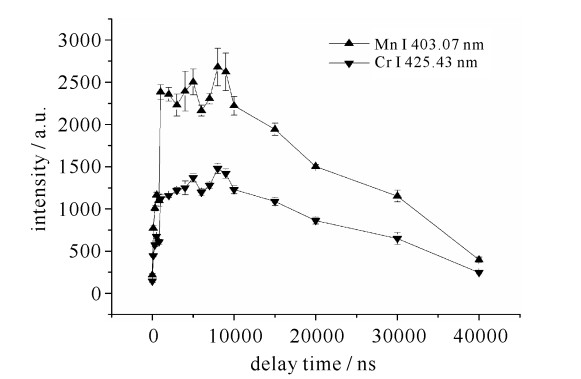
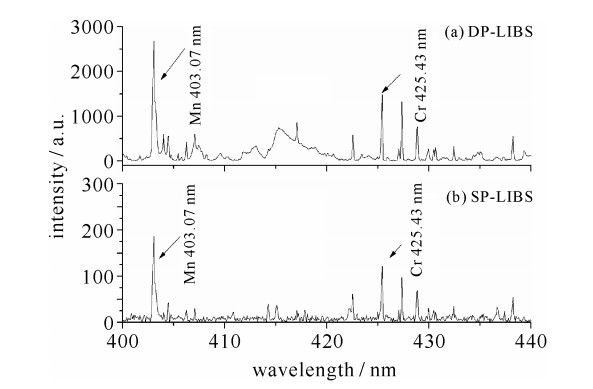
| [1] |
DeLucia F C, Samuels A C, Harmon R S, et al. Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy(LIBS): A promising versatile chemical sensor technology for hazardous material detection[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2005, 5(4): 681-689. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2005.848151
|
| [2] |
Wang Zhe, Yuan Tingbi, Hou Zongyu, et al. Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy in China[J]. Front Phys, 2014, 9(4): 419-438. doi: 10.1007/s11467-013-0410-0
|
| [3] |
Sturm V, Schmitz H U, Reuter T, et al. Fast vacuum slag analysis in a steel works by laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part B, 2008, 63(10): 1167-1170. doi: 10.1016/j.sab.2008.08.004
|
| [4] |
Goueguel C, Laville S, Vidal F, et al. Resonant laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy for analysis of lead traces in copper alloys[J]. J Anal Atom Spectrom, 2011, 26(12): 2452-2460. doi: 10.1039/c1ja10112a
|
| [5] |
Santagata A, Spera D, Albano G, et al. Orthogonal fs/ns double-pulse libs for copper-based-alloy analysis[J]. Applied Physics A: Materials Science and Processing, 2008, 93(4): 929-934. doi: 10.1007/s00339-008-4738-1
|
| [6] |
Doucet F R, Belliveau T F, Fortier J L, et al. Use of chemometrics and laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy for quantitative analysis of major and minor elements in aluminum alloys[J]. Applied Spectroscopy, 2007, 61(3): 327-332. doi: 10.1366/000370207780220813
|
| [7] |
Inakollu P, Philip T, Rai A K, et al. A comparative study of laser induced breakdown spectroscopy analysis for element concentrations in aluminum alloy using artificial neural networks and calibration methods[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part B, 2009, 64(1): 99-104. doi: 10.1016/j.sab.2008.11.001
|
| [8] |
Li Xiafen, Zhou Weidong, Li Kexue, et al. Laser ablation fast pulse discharge plasma spectroscopy analysis of Pb, Mg and Sn in soil[J]. Opt Commun, 2012, 285(1): 54-58. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2011.08.074
|
| [9] |
Li Xiafen, Zhou Weidong, Cui Zhifeng. Temperature and electron density of soil plasma generated by LA-FPDPS[J]. Front Phys, 2012, 7(6): 721-727. doi: 10.1007/s11467-012-0254-z
|
| [10] |
Su Xuejiao, Zhou Weidong, Qian Huiguo. Optimization of cavity size for spatial confined laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy[J]. Optics Express, 2014, 22(23): 28437-28442. doi: 10.1364/OE.22.028437
|
| [11] |
Su Xuejiao, Zhou Weidong, Qian Huiguo. Optical emission character of collinear dual pulse laser plasma with cylindrical cavity confinement[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2014, 29: 2356-2361. doi: 10.1039/C4JA00296B
|
| [12] |
Yu Youli, Zhou Weidong, Su Xuejiao. Detection of Cu in solution with double pulse laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy[J]. Optics Communications, 2014, 333: 62-66. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2014.07.053
|
| [13] |
Song Chao, Gao Xun, Shao Yan. Pre-ablation laser parameter effects on the spectral enhancement of 1064 nm/1064 nm dual-pulse laser induced breakdown spectroscopy[J]. Optik, 2016, 127: 3979-3983. doi: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2016.01.109
|
| [14] |
Freedman A, Iannarilli F J, Wormhoudt J C. Aluminum alloy analysis using microchip-laser induced breakdown spectroscopy[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part B, 2005, 60(7/8): 1076-1082.
|
| [15] |
Ismail M A, Cristoforetti G, Legnaioli, S, et al. Comparison of detection limits, for two metallic matrices, of laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy in the single and double-pulse configurations[J]. Anal Bioanal Chem, 2006, 385(2): 316-325. doi: 10.1007/s00216-006-0363-z
|
| [16] |
Mohamed W T Y. Improved LIBS limit of detection of Be, Mg, Si, Mn, Fe and Cu in aluminum alloy samples using a portable Echelle spectrometer with ICCD camera[J]. Opt Laser Technol, 2008, 40(1): 30-38. doi: 10.1016/j.optlastec.2007.04.004
|
| [17] |
Elnasharty I Y, Doucet F R, Gravel J F Y, et al. Double-pulse LIBS combining short and long nanosecond pulses in the microjoule range[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2014, 29(9): 1660-1666. doi: 10.1039/C4JA00099D
|
| [18] |
Li Shuo, Liu Lei, Yan Aidong, et al. A compact field-portable double-pulse laser system to enhance laser induced breakdown spectroscopy[J]. Rev Sci Instr, 2017, 88: 023109. doi: 10.1063/1.4975597
|
| [19] |
王琦, 董凤忠, 梁云仙, 等. 再加热双脉冲与单脉冲激光诱导Fe等离子体发射光谱实验对比研究[J]. 光学学报, 2011, 31(10): 281-287. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXXB201110051.htmWang Qi, Dong Fengzhong, Liang Yunxian, et al. Experimental comparison investigation on emission spectra of reheating double and single pulses laser-induced Fe plasmas. Acta Optica Sinica, 2011, 31(10): 281-287 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXXB201110051.htm
|
| [20] |
Babushok V I, DeLucia Jr F C, Gottfried J L, et al. Double pulse laser ablation and plasma: laser induced breakdown spectroscopy signal enhancement[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part B: Atomic Spectroscopy, 2006, 61(9): 999-1014. doi: 10.1016/j.sab.2006.09.003
|
| [21] |
Colao F, Lazic V, Fantoni R, et al. A comparison of single and double pulse laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy of aluminum samples[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part B: Atomic Spectroscopy, 2002, 57(7): 1167-1179. doi: 10.1016/S0584-8547(02)00058-7
|
| [22] |
Chen Fangfang, Su Xuejiao, Zhou Weidong. Effect of parameters on Si plasma emission in collinear double-pulse laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy[J]. Front Phys, 2015, 10: 104207. doi: 10.1007/s11467-015-0500-2
|
| [23] |
Jedlinszki N, Galbács G. An evaluation of the analytical performance of collinear multi-pulse laser induced breakdown spectroscopy[J]. Microchemical Journal, 2011, 97(2): 255-263. doi: 10.1016/j.microc.2010.09.009
|




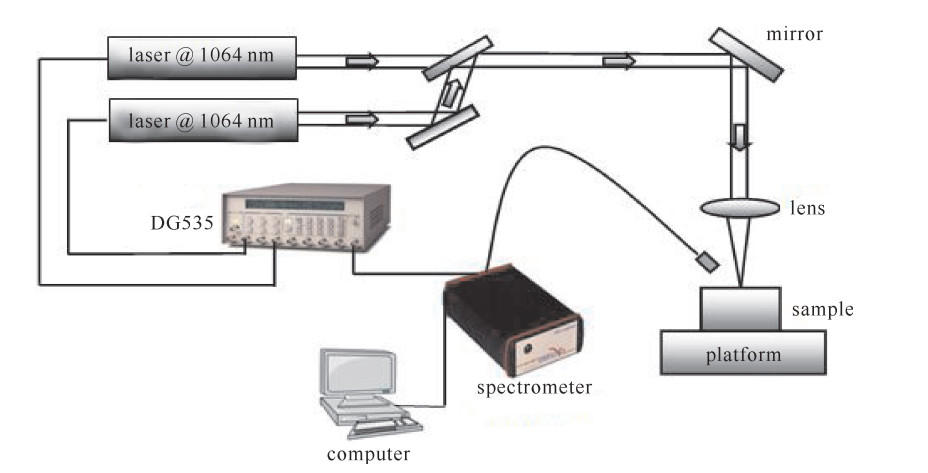
 下载:
下载: