High-power wavelength-tunable ultrashort pulse fiber laser at 2 µm
-
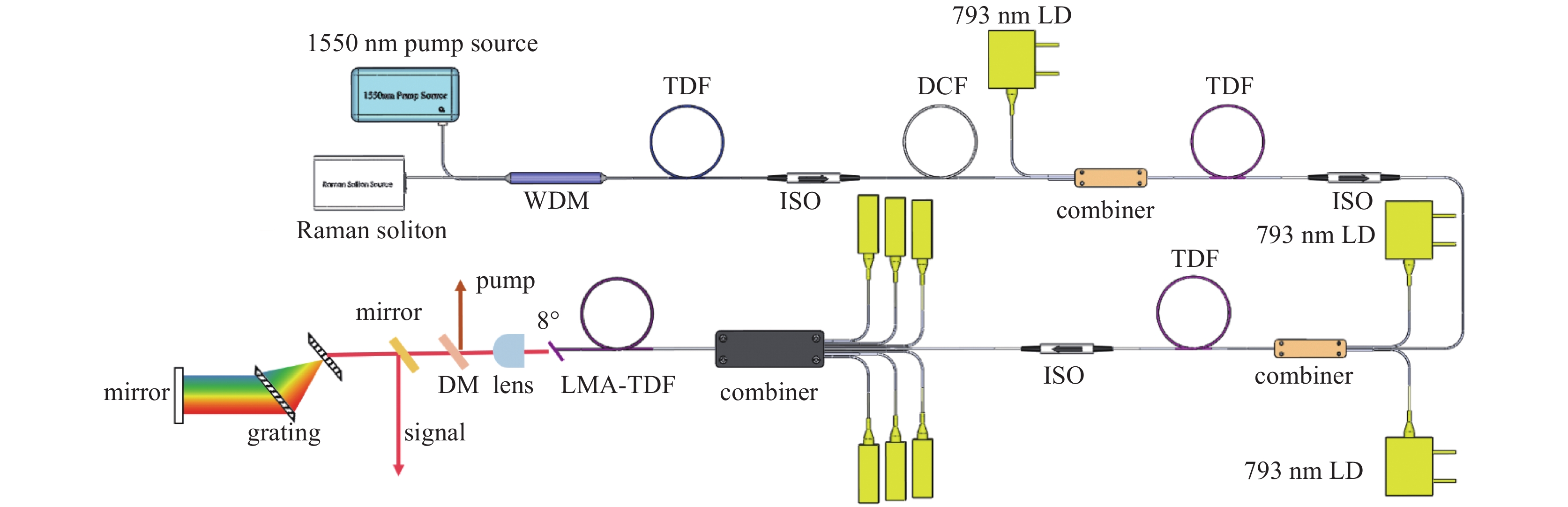
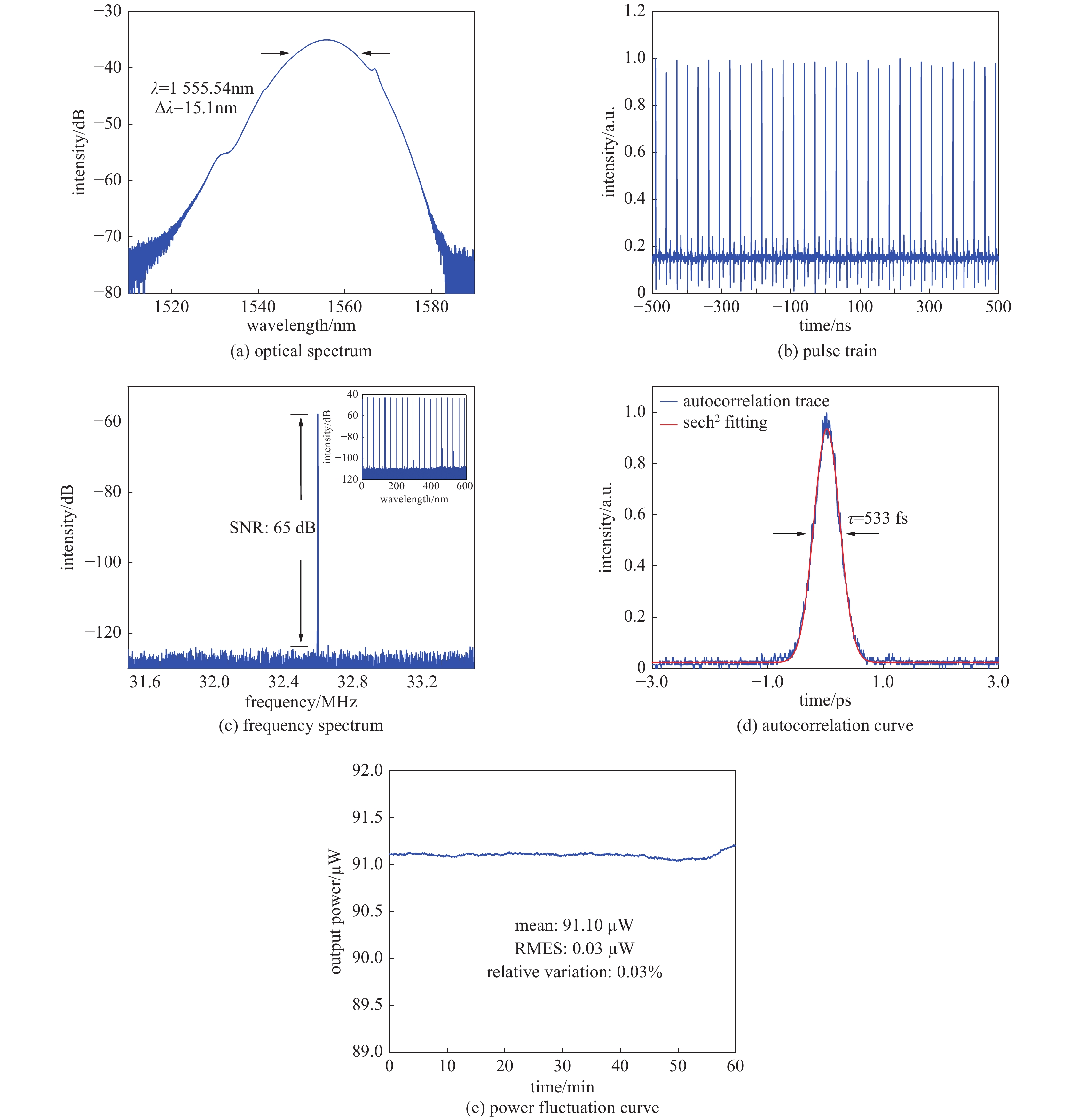
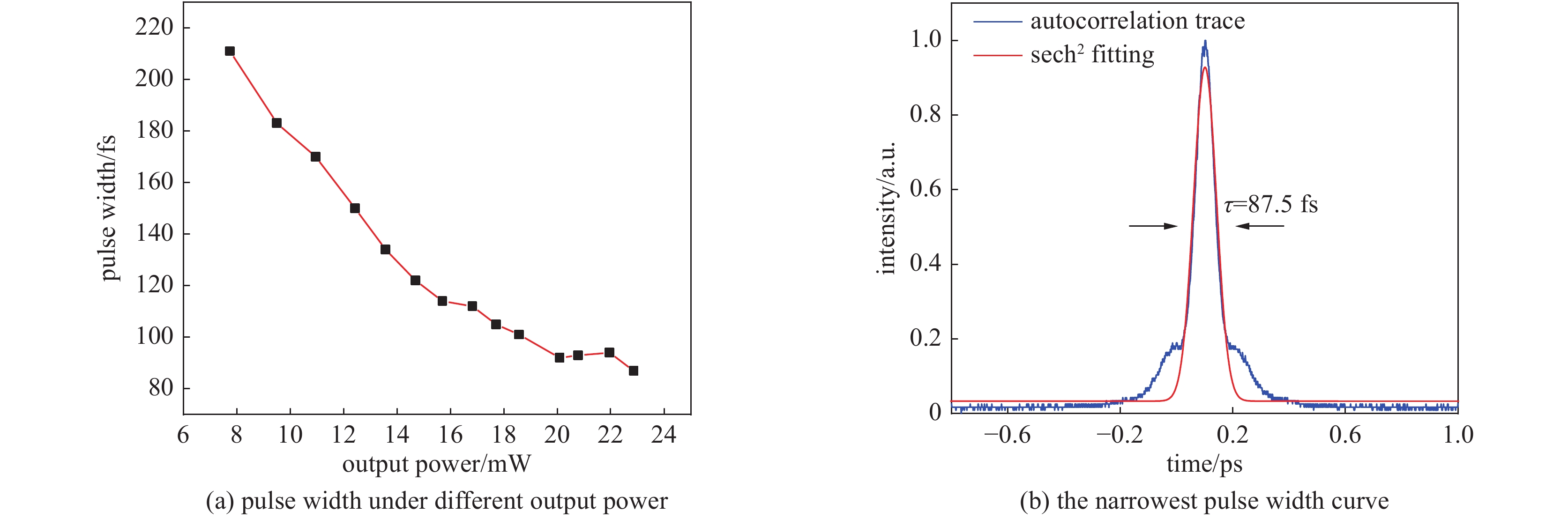
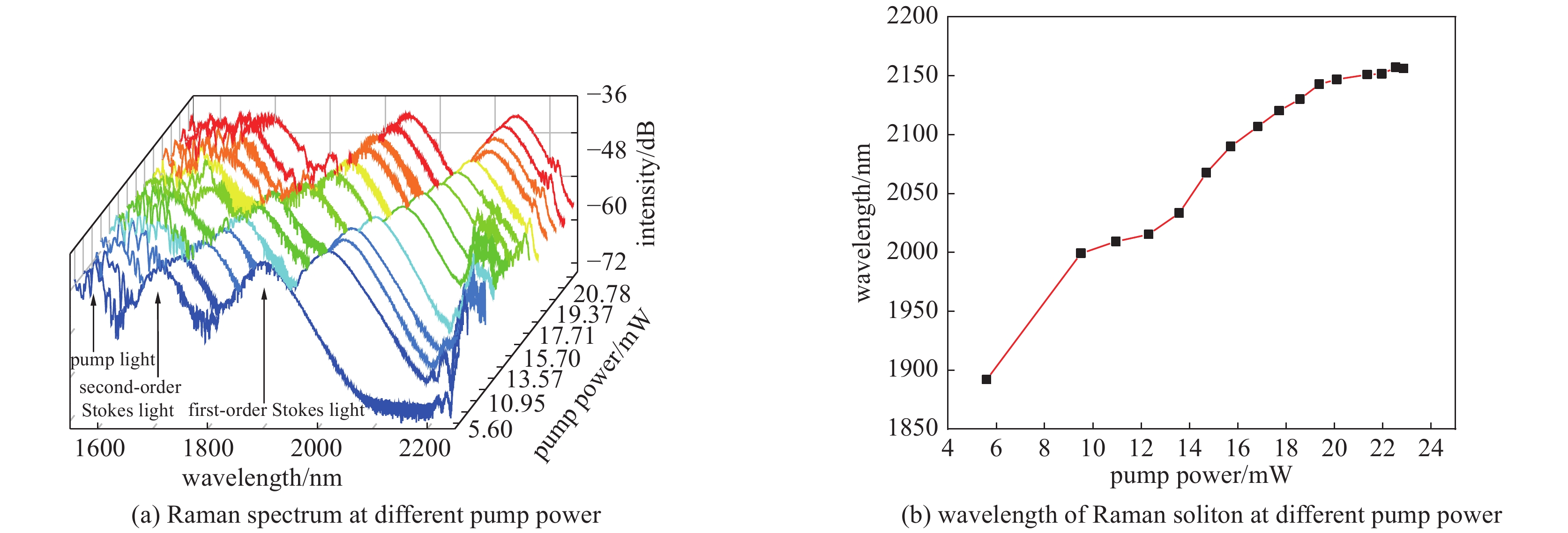
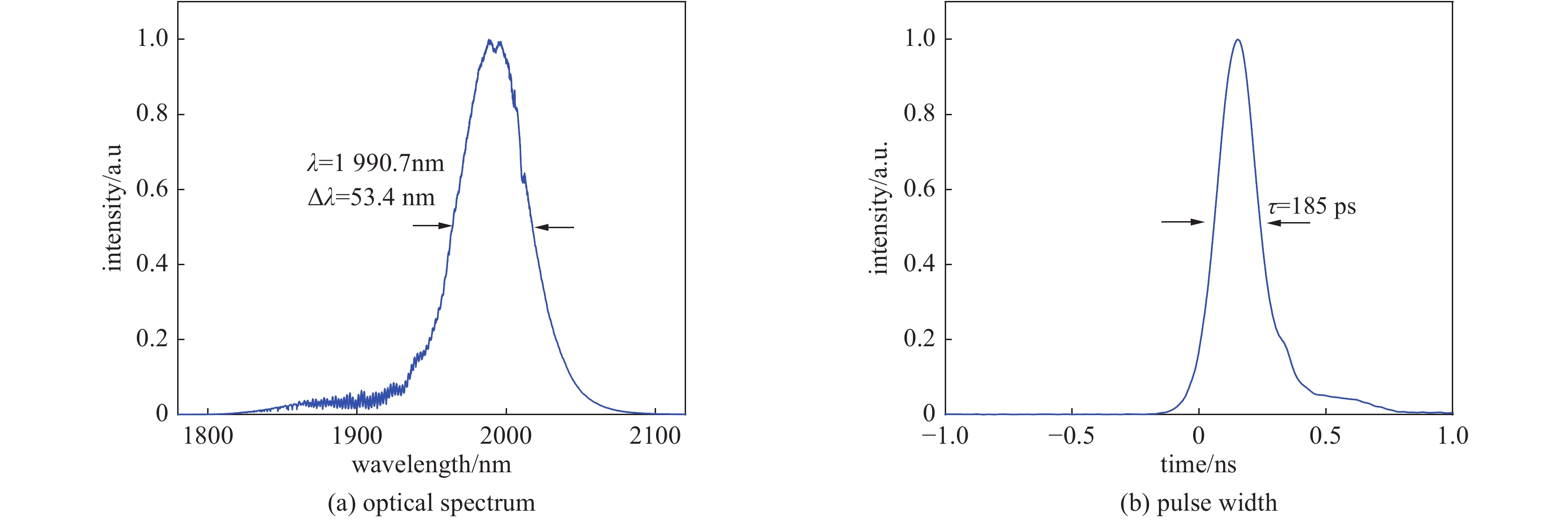
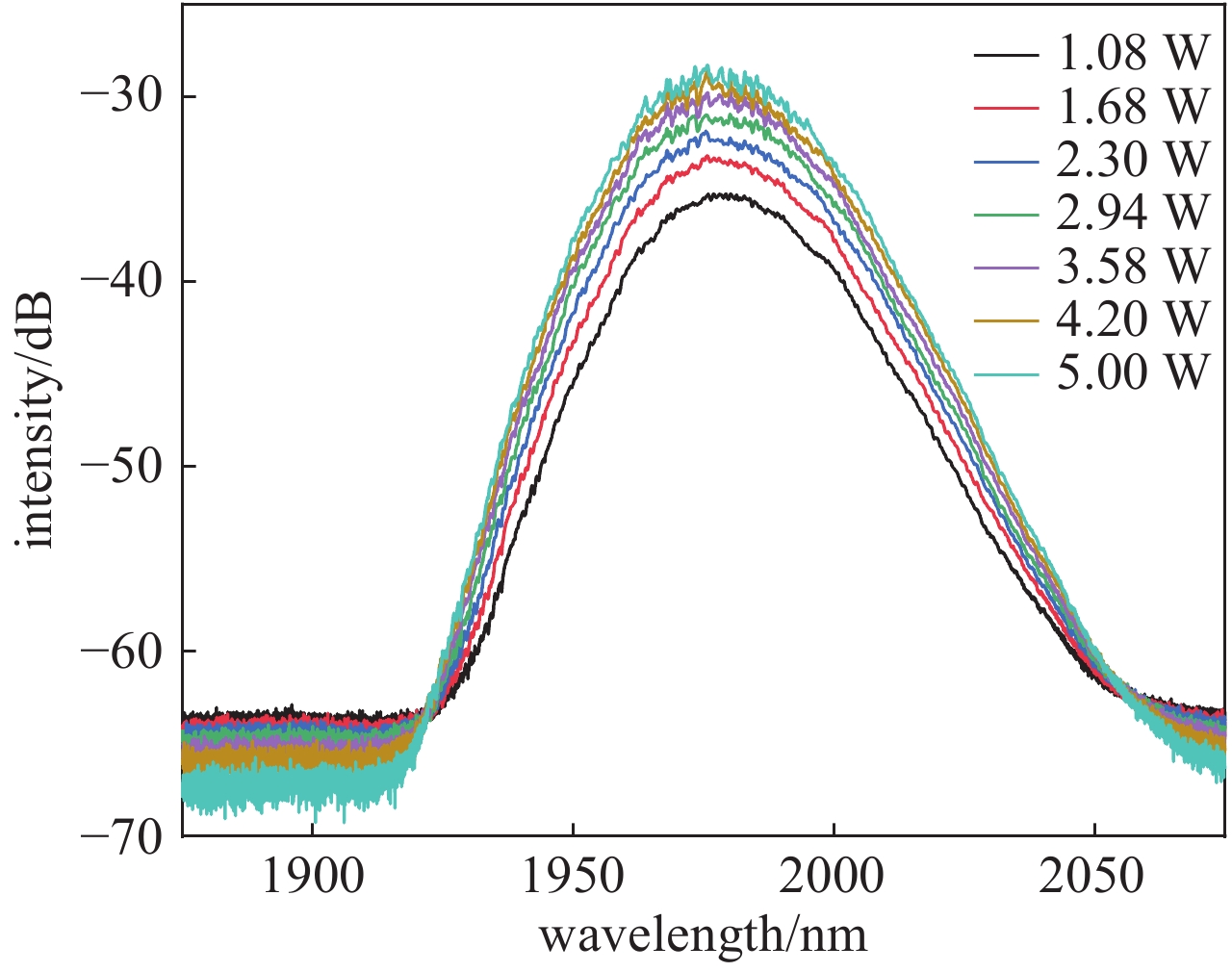
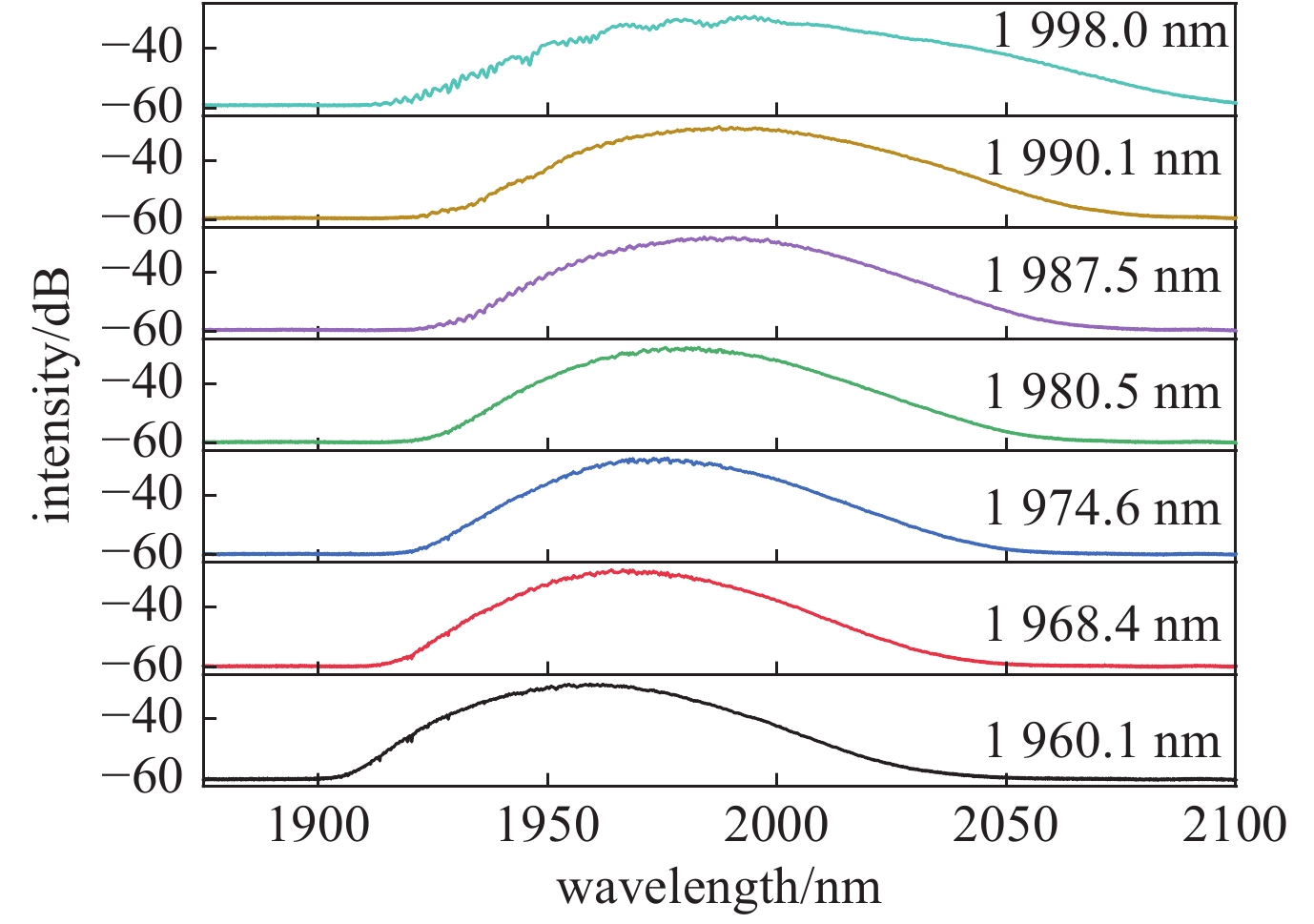
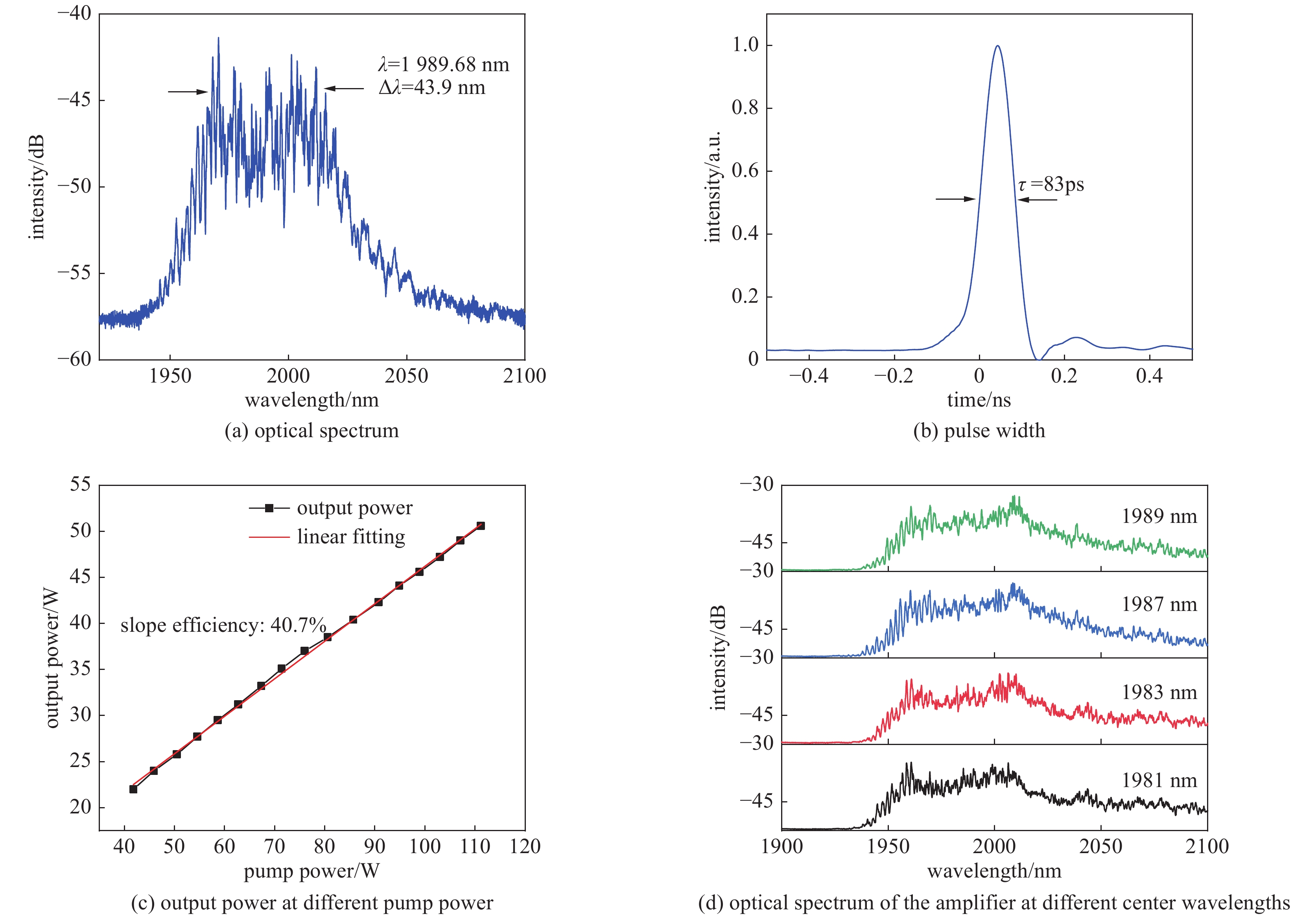
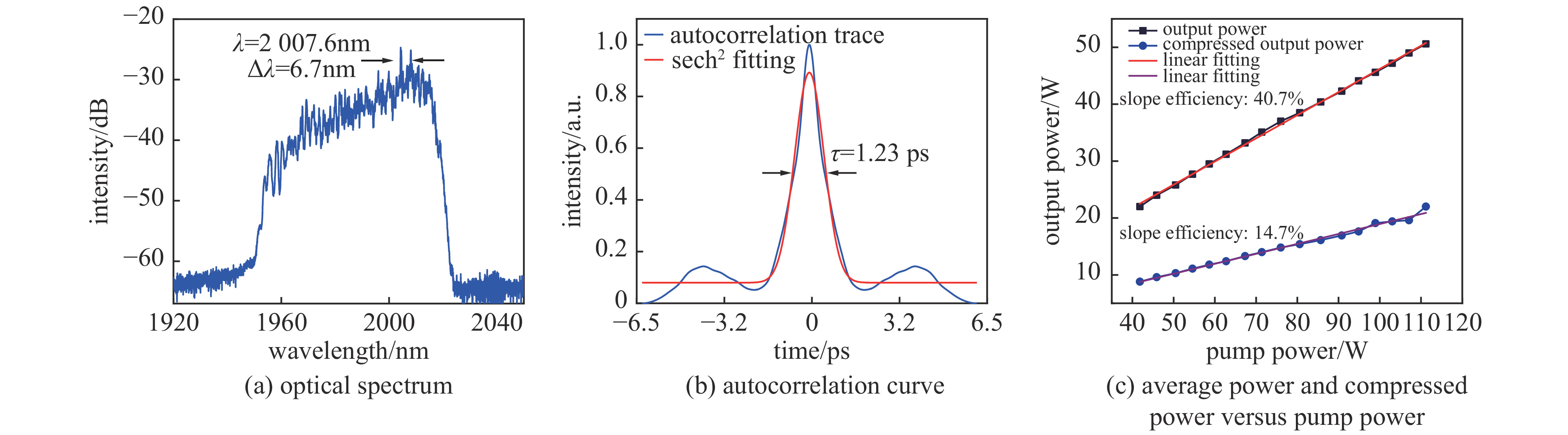
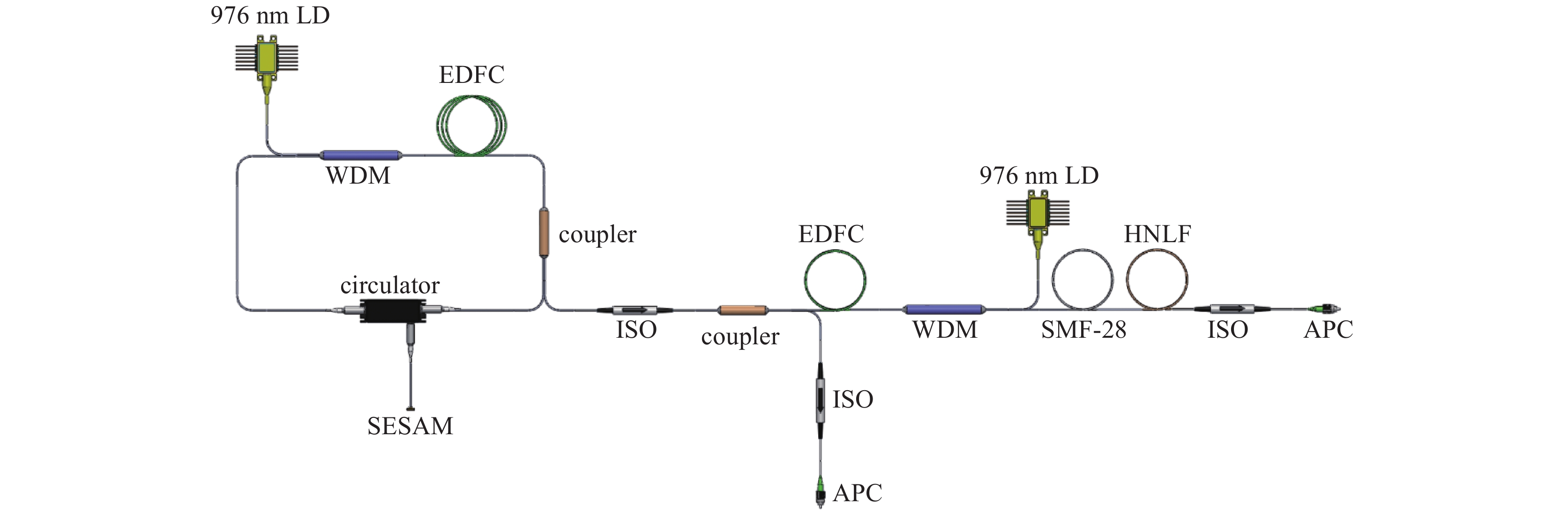
摘要: 高功率2 µm波长可调谐的超短脉冲激光具有峰值功率高、脉冲宽度窄、波长可调谐等优势,在医疗手术、大气通信、光电对抗等领域具有广泛的应用。利用高峰值功率的掺铒光纤放大器泵浦高非线性光纤,在全光纤化结构中获得了1895~2165 nm可调谐的拉曼孤子输出。采用啁啾脉冲放大技术对拉曼孤子的脉冲能量进行提升,放大后拉曼孤子的单脉冲能量为1.56 µJ,平均功率达到50.6 W,脉冲宽度为83 ps。经过光栅对压缩后,脉冲宽度降低至1.23 ps,平均功率为22 W,峰值功率达到0.55 MW。放大后的脉冲仍具有波长调谐的能力,当输出功率为5 W和50.6 W时,脉冲的波长调谐范围分别为38 nm和8 nm。Abstract: Two-µm ultrashort pulse laser with high power and tunable wavelength has been widely applied in medical surgery, atmospheric communication, photoelectric countermeasures and other fields, owning to the advantages of high peak power, narrow pulse width, tunable-wavelength, etc. We achieved a tunable Raman soliton output at 1895~2165 nm in an all-optical fiber thinning structure using a high nonlinear fiber pumped by an erbium-doped fiber amplifier with high peak power. The pulse energy of the Raman soliton was enhanced by the chirped pulse amplification technique. After amplification, a single pulse energy of 1.56 μJ, an average power of 50.6 W and a pulse width of 83 ps were achieved. After grating pair compression, a pulse width of 1.23 ps, an average power of 22 W and a peak power of 0.55 MW could be realized. The amplified pulse still has the ability of wavelength tuning. The wavelength tuning ranges of the pulse are 38 nm at average power of 5 W and 8 nm at average power of 50.6 W, respectively.
-
Key words:
- Raman soliton /
- wavelength tunable /
- ultrashort pulse /
- high power fiber laser /
- all-fiber
-
表 1 色散管理掺铒光纤振荡器中的光纤参数
Table 1. Fiber parameters of the dispersion managed erbium-doped fiber laser
fiber type dispersion/(ps2/km,@1550 nm) fiber length/m net dispersion/ps2 EDFC 23.495 2.5 −0.028 SMF-28 −22.86 3.8 -
[1] Kadwani P, Sims R A, Baudelet M, et al. Atmospheric propagation testing using broadband thulium fiber systems[C]//Fiber Laser Applications 2011. Istanbul: Optical Society of America, 2011. [2] Scholle K, Lamrini S, Koopmann P, et al. 2 µm laser sources and their possible applications[M]//Pal B. Frontiers in Guided Wave Optics and Optoelectronics. Vukovar: Intech, 2010. [3] Sarp A S K, Gulsoy M. Determining the optimal dose of 1940-nm thulium fiber laser for assisting the endodontic treatment[J]. Lasers in Medical Science, 2017, 32(7): 1507-1516. doi: 10.1007/s10103-017-2272-0 [4] Hutchens T C, Gonzalez D A, Irby P B, et al. Fiber optic muzzle brake tip for reducing fiber burnback and stone retropulsion during thulium fiber laser lithotripsy[J]. Journal of Biomedical Optics, 2017, 22: 018001. doi: 10.1117/1.JBO.22.1.018001 [5] Corkum P B. Plasma perspective on strong field multiphoton ionization[J]. Physical Review Letters, 1993, 71(13): 1994-1997. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.71.1994 [6] Krausz F, Ivanov M. Attosecond physics[J]. Reviews of Modern Physics, 2009, 81(1): 163-234. doi: 10.1103/RevModPhys.81.163 [7] Sepp G, Protz R. Laser beam source for a directional infrared countermeasures (DIRCM) weapon system: 6587486[P]. 2003-07-01. [8] Luo Hongyu, Yang Jian, Li Jianfeng, et al. Tunable sub-300 fs soliton and switchable dual-wavelength pulse generation from a mode-locked fiber oscillator around 2.8 μm[J]. Optics Letters, 2021, 46(4): 841-844. doi: 10.1364/OL.416559 [9] Qian Kai, Luo Hao, Qiu Da, et al. Broadband and tunable 920-nm femtosecond pulse generated by an all-fiber Er: fiber laser system[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 29600-29664. [10] 张怡静, 刘江, 王璞. 全光纤结构波长可调谐被动锁模掺铥光纤激光器[J]. 中国激光, 2018, 45:1001003. (Zhang Yijing, Liu Jiang, Wang Pu. All-fiber wavelength-tunable passively mode-locked thulium-doped fiber laser[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2018, 45: 1001003 doi: 10.3788/CJL201845.1001003 [11] Dai Ruihong, Meng Yafei, Li Yao, et al. Nanotube mode-locked, wavelength and pulsewidth tunable thulium fiber laser[J]. Optics Express, 2019, 27(3): 3518-3527. doi: 10.1364/OE.27.003518 [12] Yao Chuanfei, Zhao Zhipeng, Jia Zhixu, et al. Mid-infrared dispersive waves generation in a birefringent fluorotellurite microstructured fiber[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2016, 109: 101102. doi: 10.1063/1.4962391 [13] Wang Peng, Shi Hongxing, Tan Fangzhou, et al. Tunable femtosecond pulse source from 1.6 to 2.3 μm with 100 kW peak power in an all-fiber system[J]. Chinese Optics Letters, 2016, 14: 091405. doi: 10.3788/COL201614.091405 [14] Hua Yi, Zhou Gengji, Liu Wei, et al. Femtosecond two-color source synchronized at 100-as-precision based on SPM-enabled spectral selection[J]. Optics Letters, 2020, 45(13): 3410-3413. doi: 10.1364/OL.391161 [15] Wang Peng, Shi Hongxing, Tan Fangzhou, et al. Enhanced tunable Raman soliton source between 1.9 and 2.36 μm in a Tm-doped fiber amplifier[J]. Optics Express, 2017, 25(14): 16643-16651. doi: 10.1364/OE.25.016643 [16] Li Yanhong, Du Tuanjie, Xu Bin, et al. Compact all-fiber 2.1-2.7 μm tunable Raman soliton source based on germania-core fiber[J]. Optics Express, 2019, 27(20): 28544-28550. doi: 10.1364/OE.27.028544 [17] Liu Fei, Li Jianfeng, Luo Hongyu, et al. Study on soliton self-frequency shift in a Tm-doped fiber amplifier seeded by a Kelly-sideband-suppressed conventional soliton[J]. Optics Express, 2021, 29(5): 6553-6562. doi: 10.1364/OE.412345 [18] Liu Lai, Tian Qijun, Liao Meisong, et al. All-optical control of group velocity dispersion in tellurite photonic crystal fibers[J]. Optics Letters, 2012, 37(24): 5124-5126. doi: 10.1364/OL.37.005124 [19] Li Zhenrui, Li Nan, Yao Chuanfei, et al. Tunable mid-infrared Raman soliton generation from 1.96 to 2.82 μm in an all-solid fluorotellurite fiber[J]. AIP Advances, 2018, 8: 115001. doi: 10.1063/1.5042137 [20] Cheng Tonglei, Kanou Y, Asano K, et al. Soliton self-frequency shift and dispersive wave in a hybrid four-hole AsSe2-As2S5 microstructured optical fiber[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2014, 104: 121911. doi: 10.1063/1.4869756 [21] Tang Yuxing, Wright L G, Charan K, et al. Generation of intense 100 fs solitons tunable from 2 to 4.3 μm in fluoride fiber[J]. Optica, 2016, 3(9): 948-951. doi: 10.1364/OPTICA.3.000948 [22] Klimentov D, Dvoyrin V V, Tolstik N, et al. Raman soliton fiber lasers tunable between 1.98-2.22 µm[C]//Mid-Infrared Coherent Sources 2016. Long Beach: Optical Society of America, 2016. [23] Tan Fangzhou, Shi Hongxing, Sun Ruoyu, et al. 1 μJ, sub-300 fs pulse generation from a compact thulium-doped chirped pulse amplifier seeded by Raman shifted erbium-doped fiber laser[J]. Optics Express, 2016, 24(20): 22461-22468. doi: 10.1364/OE.24.022461 [24] Fermann M E, Andrejco M J, Stock M L, et al. Passive mode locking in erbium fiber lasers with negative group delay[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 1993, 62(9): 910-912. doi: 10.1063/1.108516 [25] Herrmann J, Kalosha V P, Müller M. Higher-order phase dispersion in femtosecond Kerr-lens mode-locked solid-state lasers: sideband generation and pulse splitting[J]. Optics Letters, 1997, 22(4): 236-238. doi: 10.1364/OL.22.000236 -




 下载:
下载: