Laser damage of KDP crystals and their analogues
-
摘要:
KDP类晶体是唯一可以满足ICF激光驱动装置通光口径的非线性光学晶体材料。该类晶体采用水溶液生长法生长,易于产生宏观包裹体和微观晶格缺陷,在高功率激光辐照下晶体内部易产生高密度pinpoint损伤现象,这与其他方法生长的晶体只是受限于光学加工的表面损伤问题相比具有明显不同。KDP类晶体内部的缺陷或前驱体诱导激光损伤与晶体切向、激光波长及偏振方向等密切相关,使得应用于ICF激光驱动器中不同光学功能的、来源于同一晶坯的不同晶体元件也表现出损伤性能的差异性,因此其损伤机理非常复杂,迫切需要认识该类晶体的激光损伤机理问题。回顾了上海光学精密机械研究所联合福建物质结构研究所、山东大学等晶体研制单位联合开展的关于KDP类晶体激光诱导损伤特性的研究工作,进行了用于光开关、倍频以及混频等功能的KDP和不同氘含量DKDP晶体的激光损伤研究,指导了晶体生长工艺优化和过程关键因素控制,并对仍存在的问题及解决方案进行了展望,对于高性能KDP类晶体的研制以及在高功率激光系统中的合理应用具有参考价值。
Abstract:KDP-family crystals are the only nonlinear optical crystal material according with the optical aperture of ICF laser drivers. As KDP-family crystals are grown by aqueous solution method, the macroscopic inclusions and microscopic lattice defects easily occur in the bulk of the crystals. The high density pinpoints damage phenomenon appears as they are irradiated by the high power laser. All the laser induced damage properties are different from the surface damage of crystals grown by other methods, which are only limited by optical processing. The laser induced damage by defects or precursors are related to the laser wavelengths and even the laser polarization direction, and the different samples from the same as-grown single crystal and applied to different optical functions in ICF laser drivers show different laser induced damage properties. Therefore, the damage mechanism is very complicated, and it is urgent to know the laser induced damage mechanism of KDP-family crystals. In this paper, the cooperated research of Shanghai Institute of Optics and Mechanics with Fujian Institute of Research on the Structure of Matter, Shandong University and other crystal research institutes is reviewed. The laser induced damage properties of KDP and DKDP crystals applied as optical switching, frequency doubling and frequency mixing optical elements were investigated. The optimization of crystal growth process and the control of key factors were guided and the existing problems and solutions were prospected. The research has reference value for the development of high-performance KDP-family crystals and their rational application in high-power laser systems
-
Key words:
- KDP-family crystals /
- laser induced damage /
- defect /
- precursor /
- thermal absorption /
- nonlinear absorption /
- laser conditioning
-
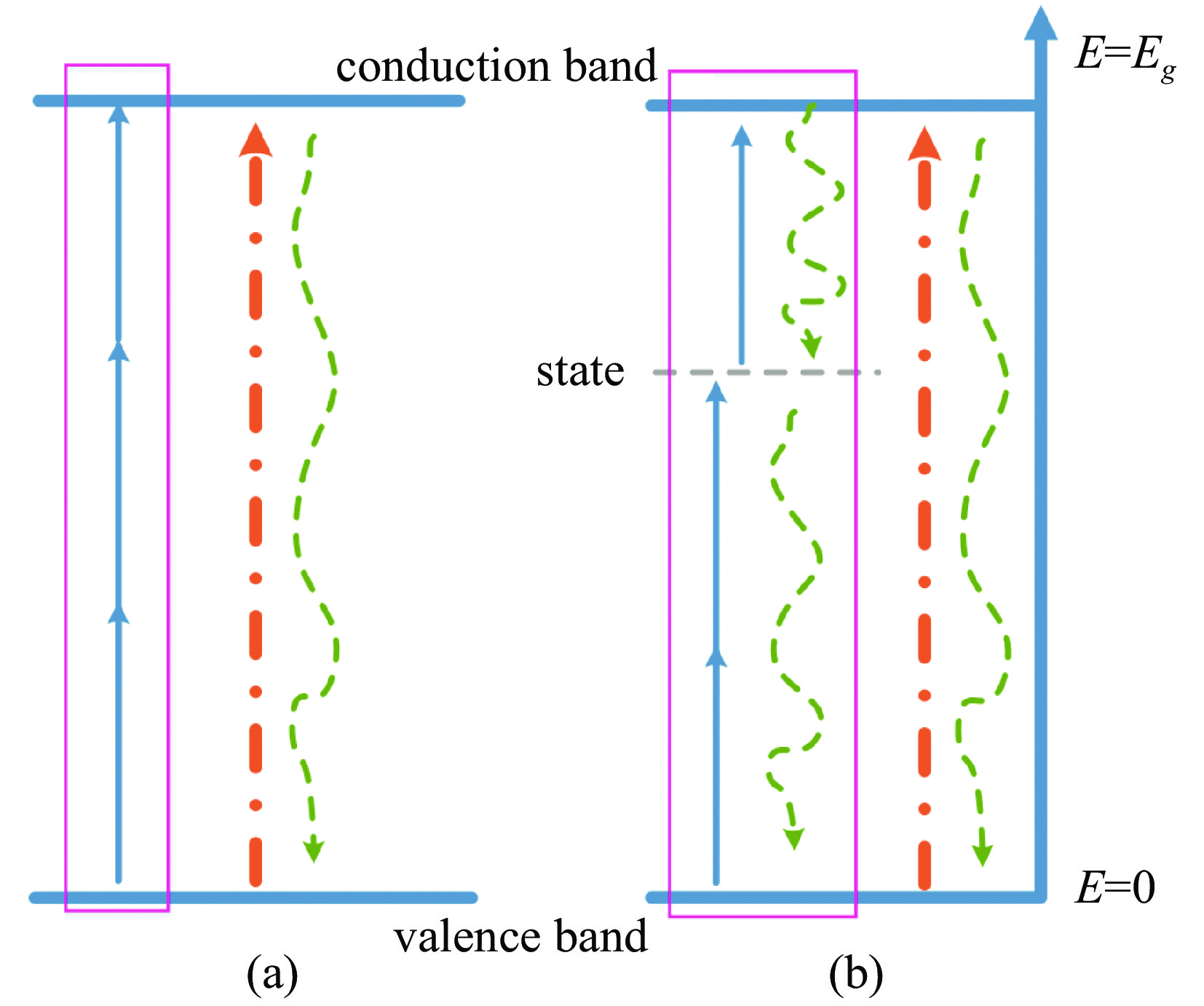
图 11 DKDP晶体在355 nm激光作用下价带电子离化示意图[37]
Figure 11. Schematic diagram of valence band electron ionization of DKDP crystal under 355 nm laser
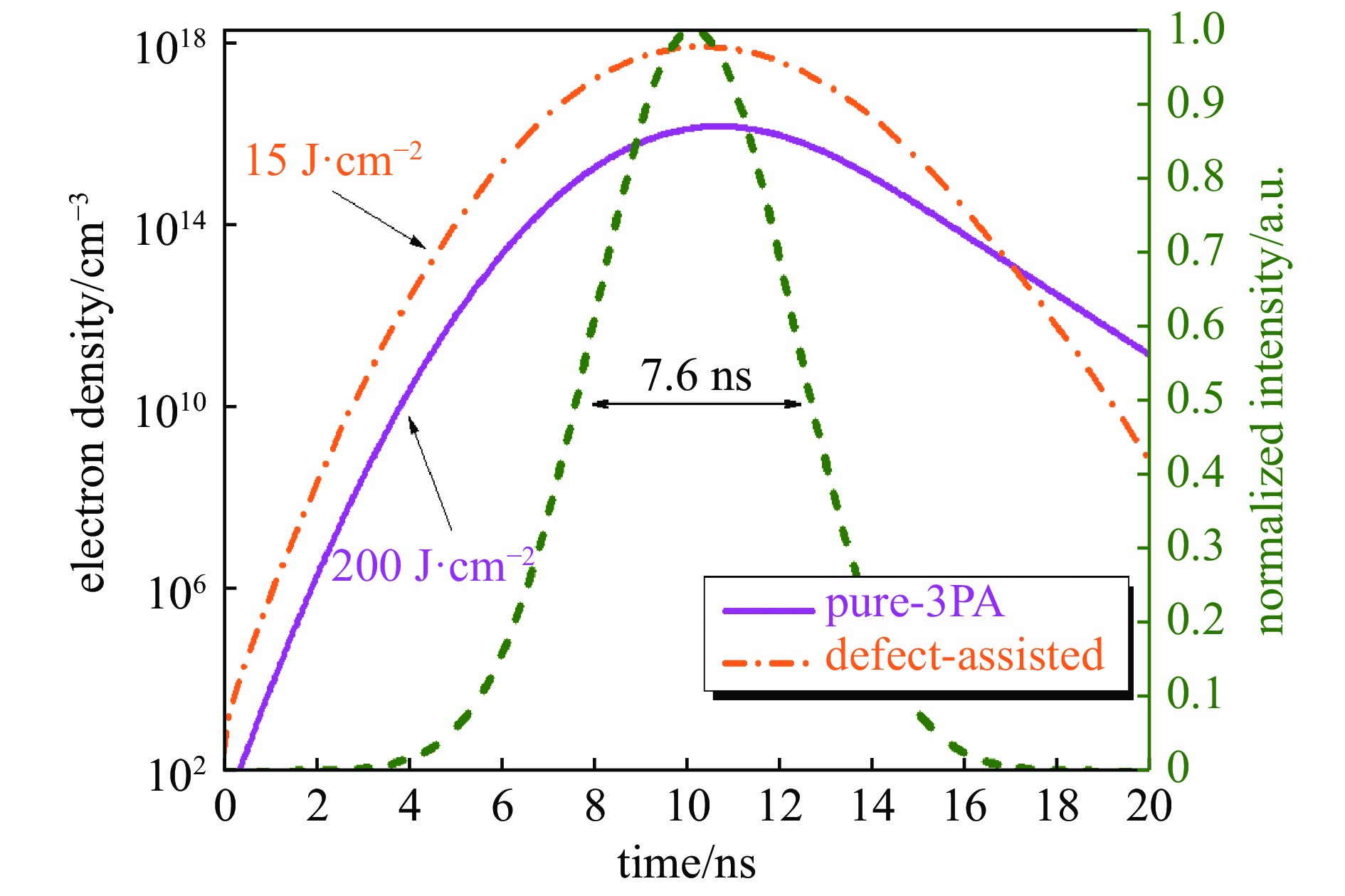
图 12 200 J·cm−2 (7.6 ns, 355 nm)经过纯3PA (实线)过程和15 J·cm−2(7.6 ns, 355 nm)经过缺陷辅助3PA (点划线)过程引起的导带电子数密度随时间变化[37]
Figure 12. Time-varying number density of conduction band electrons caused by pure 3PA (solid line) process at 200 J·cm−2 (7.6 ns, 355 nm) and defect-assisted 3PA (dotted line) process at 15 J·cm−2 (7.6 ns, 355 nm)[37]
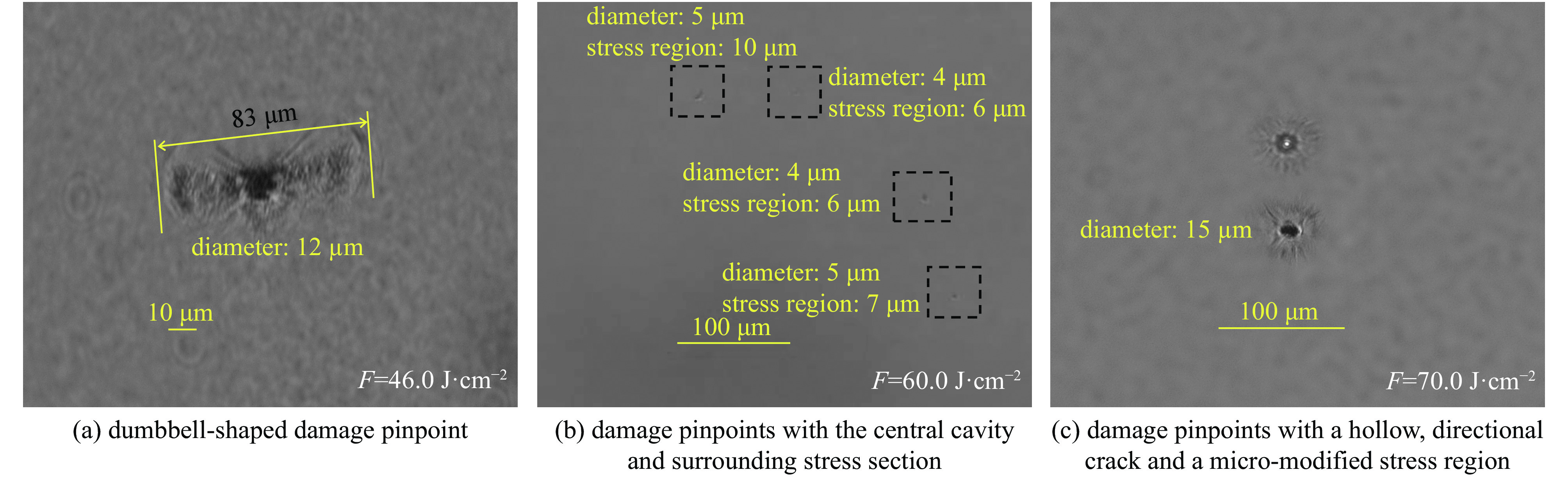
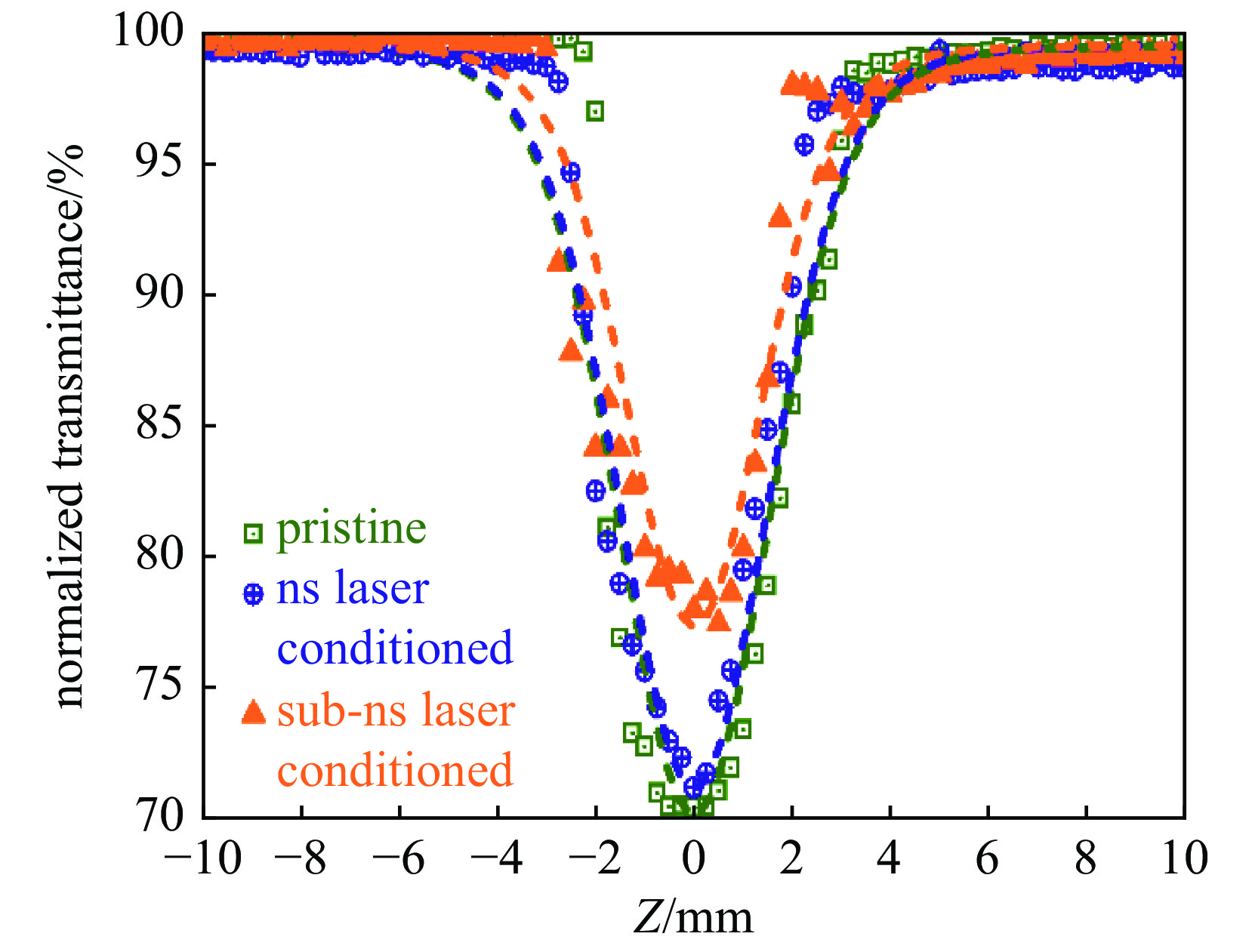
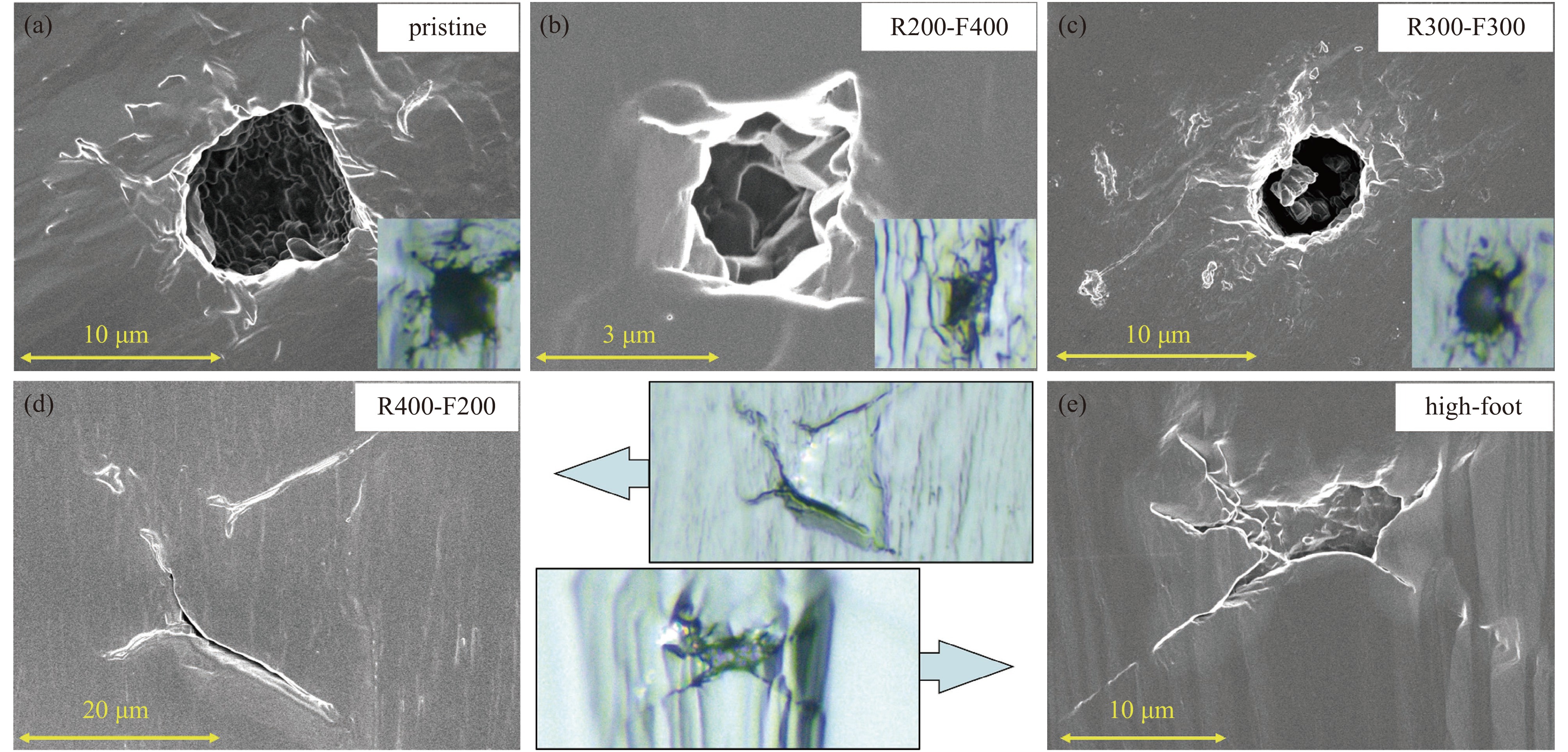
图 17 不同时间波形亚纳秒激光预处理后,DKDP晶体的纳秒激光(8 ns, F=23 J·cm−2)诱导损伤典型SEM形貌。 (a)-(e)图右上角为亚纳秒激光预处理条件,带有箭头的图像及插图均为光学显微镜下损伤点形貌[56]
Figure 17. SEM images of typical damage morphology initiated with 8 ns and 23 J·cm−2 laser. The laser conditioning parameters are marked in the upper right corners of (a)–(e). The two images with an arrow and the insets in (a)–(c) indicate the damage morphologies detected via the optical microscopy[56]
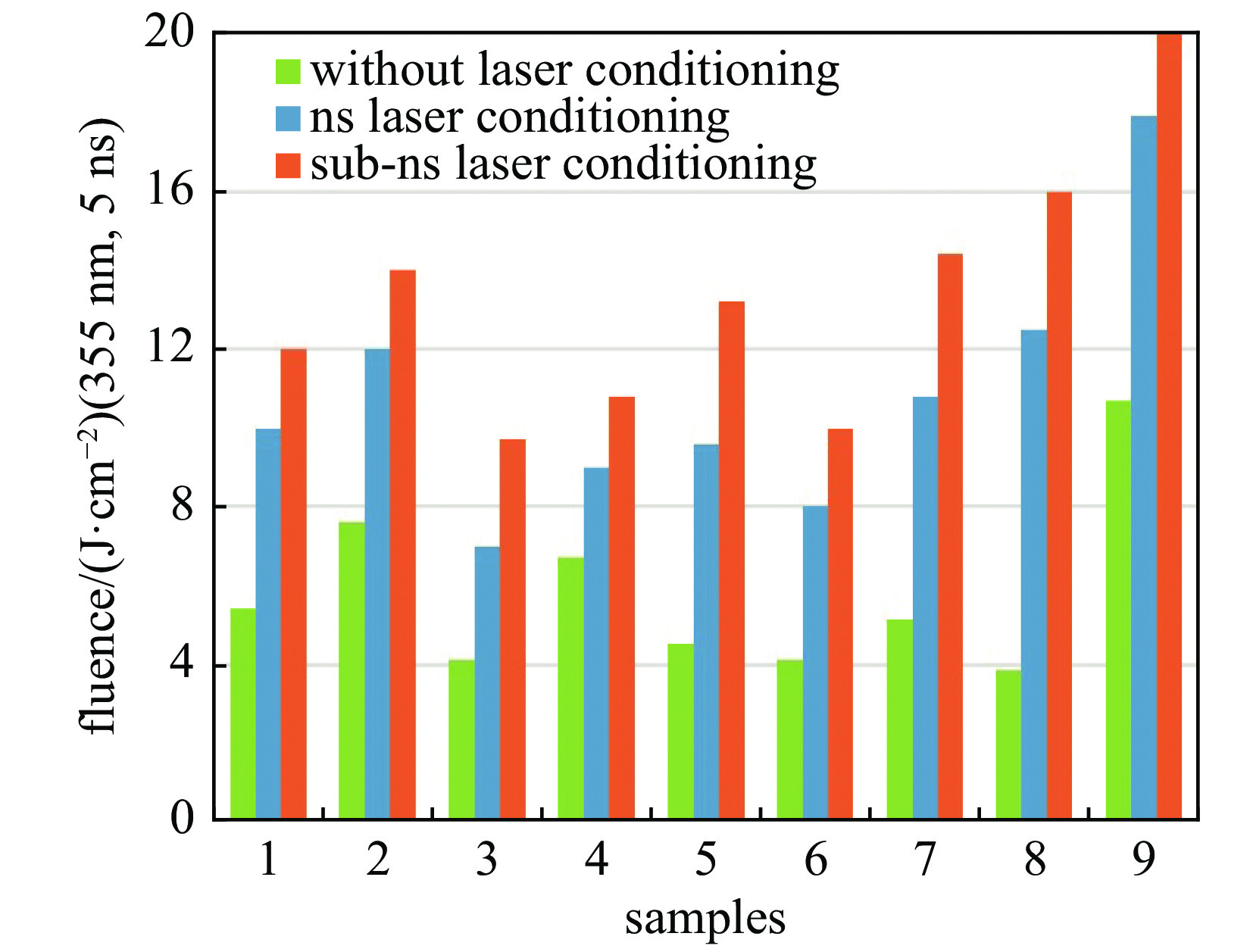
表 1 高功率激光驱动器中的KDP类晶体元件[8]
Table 1. KDP-family crystals in high power laser drivers
component function phase matching angle and
orientation angle (θ, φ)deuterium content/% application wavelength/nm
(polarization direction)switch (0 º, 0 º)[8] 0 or >90 1053 (o)[8, 57] second harmonic generation (41 º, 45 º)[8] 0 1053 (o), 527 (e)[8, 57] third harmonic generation (61 º, 0 º)[8, 58] 70 1053 (e), 527 (o), 351 (e)[8, 57] 表 2 不同1064 nm激光辐照方向及偏振方向下KDP晶体的激光诱导损伤阈值[67]
Table 2. Laser-induced damage threshold of KDP crystal under different irradiation directions and polarization directions of 1064 nm laser[67]
wavelength/nm laser incident direction laser polarization direction laser induced damage threshold /(J·cm−2@1.1ns) 1064 a(b) //c 11.7±0.5 ⊥c 12.3±0.3 c // a(b) 23.0±1.0 ⊥a(b) 19.5±1.0 -
[1] Rashkovich L N, Shlakhova O. KDP-family single crystals[M]. CRC Press, 2021. [2] Lindl J D, Mccrory R L, Campbell E M. Progress toward ignition and burn propagation in inertial confinement fusion[J]. Physics Today, 1992, 45(9): 32-40. doi: 10.1063/1.881318 [3] Campbell J H, Hawley-Fedder R A, Stolz C J, et al. NIF optical materials and fabrication technologies: an overview[C]//Proceedings of SPIE 5341, Optical Engineering at the Lawrence Optical Engineering at the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory II: The National Ignition Facility. 2004. [4] Hawley-Fedder R A, Geraghty P, Locke S N, et al. NIF Pockels cell and frequency conversion crystals[C]//Proceedings of SPIE 5341, Optical Engineering at the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory II: The National Ignition Facility. 2004. [5] Moses E I, Lindl J D, Spaeth M L, et al. Overview: Development of the National Ignition Facility and the transition to a user facility for the ignition campaign and high energy density scientific research[J]. Fusion Science and Technology, 2016, 69(1): 1-24. doi: 10.13182/FST15-128 [6] Van Wonterghem B M, Brereton S J, Burr R F, et al. Operations on the National Ignition Facility[J]. Fusion Science and Technology, 2016, 69(1): 452-469. doi: 10.13182/FST15-118 [7] Spaeth M L, Manes K R, Bowers M, et al. National Ignition Facility laser system performance[J]. Fusion Science and Technology, 2016, 69(1): 366-394. doi: 10.13182/FST15-136 [8] Baisden P A, Atherton L J, Hawley R A, et al. Large optics for the National Ignition Facility[J]. Fusion Science and Technology, 2016, 69(1): 295-351. doi: 10.13182/FST15-143 [9] Xu Mingxia, Liu Bao'an, Zhang Lisong, et al. Progress on deuterated potassium dihydrogen phosphate (DKDP) crystals for high power laser system application[J]. Light: Science & Applications, 2022, 11: 241. [10] Zhuang Xinxin, Ye Liwang, Zheng Guozong, et al. The rapid growth of large-scale KDP single crystal in brief procedure[J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 2011, 318(1): 700-702. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrysgro.2010.11.019 [11] Zaitseva N P, De Yoreo J J, Dehaven M R, et al. Rapid growth of large-scale (40-55 cm) KH2PO4 crystals[J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 1997, 180(2): 255-262. doi: 10.1016/S0022-0248(97)00223-6 [12] 秦梦飞. 大口径KDP晶体快速生长过程中几个关键问题的研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2020Qin Mengfei. Research on several key problems during the rapid growth of large-diameter KDP crystals[D]. Ji’nan: Shandong University, 2020 [13] Zaitseva N, Carman L J. Rapid growth of KDP-type crystals[J]. Progress in Crystal Growth and Characterization of Materials, 2001, 43(1): 1-118. doi: 10.1016/S0960-8974(01)00004-3 [14] Zaitseva N, Carman L, Smolsky I. Habit control during rapid growth of KDP and DKDP crystals[J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 2002, 241(3): 363-373. doi: 10.1016/S0022-0248(02)01244-7 [15] Sasaki T, Yokotani A. Growth of large KDP crystals for laser fusion experiments[J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 1990, 99(1-4): 820-826. doi: 10.1016/S0022-0248(08)80033-4 [16] Nakatsuka M, Fujioka K, Kanabe T, et al. Rapid growth over 50 mm/day of water-soluble KDP crystal[J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 1997, 171(3-4): 531-537. doi: 10.1016/S0022-0248(96)00675-6 [17] Maunier C, Bouchut P, Bouillet S, et al. Growth and characterization of large KDP crystals for high power lasers[J]. Optical Materials, 2007, 30(1): 88-90. doi: 10.1016/j.optmat.2006.11.019 [18] 庄欣欣, 叶李旺, 汪剑成, 等. 点籽晶降温法快速生长大尺寸磷酸二氢钾晶体[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2010, 22(12):2857-2859 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20102212.2857Zhuang Xinxin, Ye Liwang, Wang Jiancheng, et al. Rapid growth of large size KDP crystal by temperature reduction method[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2010, 22(12): 2857-2859 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20102212.2857 [19] 张力元, 王圣来, 刘慧, 等. 超大尺寸KDP/DKDP晶体研究进展[J]. 人工晶体学报, 2021, 50(4):724-731Zhang Liyuan, Wang Shenglai, Liu Hui, et al. Research progress of oversized KDP/DKDP crystals[J]. Journal of Synthetic Crystals, 2021, 50(4): 724-731 [20] Li Guohui, Zheng Guozong, Qi Yingkun, et al. Rapid growth of a large-scale (600 mm aperture) KDP crystal and its optical quality[J]. High Power Laser Science and Engineering, 2014, 2: e2. doi: 10.1017/hpl.2014.3 [21] 蔡序敏, 祁英昆, 赵元安, 等. 横向双锥快速生长35% DKDP晶体的研究[J]. 人工晶体学报, 2019, 48(4):587-591,597Cai Xumin, Qi Yingkun, Zhao Yuan'an, et al. Study on the growth of 35% DKDP crystals by rapid horizontal growth method[J]. Journal of Synthetic Crystals, 2019, 48(4): 587-591,597 [22] Xie Xiaoyi, Qi Hongji, Wang Bin, et al. The performance studies of DKDP crystals grown by a rapid horizontal growth method[J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 2018, 487: 45-49. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrysgro.2018.02.005 [23] Chen Duanyang, Wang Bin, Wang Hu, et al. Rapid growth of a cuboid DKDP (KDxH2–xPO4) crystal[J]. Crystal Growth & Design, 2019, 19(5): 2746-2750. [24] Chen Duanyang, Wang Bin, Wang Hu, et al. Rapid growth of a long-seed KDP crystal[J]. High Power Laser Science and Engineering, 2020, 8: e6. doi: 10.1017/hpl.2019.54 [25] Barrett J J, Weber A. Temperature dependence of optical harmonic generation in KDP and ADP crystals[J]. Physical Review, 1963, 131(4): 1469-1472. doi: 10.1103/PhysRev.131.1469 [26] Barrett J J. Investigations of nonlinear optical phenomena using a pulsed ruby laser[M]. Fordham University, 1964. [27] Wright J K. Non-linear optics[J]. Contemporary Physics, 1964, 6(1): 1-14. doi: 10.1080/00107516408202123 [28] Ristau D. Laser-induced damage in optical materials[M]. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2014. [29] 孙洵, 顾庆天, 王圣来, 等. KDP晶体中散射颗粒形成机理的研究[J]. 人工晶体学报, 2003, 32(6):541-545Sun Xun, Gu Qingtian, Wang Shenglai, et al. Formation mechanism of scatter particles in KDP crystals[J]. Journal of Synthetic Crystals, 2003, 32(6): 541-545 [30] 孙洵. KDP(DKDP)晶体中散射颗粒的研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2002Sun Xun. Study on scatters in KDP and DKDP crystals[D]. Ji’nan: Shandong University, 2002 [31] 胡国行. KDP/DKDP晶体和熔石英激光损伤及抑制技术研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学, 2011Hu Guoxing. Laser induced damage and suppression techniques for KDP/DKDP crystal and fused silica [D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2011 [32] 刘征宙, 孙文伟, 王伟, 等. 强激光用KDP晶体原料批量生产纯化技术的研究[C]//强激光材料与元器件学术研讨会暨激光破坏学术研讨会论文集. 2016Liu Zhengzhou, Sun Wenwei, Wang Wei, et al. Study on KDP crystals raw material batch production and purification technology in strong laser application[C]. Proceedings of the Symposium on High Power Laser Materials and Components and the Symposium on Laser Destruction. 2016 [33] 汪剑成. 溶液连续过滤快速生长KDP(DKDP)晶体的研究[D]. 福州: 中国科学院福建物质结构研究所, 2009Wang Jiancheng. Study on the rapid growth of KDP(DKDP) crystal with solution continuous filtration technic[D]. Fuzhou: Fujian Institute of Research on the Structure, 2009 [34] 汪剑成, 苏根博, 郑国宗, 等. 溶液连续过滤快速生长KDP晶体及其品质分析[J]. 人工晶体学报, 2010, 39(1):1-4Wang Jiancheng, Su Genbo, Zheng Guozong, et al. Continuous filtration system for rapid growth and quality analysis of KDP crystals[J]. Journal of Synthetic Crystals, 2010, 39(1): 1-4 [35] Wang Yueliang, Zhao Yuan'an, Xie Xiaoyi, et al. Laser damage dependence on the size and concentration of precursor defects in KDP crystals: view through differently sized filter pores[J]. Optics Letters, 2016, 41(7): 1534-1537. doi: 10.1364/OL.41.001534 [36] 谢晓义. KDP/DKDP晶体生长关键技术研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学, 2018Xie Xiaoyi. Research study on key technologies of KDP/DKDP crystal growth[D]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2018 [37] 王岳亮. Ⅰ类KDP和Ⅱ类DKDP晶体激光损伤机理及激光预处理特性研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学, 2017: 53-66Wang Yueliang. Laser damage mechanisms and laser conditioning properties in I-type KDP and II-type DKDP crystals[D]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2017: 53-66 [38] 彭小聪. KDP/DKDP晶体吸收特性及缺陷辅助多光子吸收机理研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学, 2019Peng Xiaocong. Absorption properties and defect-assisted multiphoton absorption mechanism in KDP/DKDP crystals [D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2019 [39] 连亚飞. 短波长下ADP晶体的非线性及损伤性能研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2019Lian Yafei. Research on nonlinear properties and laser induced damage performance of ADP crystals at short wavelengths[D]. Ji’nan: Shandong University, 2019 [40] Carr C W, Radousky H B, Demos S G. Wavelength dependence of laser-induced damage: determining the damage initiation mechanisms[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2003, 91: 127402. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.91.127402 [41] Demos S G, Demange P, Negres R A, et al. Investigation of the electronic and physical properties of defect structures responsible for laser-induced damage in DKDP crystals[J]. Optics Express, 2010, 18(13): 13788-13804. doi: 10.1364/OE.18.013788 [42] Duchateau G, Feit M D, Demos S G. Transient material properties during defect-assisted laser breakdown in deuterated potassium dihydrogen phosphate crystals[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2014, 115: 103506. doi: 10.1063/1.4868161 [43] Han Wei, Wang Fang, Zhou Lidan, et al. Suppression of transverse stimulated Raman scattering with laser-induced damage array in a large-aperture potassium dihydrogen phosphate crystal[J]. Optics Express, 2013, 21(25): 30481-30491. doi: 10.1364/OE.21.030481 [44] Demos S G, Raman R N, Yang S T, et al. Estimation of the transverse stimulated Raman scattering gain coefficient in KDP and DKDP at 2ω, 3ω, and 4ω[C]//Proceedings of SPIE 8190, Laser-Induced Damage in Optical Materials. 2011. [45] Kosc T Z, Huang H, Kessler T J, et al. Angular dependence of the transverse Raman scattering in KDP and DKDP in geometries suitable for beam polarization control[J]. Optics Express, 2022, 30(8): 12918-12928. doi: 10.1364/OE.448388 [46] Peng Xiaocong, Zhao Yuan'an, Wang Yueliang, et al. Variation of the band structure in DKDP crystal excited by intense sub-picosecond laser pulses[J]. High Power Laser Science and Engineering, 2018, 6: e41. doi: 10.1017/hpl.2018.35 [47] Peng Xiaocong, Zhao Yuan'an, Wang Yueliang, et al. Absorption modification by laser irradiation in DKDP crystals[J]. Chinese Optics Letters, 2018, 16(5): 051601. doi: 10.3788/COL201816.051601 [48] Manes K R, Spaeth M L, Adams J J, et al. Damage mechanisms avoided or managed for NIF large optics[J]. Fusion Science and Technology, 2016, 69(1): 146-249. doi: 10.13182/FST15-139 [49] Runkel M J, Nostrand M C. Overview of raster scanning for ICF-class laser optics[C]//Proceedings of SPIE 4932, Laser-Induced Damage in Optical Materials: 2002 and 7th International Workshop on Laser Beam and Optics Characterization. 2003. [50] Staggs M C, Yan Ming, Runkel M J. Laser raster conditioning of KDP and DKDP crystals using XeCl and Nd: YAG lasers[C]//Proceedings of SPIE 4347, Laser-Induced Damage in Optical Materials: 2000. 2001. [51] Zhi M. Liao, Spaeth M L, Manes K, et al. Predicting laser-induced bulk damage and conditioning for deuterated potassium dihydrogen phosphate crystals using an absorption distribution model[J]. Optics Letters, 2010, 35(15): 2538-2540. doi: 10.1364/OL.35.002538 [52] Adams J J, Bruere J R, Bolourchi M, et al. Wavelength and pulselength dependence of laser conditioning and bulk damage in doubler-cut KH2PO4[C]//Proceedings of SPIE 5991, Laser-Induced Damage in Optical Materials: 2005; 59911R. 2006. [53] Runkel M J, Burnham A K, Milam D, et al. Results of pulse-scaling experiments on rapid-growth DKDP triplers using the optical sciences laser at 351 nm[C]//Proceedings of SPIE 4347, Laser-Induced Damage in Optical Materials: 2000. 2001. [54] Adams J J, Jarboe J A, Carr C W, et al. Results of sub-nanosecond laser-conditioning of KD2PO4 crystals[C]//Proceedings of SPIE 6403, Laser-Induced Damage in Optical Materials: 2006. 2007. [55] Honig J, Halpin J. Diode-pumped 22-W average-power uv laser with user-selectable pulse width and >50% conversion efficiency[C]//Proceedings of the Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics. 2007. [56] Li Ting, Zhao Yuan'an, Lian Yafei, et al. Optimizing sub-nanosecond laser conditioning of DKDP crystals by varying the temporal shape of the pulse[J]. Optics Express, 2021, 29(22): 35993-36004. doi: 10.1364/OE.441918 [57] 刘宝安. DKDP系统晶体制备及性质研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2013Liu Bao'an. Study on the growth and properties of DKDP crystals[D]. Ji’nan: Shandong University, 2013 [58] 蔡东廷. DKDP晶体的紫外非线性及损伤特性研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2020Cai Dongting. Research on nonlinear properties and damage characteristics of DKDP crystal in ultraviolet wavelengths[D]. Ji’nan: Shandong University, 2020 [59] Natoli J Y, Capoulade J, Piombini H, et al. Influence of laser beam size and wavelength in the determination of LIDT and associated laser damage precursor densities in KH2PO4[C]//Proceedings of SPIE 6720, Laser-Induced Damage in Optical Materials: 2007. 2007. [60] Reyné S, Duchateau G, Natoli J Y, et al. Laser-induced damage of KDP crystals by 1ω nanosecond pulses: influence of crystal orientation[J]. Optics Express, 2009, 17(24): 21652-21665. doi: 10.1364/OE.17.021652 [61] Cross D A, Carr C W. Analysis of 1ω bulk laser damage in KDP[J]. Applied Optics, 2011, 50(22): D7-D11. doi: 10.1364/AO.50.0000D7 [62] Burnham A K, Runkel M, Feit M D, et al. Laser-induced damage in deuterated potassium dihydrogen phosphate[J]. Applied Optics, 2003, 42(27): 5483-5495. doi: 10.1364/AO.42.005483 [63] Demange P P. Laser-induced defect reactions governing the damage performance of KDP and DKDP[D]. Davis: University of California, 2006. [64] Lian Yafei, Zhao Yuan'an, Zheng Guozong, et al. Optical and laser damage properties of 98% deuterium DKDP crystal in different crystal orientations[J]. Optical Materials, 2022, 134: 113130. doi: 10.1016/j.optmat.2022.113130 [65] 刘发付. KDP/DKDP晶体生长及其残余应力研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2017Liu Fafu. Research on growth and residual stress of KDP/DKDP Crystals[D]. Ji’nan: Shandong University, 2017 [66] Cai Xumin, Lin Xiuqing, Li Guohui, et al. Rapid growth and properties of large-aperture 98%-deuterated DKDP crystals[J]. High Power Laser Science and Engineering, 2019, 7: e46. doi: 10.1017/hpl.2019.24 [67] Yoshida H, Jitsuno T, Fujita H, et al. Investigation of bulk laser damage in KDP crystal as a function of laser irradiation direction, polarization, and wavelength[J]. Applied Physics B, 2000, 70(2): 195-201. doi: 10.1007/s003400050032 [68] Spaeth M L, Manes K R, Kalantar D H, et al. Description of the NIF laser[J]. Fusion Science and Technology, 2016, 69(1): 25-145. doi: 10.13182/FST15-144 [69] Zaitseva N, Carman L, Smolsky I, et al. The effect of impurities and supersaturation on the rapid growth of KDP crystals[J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 1999, 204(4): 512-24. doi: 10.1016/S0022-0248(99)00194-3 [70] Hu Guohang, Zhao Yuan'an, Li Dawei, et al. Transmittance increase after laser conditioning reveals absorption properties variation in DKDP crystals[J]. Optics Express, 2012, 20(22): 25169-25180. doi: 10.1364/OE.20.025169 [71] Zaitseva N, Atherton J, Rozsa R, et al. Design and benefits of continuous filtration in rapid growth of large KDP and DKDP crystals[J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 1999, 197(4): 911-920. doi: 10.1016/S0022-0248(98)01095-1 [72] Demange P, Negres R A, Carr C W, et al. Laser-induced defect reactions governing damage initiation in DKDP crystals[J]. Optics Express, 2006, 14(12): 5313-5328. doi: 10.1364/OE.14.005313 [73] Duchateau G. Simple models for laser-induced damage and conditioning of potassium dihydrogen phosphate crystals by nanosecond pulses[J]. Optics Express, 2009, 17(13): 10434-10456. doi: 10.1364/OE.17.010434 [74] Zhi M. Liao, Roussell R, Adams J J, et al. Defect population variability in deuterated potassium di-hydrogen phosphate crystals[J]. Optical Materials Express, 2012, 2(11): 1612-1623. doi: 10.1364/OME.2.001612 [75] Wang Yueliang, Zhao Yuanan, Hu Guohang, et al. Mitigation of scattering defect and absorption of DKDP crystals by laser conditioning[J]. Optics Express, 2015, 23(12): 16273-16280. doi: 10.1364/OE.23.016273 [76] Liu C S, Kioussis N, Demos S G, et al. Electron-or hole-assisted reactions of H defects in hydrogen-bonded KDP[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2003, 91(1): 015505. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.91.015505 [77] Liu C S, Zhang Q, Kioussis N, et al. Electronic structure calculations of intrinsic and extrinsic hydrogen point defects in KH2PO4[J]. Physical Review B, 2003, 68(22): 224107. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.68.224107 [78] Liu C S, Hou C J, Kioussis N, et al. Electronic structure calculations of an oxygen vacancy in KH2PO4[J]. Physical Review B, 2005, 72(13): 134110. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.72.134110 [79] Wang Kunpeng, Fang Changshui, Zhang Jianxiu, et al. First-principles study of interstitial oxygen in potassium dihydrogen phosphate crystals[J]. Physical Review B, 2005, 72: 184105. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.72.184105 [80] Wei Liening, Li Yang, Jiang Xuanyu, et al. Electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy and first-principles calculations of Cr3+ doped KDP crystals[J]. CrystEngComm, 2022, 24(27): 4948-4954. doi: 10.1039/D2CE00335J [81] Li Yang, Liu Bao'an, Li Yanlu, et al. Hybrid density functional theory calculations for the electronic and optical properties of Fe3+ doped KDP crystal[J]. CrystEngComm, 2022, 24(46): 8082-8088. doi: 10.1039/D2CE01285E [82] Li Yang, Jiang Xuanyu, Wu Pengcheng, et al. Insight into the stability and properties of Zn-doped KH2PO4 crystal by hybrid density functional theory[J]. Crystal Research and Technology, 2023, 58: 2200107. doi: 10.1002/crat.202200107 [83] Setzler S D, Stevens K T, Halliburton L E, et al. Hydrogen atoms in KH2PO4 crystals[J]. Physical Review B, 1998, 57(5): 2643-2646. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.57.2643 [84] Garces N Y, Stevens K T, Halliburton L E, et al. Identification of electron and hole traps in KH2PO4 crystals[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2001, 89(1): 47-52. doi: 10.1063/1.1320030 [85] Chirila M M, Garces N Y, Halliburton L E, et al. Production and thermal decay of radiation-induced point defects in KD2PO4 crystals[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2003, 94(10): 6456-6462. doi: 10.1063/1.1620680 [86] Keldysh L V. Ionization in the field of a strong electromagnetic wave[J]. 1Soviet Physics Jetp, 1965, 20(5): 1307-1314. [87] 鲁智宽, 高樟寿, 李义平, 等. 溶液循环流动法生长大尺寸KDP晶体[J]. 人工晶体学报, 1996, 25(1):19-22Lu Zhikuan, Gao Zhangshou, Li Yiping, et al. Growth of large KDP crystals by solution circulating method[J]. Journal of Synthetic Crystals, 1996, 25(1): 19-22 [88] 房昌水, 王圣来, 李义平, 等. 大尺寸高质量KDP及DKDP单晶的研究[C]//中国硅酸盐学会2003年学术年会论文摘要集. 2003Fang Changshui, Wang Shenglai, Li Yiping, et al. Research on large-size and high-quality KDP and DKDP single crystals[C]//Abstracts of Papers of the 2003 Academic Annual Meeting of China Silicate Society. 2003 [89] 赵元安, 胡国行, 刘晓凤, 等. 激光预处理技术及其应用[J]. 光学 精密工程, 2016, 24(12):2938-2947 doi: 10.3788/OPE.20162412.2938Zhao Yuan'an, Hu Guoxing, Liu Xiaofeng, et al. Laser conditioning technology and its applications[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2016, 24(12): 2938-2947 doi: 10.3788/OPE.20162412.2938 [90] Dyan A, Pommiès M, Duchateau G, et al. Revisited thermal approach to model laser-induced damage and conditioning process in KH2PO4 and D2xKH2(1− x)PO4 crystals[C]//Proceedings of SPIE 6403, Laser-Induced Damage in Optical Materials: 2006. 2007. [91] Strickland D, Mourou G. Compression of amplified chirped optical pulses[J]. Optics Communications, 1985, 56: 219-221. doi: 10.1016/0030-4018(85)90120-8 [92] Dubietis A, Jonušauskas G, Piskarskas A. Powerful femtosecond pulse generation by chirped and stretched pulse parametric amplification in BBO crystal[J]. Optics Communications, 1992, 88(4/6): 437-440. [93] Lureau F, Matras G, Chalus O, et al. High-energy hybrid femtosecond laser system demonstrating 2×10 PW capability[J]. High Power Laser Science and Engineering, 2020, 8: e43. doi: 10.1017/hpl.2020.41 [94] Danson C N, Haefner C, Bromage J, et al. Petawatt and exawatt class lasers worldwide[J]. High Power Laser Science and Engineering, 2019, 7: e54. doi: 10.1017/hpl.2019.36 [95] Galimberti M, Hernandez-Gomez C, Musgrave I, et al. Influence of the deuteration level of the KD*P crystal on multi-PW class OPCPA laser[J]. Optics Communications, 2013, 309: 80-84. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2013.06.065 [96] Galimberti M, Boyle A, Musgrave I O, et al. Spectral gain investigation of large size OPCPA based on partially deuterated KDP[J]. EPJ Web of Conferences, 2018, 167: 01006. doi: 10.1051/epjconf/201816701006 [97] 梁潇, 康俊, 孙美智, 等. 基于DKDP晶体的808nm波段光参量放大研究[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2016, 53:081901Liang Xiao, Kang Jun, Sun Meizhi, et al. 808-nm optical parametric amplification based on DKDP crystals[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2016, 53: 081901 [98] 孙子茗, 刘德安, 韩璐, 等. 基于电光调制的DKDP晶体OPCPA增益带宽特性研究[J]. 中国激光, 2020, 47:1008001 doi: 10.3788/CJL202047.1008001Sun Ziming, Liu De'an, Han Lu, et al. Study on gain bandwidth characteristics of DKDP-OPCPA based on electro-optic modulation[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2020, 47: 1008001 doi: 10.3788/CJL202047.1008001 -




 下载:
下载: