Beam combining/splitting technology of sodium beacon laser for generating sodium guidestars constellation
-
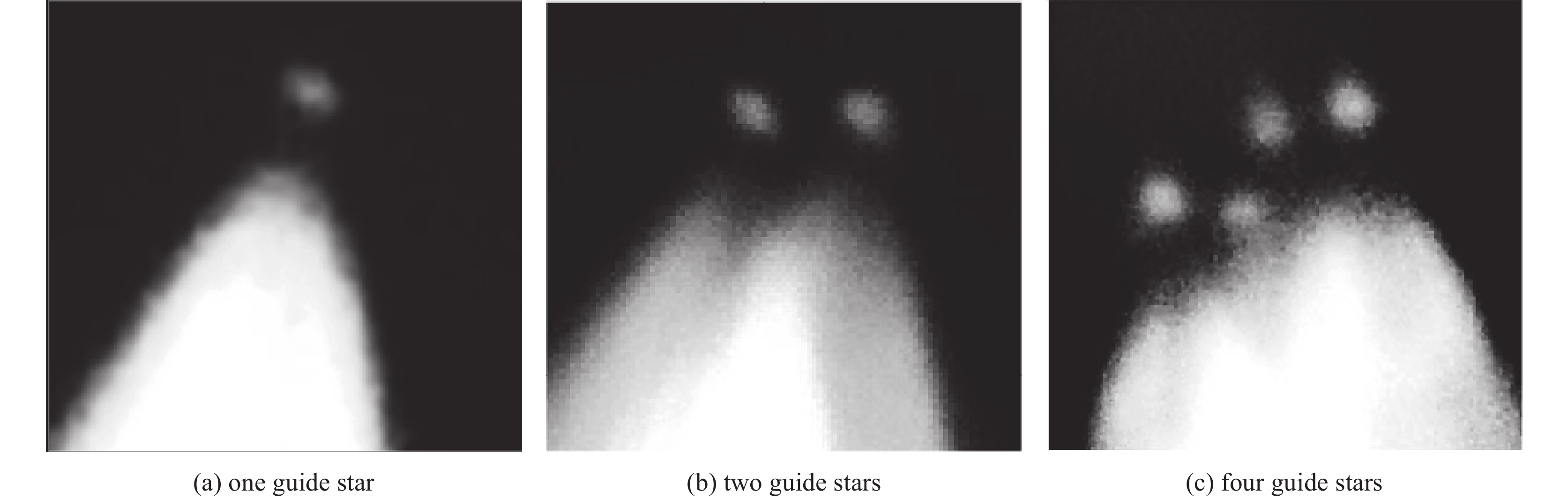
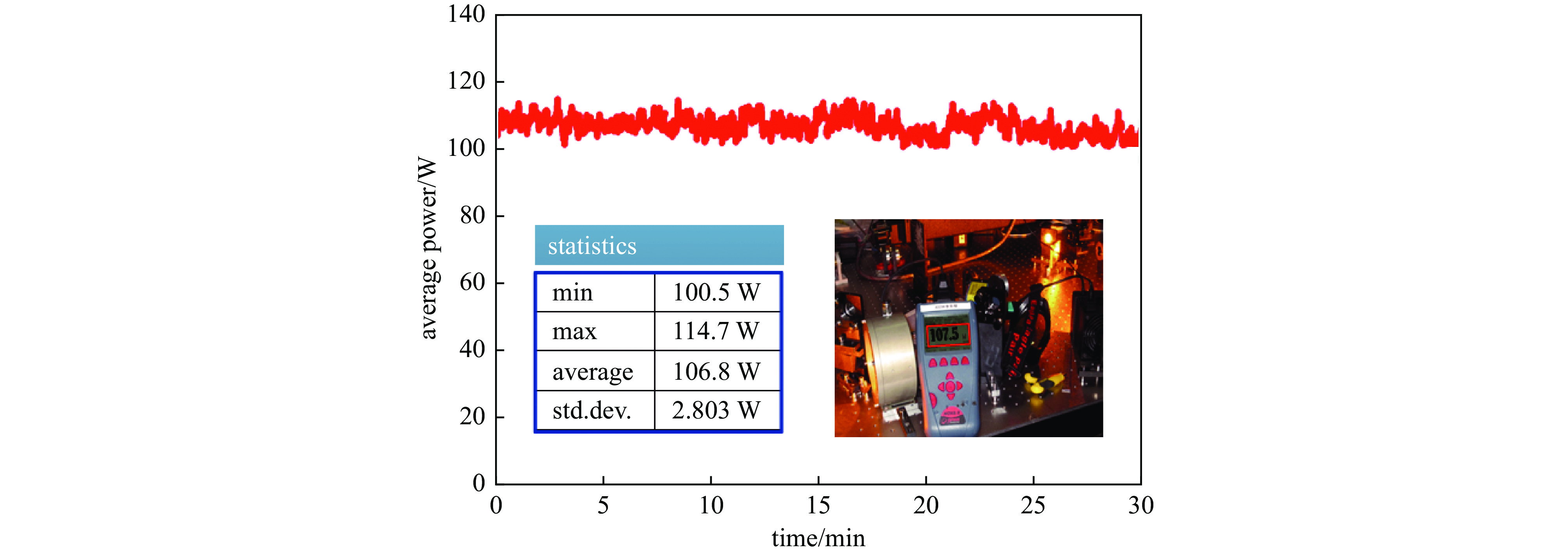
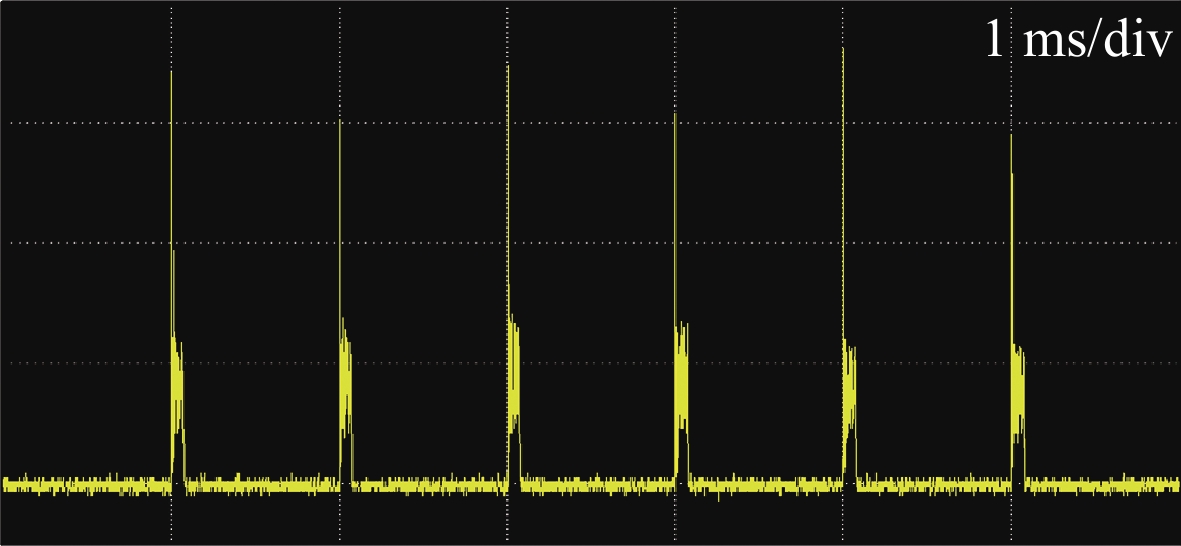
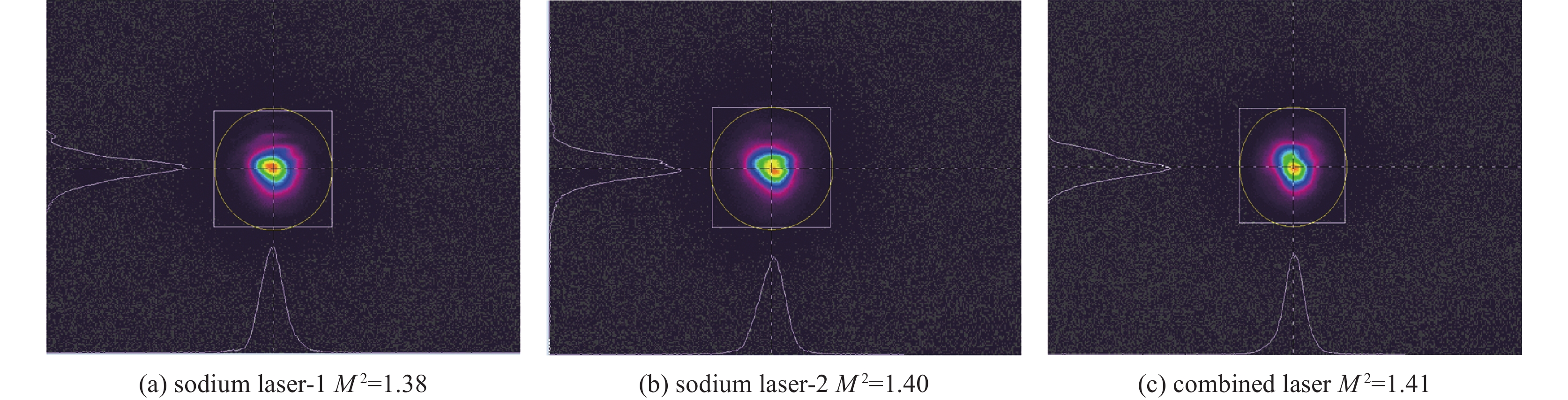
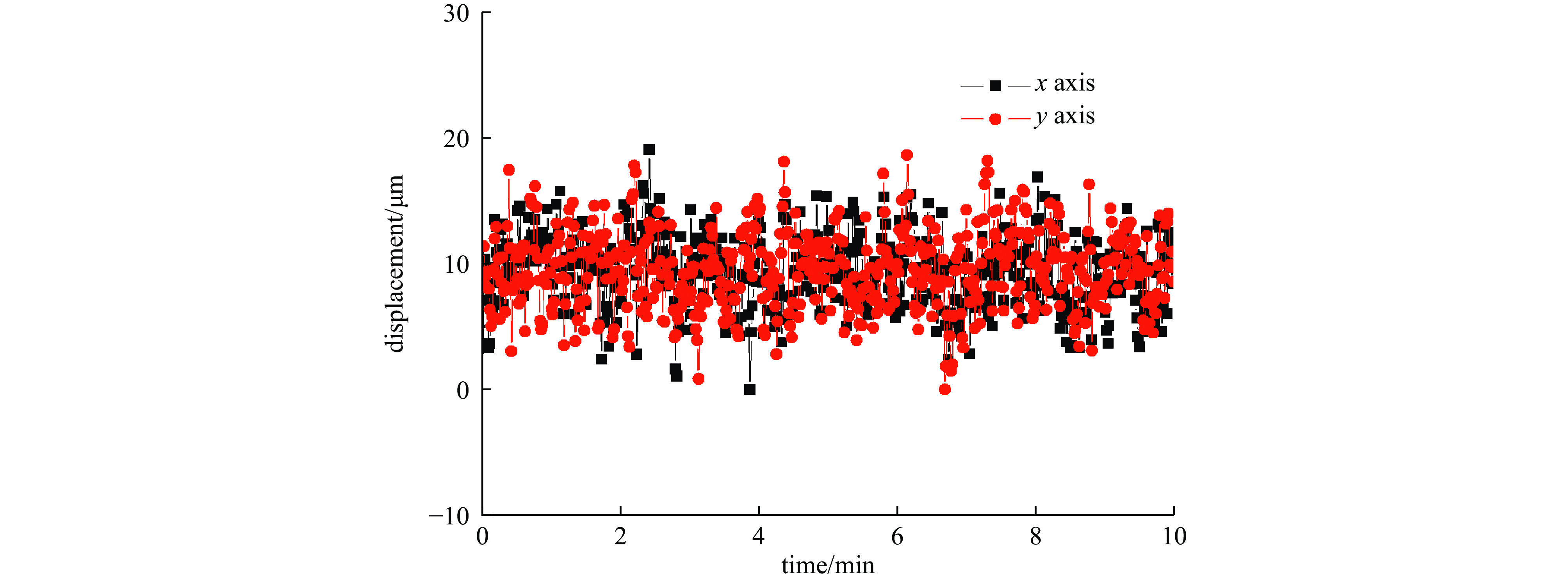
摘要: 研究了脉冲光束的偏振和时序非相干合成技术,通过偏振合束器将两路50 W级500 Hz的589 nm钠信标激光在空间上合为一束光线,成功突破了100 W级μs脉冲全固态钠信标激光输出;利用脉冲激光同步延时器控制两路激光脉冲的时序,使其按先后顺序合成一束脉冲激光,重复频率提升到1 kHz。合束后的激光光束质量M2约为1.41,与单光束的光束质量基本保持一致,光斑抖动性约为40 μrad,可满足激光钠导引星自适应光学系统的应用需求。与传统的相干合成方法相比,该偏振和时序非相干合成方案具有结构简单、稳定、效率高的优点,且整个系统无需复杂的相位控制机制,为脉冲激光功率扩展提供了新途径。基于上述技术基础,结合自主提出的精密偏振分光专利技术,在丽江天文台通过一台发射望远镜将四束25 W/束的µs脉冲黄激光发射到钠层,成功产生了四颗钠导引星,这一结果将有助于推动大型地基光学望远镜中多层共轭自适应光学技术的发展。Abstract: A polarization and sequence incoherent combining technology of pulsed laser beam is introduced. A 100 W level microsecond-pulse all-solid-state sodium beacon laser is performed, via combining two independent 50 W level 589 nm lasers at 500 Hz to be one beam by a polarized coupler. Through a pulsed laser synchronizing and delay controller, the two pulsed laser beams are added successfully at time sequence, and the corresponding repetition rate is up to 1 kHz. The beam quality factor M2 of the combined laser is about 1.41, maintaining at almost equal level with one of two laser beams, and the beam pointing stability is measured to be about 40 μrad, which can well meet the requirements at the time of laser guide star testing. Compared with the coherent beam combining, the approach of polarization and sequence incoherent combining has high efficiency, simple combination, and no specific restriction on phase and frequency spectrum, providing a new way for pulsed laser power scaling. Based on a self-proposed precise polarized splitting technology, four beams of (25 W/beam) μs-pulsed yellow laser are projected up to the sodium layer through one launching telescope at Lijiang Observatory, and successfully generate four sodium guidestars, which could promote the development of multi-conjugate adaptive optics systems on large-aperture ground-based telescopes.
-
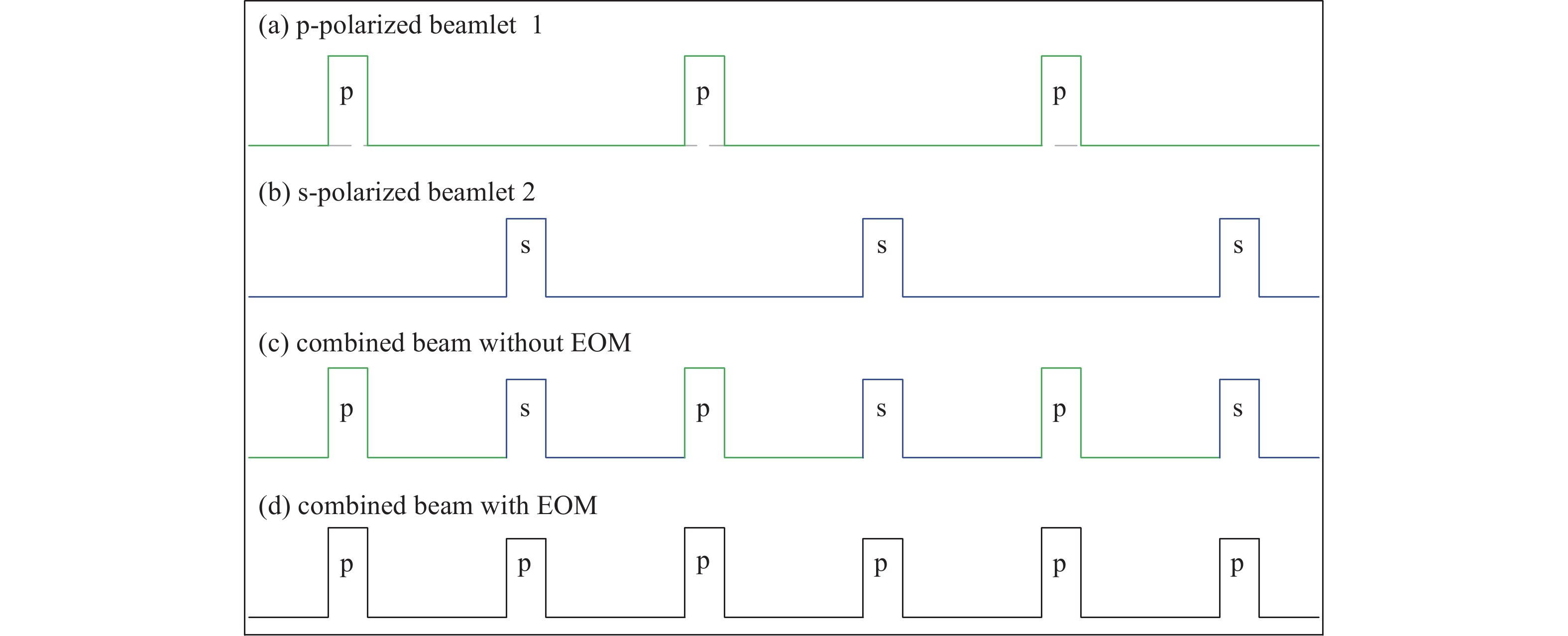
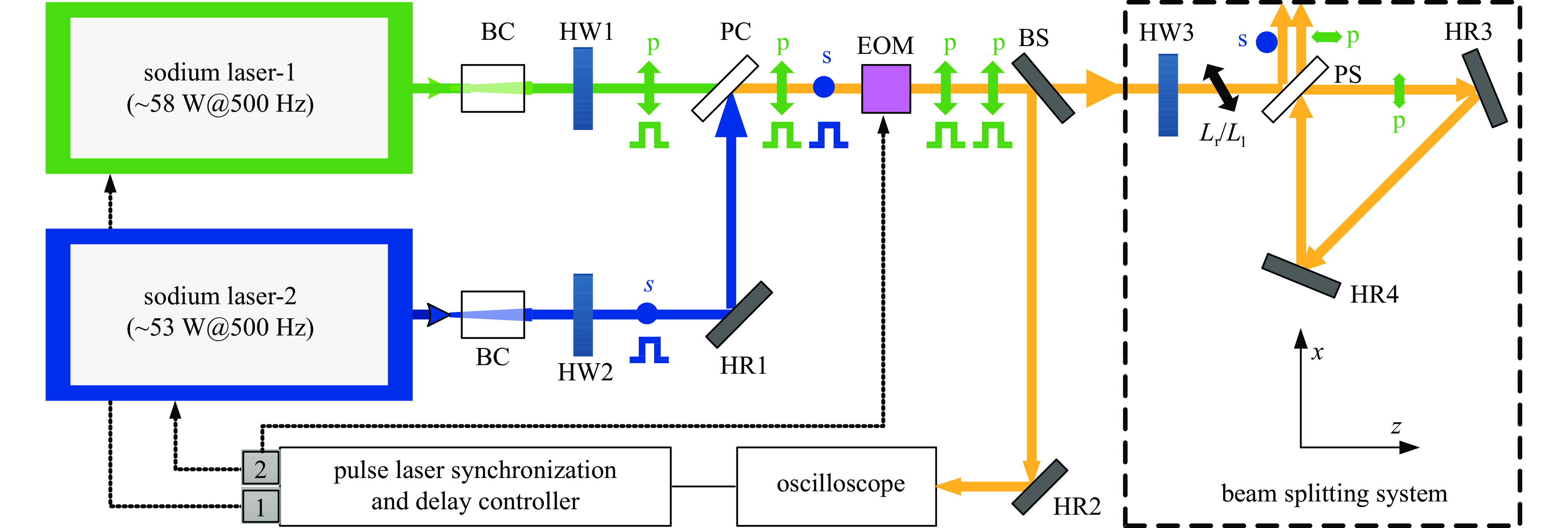
图 1 两路脉冲钠信标激光非相干合成与偏振分束技术方案示意图
Figure 1. Schematic of incoherent beam combining and polarization splitting for two pulsed sodium lasers. BC, beam collimator; HW, half-wave plate; HR: high reflective mirror; PC: polarization coupler; EOM: electro-optical modulator; BS: beam splitter; PS: polarization splitter
-
[1] Max C E, Olivier S S, Friedman H W, et al. Image improvement from a sodium-layer laser guide star adaptive optics system[J]. Science, 1997, 277(5332): 1649-1652. doi: 10.1126/science.277.5332.1649 [2] Neichel B, Lu J R, Rigaut F, et al. Astrometric performance of the Gemini multiconjugate adaptive optics system in crowded fields[J]. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 2014, 445(1): 500-514. doi: 10.1093/mnras/stu1766 [3] Denman C A, Hillman P D, Moore G T, et al. Realization of a 50-watt facility-class sodium guidestar pump laser[C]//Proceedings of SPIE 5707, Solid State Lasers XIV: Technology and Devices. 2005: 46-49. [4] Hankla A K, Bartholomew J, Groff K, et al. 20-W and 50-W solid-state sodium beacon guidestar laser systems for the Keck I and Gemini South Telescopes[C]//Proceedings of SPIE 6272, Advances in Adaptive Optics II. 2006: 62721G. [5] Taylor L R, Feng Y, Calia D B. 50W CW visible laser source at 589nm obtained via frequency doubling of three coherently combined narrow-band Raman fibre amplifiers[J]. Optics Express, 2010, 18(8): 8540-8555. doi: 10.1364/OE.18.008540 [6] Zhang Lei, Jiang Huawei, Cui Shuzhen, et al. Versatile Raman fiber laser for sodium laser guide star[J]. Laser & Photonics Reviews, 2014, 8(6): 889-895. [7] Bian Qi, Bo Yong, Zuo Junwei, et al. High-power QCW microsecond-pulse solid-state sodium beacon laser with spiking suppression and D2b re-pumping[J]. Optics Letters, 2016, 41(8): 1732-1735. doi: 10.1364/OL.41.001732 [8] Andrusyak O, Smirnov V, Venus G, et al. Spectral combining and coherent coupling of lasers by volume Bragg gratings[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics, 2009, 15(2): 344-353. doi: 10.1109/JSTQE.2009.2012438 [9] 马毅, 颜宏, 田飞, 等. 光纤激光共孔径光谱合成实现5 kW高效优质输出[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2015, 27:040101 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201527.040101Ma Yi, Yan Hong, Tian Fei, et al. Common aperture spectral beam combination of fiber lasers with 5 kW power high-efficiency and high-quality output[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2015, 27: 040101 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201527.040101 [10] Honea E, Afzal R S, Savage-Leuchs M, et al. Advances in fiber laser spectral beam combining for power scaling[C]//Proceedings of SPIE 9730, Components and Packaging for Laser Systems II. 2016: 97300Y. [11] Marmo J, Injeyan H, Komine H, et al. Joint high power solid state laser program advancements at Northrop Grumman[C]//Proceedings of SPIE 7195, Fiber Lasers VI: Technology, Systems, and Applications. 2009: 719507. [12] Yu C X, Augst S J, Redmond S M, et al. Coherent combining of a 4 kW, eight-element fiber amplifier array[J]. Optics Letters, 2011, 36(14): 2686-2688. doi: 10.1364/OL.36.002686 [13] 王小林, 周朴, 马阎星, 等. 基于主动相位控制的脉冲激光相干合成技术[J]. 国防科技大学学报, 2012, 34(1):33-37 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2486.2012.01.008Wang Xiaolin, Zhou Pu, Ma Yanxing, et al. Investigation of coherent beam combining pulsed fiber lasers with active phase control[J]. Journal of National University of Defense Technology, 2012, 34(1): 33-37 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2486.2012.01.008 [14] Uberna R, Bratcher A, Tiemann B G. Coherent polarization beam combination[J]. IEEE Journal of Quantum Electronics, 2010, 46(8): 1191-1196. doi: 10.1109/JQE.2010.2044976 [15] 颜宏, 叶一东, 卢飞, 等. 基于偏振鉴相的相干合成技术[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2013, 25(s1):5-8Yan Hong, Ye Yidong, Lu Fei, et al. Coherent beam combining based on polarization phase discrimination[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2013, 25(s1): 5-8 [16] 马鹏飞, 王小林, 粟荣涛, 等. 2kW级光纤激光相干偏振合成[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2016, 28:040102 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201628.120102Ma Pengfei, Wang Xiaolin, Su Rongtao, et al. Coherent polarization beam combining of fiber lasers to 2 kW power-level[J]. High Power Laser And Particle Beams, 2016, 28: 040102 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201628.120102 [17] Wirth C, Schmidt O, Tsybin I, et al. 2 kW incoherent beam combining of four narrow-linewidth photonic crystal fiber amplifiers[J]. Optics Express, 2009, 17(3): 1178-1183. doi: 10.1364/OE.17.001178 [18] Sprangle P, Ting A, Penano J, et al. Incoherent combining and atmospheric propagation of high-power fiber lasers for directed-energy applications[J]. IEEE Journal of Quantum Electronics, 2009, 45(2): 138-148. doi: 10.1109/JQE.2008.2002501 [19] Xu Jian, Gao Hongwei, Xu Yiting, et al. Sequence combining of pulsed lasers using refraction-beam-displacement[J]. Applied Optics, 2013, 52(2): 208-211. doi: 10.1364/AO.52.000208 [20] Fan Tingwei, Zhou Tianhua, Feng Yan. Improving sodium laser guide star brightness by polarization switching[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 19859. doi: 10.1038/srep19859 [21] Calia D B, Hackenberg W, Holzlöhner R, et al. The four-laser guide star facility: design considerations and system implementation[J]. Advanced Optical Technologies, 2014, 3(3): 345-361. [22] Bian Qi, Bo Yong, Zuo Junwei, et al. First implementation of pulsed sodium guidestars constellation for large-aperture multi-conjugate adaptive optics telescopes[J]. Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific, 2022, 134: 074502. doi: 10.1088/1538-3873/ac7c8e -




 下载:
下载: