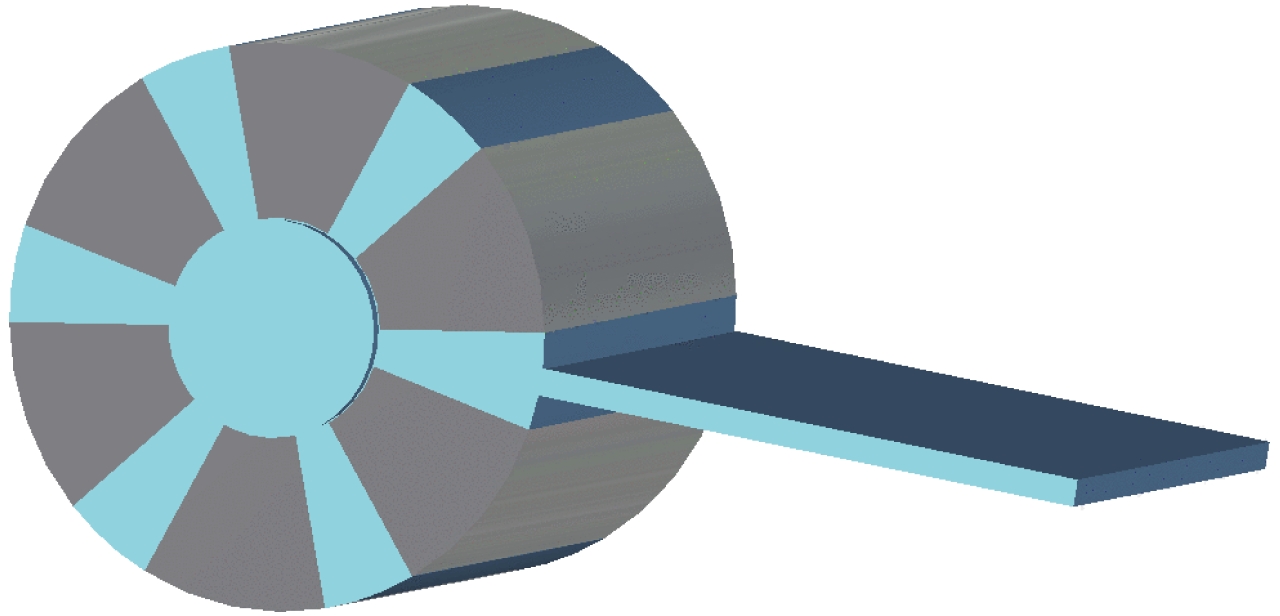
Research on the mode of relativistic magnetron
-
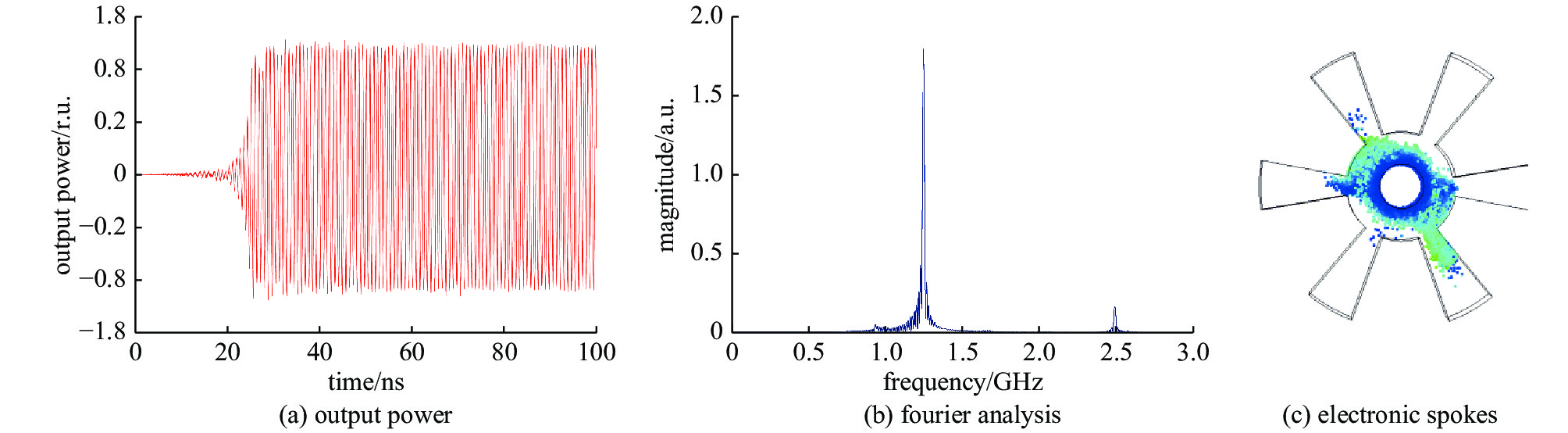
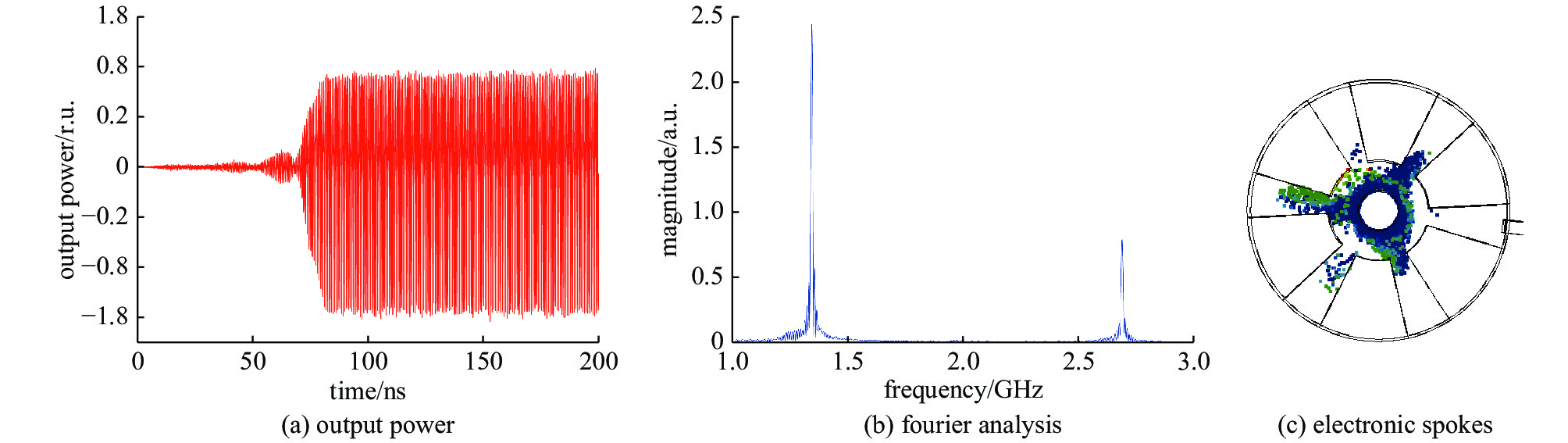
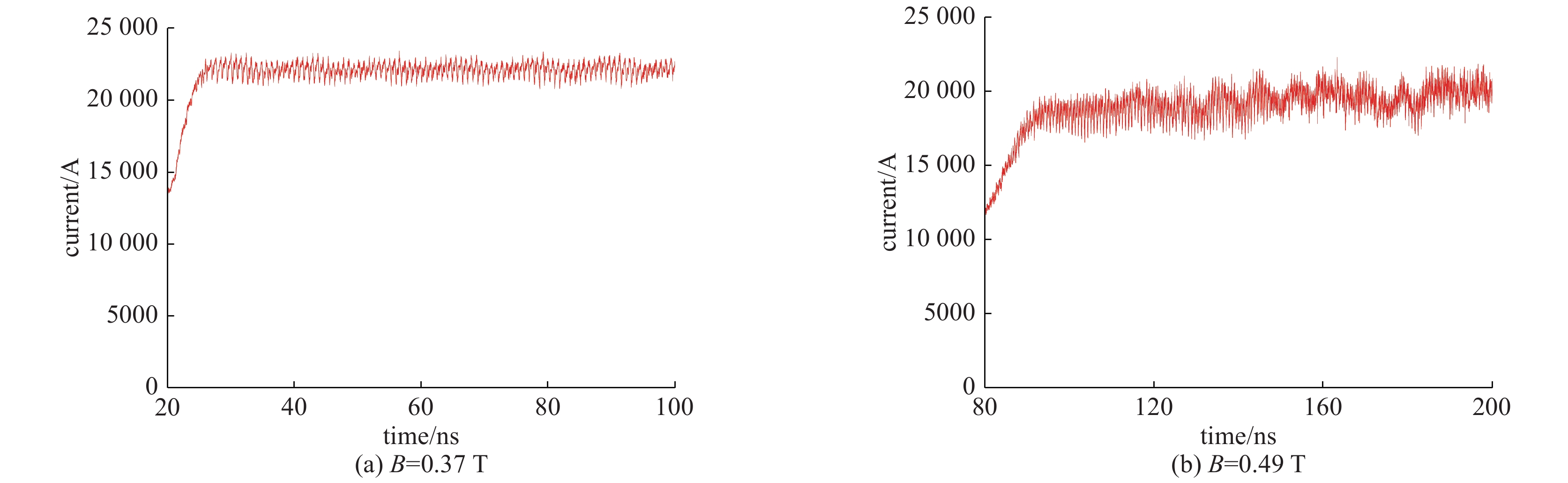
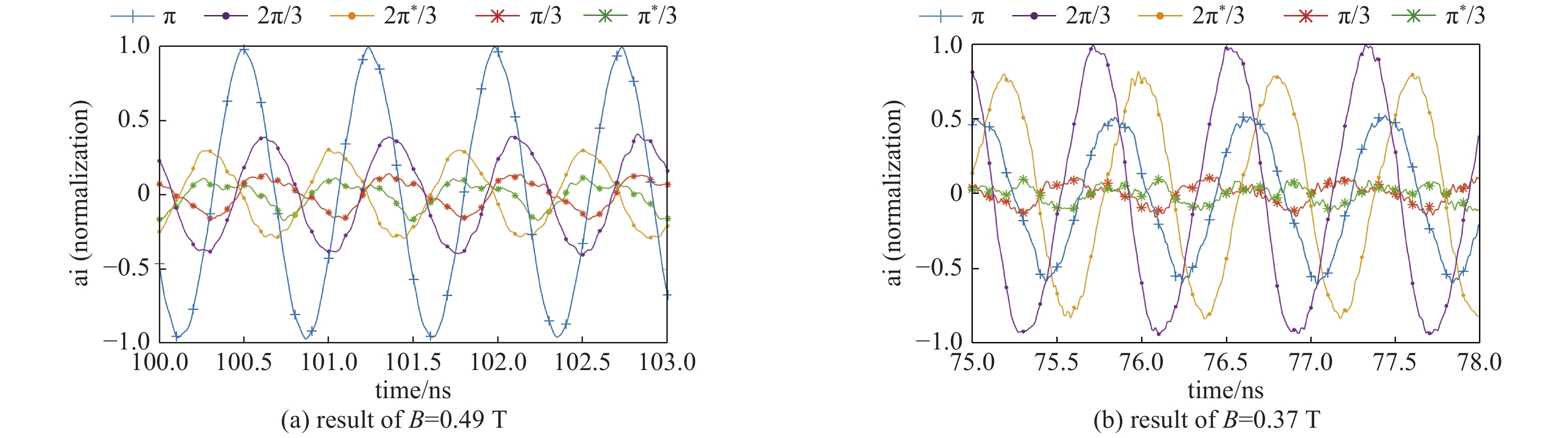
摘要: 随着磁控管的发展,磁控管中的模式关系变得愈发复杂,模式间的竞争也愈发激烈。为了更好地进行磁控管的模式研究,基于本征模的正交性,推导并提出了一种模式分解的方法,并以A6型相对论磁控管作为研究对象,对其不同振荡状态下的工作场进行了模式分解的应用。结果表明,相对论磁控管振荡时,将会出现多模共存的现象,且磁控管将会振荡在成分最高的本征模频率上。同时,结果中展现了简并模式同时存在,以同趋势振荡的现象,结合PIC模拟方法,确定了具有径向输出结构的相对论磁控管能够在简并模式振荡的情况下,能够实现稳定的输出。Abstract: As the mode competition of magnetrons becomes more intense, to better study the mode of magnetron, a mode decomposition method is proposed in this paper, and the A6 relativistic magnetron is selected as the research object. The results of mode decomposition show that when the relativistic magnetron oscillates, there will be a phenomenon of multi-mode coexistence, and the magnetron will oscillate at the frequency of the eigenmode with the strongest field strength. At the same time, the results show that the degenerate mode coexists and oscillates in the same trend. Combined with PIC simulations, it can be inferred that the relativistic magnetron with radial output structure can operate at the degenerate mode and obtain stable output signal.
-
Key words:
- mode decomposition /
- relativistic magnetron /
- degenerate mode /
- eigenmode /
- mode competition
-
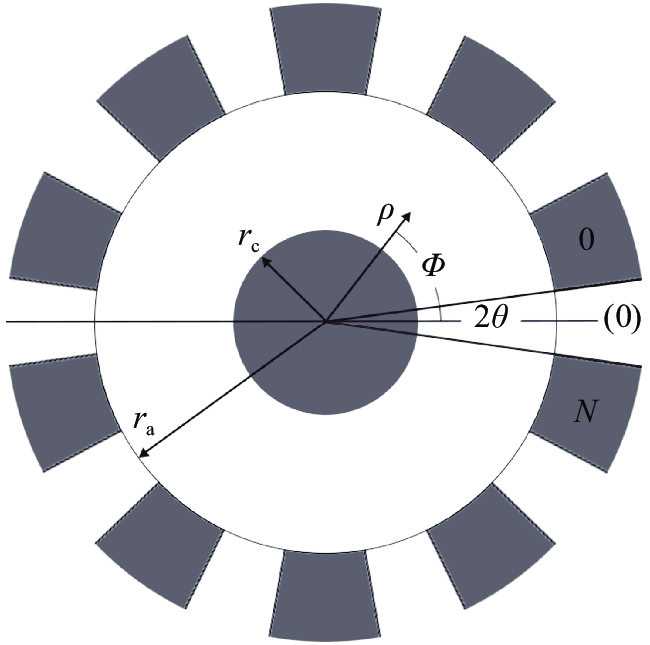
表 1 本征模式频率分布
Table 1. Eigenmode frequency distribution
mode frequency/GHz 0 0.70 π/3 1.23 π/3* 1.22 2π/3 1.33 2π/3* 1.34 π 1.36 -
[1] 钱民权, 杨茂荣, 潘清, 等. 激光驱动的光阴极研究[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 1997, 9(2):185-191. (Qian Minquan, Yang Maorong, Pan Qing, et al. Investigation of photocathode driven by a laser[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 1997, 9(2): 185-191 [2] 张兆镗. 磁控管的历史、现状与未来发展——兼论微波功率应用的前景[J]. 真空电子技术, 2016(2):38-41, 46. (Zhang Zhaotang. The history, present status and future development of magnetrons—foreground of microwave power applications[J]. Vacuum Electronics, 2016(2): 38-41, 46 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-8935.2016.02.010 [3] 张兆镗. 真空微波电子器件的发展态势与前途[J]. 真空电子技术, 2019(3):1-7, 37. (Zhang Zhaotang. Development trend and future of microwave vacuum electron devices[J]. Vacuum Electronics, 2019(3): 1-7, 37 [4] Fuks M I, Schamiloglu E. 70% efficient relativistic magnetron with axial extraction of radiation through a horn antenna[J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2010, 38(6): 1302-1312. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2010.2042823 [5] Fuks M I, Prasad S, Schamiloglu E. Efficient magnetron with a virtual cathode[J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2016, 44(8): 1298-1302. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2016.2525921 [6] Kim J I, Jeon S G, Kim G J, et al. Investigation of millimeter-wavelength 20-vane spatial-harmonic magnetron using three-dimensional particle-in-cell simulation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2012, 40(8): 1966-1971. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2012.2202693 [7] Schunemann K, Sosnytskiy S V, Vavriv D M. Self-consistent simulation of the spatial-harmonic magnetron with cold secondary-emission cathode[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 2001, 48(5): 993-998. doi: 10.1109/16.918248 [8] Vavriv D M, Sosnytskiy S V, Schunemann K. Mode-interaction effects in spatial-harmonic magnetrons[C]//Third IEEE International Vacuum Electronics Conference (IEEE Cat. No. 02EX524). 2002: 207-208. [9] Collins G B. Microwave magnetrons[M]. New York: McGraw-Hill, 1948. [10] Kroll N M, Lamb W E Jr. The resonant modes of the rising sun and other unstrapped magnetron anode blocks[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1948, 19(2): 166-186. doi: 10.1063/1.1698386 [11] Riyopoulos S. Magnetron theory[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 1996, 3(3): 1137-1161. doi: 10.1063/1.871770 [12] 李天明, 李家胤, 于秀云, 等. A6磁控管谐振系统的计算与模拟分析[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2002, 14(3):426-430. (Li Tianming, Li Jiayin, Yu Xiuyun, et al. Calculation and simulation analysis of A6 relativistic magnetron’s resonated system[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2002, 14(3): 426-430 [13] 李天明, 李家胤, 董斐斐, 等. 相对论磁控管中自磁场的影响[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2010, 22(11):2639-2642. (Li Tianming, Li Jiayin, Dong Feifei, et al. Self-magnetic field in relativistic magnetron[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2010, 22(11): 2639-2642 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20102211.2639 -




 下载:
下载: