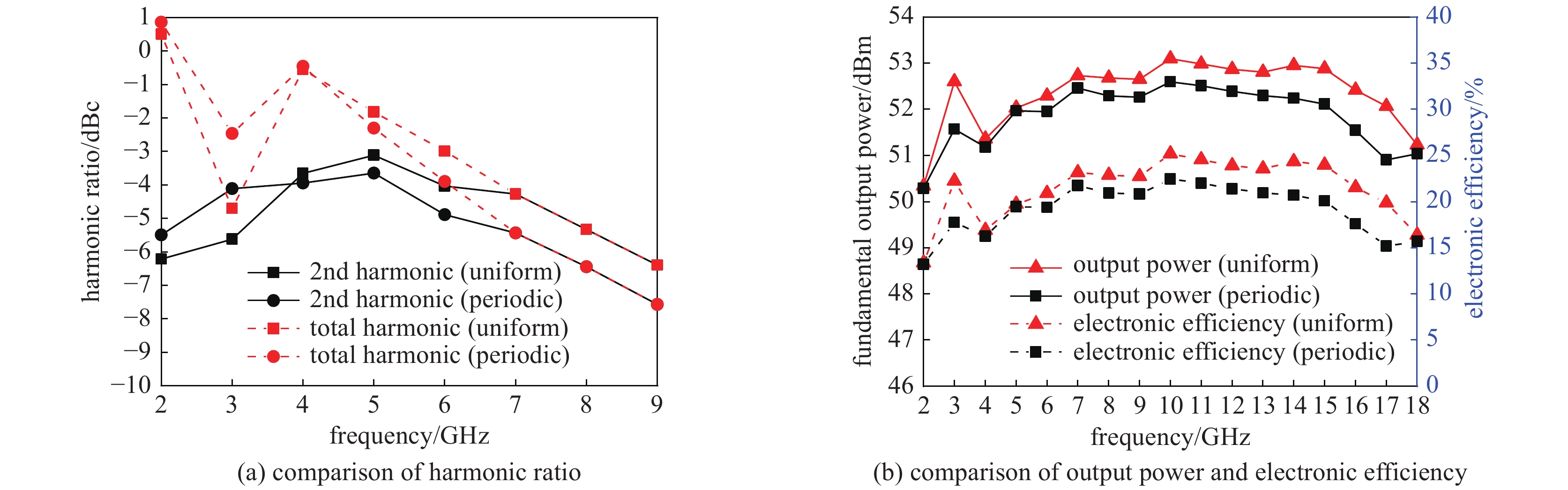
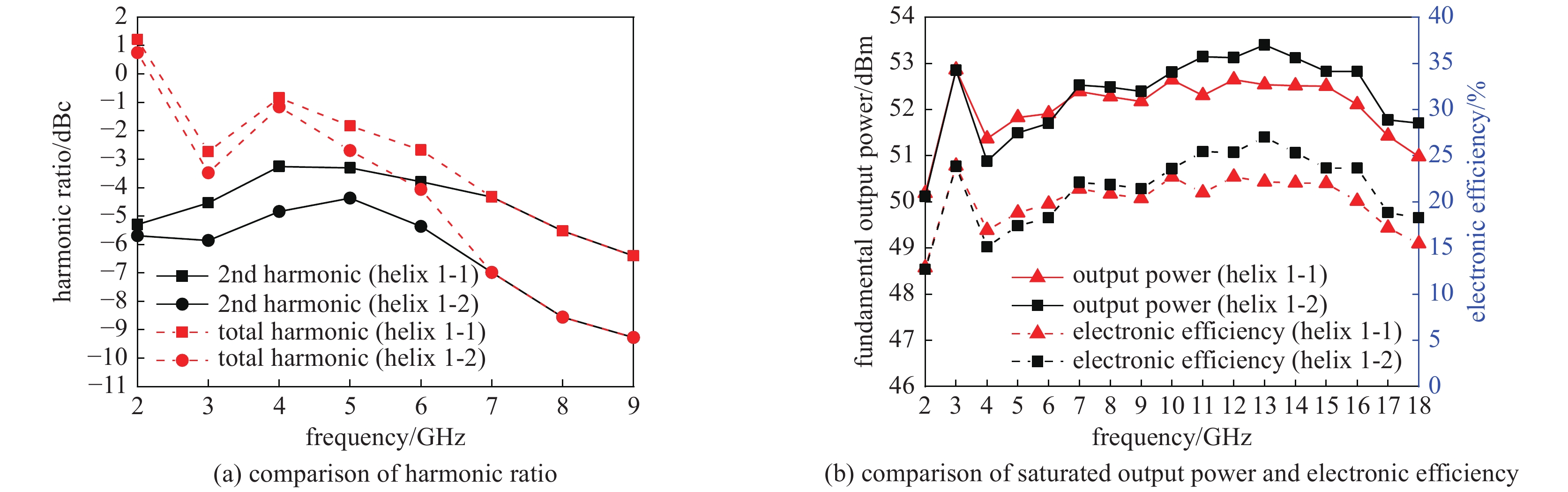
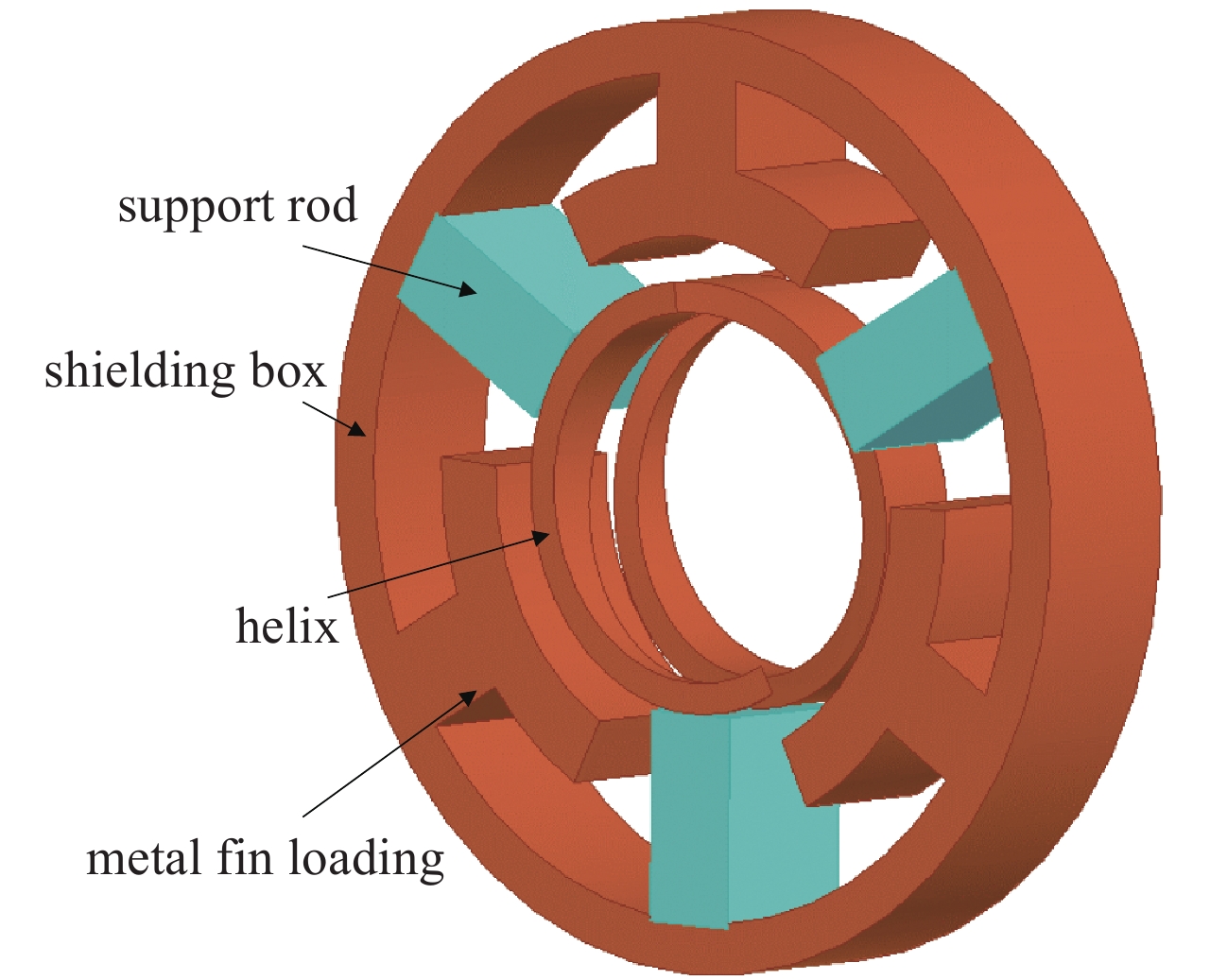
摘要: 为满足现代信息化战争对超宽带行波管的需求,对2~18 GHz超宽带行波管的高频慢波结构进行了研究分析。在传统宽带行波管的基础上引入非翼片加载段的正常色散特性,首次实现2~18 GHz 超宽带高频慢波结构设计,最大带宽达到9∶1。同时输出端螺旋线螺距调整为正渐变分布,能够进一步优化低频段二次谐波抑制比,提高高频段饱和输出功率。结果表明,全频带的基波输出功率达到100 W,二次谐波抑制比优于−3 dBc,2 GHz频点二次谐波抑制比优于−5 dBc,为超宽带大功率器件的设计提供了理论基础。Abstract: The high-frequency slow-wave structure of 2−18 GHz ultra-wideband traveling-wave tube (TWT) is studied and analyzed to meet the requirements of modern information warfare for TWT. Based on the traditional wideband TWT, the positive dispersion characteristics of non-fin loading section were introduced to realize the 2−18 GHz ultra-wideband high-frequency slow wave structure, with the maximum bandwidth of 9∶1. Results show that the output power of fundamental wave is up to 100 W, the second harmonic suppression ratio is better than −3 dBc in the full frequency band, and the second harmonic suppression ratio is better than −5 dBc at 2 GHz, which provides a theoretical basis for the design of ultra-wideband high-power devices. At the same time, the spiral pitch at the output end is adjusted to a positive gradient distribution to further optimize the low frequency secondary wave suppression ratio and improve the saturation output power of the high frequency band.
-
Key words:
- ultra-wide band /
- positive dispersion /
- negative dispersion /
- helix /
- traveling-wave tube
-
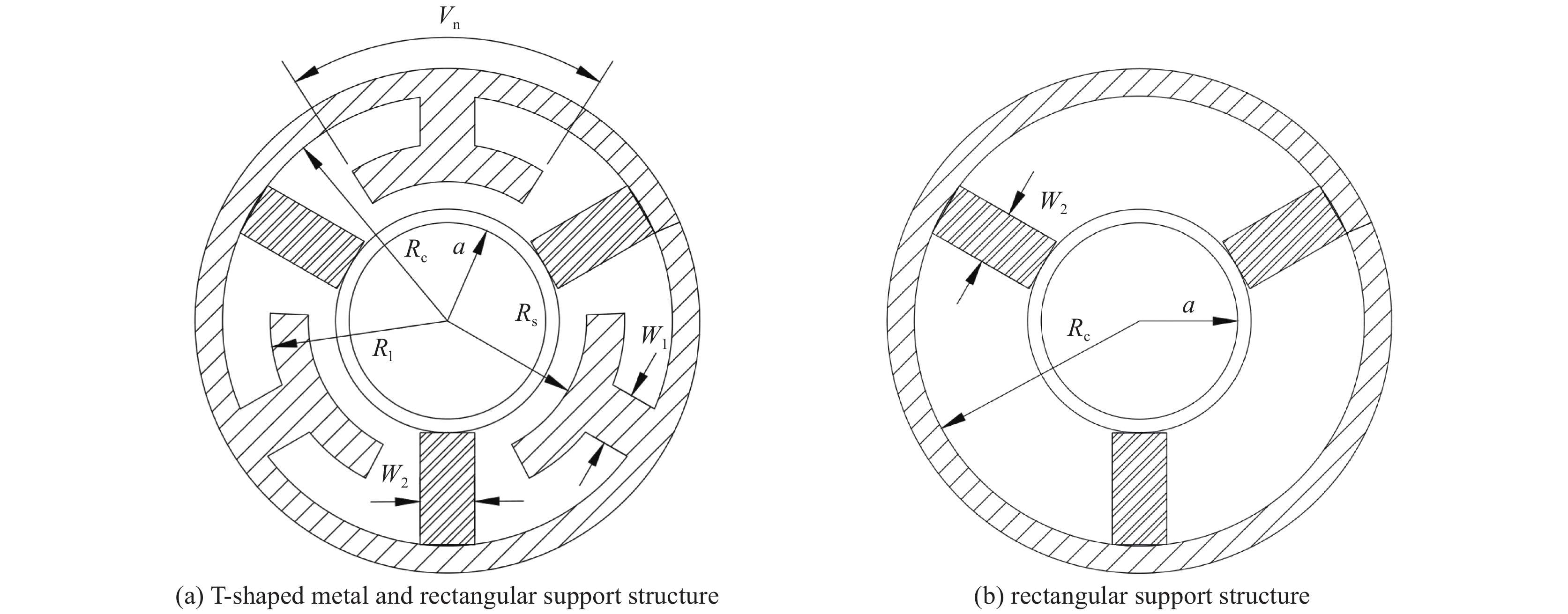
表 1 基本参量
Table 1. The basic parameters
$ {V_0} $/V $ {I_0} $/A $ a $/mm $ {r_0} $/mm 4500 0.18 0.72 0.288 表 2 高频慢波结构参量
Table 2. High frequency slow wave structure parameters
Vn/(°) Rl/mm Rs/mm W1/mm W2/mm Rc/mm 65 1.27 1.02 0.4 0.4 1.65 -
[1] Gilmour A S. 速调管、行波管、磁控管、正交场放大器和回旋管[M]. 丁耀根, 张兆传, 译. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2012GilmourAS. Klystrons, traveling wave tubes, magnetrons, crossed-field amplifiers and gyrotrons[M]. Ding Yaogen, Zhang Zhaochuan, trans. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2012 [2] VED IPP. Rethinking what we know about vacuum electronic devices[J]. The Journal of Electronic Defense, 2019, 42(2): 1-4. [3] Levush B. The design and manufacture of vacuum electronic amplifiers: progress and challenges[C]//Proceedings of 2019 International Vacuum Electronics Conference. 2019: 1-5. [4] 李建兵, 林鹏飞, 郝保良, 等. 微波功率放大器发展概述[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2020, 32:073001. (Li Jianbing, Lin Pengfei, Hao Baoliang, et al. Overview of development of microwave power amplifiers[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2020, 32: 073001 [5] 王斌, 王风岩, 周旭, 等. 微波功率行波管及模块的应用发展趋势[J]. 真空电子技术, 2019(2):1-7. (Wang Bin, Wang Fengyan, Zhou Xu, et al. Application and development trend of TWTs and MPMs[J]. Vacuum Electronics, 2019(2): 1-7 [6] Seo W B, Kim H J, Joo J H, et al. Fabrication and experiments on a 6-18 GHz, vaned helix TWT amplifier[C]//Proceedings of 2006 IEEE International Vacuum Electronics Conference Held Jointly with 2006 IEEE International Vacuum Electron Sources. 2006: 187-188. [7] Ghosh T K, Challis A J, Tokeley A, et al. Design and development of 2 to 3 octave band helix mini-TWTs[C]//Proceedings of 2011 IEEE International Vacuum Electronics Conference. 2011. [8] Wei Yixue, Gan Yuan, Chen Yinxing, et al. A 50-W broadband mini-MPM for electronic countermeasure[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 2018, 65(6): 2206-2211. doi: 10.1109/TED.2018.2791723 [9] 雷禄容, 袁欢, 刘振帮, 等. 宽带相对论速调管放大器模拟设计[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2016, 28:023003. (Lei Lurong, Yuan Huan, Liu Zhenbang, et al. Design of broadband relativistic klystron amplifier[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2016, 28: 023003 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201628.023003 [10] Sumathy M, Gupta S K, Kumar B, et al. Cold circuit analysis of a coupled-cavity slow wave structure for mm-wave TWT[J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2020, 48(9): 3024-3029. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2020.3015513 [11] 胡玉禄. 行波管注波互作用基础理论与CAD技术研究[D]. 成都: 电子科技大学, 2011: 55-75Hu Yulu. Study of beam wave interaction basic theory and CAD technique for traveling wave tube[D]. Chengdu: University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2011: 55-75 [12] Frisoni M A. Theoretical design study of a 2-18 GHz bandwidth helix TWT (Traveling Wave Tube) amplifier[R]. BADC-TR-87-22, 1987. [13] 罗健. 行波管的正向设计理论及技术研究[D]. 成都: 电子科技大学, 2015: 15-30Luo Jian. Research on theory and forward design technology of TWTs[D]. Chengdu: University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2015: 15-30 [14] Hu Yulu, Wang Yanmei, Yang Zhonghai, et al. Study the effect of positive dispersion in input circuit of broadband helix traveling wave tubes[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE 14th International Vacuum Electronics Conference. 2013. [15] Srivastava V, Carter R G, Ravinder B, et al. Design of helix slow-wave structures for high efficiency TWTs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 2000, 47(12): 2438-2443. doi: 10.1109/16.887034 [16] Xu Li, Yang Zhonghai, Li Bin, et al. High-frequency circuit simulator: an advanced three-dimensional finite-element electromagnetic-simulation tool for microwave tubes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 2009, 56(5): 1141-1151. doi: 10.1109/TED.2009.2016078 [17] 刘盛纲, 李宏福, 王文祥, 等. 微波电子学导论[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 1995: 161-184Liu Shenggang, Li Hongfu, Wang Wenxiang, et al. Introduction to microwave electronics[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 1995: 161-184 [18] 杜秉初, 汪健如. 电子光学[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2002: 400-422Du Bingchu, Wang Jianru. Electron optics[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2002: 400-422 [19] Ghosh T K, Challis A J, Jacob A, et al. Design of helix pitch profile for broadband traveling-wave tubes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 2009, 56(5): 1135-1140. doi: 10.1109/TED.2009.2015137 [20] Ghosh T K, Challis A J, Jacob A, et al. Improvements in performance of broadband helix traveling-wave tubes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 2008, 55(2): 668-673. doi: 10.1109/TED.2007.913006 -




 下载:
下载: