Numerical studies of the implosion behavior and radiation field of Z-pinch dynamic hohlraums with embedded hard foam layer and capsule
-
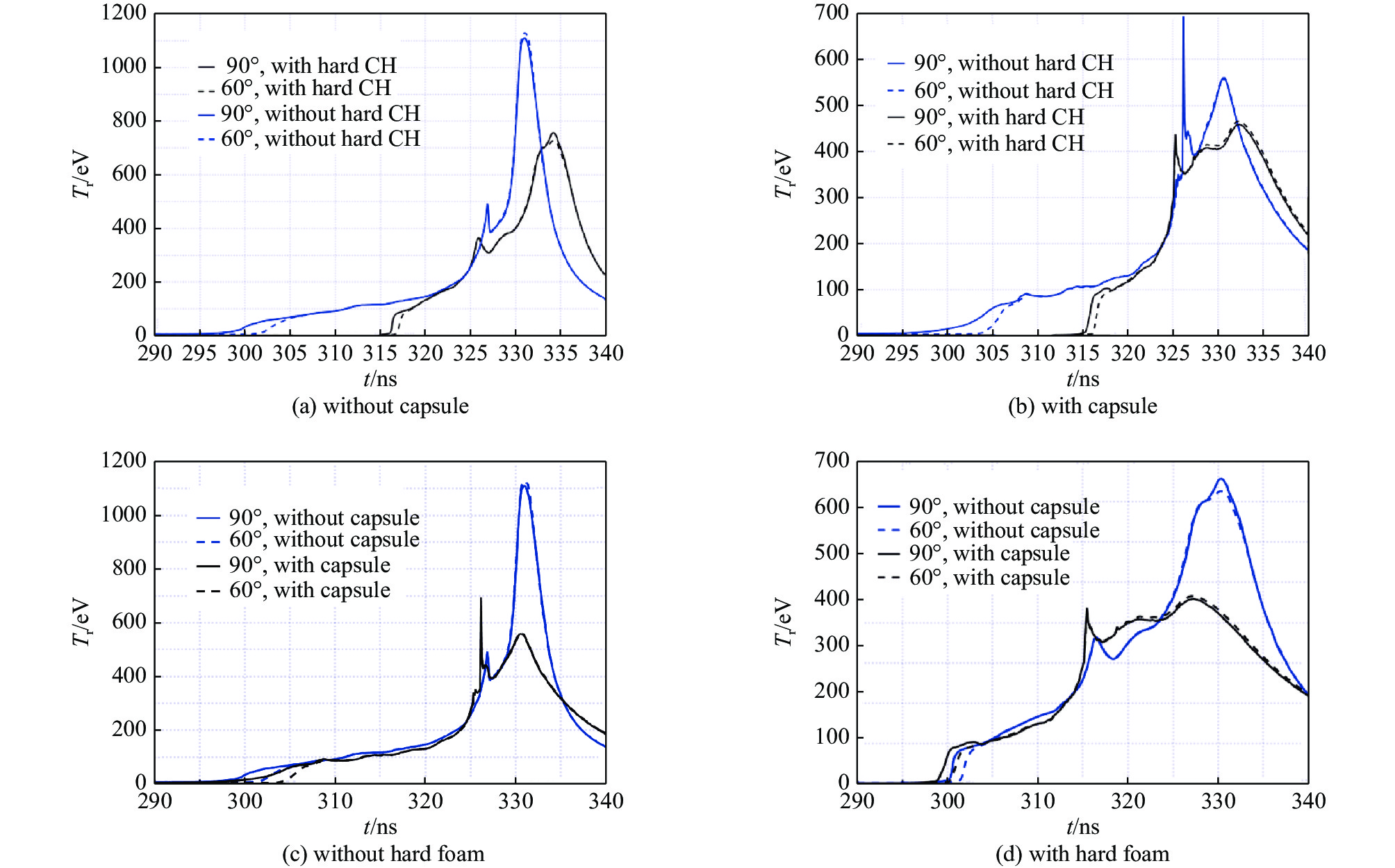
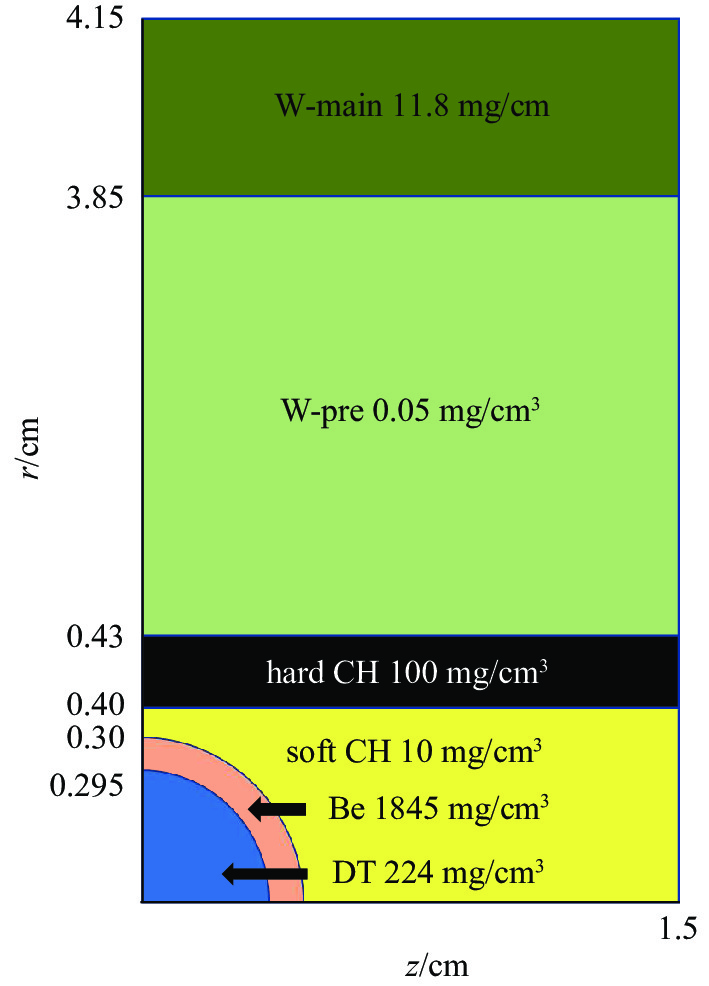
摘要: 利用自行开发的二维辐射磁流体力学程序,模拟研究在软泡沫柱外嵌套硬泡沫层、中心嵌套结构靶丸的动态黑腔整体动力学行为和热力学性能,以发现硬泡沫层对动态黑腔辐射场的影响和调制作用,以及腔靶耦合相互作用规律。对峰值50 MA、全上升时间300 ns的驱动电流,模拟结果的比较分析表明,嵌套硬泡沫层后靶丸感受到的辐射场温度开始升高时刻延后,辐射均匀更迅速,辐射温度第一峰下降,变化更顺滑,黑腔存在时间变长,达到10 ns以上,后期辐射温度大于350 eV,波形与美国靶丸点火成功实验中的黑腔辐射温度变化曲线比较接近;与没有靶丸的动态黑腔的相同区域辐射温度相比较,嵌入靶丸后,靶丸在烧蚀后期感受到的辐射驱动温度增加。故嵌套硬泡沫层和腔靶耦合都有益于聚变靶丸的烧蚀内爆。Abstract: In this paper, by means of the developed two dimensional radiation magneto-hydrodynamic Lagrangian code, the dynamic hohlraums, which are consisted of tungsten plasma shell and low density foam cylinder with or without an embedded hard foam layer on the cylinder and a capsule in the center, are simulated. We understand the effects of the hard foam layer on the hohlraum radiation field, and the coupling of capsule and hohlraum for the capsule fusion, by comparing the simulated results of different configuration hohlraums. After applying a hard foam layer on the low density foam cylinder, the time, uniformity, and the first peak value of radiation field, receipted by the capsule, is delayed, increased, and reduced, respectively. Furthermore, the radiation temperature on the capsule surface is increasing smoothly, and the dwelling time of the hohlraum is prolonged. For a driven current of peak 50 MA and full rise time 300 ns, the dwelling time can be longer than 10 ns, and the radiation temperature at the late time can be higher than 350 eV. The time variation of the radiation temperature is close to that measured in American National Ignition Facility (NIF) hohlraum in which the capsule was imploded and the fusion energy of 1.37 MJ was released. After embedding a capsule into the center of low density foam cylinder, the radiation temperature receipted by the capsule during the late process increases. This implies that both the hard foam layer and the coupling of the capsule and the dynamic hohlraum are good for the capsule ablating implosion.
-
Key words:
- Z-pinch /
- dynamic hohlraum /
- radiation field modulation /
- inertial confinement fusion /
- capsule
-
图 2 无靶丸情况下动态黑腔内爆流线和径向X光辐射功率随时间的变化
Figure 2. Trajectories of imploding plasma of dynamic hohlraum and X-ray power without a capsule in the center. The red lines, black lines, blue lines, and the green lines depict the W plasma, the hard foam layer, the soft foam, and the variation of X-ray power, respectively
图 6 无靶丸情况下,距中心0.3 cm,与中心连线与z轴成45°,60°,90° 的三个软泡沫物质点的密度和辐射温度随动态黑腔内爆形成过程的变化
Figure 6. Time variations of mass density and radiation temperature of three mass points, which are located in a circle of radius 0.3 cm with angles of 45°,60°,90° from z-axis, in soft foam (CH) without a capsule in the center
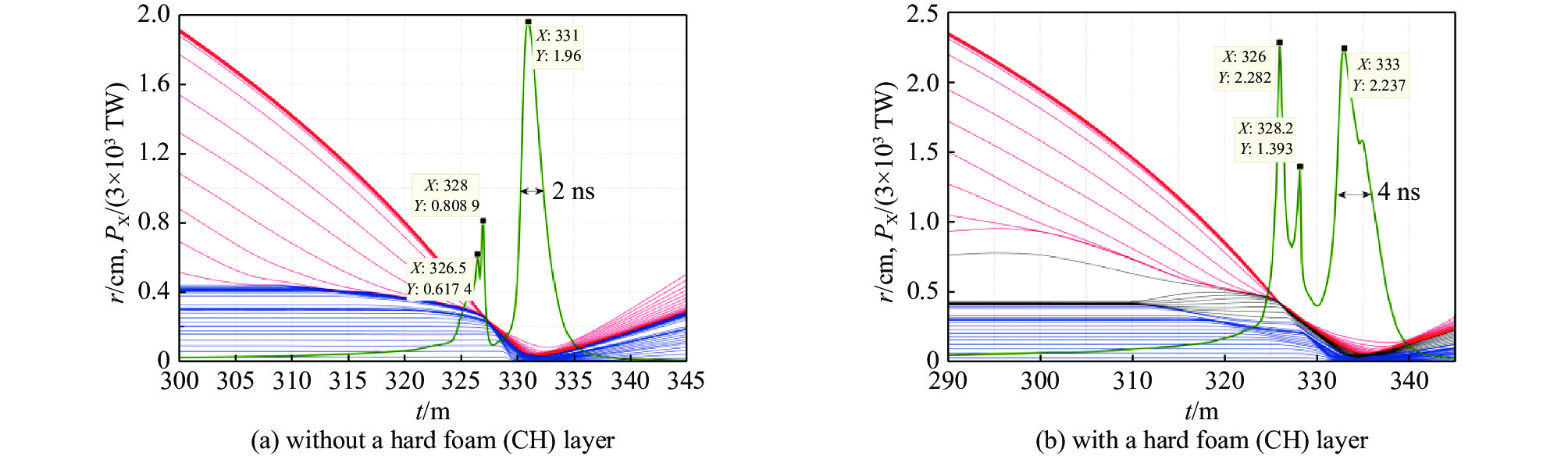
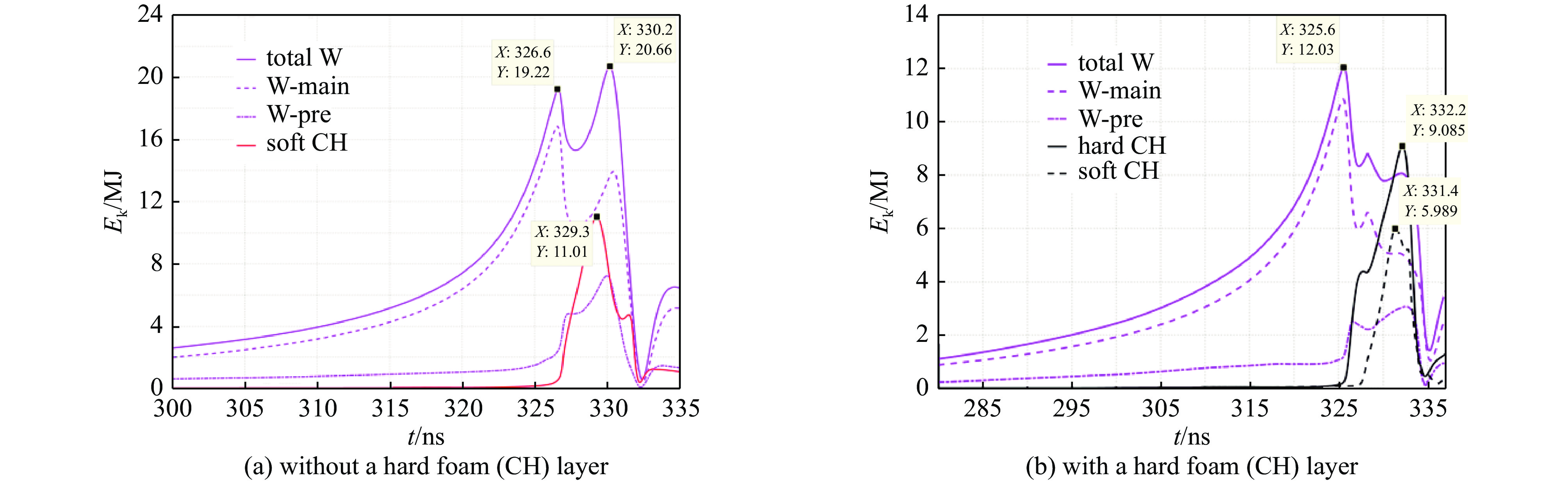
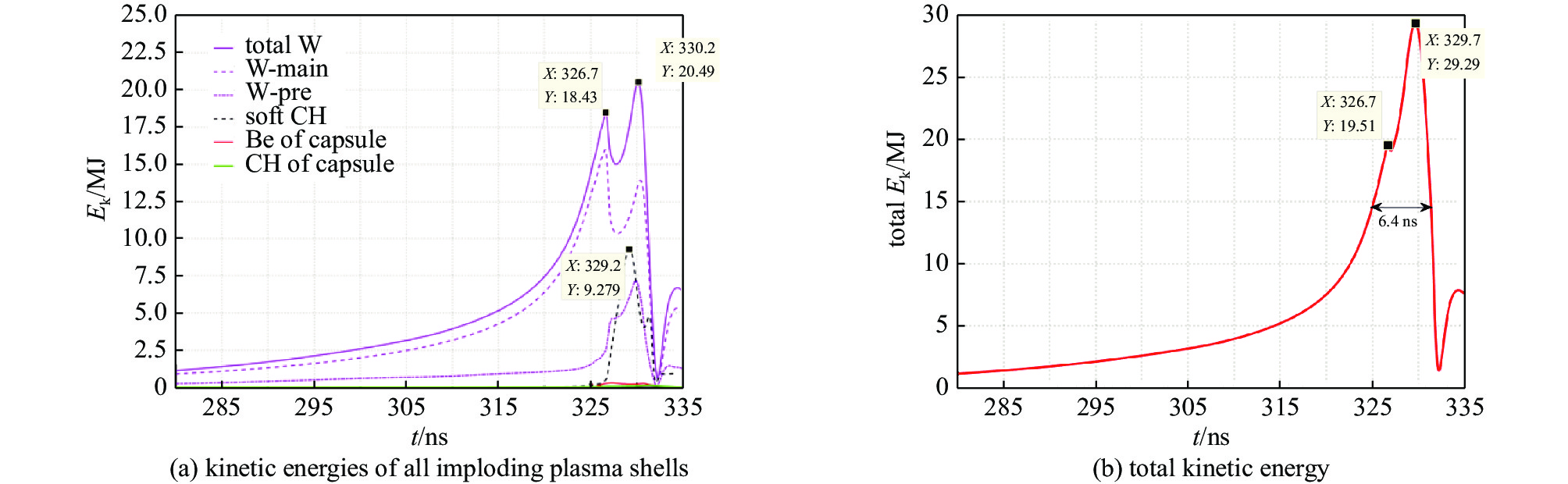
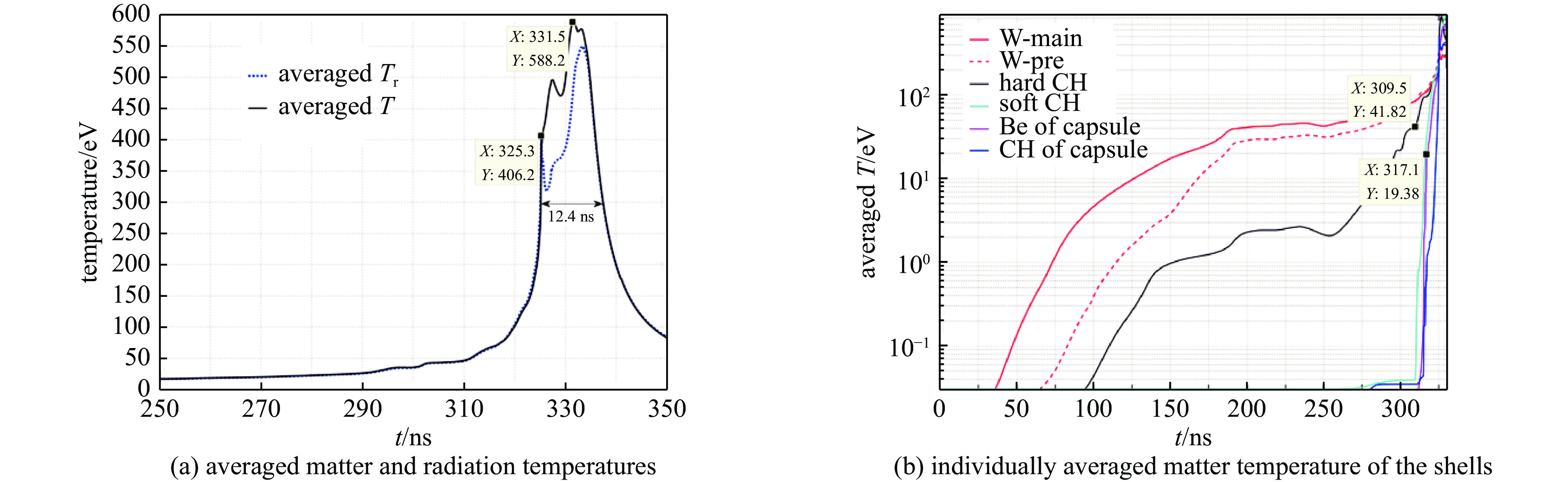
图 7 有靶丸、无硬泡沫层情况下,(a) 动态黑腔内爆流线和径向X光辐射功率随时间的变化,其中红色线为钨等离子体,青色线为软泡沫柱,品红色线为铍层,蓝色线为靶丸内层泡沫,以及绿色线为X光辐射功率; (b) 动态黑腔内爆过程中全域平均物质温度和平均辐射温度随时间的变化
Figure 7. Data of the dynamic hohlraum with a capsule but without a hard foam (CH) layer. (a) Imploding plasma trajectories and X-ray power. In figure (a), the red lines, cyan lines, fuchsine lines, blue lines, and the green lines depict the W plasma, the soft foam, the Be layer, the foam inside the capsule, and the variation of X-ray power, respectively. (b) Time variations of averaged matter and radiation temperatures over the whole simulation domain
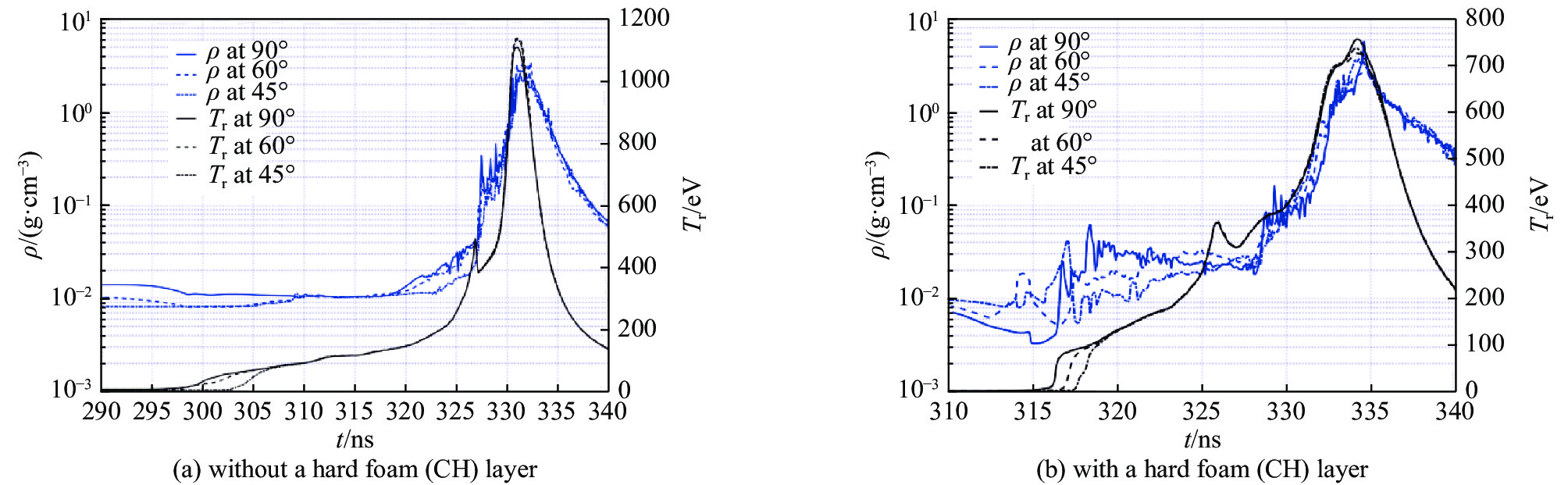
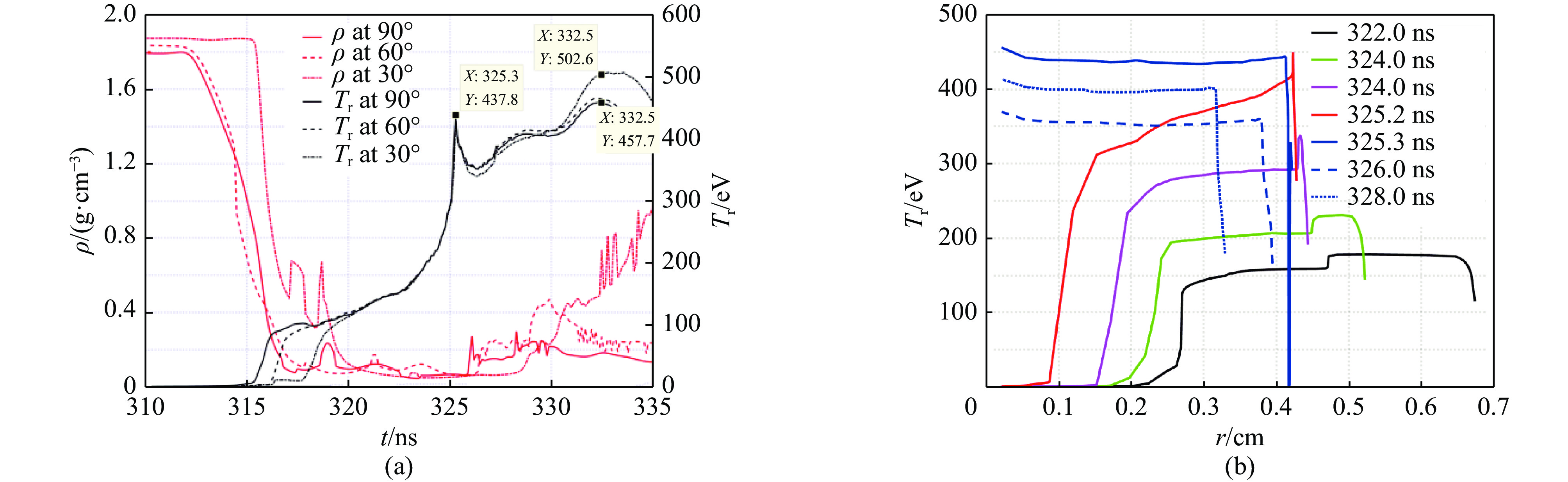
图 9 有靶丸、无硬泡沫层情况下,半径为0.3 cm的靶丸表面上,三个铍物质点(它们的半径方向与z轴分别成30°,60°和90°)的密度和辐射温度随动态黑腔内爆形成过程的变化
Figure 9. In the dynamic hohlraum with a capsule but without a hard foam (CH) layer, the time variations of Be mass density and radiation temperature of the three mass points, which are located in a circle of radius 0.3 cm with angles of 30°,60°,and 90° from z-axis
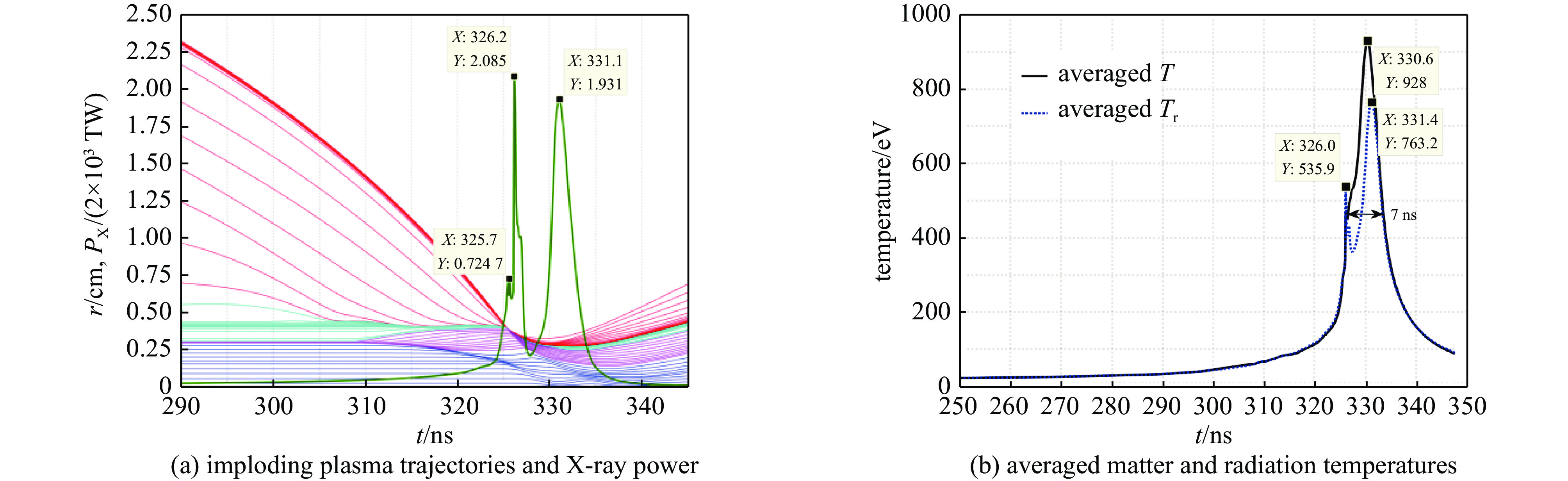
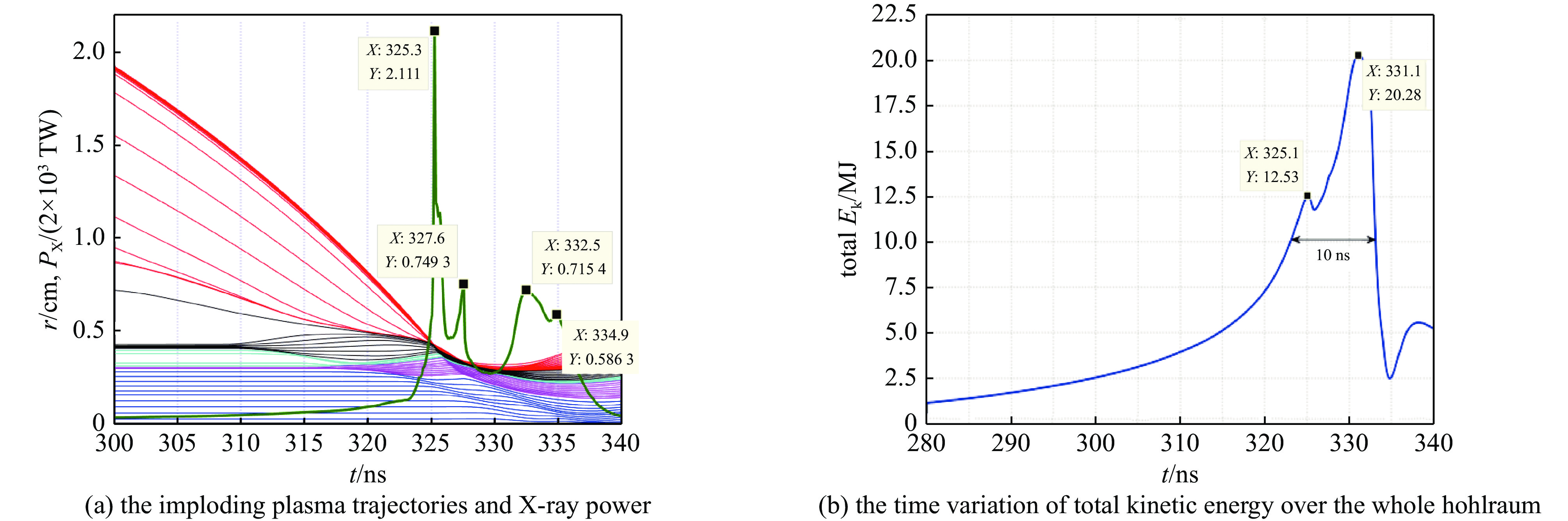
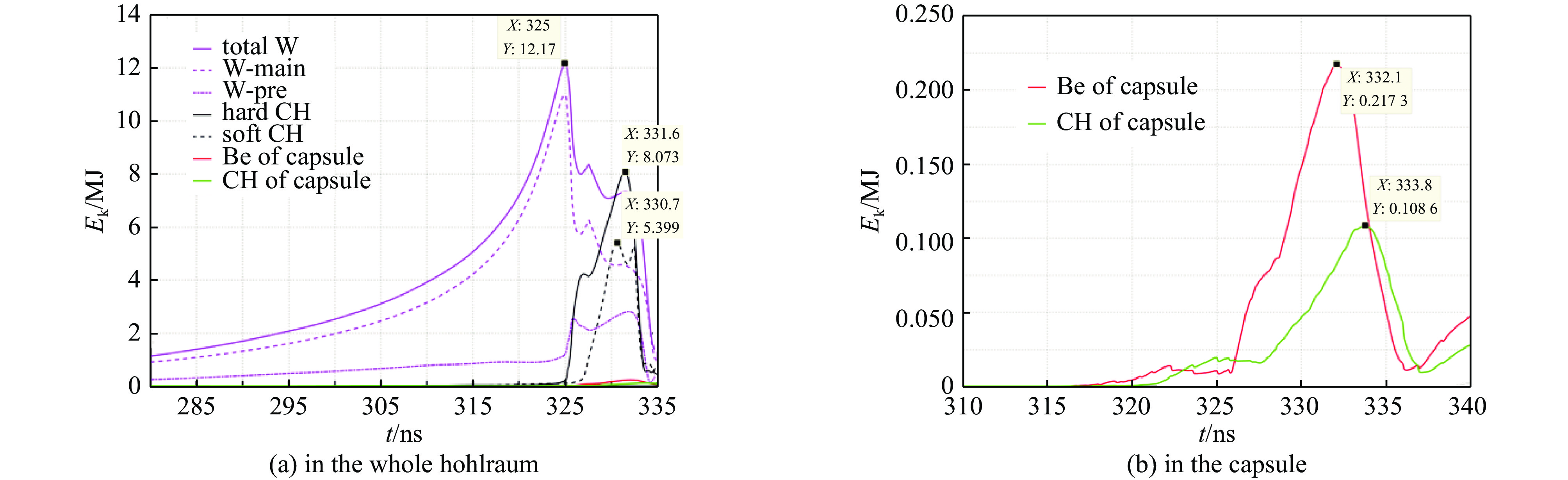
图 10 有靶丸和硬泡沫层情况下,动态黑腔内爆流线和径向X光辐射功率随时间的变化及动态黑腔内爆过程中总动能随时间的变化
Figure 10. Data of the dynamic hohlraum with a capsule and a hard foam (CH) layer. (a) The imploding plasma trajectories and X-ray power. In figure (a), the red lines, black lines, cyan lines, fuchsine lines, blue lines, and the green line depict the W plasma, the hard foam layer, the soft foam, the Be layer, the foam inside the capsule, and the variation of x-ray power, respectively. (b) The time variation of total kinetic energy over the whole hohlraum
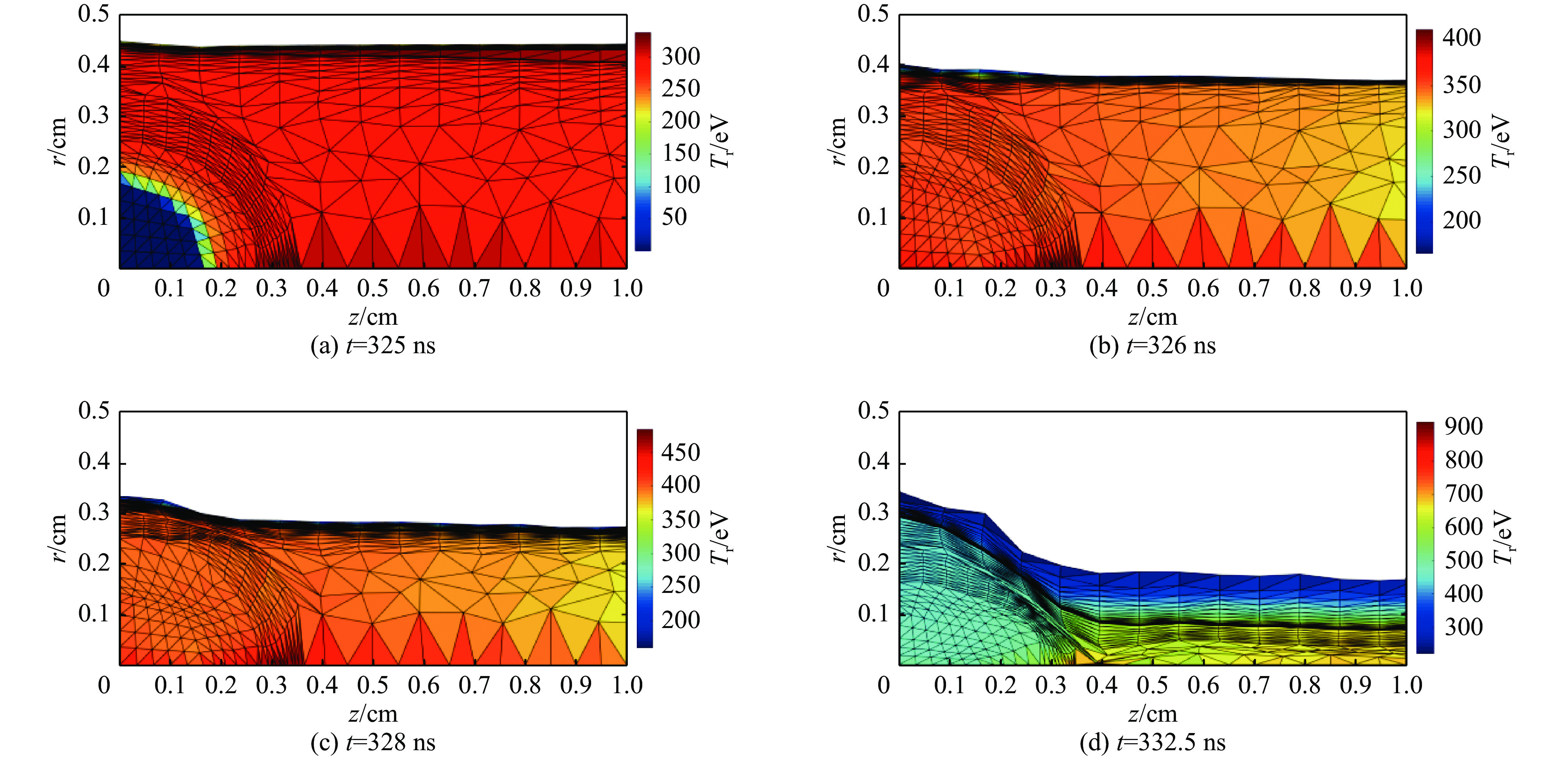
图 13 有靶丸和硬泡沫层情况下,(a)半径为0.3 cm的靶丸表面上,三个铍物质点的密度和辐射温度随动态黑腔内爆形成过程的变化;(b)辐射温度沿赤道(90°方向)径向的分布和演化
Figure 13. In the dynamic hohlraum with a capsule and a hard foam (CH) layer, (a) the time variations of Be mass density and radiation temperature of three mass points, which are located in a circle of radius 0.3 cm; (b) radial profile of the radiation temperature along the equator at different time
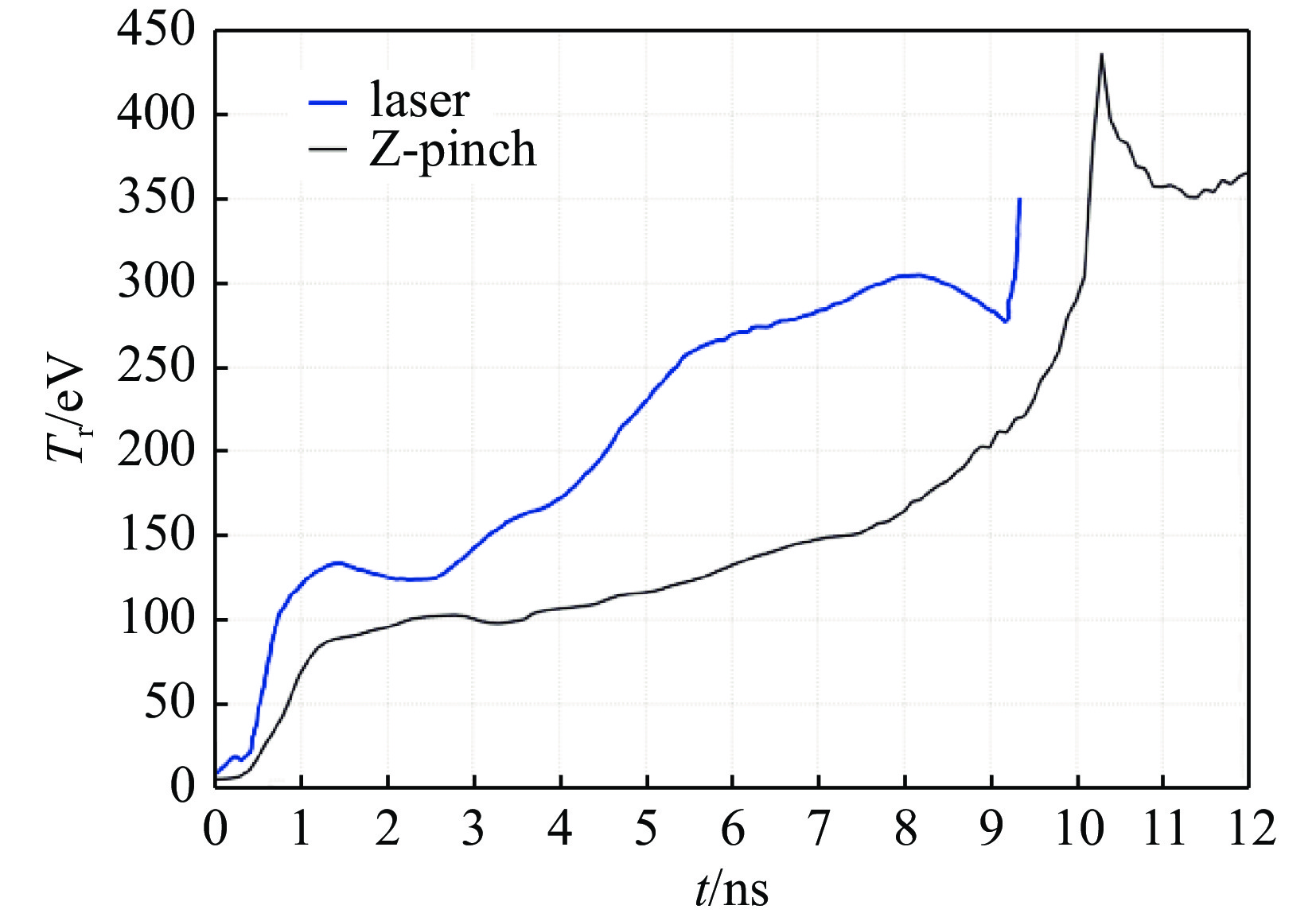
图 14 NIF上的黑腔辐射温度(文献[2]中图1)波形与Z箍缩动态黑腔中靶丸感受到的辐射温度(90°方向)变化的比较
Figure 14. Comparison between the huhlraum radiation temperature of NIF (data from Fig.1 in Ref. [2]) and the radiation temperature, which is received by the capsule in the Z-pinch dynamic hohlraum with an embedded hard foam layer, at 90° from z-axis
-
[1] Tollefson J, Gibney E. Nuclear-fusion lab achieves ‘ignition’: what does it mean?[J]. Nature, 2022, 612(7941): 597-598. doi: 10.1038/d41586-022-04440-7 [2] Abu-Shawareb H, Acree R, Adams P, et al. Lawson criterion for ignition exceeded in an inertial fusion experiment[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2022, 129: 075001. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.129.075001 [3] Kritcher A L, Zylstra A B, Callahan D A, et al. Design of an inertial fusion experiment exceeding the Lawson criterion for ignition[J]. Physical Review E, 2022, 106: 025201. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.106.025201 [4] Zylstra A B, Kritcher A L, Hurricane O A, et al. Experimental achievement and signatures of ignition at the National Ignition Facility[J]. Physical Review E, 2022, 106: 025202. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.106.025202 [5] Lindl J. Development of the indirect-drive approach to inertial confinement fusion and the target physics basis for ignition and gain[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 1995, 2(11): 3933-4024. doi: 10.1063/1.871025 [6] Lan Ke, Liu Jie, Lai Dongxian, et al. High flux symmetry of the spherical hohlraum with octahedral 6LEHs at the hohlraum-to-capsule radius ratio of 5.14[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2014, 21: 010704. doi: 10.1063/1.4863435 [7] Lan Ke. Dream fusion in octahedral spherical hohlraum[J]. Matter and Radiation at Extremes, 2022, 7: 055701. doi: 10.1063/5.0103362 [8] Huo Wenyi, Li Zhichao, Chen Yaohua, et al. First octahedral spherical hohlraum energetics experiment at the SGIII laser facility[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2018, 120: 165001. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.120.165001 [9] Li Xin, Dong Yunsong, Kang Dongguo, et al. First indirect drive experiment using a six-cylinder-port hohlraum[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2022, 128: 195001. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.128.195001 [10] Leeper R J, Alberts T E, Asay J R, et al. Z pinch driven inertial confinement fusion target physics research at Sandia National Laboratories[J]. Nuclear Fusion, 1999, 39(9Y): 1283-1294. doi: 10.1088/0029-5515/39/9Y/306 [11] Nash T J, Derzon M S, Chandler G A, et al. High-temperature dynamic hohlraums on the pulsed power driver Z[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 1999, 6(5): 2023-2029. doi: 10.1063/1.873457 [12] Bailey J E, Chandler G A, Slutz S A, et al. X-ray imaging measurements of capsule implosions driven by a Z-pinch dynamic hohlraum[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2002, 89: 095004. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.89.095004 [13] Rochau G A, Bailey J E, Maron Y, et al. Radiating shock measurements in the Z-pinch dynamic hohlraum[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2008, 100: 125004. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.100.125004 [14] Bailey J E, Chandler G A, Mancini R C, et al. Dynamic hohlraum radiation hydrodynamics[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2006, 13: 056301. doi: 10.1063/1.2177640 [15] Rochau G A, Bailey J E, Chandler G A, et al. High performance capsule implosions driven by the Z-pinch dynamic hohlraum[J]. Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 2007, 49(12B): B591-B600. doi: 10.1088/0741-3335/49/12B/S55 [16] Ruiz C L, Cooper G W, Slutz S A, et al. Production of thermonuclear neutrons from deuterium-filled capsule implosions driven by Z-pinch dynamic hohlraums[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2004, 93: 015001. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.93.015001 [17] Slutz S A, Peterson K J, Vesey R A, et al. Integrated two-dimensional simulations of dynamic hohlraum driven inertial fusion capsule implosions[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2006, 13: 102701. doi: 10.1063/1.2354587 [18] 蒋树庆, 甯家敏, 陈法新, 等. Z箍缩动态黑腔动力学及辐射特性初步实验研究[J]. 物理学报, 2013, 62:155203 doi: 10.7498/aps.62.155203Jiang Shuqing, Ning Jiamin, Chen Faxin, et al. Preliminary experimental study on implosion dynamics and radiation character of Z-pinch dynamic hohlraum[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2013, 62: 155203 doi: 10.7498/aps.62.155203 [19] Huang Xianbin, Ren Xiaodong, Dan Jiakun, et al. Radiation characteristics and implosion dynamics of Z-pinch dynamic hohlraums performed on PTS facility[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2017, 24: 092704. doi: 10.1063/1.4998619 [20] Chu Y Y, Wang Z, Qi J M, et al. Numerical performance assessment of double-shell targets for Z-pinch dynamic hohlraum[J]. Matter and Radiation at Extremes, 2022, 7: 035902. doi: 10.1063/5.0079074 [21] 吴福源, 禇衍运, 叶繁, 等. Z箍缩动态黑腔形成过程MULTI程序一维数值模拟[J]. 物理学报, 2017, 66:215201 doi: 10.7498/aps.66.215201Wu Fuyuan, Chu Yanyun, Ye Fan, et al. One-dimensional numerical investigation on the formation of Z-pinch dynamic hohlraum using the code MULTI[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2017, 66: 215201 doi: 10.7498/aps.66.215201 [22] Mao Chongyang, Wen Wu, Xiao Delong, et al. Analytical physical models for cryogenic double-shell capsule design driven by Z-pinch dynamic Hohlraum[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2021, 28: 092706. doi: 10.1063/5.0057626 [23] Chen Shijia, Ma Yanyun, Wu Fuyuan, et al. Simulations on the multi-shell target ignition driven by radiation pulse in Z-pinch dynamic hohlraum[J]. Chinese Physics B, 2021, 30: 115201. doi: 10.1088/1674-1056/ac01c2 [24] Ramis R, Meyer-ter-Vehn J, Ramírez J. MULTI2D–a computer code for two-dimensional radiation hydrodynamics[J]. Computer Physics Communications, 2009, 180(6): 977-994. doi: 10.1016/j.cpc.2008.12.033 [25] Ning Cheng, Chen Zhongwang. 2-D numerical investigation of the formation of Z-pinch-driven dynamic hohlraum at 8-MA current level[J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2018, 46(11): 3794-3804. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2018.2871217 [26] 陈忠旺, 宁成. 基于MULTI2D-Z程序的Z箍缩动态黑腔形成过程模拟[J]. 物理学报, 2017, 66:125202 doi: 10.7498/aps.66.125202Chen Zhongwang, Ning Cheng. Simulation of forming process of Z-pinch dynamic hohlraum based on the program MULTI2D-Z[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2017, 66: 125202 doi: 10.7498/aps.66.125202 [27] 宁成, 丰志兴, 薛创. Z箍缩驱动动态黑腔中的基本能量转移特征[J]. 物理学报, 2014, 63:125208 doi: 10.7498/aps.63.125208Ning Cheng, Feng Zhixing, Xue Chuang. Basic characteristics of kinetic energy transfer in the dynamic hohlraums of Z-pinch[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2014, 63: 125208 doi: 10.7498/aps.63.125208 -




 下载:
下载: