Design and simulation of interferometer for synchrotron radiation beam size measurement
-
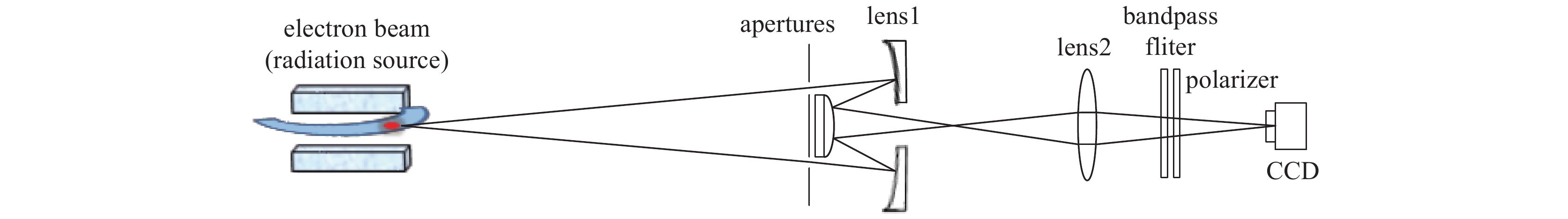
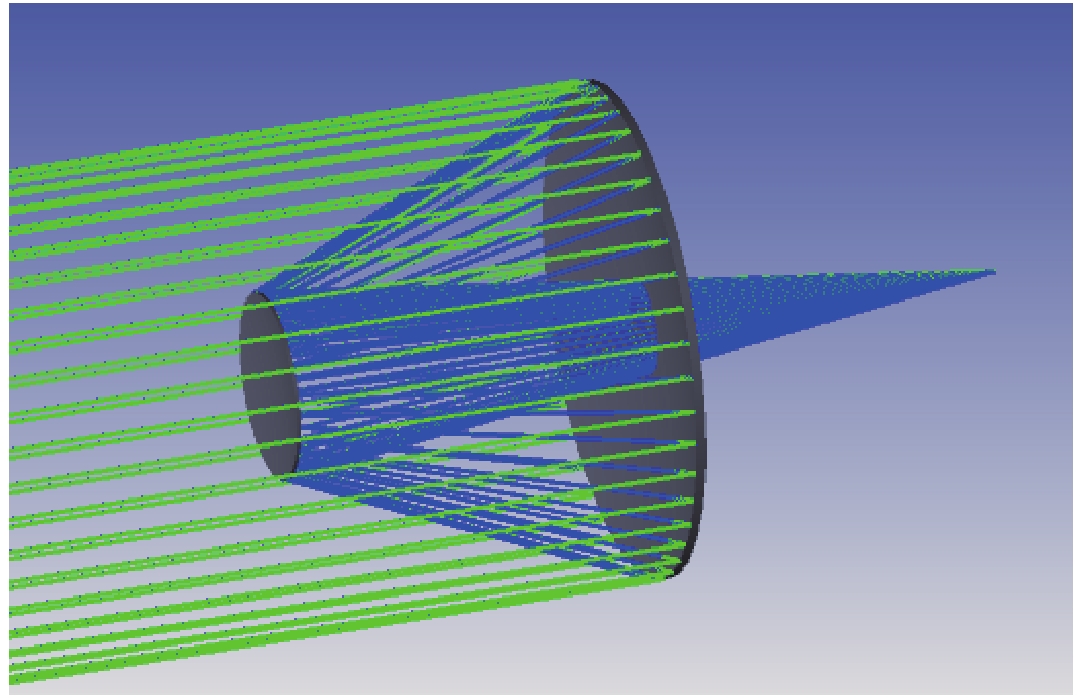
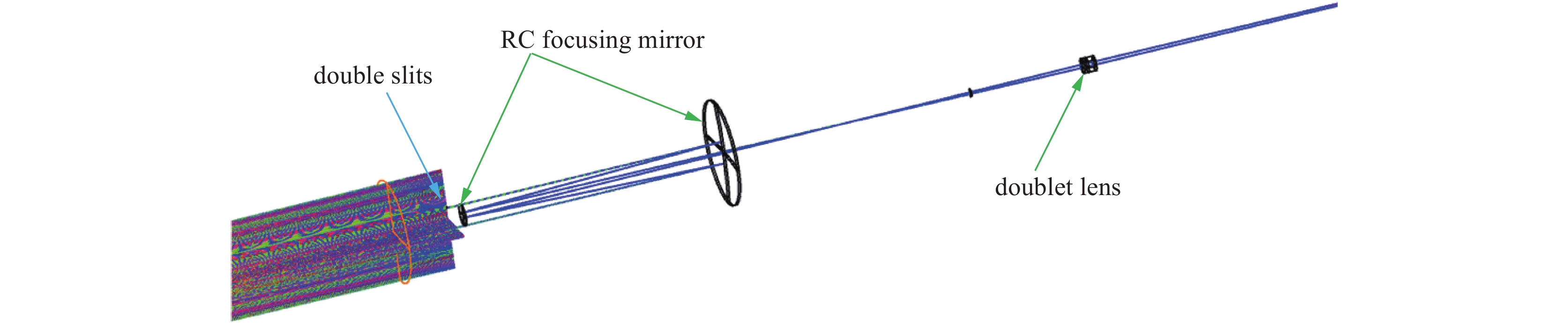
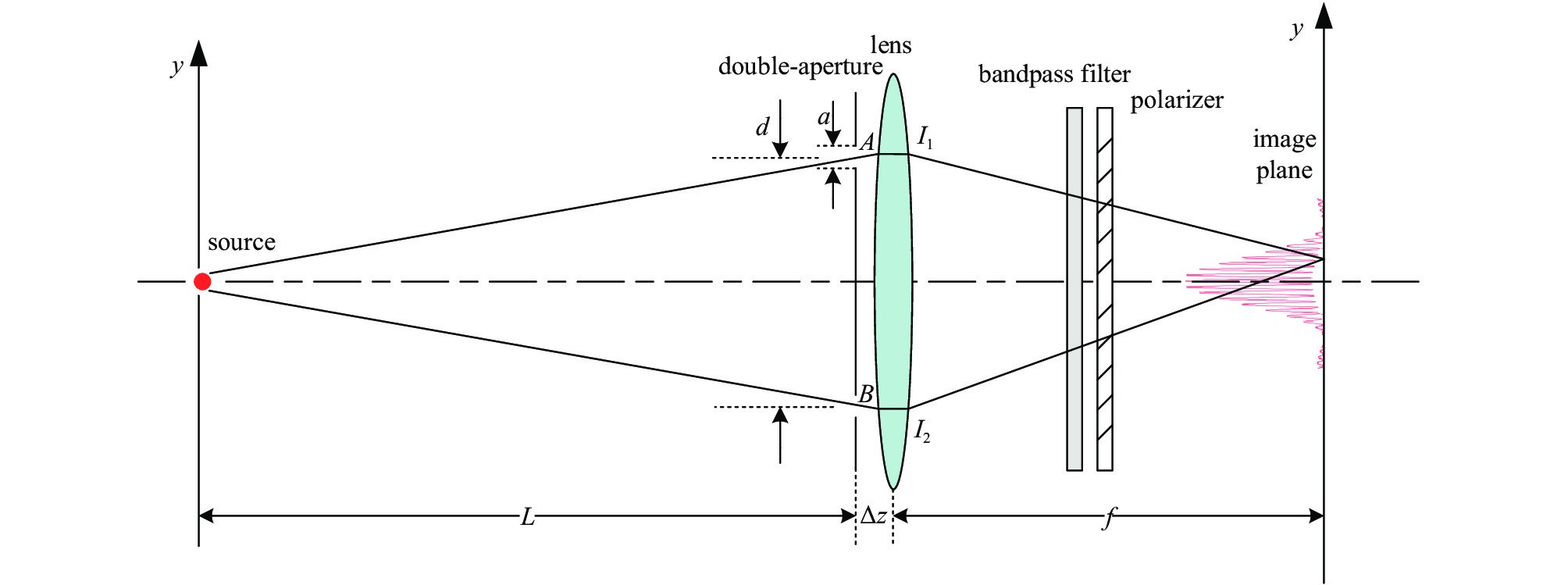
摘要: 基于同步光的干涉法,是一种非拦截高精度的束流截面测量手段。相比传统成像法,干涉法可以测量更小的束团尺寸、分辨率更好,较短测量波长下有望获得亚μm级的分辨率,因此在同步辐射光源中得到广泛应用。对合肥光源HLS II的原有同步光干涉装置,提出了将原有的干涉光路中第一面聚焦透镜换成RC结构聚焦反射镜,第二面单透镜换成双胶合透镜,以达到在不改变光路光轴情况下减小色散和几何像差,从而提高光路成像质量的目的。采用几何光路设计方法对成像质量进行评价,并进行物理光学仿真计算,得到测量系统的干涉条纹。仿真结果表明:光学系统成像的艾里斑半径减小约35%,点列图的均方根半径减小了约99%,波前差也减小了约75%,调制传递函数(MTF)的截止频率提高了约65%,采用聚焦反射镜代替原有的聚焦透镜可大幅提升光路成像质量。Abstract: The interferometric measurement of the transverse beam size based on synchrotron radiation is a non-intercepting high precision measurement method. Compared with the imaging method, the interferometric method can measure smaller beam size and get better resolution. It is expected to obtain submicron resolution at shorter measurement wavelength, so it is widely used in synchrotron radiation sources. The upgraded scheme of current interference device in Hefei Light Source HLS-II is presented in this paper. It is proposed to replace the first focusing lens in the original interference light path with an RC structure focusing mirror, and the second single lens with a doublet lens. The design goal of this paper is to reduce dispersion and geometric aberration without changing the optical axis of the optical path, so as to improve the imaging quality of the optical path. The geometrical optical path design is used to evaluate the imaging quality of the optical path, and physical optical simulation is performed to obtain the interference fringes of the measurement system. The simulation results show that the radius of Airy spot is reduced by about 35%, the root mean square radius of dot array is reduced by about 99%, the wavefront difference is reduced by about 75%, and the cutoff frequency of MTF function is increased by about 65%, using a focusing mirror to replace the original focusing lens can greatly improve the image quality of the optical path.
-
Key words:
- synchrotron radiation /
- interferometer /
- RC focusing mirror /
- transverse beam size /
- optical design
-
表 1 干涉仪光路结构参数
Table 1. Structure parameters of interferometer
$ {L}_{{x}} $/m $ {L}_{{y}} $/m $ \lambda /\mathrm{n}\mathrm{m} $ $ \Delta \lambda $/nm ${w}_{{x} }\times {w}_{{y} }$ $ {d}_{{y}} $/mm $ {d}_{{x}} $/mm $ {f}_{1} $/mm $ {f}_{2} $/mm vertical horizontal 40 30 500 10 $ 2\;\mathrm{m}\mathrm{m}\times 1\;\mathrm{m}\mathrm{m} $ $ 1\;\mathrm{m}\mathrm{m}\times 2\;\mathrm{m}\mathrm{m} $ 16 18 1000 100 表 2 干涉仪光路质量评价结果对比
Table 2. Comparison of the results of interferometer optical path quality evaluation
Airy disk radius/μm RMS radius of spot diagram/μm wave front error/$ \lambda $ cut-off frequency of MTF/(lp·mm−1) original design $ 56.55 $ $ 24.25 $ $ 0.207 $ $ 20.2 $ new design $ 36.48 $ $ 0.05 $ $0.050$ $ 33.5 $ 表 3 仿真结果
Table 3. Results of simulation
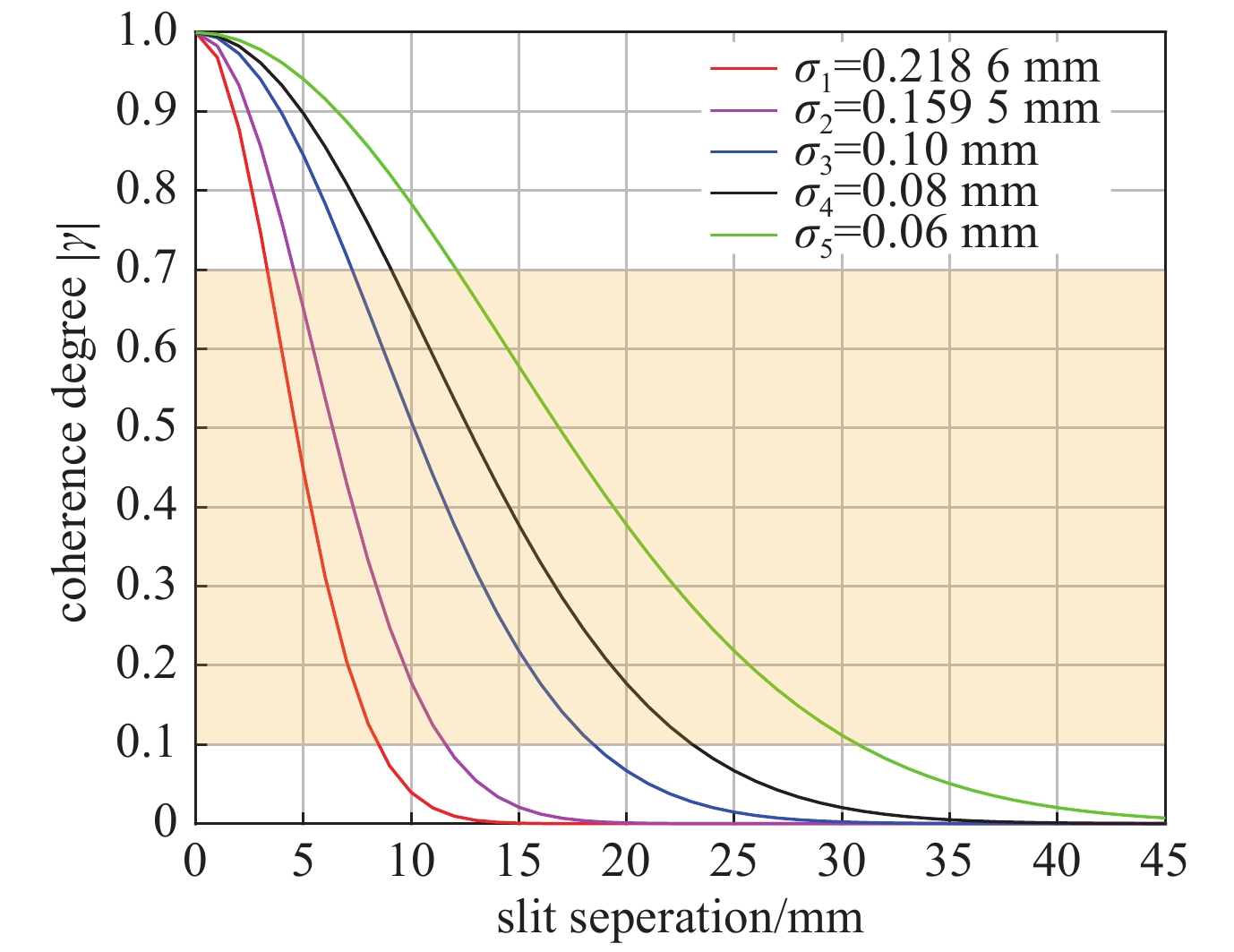
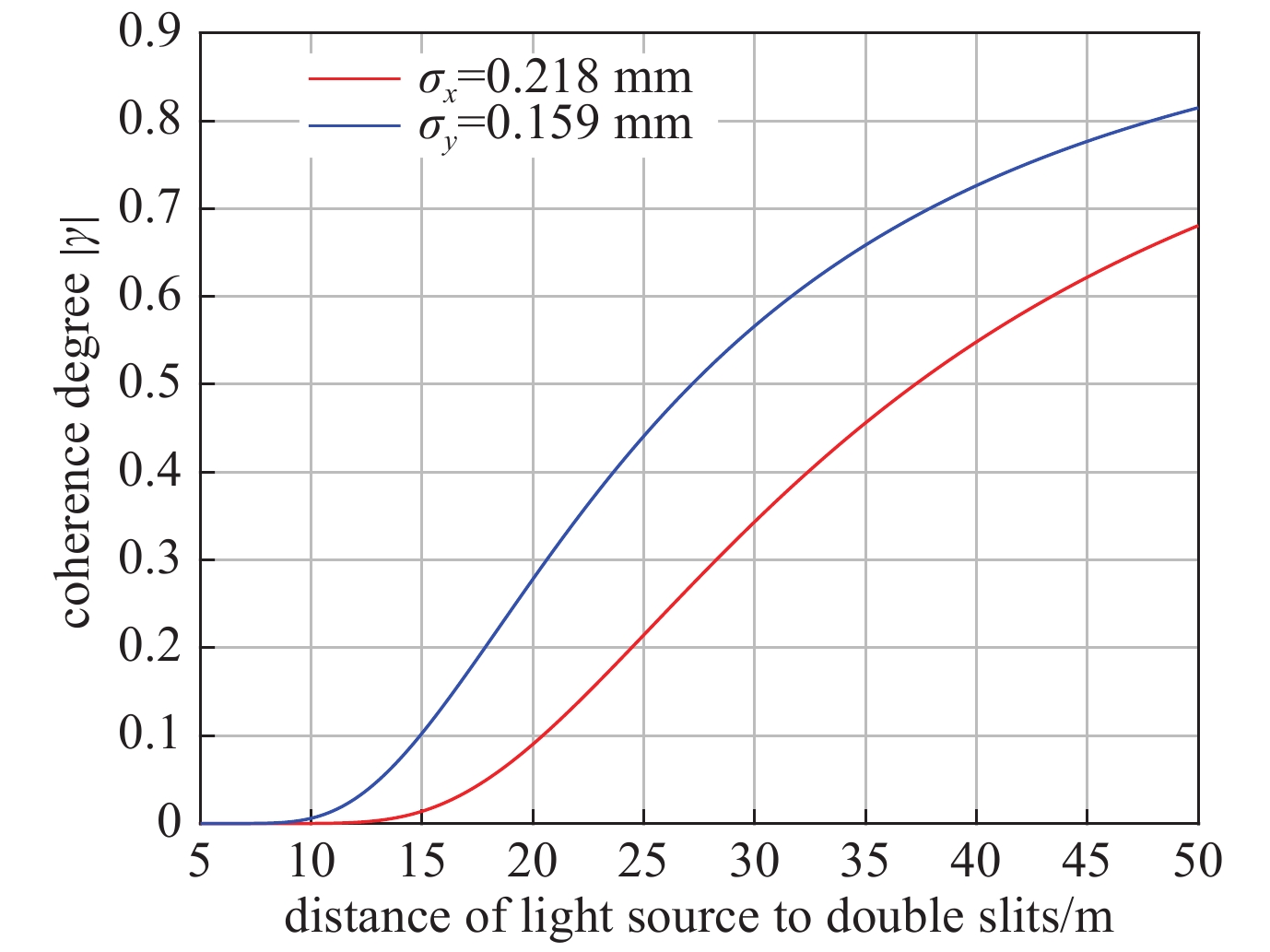
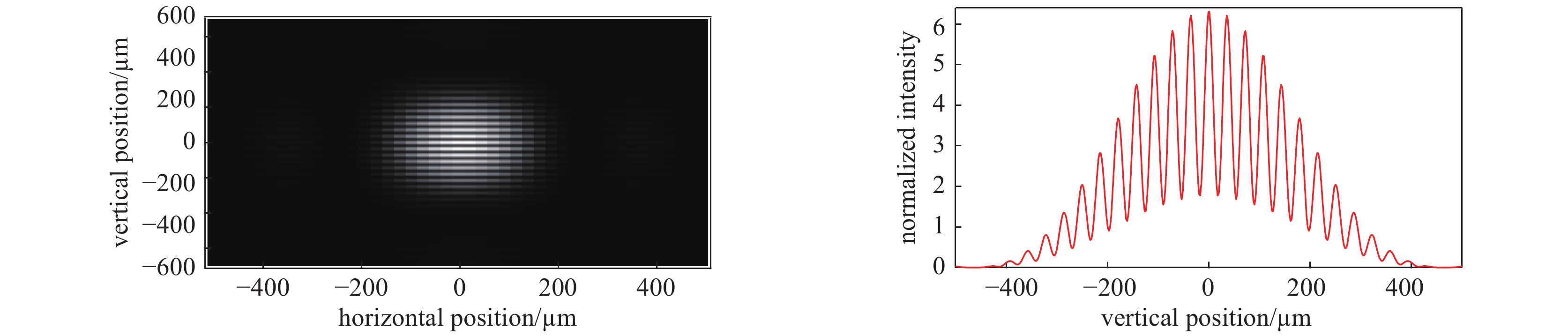
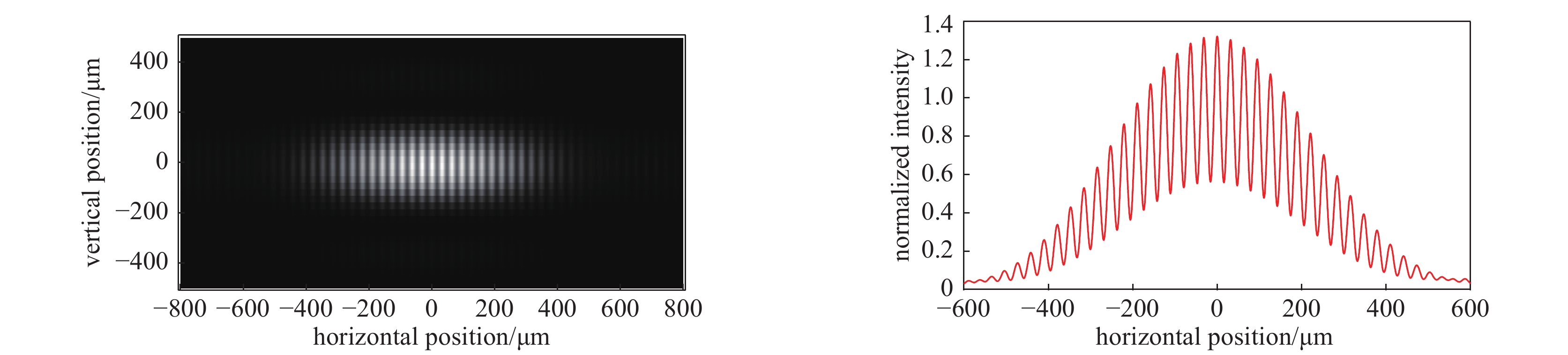
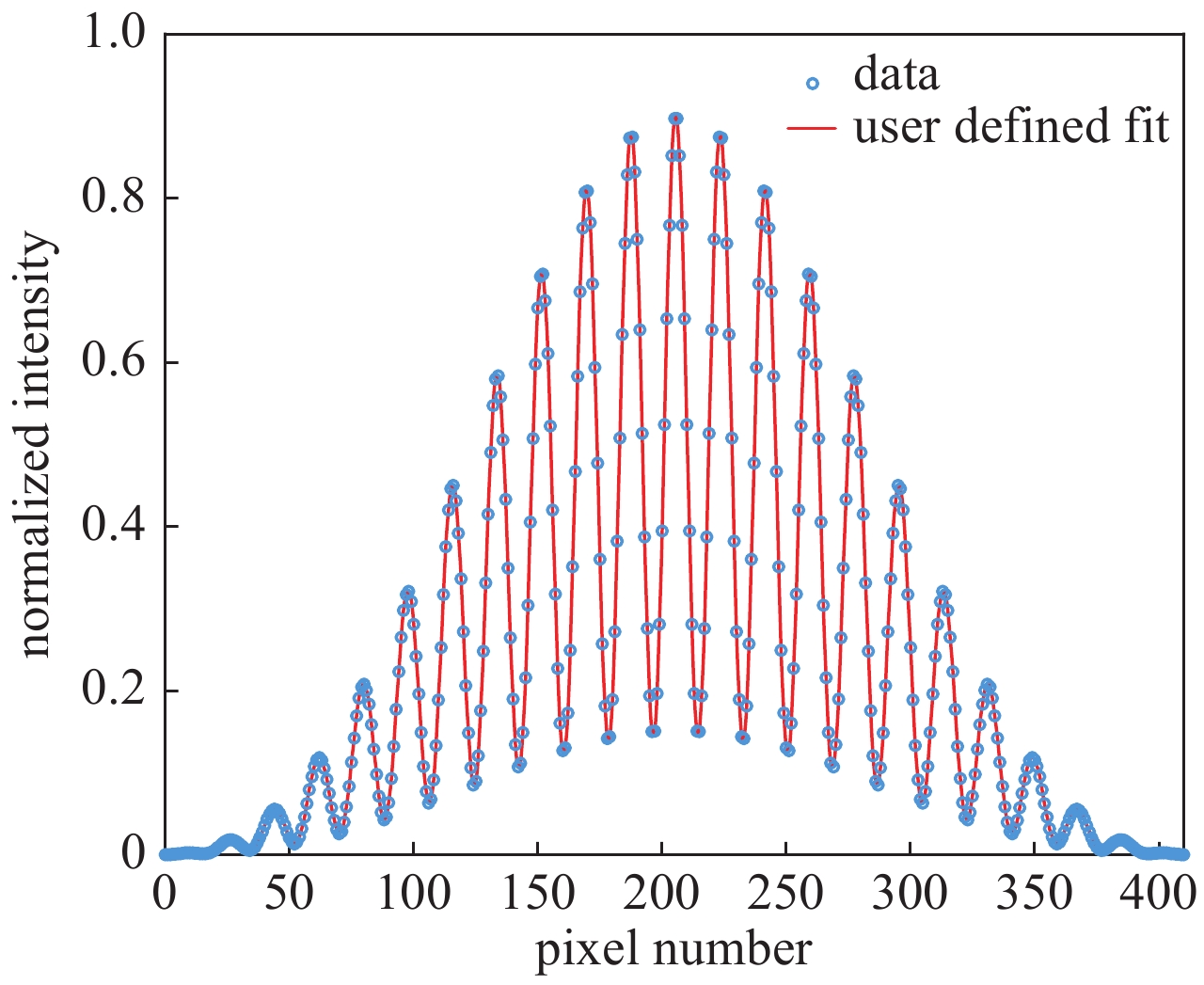
L/m d/mm $ \left|\gamma \right| $ $\sigma /{\text{μ}}\mathrm{m}$ vertical profile 30 16 0.56 160.7 30 18 0.47 162.9 30 20 0.40 161.5 horizontal profile 40 16 0.52 227.5 40 18 0.40 239.4 40 20 0.42 209.6 表 4 误差计算表
Table 4. Error calculation table
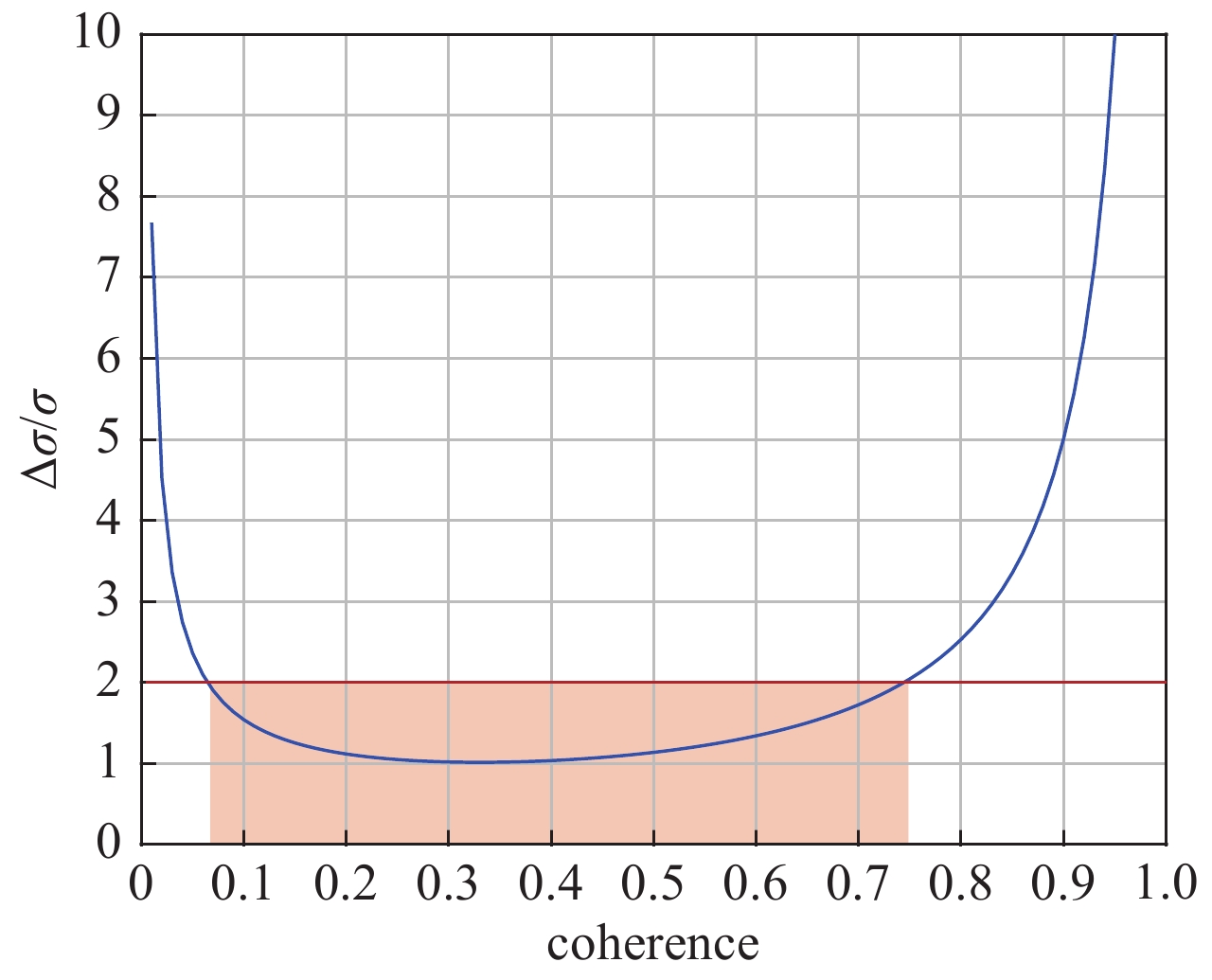
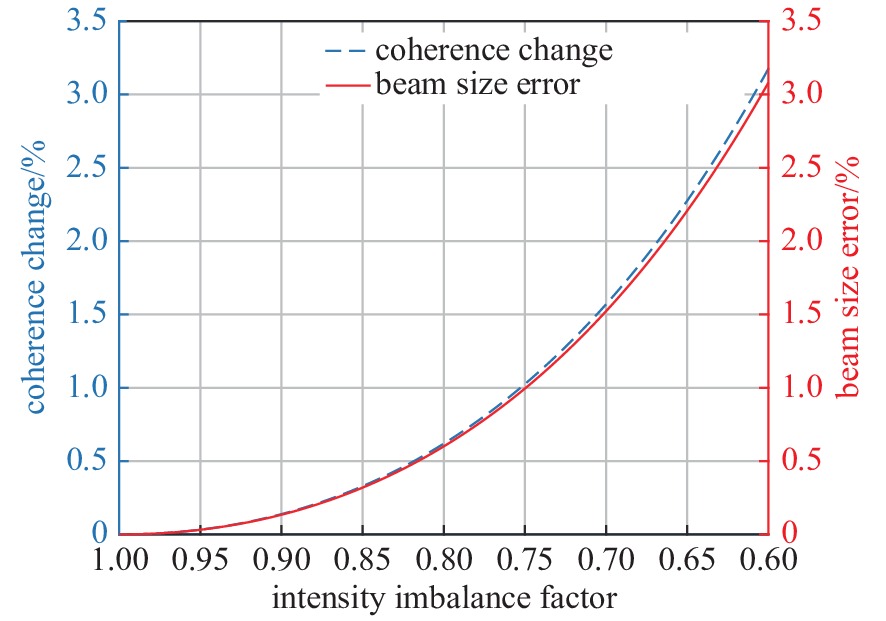
fitting value of visibility true value of the degree of coherence absolute error of visibility $ {u}_{\left|\gamma \right|} $ relative error of visibility $ {\delta }_{\left|\gamma \right|} $ $ {V}_{\rm{y}}=\dfrac{2\sqrt{\rho }}{1+\rho }\left|{\gamma }_{\rm{y}}\right| $ $ \left|{\gamma }_{\rm{y}}\right| $ $ \dfrac{2\sqrt{\rho }}{1+\rho }\left|{\gamma }_{\rm{y}}\right|-\left|{\gamma }_{\rm{y}}\right| $ $ \left(\dfrac{2\sqrt{\rho }}{1+\rho }\left|{\gamma }_{\rm{y}}\right|-\left|{\gamma }_{\rm{y}}\right|\right)/\left|{\gamma }_{\rm{y}}\right| $ 表 5 垂直干涉仪光路参数和测量标准差
Table 5. Parameters of vertical interferometer and measurement standard deviation
L/mm $ \lambda /\mathrm{n}\mathrm{m} $ d/mm $ \left|\gamma \right| $ 30000±10 500±10 16±0.01 0.6±0.06 -
[1] Chevtsov P, Freyberger A, Hicks R, et al. Synchrotron light interferometer at Jefferson Lab[C]//Proceedings of the 2003 Particle Accelerator Conference. 2003: 2560-2562. [2] Fisher A S, Holtzapple R L, Petree M, et al. Beam-size measurements on PEP-II using synchrotron-light interferometry[C]//Proceedings of the 2001 Particle Accelerator Conference. 2001: 547-549. [3] Corbett J, Cheng W, Fisher A S, et al. Interferometer beam size measurements in SPEAR3[C]//Proceedings of PAC09. 2009: 4018-4020. [4] Koopmans M, Goslawski P, Hwang J G, et al. Status of a double slit interferometer for transverse beam size measurements at BESSY II[C]//Proceedings of IPAC2017. 2017: 149-152. [5] Masaki M, Takano S. Beam size measurement of the Spring-8 storage ring by two-dimensional interferometer[C]//Proceedings DIPAC 2001. 2001: 142-144. [6] 王理, 赵敬霞, 曹建社, 等. 同步光干涉方法对BEPCII储存环束流的测量[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2011, 23(9):2512-2514. (Wang Li, Zhao Jingxia, Cao Jianshe, et al. Beam size measurement of BEPC II storage ring by using visible synchrotron light interferometry[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2011, 23(9): 2512-2514 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20112309.2512 [7] 高波. 上海光源诊断线站升级中的若干关键技术研究[D]. 上海: 中国科学院上海应用物理研究所, 2018: 73-91.Gao Bo. Study on several key techniques in upgrading of the diagnostic beam line at Shanghai Synchrotron Radition Facility[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Institute of Applied Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2018: 73-91 [8] 唐凯. HLSII基于光学的测量系统及其相关研究[D]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学, 2016: 83-94.Tang Kai. The related research of the measurement system based on optics of HLS Ⅱ[D]. Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China, 2016: 83-94 [9] 唐雷雷. HLS Ⅱ束流横向截面测量系统的研制及相关研究[D]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学, 2013: 55-76.Tang Leilei. Development and study of beam profile measurement system for HLS Ⅱ[D]. Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China, 2013: 55-76 [10] 陈杰. 干涉仪测量电子储存环束流截面的研究[D]. 上海: 中国科学院上海应用物理研究所, 2012: 36-56.Chen Jie. The research of measuring beam size of electron storage ring with interferometer[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Institute of Applied Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2012: 36-56 [11] Naito T, Mitsuhashi T. Very small beam-size measurement by a reflective synchrotron radiation interferometer[J]. Physical Review Accelerators and Beams, 2006, 9: 122802. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevSTAB.9.122802 [12] Li C L, Xu Y H, Boland M J, et al. Double-slit interferometer measurements at SPEAR3[C]//Proceedings of IPAC2016. 2016. [13] 孙葆根. 加速器中的束流诊断技术讲义, 第五章: 束流横向尺寸发射度测量[M]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学, 2008.Sun Baogen. Beam diagnostics in accelerators—Chapter 5: measurement of beam transverse size emittance[M]. Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China, 2008 [14] Mitsuhashi T. Spatial coherency of the synchrotron radiation at the visible light region and its application for the electron beam profile measurement[C]//Proceedings of the 1997 Particle Accelerator Conference. 1997: 766-768. [15] Mitsuhashi T. Beam profile and size measurement by SR interferometers[C]//Proceedings of the Joint US-CERN-Russia-Japan School on Particle Accelerators. 1999: 399-427. [16] Garg A D, Modi M H, Puntambekar T A. Design of synchrotron radiation interferometer (SRI) for beam size measurement at visible diagnostics beamline in Indus-2 SRS[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 2018, 902: 164-172. [17] Koopmans M, Goslawski P, Hwang J G, et al. Applications of the interferometric beam size monitor at BESSY II[C]//Proceedings of the 9th International Particle Accelerator Conference. 2018: 2103-2106. [18] Butti D. Synchrotron radiation interferometry for beam size measurement in the Large Hadron Collider[D]. Milan: Polytechnic University of Milan, 2019: 29-44. [19] 费业泰. 误差理论与数据处理[M]. 7版. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 2015: 83-89.Fei Yetai. Error theory and data processing[M]. 7th ed. Beijing: China Machine Press, 2015: 83-89 -




 下载:
下载: