Research progress in high-energy laser-induced damage of ultraviolet fluorophosphate glass
-
摘要:
激光驱动惯性约束聚变(ICF),因有望解决全球能源危机问题而备受瞩目。然而,熔石英作为ICF装置终端光学组件中一类重要的功能性紫外元件,其高能激光诱导损伤问题成为限制ICF装置输出能量向更高更强方向发展的关键因素。因此,ICF装置负载能力继续提升对新型高抗强激光损伤紫外元件提出重大应用需求。综述了中国科学院西安光学精密机械研究所研制的紫外氟磷玻璃在高能紫外激光损伤方面的研究现状,并分析了现存的实际问题,最后对高抗损伤紫外氟磷玻璃的发展方向进行了展望。
Abstract:Laser driven inertial confinement fusion (ICF) has attracted much attention for its potential to solve the global energy crisis. As fused silica is an important functional ultraviolet (UV) element in the final optics assembly of ICF device, its laser-induced damage has become a key factor limiting the development of ICF output energy to a stronger and higher level. Therefore, the further increase of ICF output energy puts forward a significant application demand for the new UV components that have superior UV laser-induced damage resistance. In this paper, the research status of high-energy UV laser-induced damage of UV fluorophosphate glasses developed by Xi’an Institute of Optics and Precision Mechanics, CAS was reviewed, and the existing practical problems are analyzed. Finally, the development direction of UV fluorophosphate glasses with high laser-induced damage resistance is prospected.
-
Key words:
- inertial confinement fusion /
- laser-induced damage /
- fluorophosphate glass
-
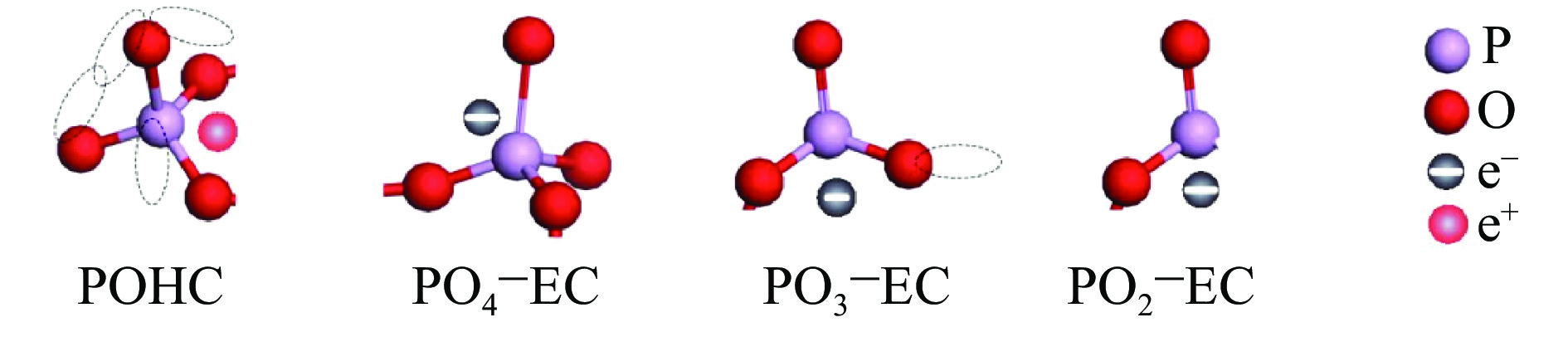
图 4 紫外氟磷玻璃中POHC、PO4−EC、PO3−EC和PO2−EC缺陷中心结构示意图[46]
Figure 4. Schematic diagram of POHC, PO4−EC, PO3−EC and PO2−EC defects in UV fluorophosphate glass
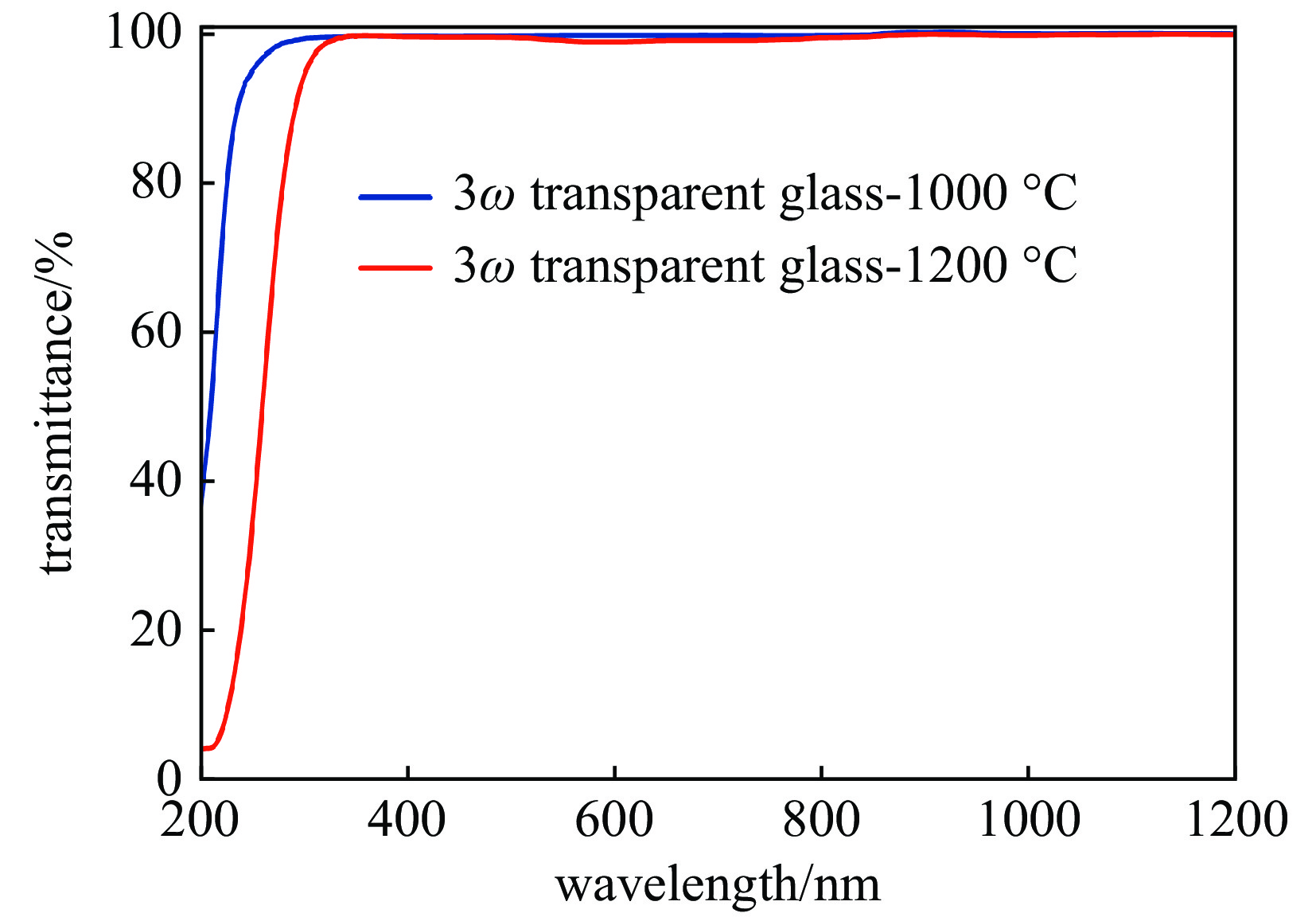
图 5 不同熔制温度制备的紫外氟磷玻璃内透过率光谱[52]
Figure 5. Internal transmission spectra of UV fluorophosphate glasses prepared at different melting temperature
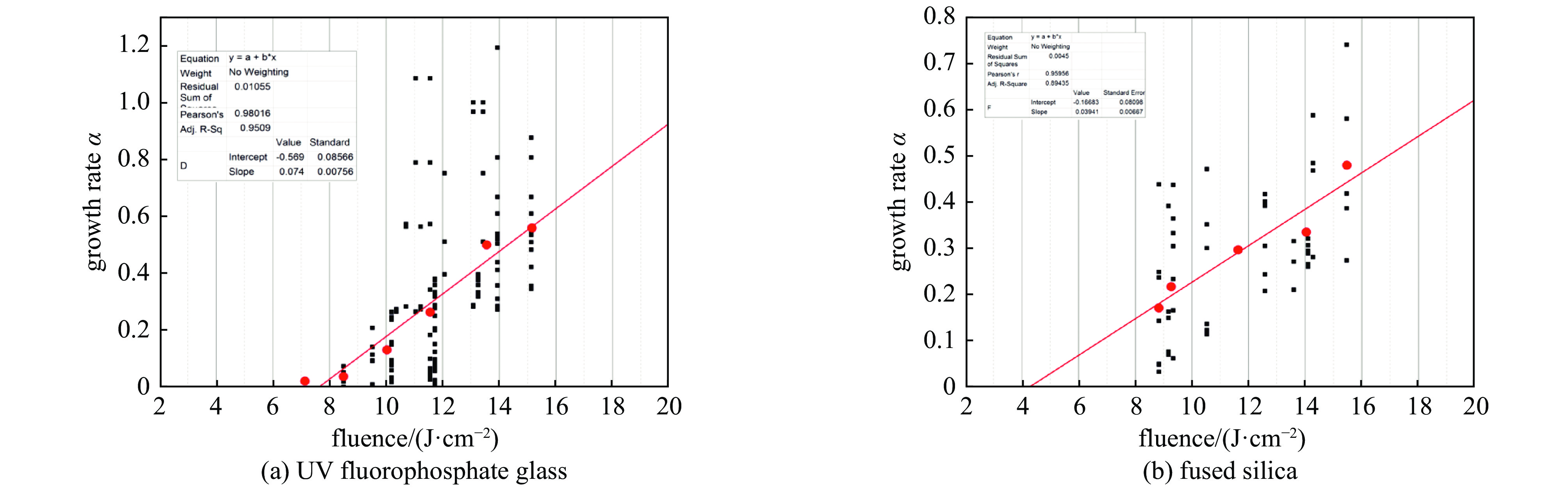
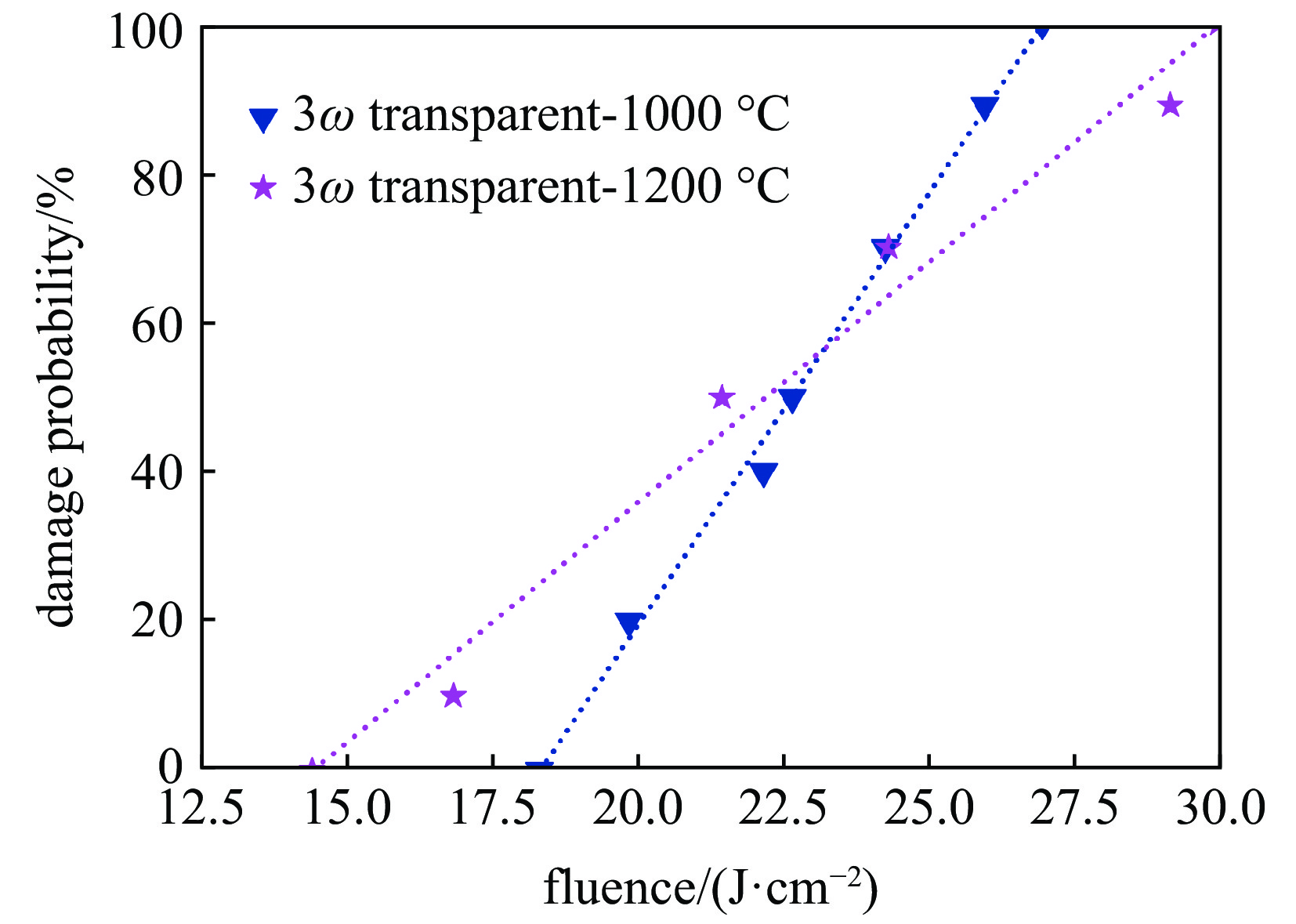
图 6 不同熔制温度制备的紫外氟磷玻璃的激光损伤阈值(355 nm, 6.7 ns, 1-on-1)[52]
Figure 6. Laser-induced damage threshold of UV fluorophosphate glasses prepared at different melting temperature (355 nm, 6.7 ns, 1-on-1 mode)
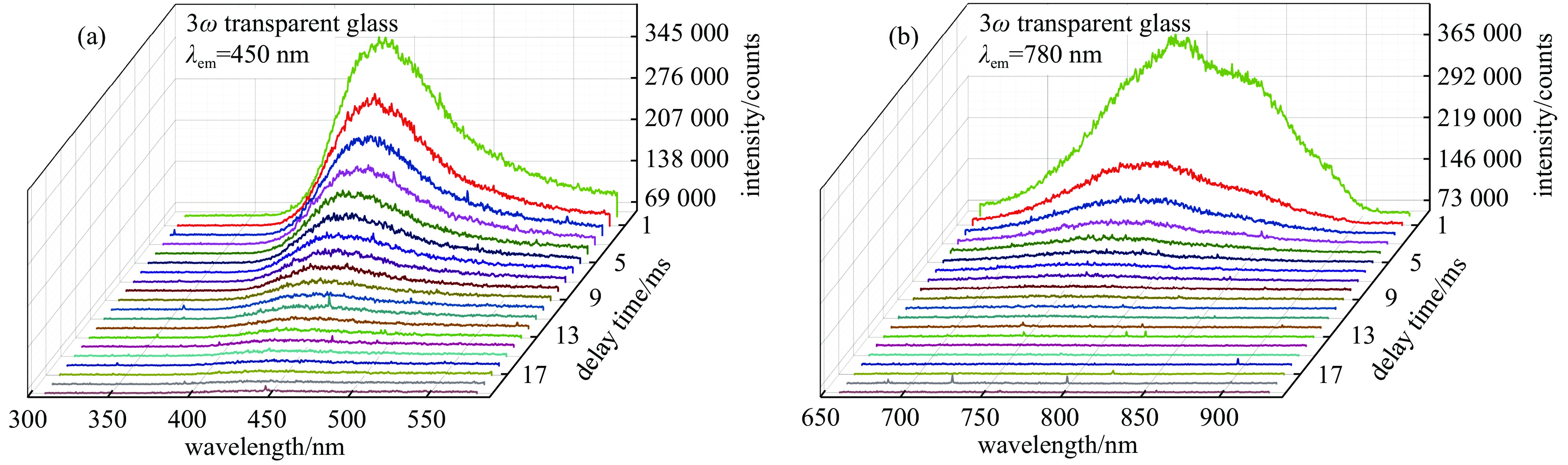
图 7 紫外氟磷玻璃中450 nm和780 nm特征荧光的动态变化[57]
Figure 7. Dynamic decay processes of 450 nm and 780 nm fluorescence in the UV fluorophosphate glass
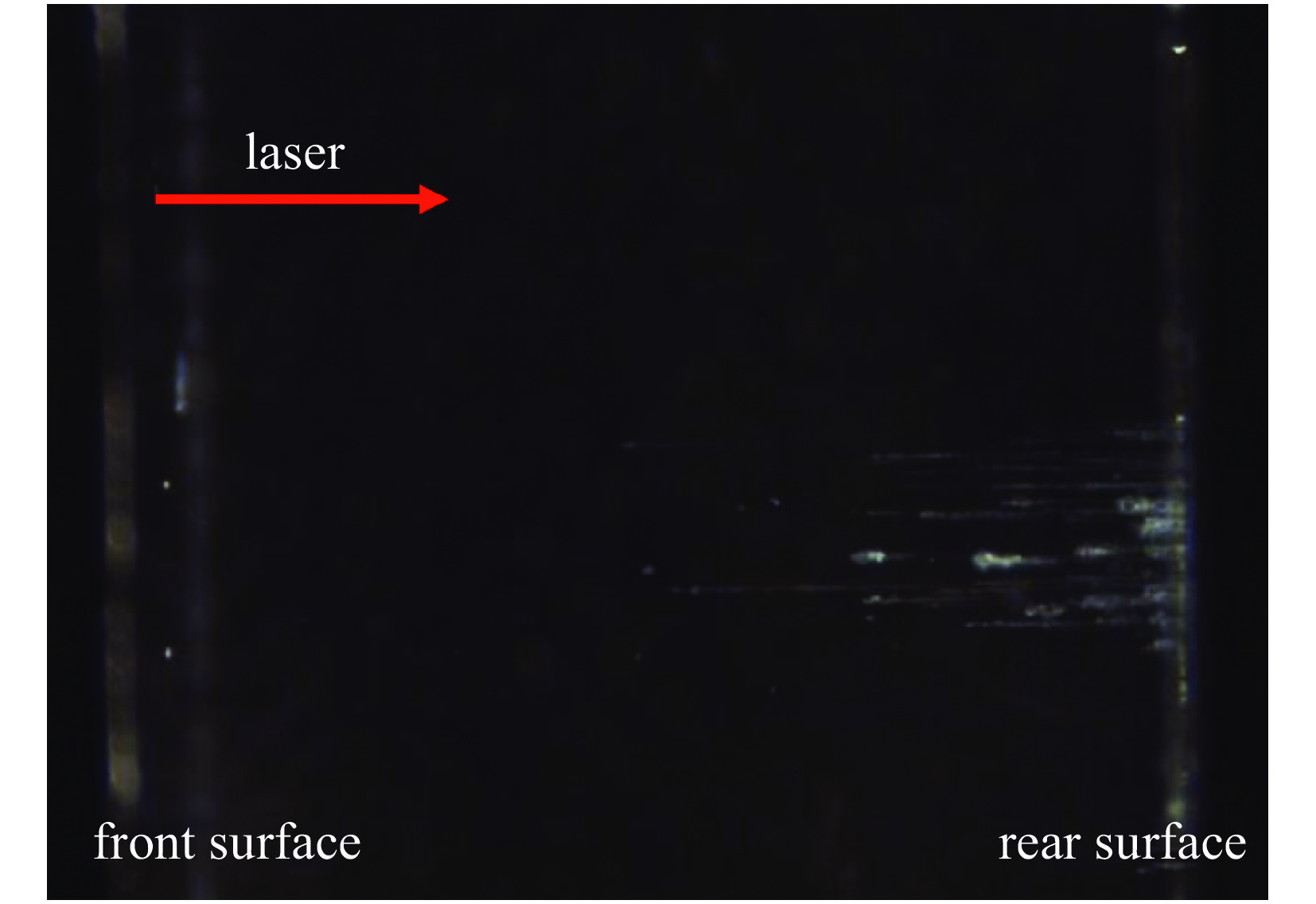
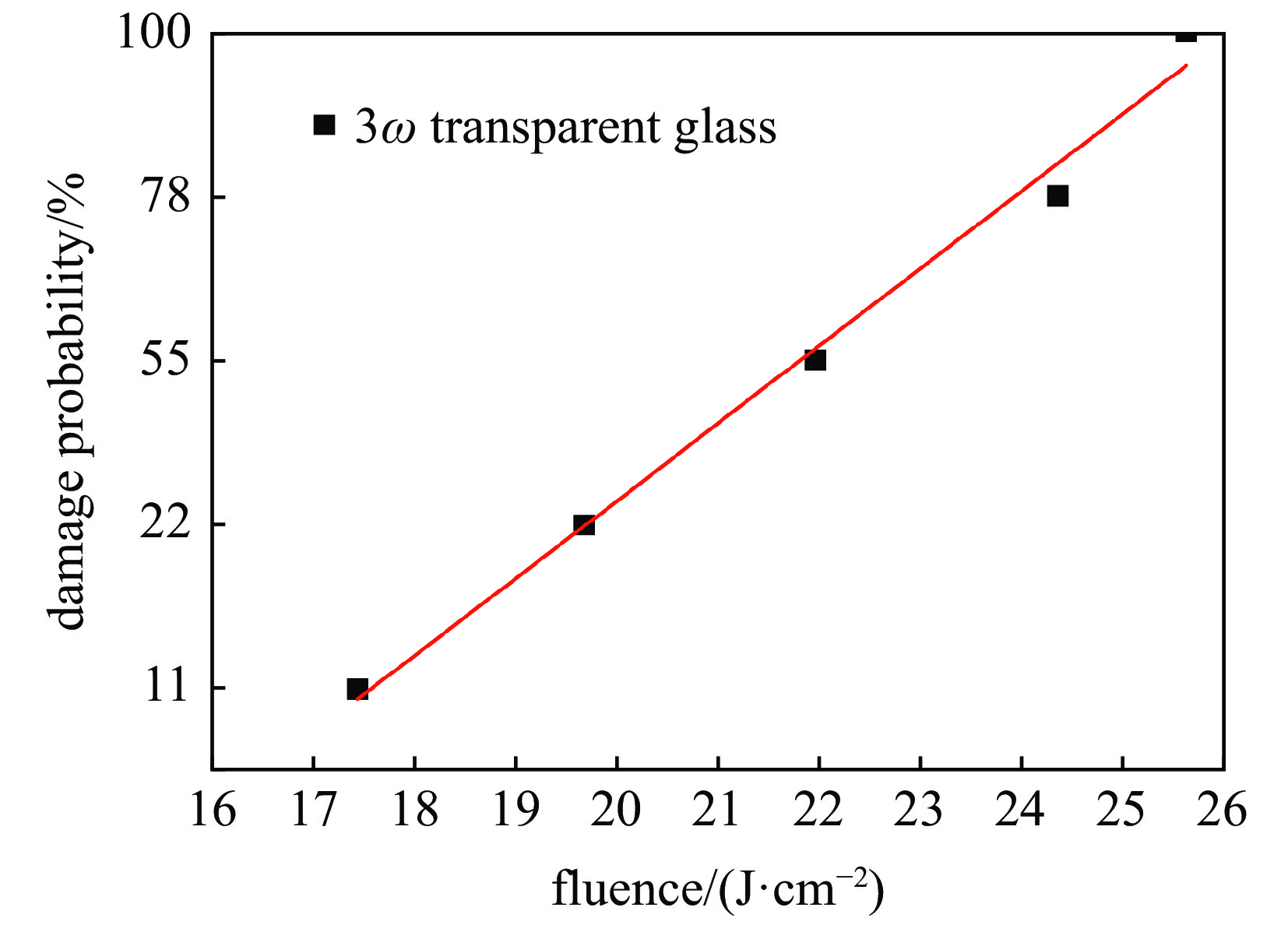
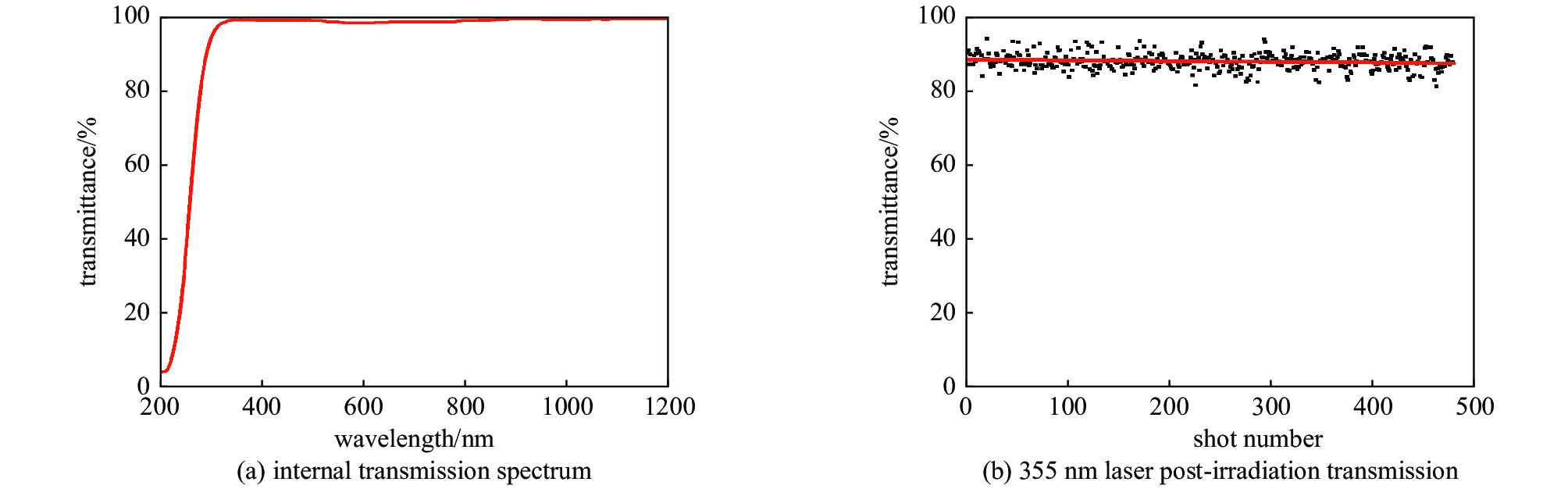
图 8 紫外氟磷玻璃的351 nm激光损伤[51]
Figure 8. 351 nm laser-induced damage of UV fluorophosphate glass
-
[1] Nuckolls J, Wood L, Thiessen A, et al. Laser compression of matter to super-high densities: thermonuclear (CTR) applications[J]. Nature, 1972, 239(5368): 139-142. doi: 10.1038/239139a0 [2] Hora H, Schwarz H J. Laser interaction and related plasma phenomena (Report on the 4th International Workshop, Troy, 1976)[J]. Nuclear Fusion, 1977, 17(1): 165-170. doi: 10.1088/0029-5515/17/1/019 [3] 王淦昌. 激光惯性约束核聚变(ICF)最新进展简述[J]. 核科学与工程, 1997, 17(3):266-269Wang Ganchang. A brief review of the progress of laser inertial confinement fusion in recent years[J]. Chinese Journal of Nuclear Science and Engineering, 1997, 17(3): 266-269 [4] Basov N G. Progress and prospect of laser thermonuclear fusion[J]. Kvantovaya Elektronika, 1993, 20: 305-309. [5] Nakai S, Mima K. Laser driven inertial fusion energy: present and prospective[J]. Reports on Progress in Physics, 2004, 67(3): 321-349. doi: 10.1088/0034-4885/67/3/R04 [6] Bodner S E, Colombant D G, Gardner J H, et al. Direct-drive laser fusion: status and prospects[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 1998, 5(5): 1901-1918. doi: 10.1063/1.872861 [7] 范滇元, 贺贤土. 惯性约束聚变能源与激光驱动器[J]. 大自然探索, 1999, 18(1):31-35Fan Dianyuan, He Xiantu. Inertial confinement fusion energy and laser driver[J]. Discovery of Nature, 1999, 18(1): 31-35 [8] Moses E I, Campbell J H, Stolz C J, et al. The National Ignition Facility: the world's largest optics and laser system[C]//Proceedings of SPIE 5001, Optical Engineering at the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory. 2003: 500351. [9] Spaeth M L, Manes K R, Bowers M, et al. National Ignition Facility laser system performance[J]. Fusion Science and Technology, 2016, 69(1): 366-394. doi: 10.13182/FST15-136 [10] Haynam C A, Wegner P J, Auerbach J M, et al. National ignition facility laser performance status[J]. Applied Optics, 2007, 46(16): 3276-3303. doi: 10.1364/AO.46.003276 [11] Fusion news ignites optimism[J]. Nature Photonics, 2021, 15: 713. [12] Baisden P A, Atherton L J, Hawley R A, et al. Large optics for the National Ignition Facility[J]. Fusion Science and Technology, 2016, 69(1): 295-351. doi: 10.13182/FST15-143 [13] Spaeth M L, Mane K R, Kalantar D H, et al. Description of the NIF laser[J]. Fusion Science and Technology, 2016, 69(1): 25-145. doi: 10.13182/FST15-144 [14] Néauport J, Journot E, Gaborit G, et al. Design, optical characterization, and operation of large transmission gratings for the laser integration line and Laser Megajoule facilities[J]. Applied Optics, 2005, 44(16): 3143-3152. doi: 10.1364/AO.44.003143 [15] de Yoreo J J, Burnham A K, Whitman P K. Developing KH2PO4 and KD2PO4 crystals for the world’s most power laser[J]. International Materials Reviews, 2002, 47(3): 113-152. doi: 10.1179/095066001225001085 [16] Wegner P J, Henesian M A, Speck D R. Harmonic conversion of large-aperture 1.05-μm laser beams for inertial-confinement fusion research[J]. Applied Optics, 1992, 31(30): 6414-6426. doi: 10.1364/AO.31.006414 [17] Zheng Wanguo, Wei Xiaofeng, Zhu Qihua, et al. Laser performance of the SG-III laser facility[J]. High Power Laser Science and Engineering, 2016, 4: e21. doi: 10.1017/hpl.2016.20 [18] Wang Zhuo, Wang Lin, Peng Wenqiang, et al. Origin and distribution of redeposition layer in polished fused silica[J]. Optical Engineering, 2015, 54: 085102. doi: 10.1117/1.OE.54.8.085102 [19] Cheng Jian, Wang Jinghe, Hou Jing, et al. Effect of polishing-induced subsurface impurity defects on laser damage resistance of fused silica optics and their removal with HF acid etching[J]. Applied Sciences, 2017, 7: 838. doi: 10.3390/app7080838 [20] Liu Hongjie, Wang Fengrui, Huang Jin, et al. Experimental study of 355 nm laser damage ignited by Fe and Ce impurities on fused silica surface[J]. Optical Materials, 2019, 95: 109231. doi: 10.1016/j.optmat.2019.109231 [21] Li Bo, Hou Chunyuan, Tian Chengxiang, et al. Layer by layer exposure of subsurface defects and laser-induced damage mechanism of fused silica[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2020, 508: 145186. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.145186 [22] Jiang Yong, Zhang Binjie, Liu Hufeng, et al. Light field modulation of ejected SiO2 particles on fused silica surface[J]. The European Physical Journal D, 2021, 75: 282. doi: 10.1140/epjd/s10053-021-00293-3 [23] 刘娅丽, 戚磊, 郑梦珂, 等. 划痕缺陷对熔融石英光诱导损伤特性的影响分析[J]. 物理学报, 2021, 70:134203Liu Yali, Qi Lei, Zheng Mengke, et al. Effect of scratch defects on photoinduced damage characteristics of fused quartz[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2021, 70: 134203 [24] Fournier J, Néauport J, Grua P, et al. Evidence of a green luminescence band related to surface flaws in high purity silica glass[J]. Optics Express, 2010, 18(21): 21557-21566. doi: 10.1364/OE.18.021557 [25] Fournier J, Neauport J, Grua P, et al. Green luminescence in silica glass: a possible indicator of subsurface fracture[J]. Applied Physics Letter, 2012, 100: 114103. doi: 10.1063/1.3693393 [26] Köhler R, Gerhard C. XPS analysis of metallic trace contaminations on fused silica surfaces induced by classical optics manufacturing[J]. Optical Materials Express, 2021, 11(11): 3844-3853. doi: 10.1364/OME.436310 [27] Li Yaguo, Yuan Zhigang, Wang Jian, et al. Laser-induced damage characteristics in fused silica surface due to mechanical and chemical defects during manufacturing processes[J]. Optics & Laser Technology, 2017, 91: 149-158. [28] Ye Hui, Li Yaguo, Xu Qiao, et al. Resistance of scratched fused silica surface to UV laser induced damage[J]. Scientific Reports, 2019, 9: 10741. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-46048-4 [29] Wang Hongyu, Xiang Sunlin, Xiong Baoxing, et al. The light modulation of scratches on the surface of fused silica glass[C]//Proceedings of SPIE 11717, 24th National Laser Conference & Fifteenth National Conference on Laser Technology and Optoelectronics. 2020: 117172R. [30] Pile D F P. Redlining lasers for nuclear fusion[J]. Nature Photonics, 2021, 15(12): 863-865. doi: 10.1038/s41566-021-00917-5 [31] Ye Hui, Li Yaguo, Xu Qiao, et al. Effects of wet chemical etching on scratch morphology and laser damage resistance of fused silica[J]. Silicon, 2020, 12(2): 425-432. doi: 10.1007/s12633-019-00150-4 [32] Shao Ting, Shi Zhaohua, Sun Laixi, et al. Role of each step in the combined treatment of reactive ion etching and dynamic chemical etching for improving the laser-induced damage resistance of fused silica[J]. Optics Express, 2021, 29(8): 12365-12380. doi: 10.1364/OE.415438 [33] Sun Laixi, Huang Jin, Shao Ting, et al. Effects of combined process of reactive ion etching and dynamic chemical etching on UV laser damage resistance and surface quality of fused silica optics[J]. Optics Express, 2018, 26(14): 18006-18018. doi: 10.1364/OE.26.018006 [34] He Xiang, Cai Chao, Zhao Heng, et al. Effect of ion beam etching on surface/subsurface structural defect evolution in fused silica optics[J]. Optical Materials, 2021, 116: 111096. doi: 10.1016/j.optmat.2021.111096 [35] Catrin R, Neauport J, Taroux D, et al. Magnetorheological finishing for removing surface and subsurface defects of fused silica optics[J]. Optical Engineering, 2014, 53: 092010. doi: 10.1117/1.OE.53.9.092010 [36] Doualle T, Gallais L, Cormont P, et al. Effect of annealing on the laser induced damage of polished and CO2 laser-processed fused silica surfaces[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2016, 119: 213106. doi: 10.1063/1.4953146 [37] Cao Zhen, Wei Chaoyang, Cheng Xin, et al. Ground fused silica processed by combined chemical etching and CO2 laser polishing with super-smooth surface and high damage resistance[J]. Optics Letters, 2020, 45(21): 6014-6017. doi: 10.1364/OL.409857 [38] Tsujibayashi T, Toyoda K, Sakuragi S, et al. Spectral profile of the two-photon absorption coefficients in CaF2 and BaF2[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2002, 80(16): 2883-2885. doi: 10.1063/1.1471939 [39] Su Liangbi, Dong Yongjun, Yang Weiqiao, et al. Growth, characterization and optical quality of CaF2 single crystals grown by the temperature gradient technique[J]. Materials Research Bulletin, 2005, 40(4): 619-628. doi: 10.1016/j.materresbull.2005.01.006 [40] Li Chunhong, Kang Xiaoli, Han Wei, et al. Nanosecond laser-induced surface damage and material failure mechanism of single crystal CaF2 (111) at 355 nm[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2019, 480: 1070-1077. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.02.068 [41] He Dongbing, Kang Shuai, Zhang Liyan, et al. Research and development of new neodymium laser glasses[J]. High Power Laser Science and Engineering, 2017, 5: e1. doi: 10.1017/hpl.2016.46 [42] 胡丽丽, 陈树彬, 孟涛, 等. 大口径高性能激光钕玻璃研究进展[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2011, 23(10):2560-2564 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20112310.2560Hu Lili, Chen Shubin, Meng Tao, et al. Advances in high performance large aperture neodymium laser glasses[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2011, 23(10): 2560-2564 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20112310.2560 [43] 韩勖, 张海潮, 刘峻, 等. 透紫外、高应变点磷酸盐光学玻璃的研究进展和应用[J]. 中国建材科技, 2021, 30(6):47-50Han Xu, Zhang Haichao, Liu Jun, et al. Research progress and application of ultraviolet transparent and high strain point phosphate optical glass[J]. China Building Materials Science & Technology, 2021, 30(6): 47-50 [44] Wang Pengfei, Lu Min, Gao Fei, et al. Luminescence in the fluoride-containing phosphate-based glasses: a possible origin of their high resistance to nanosecond pulse laser-induced damage[J]. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5: 8593. doi: 10.1038/srep08593 [45] 陈猛, 向霞, 蒋勇, 等. 酸蚀与紫外激光预处理结合提高熔石英损伤阈值[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2010, 22(6):1383-1387Chen Meng, Xiang Xia, Jiang Yong, et al. Enhancement of laser induced damage threshold of fused silica by acid etching combined with UV laser conditioning[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2010, 22(6): 1383-1387 [46] 贺全龙. 高能辐照诱导氟磷酸盐玻璃的损伤机理研究[D]. 西安: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院西安光学精密机械研究所), 2019He Quanlong. The research on the damage mechanism of fluorophosphate glass induced by high energy irradiation[D]. Xi’an: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Xi’an Institute of Optics Precision Mechanics of CAS), 2019 [47] He Quanlong, Wang Pengfei, Lu Min, et al. Investigations on the photoluminescence of the iron and cobalt doped fluoride-containing phosphate-based glasses and its defects-related nature[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2016, 685: 153-158. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.05.253 [48] Feng Dandan, He Quanlong, Lu Min, et al. Investigations on the photoluminescence spectra and its defect-related nature for the ultraviolet transmitting fluoride-containing phosphate-based glasses[J]. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 2015, 425: 130-137. doi: 10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2015.06.009 [49] He Quanlong, Wang Pengfei, Sun Mengya, et al. Effects of doping B2O3 on the defects-state in SiO2-containing phosphate based glasses[J]. Optical Materials Express, 2017, 7(8): 2697-2705. doi: 10.1364/OME.7.002697 [50] Wang Pengfei, He Quanlong, Lu Min, et al. Evolutionary mechanism of the defects in the fluoride-containing phosphate based glasses induced by gamma radiation[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 18926. doi: 10.1038/srep18926 [51] 侯超奇. 高损伤阈值氟磷酸盐玻璃的研究[D]. 西安: 中国科学院研究生院(西安光学精密机械研究所), 2014Hou Chaoqi. Study of fluorphosphate glass with high laser induced damage threshold[D]. Xi’an: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Xi’an Institute of Optics Precision Mechanics of CAS), 2014 [52] Li Shengwu, Wan Rui, Ma Yuan, et al. Enhancement of UV laser-induced damage resistance of the fluoride-containing phosphate glasses by regulating the intrinsic defects[J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2022, 105(4): 2546-2555. doi: 10.1111/jace.18255 [53] Demos S G, Hoffman B N, Carr C W, et al. Mechanisms of laser-induced damage in absorbing glasses with nanosecond pulses[J]. Optics Express, 2019, 27(7): 9975-9986. doi: 10.1364/OE.27.009975 [54] Shen Hong, Wang Han, Tian Chenyun. Heat accumulation in ultrafast laser scanning of fused silica[J]. Journal of Heat Transfer, 2021, 143: 022102. doi: 10.1115/1.4048829 [55] Marks M R, Cheong K Y, Hassan Z. A review of laser ablation and dicing of Si wafers[J]. Precision Engineering, 2022, 73: 377-408. doi: 10.1016/j.precisioneng.2021.10.001 [56] Naseri N, Dupras G, Ramunno L. Mechanism of laser induced filamentation in dielectrics[J]. Optics Express, 2020, 28(18): 26977-26988. doi: 10.1364/OE.395185 [57] Li Shengwu, Yang Yanqiang, Song Yunfei, et al. Laser-induced fluorescence and its effect on the damage resistance of fluoride-containing phosphate-based glasses[J]. Ceramics International, 2021, 47(9): 13164-13172. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.01.181 [58] Wong J, Ferriera J L, Lindsey E F, et al. Morphology and microstructure in fused silica induced by high fluence ultraviolet 3ω (355 nm) laser pulses[J]. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 2006, 352(3): 255-272. doi: 10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2005.11.036 [59] Cheng Qiang, Huang Jin, Zhou Xinda, et al. Comparison of fused silica and oxyfluoride glass on laser induced initial damage morphology[C]//Proceedings of SPIE 8786, Pacific Rim Laser Damage 2013: Optical Materials for High Power Lasers. 2013: 878604. [60] DeSalvo R, Said A A, Hagan D J, et al. Infrared to ultraviolet measurements of two-photon absorption and n2 in wide bandgap solids[J]. IEEE Journal of Quantum Electronics, 1996, 32(8): 1324-1333. doi: 10.1109/3.511545 [61] 罗成思, 袁晓东, 刘春明, 等. CO2激光对熔石英损伤修复的研究进展[J]. 材料导报, 2011, 25(19):118-122Luo Chengsi, Yuan Xiaodong, Liu Chunming, et al. Research development of CO2 laser treatment for repair damage in fused silica[J]. Materials Reports, 2011, 25(19): 118-122 [62] Cormont P, Gallais L, Lamaignère L, et al. Impact of two CO2 laser heatings for damage repairing on fused silica surface[J]. Optics Express, 2010, 18(25): 26068-26076. doi: 10.1364/OE.18.026068 -




 下载:
下载: