Research progress in deep learning based WFSless adaptive optics system
-
摘要:
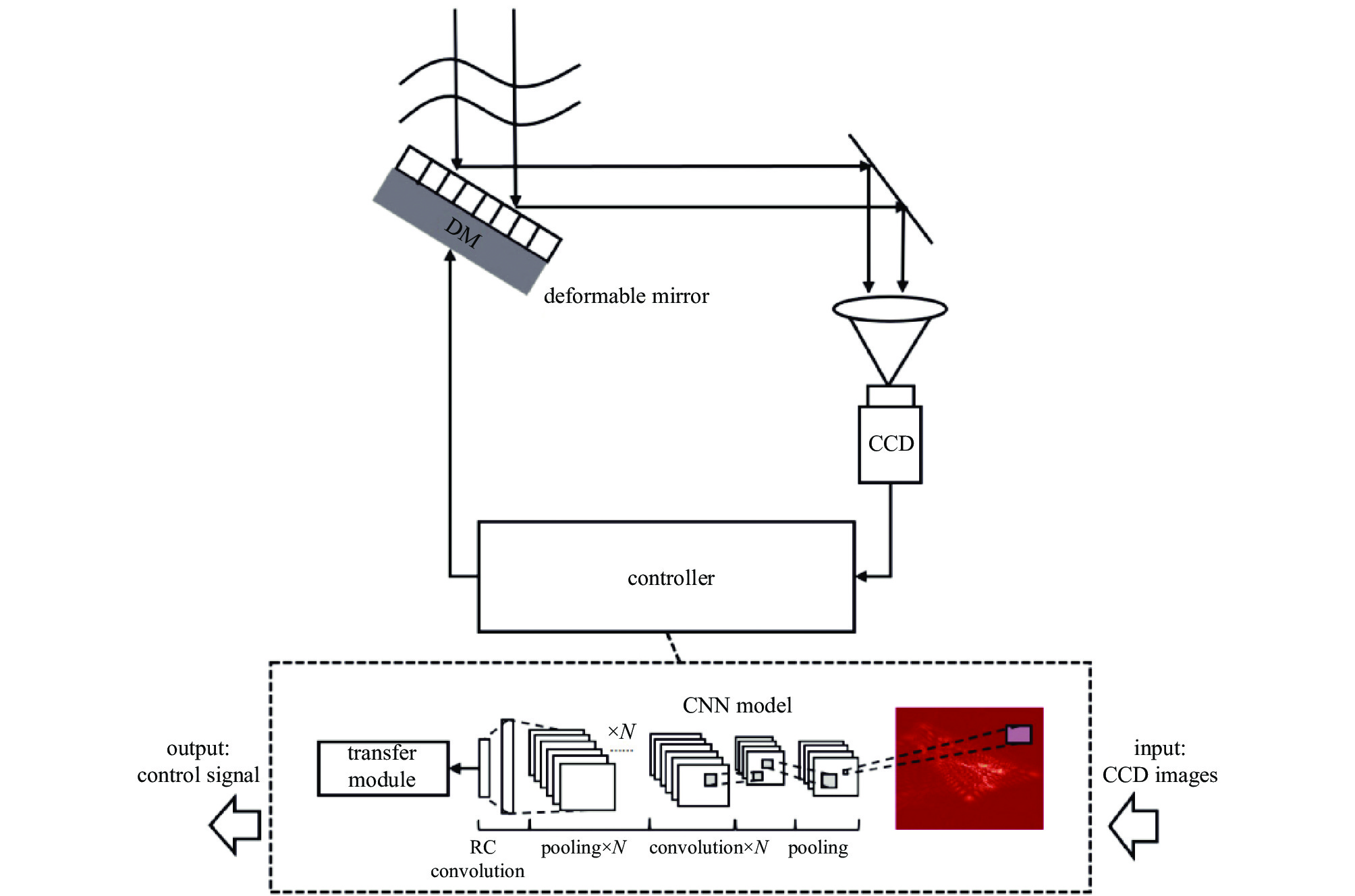
近年来自适应光学(AO)系统向着小型化和低成本化趋势发展,无波前探测自适应光学(WFSless AO)系统由于结构简单、应用范围广,成为目前相关领域的研究热点。硬件环境确定后,系统控制算法决定了WFSless AO系统的校正效果和系统收敛速度。新兴的深度学习及人工神经网络为WFSless AO系统控制算法注入了新的活力,进一步推动了WFSless AO系统的理论发展与应用发展。在回顾前期WFSless AO系统控制算法的基础上,全面介绍了近年来卷积神经网络(CNN)、长短期记忆神经网络(LSTM)、深度强化学习在WFSless AO系统控制中的应用,并对WFSless AO系统中各种深度学习模型的特点进行了总结。概述了WFSless AO技术在天文观测、显微成像、眼底成像、激光通信等领域的应用。
Abstract:In recent years, Adaptive Optics (AO) system is developing towards miniaturization and low cost. Because of its simple structure and wide application range, wavefront sensorless (WFSless) AO system has become a research hotspot in related fields. Under the condition that the hardware environment is determined, the system control algorithm determines the correction effect and convergence speed of WFSless AO system. The emerging deep learning and artificial neural network have injected new vitality into the control algorithms of WFSless AO system, and further promoted the theoretical and practical development of WFSless AO. On the basis of summarizing the previous control algorithms of WFSless AO system, the applications of convolution neural network (CNN), long-term memory neural network (LSTM) and deep reinforcement learning in WFSless AO system control in recent years are comprehensively introduced, and characteristics of various deep learning models in WFSless AO system are summarized. Applications of WFSless AO system in astronomical observation, microscopy, ophthalmoscopy, laser telecommunication and other fields are outlined.
-
Key words:
- adaptive optics /
- wavefront sensorless /
- deep learning /
- artificial neural networks
-
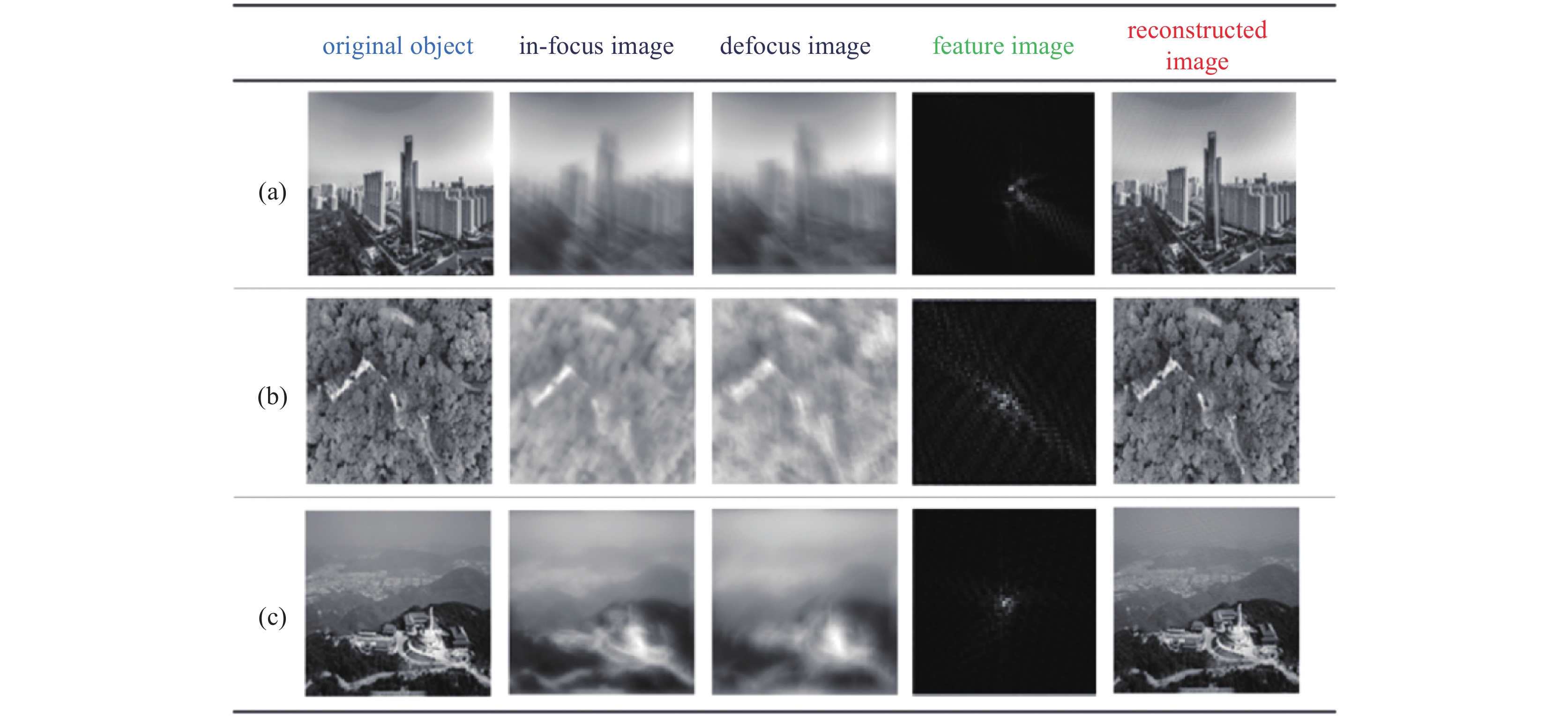
表 1 采用过曝、离焦、散射预处理后估计出的Zernike系数准确度(均方差)[23]
Table 1. Accuracy of Zernike coefficients (RMS) with overexposure, defocus and scattering preprocessing[23]
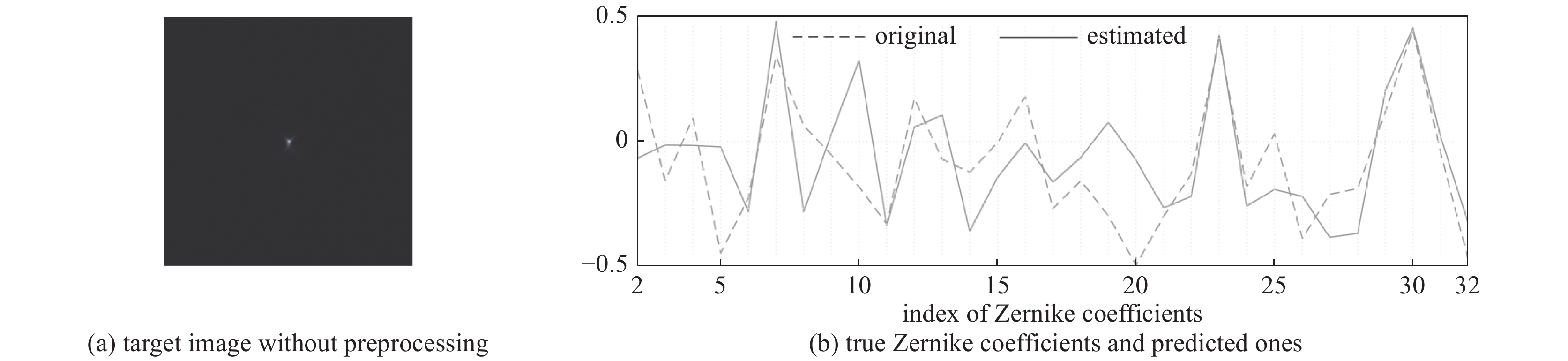
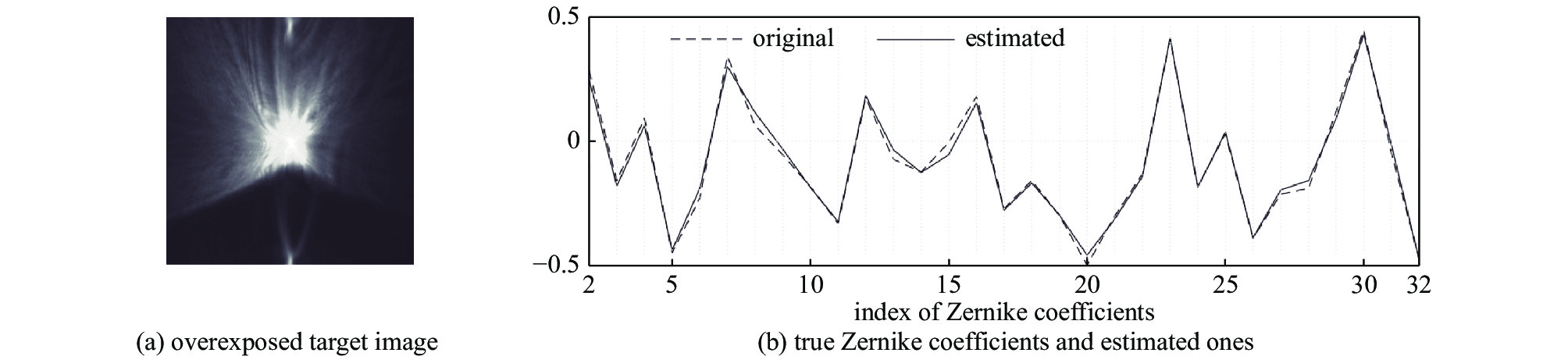
Zernike coefficients in-focus overexposure defocus scatter point source 0.142±0.032 0.036±0.013 0.040±0.016 0.057±0.018 extended source 0.288±0.024 0.214±0.051 0.099±0.064 0.195±0.064 dataset No. $ D/{r}_{0} $ $ D/{r}_{0} $
intervaldata volume/
intervaltotal data
volume$D/{r}_{0}$
intervaldata volume/interval total data
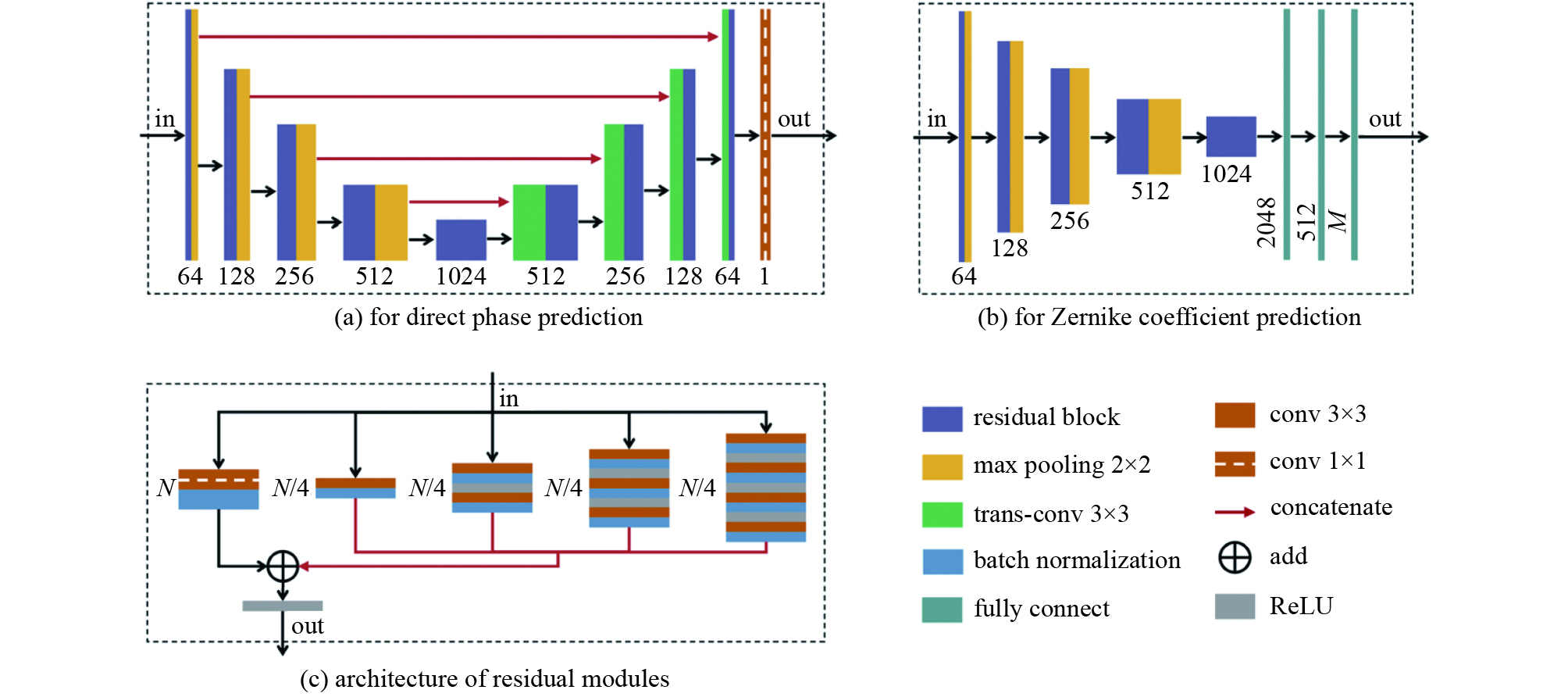
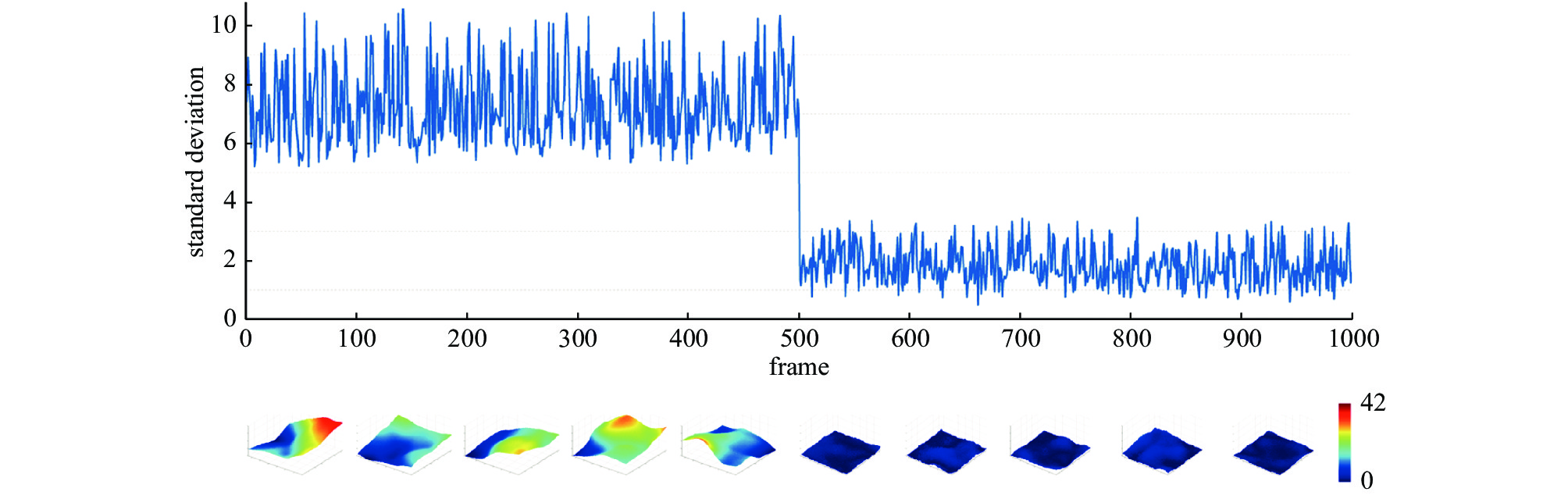
volumetraining dataset test dataset 1 5 — 100 15000 — 10 1500 2 15 — 100 15000 — 10 1500 3 1-15 1 100 15000 1 10 1500 表 3 仿真不同湍流条件时波前复原误差(NPMS:归一化像素均方 RMS:均方根)[32]
Table 3. Simulation results of wavefront restoration error under different turbulence levels (NPMS: Normalized Pixel Mean Square; RMS: Root Mean Square)[32]
$ D/{r}_{0} $ NPMS RMS/λ $ 20 $ 0.0067 0.1307 $ 15 $ 0.0041 0.0909 $ 10 $ 0.0029 0.0718 $ 6 $ 0.0025 0.0703 表 4 实验得到波前复原误差与运算时间(NPMS:归一化像素均方 RMS:均方根)[32]
Table 4. Wavefront restoration error and time consumption of experiments (NPMS: Normalized Pixel Mean Square; RMS: Root Mean Square)[32]
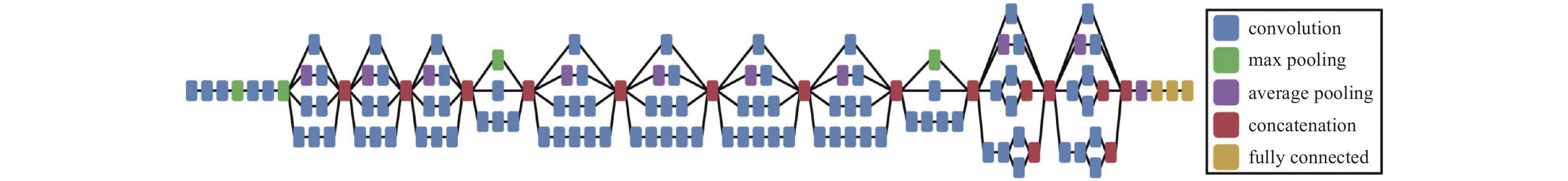
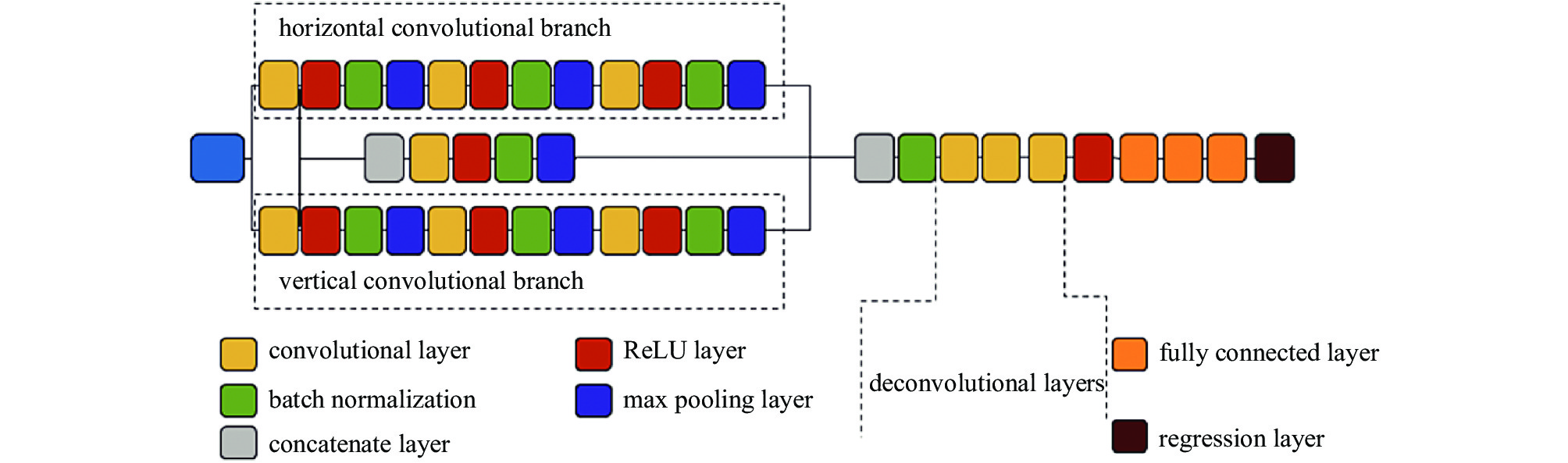
$ D/{r}_{0} $ NPMS RMS/λ running time/ms $ 20 $ 0.0066 0.1304 ~12 表 5 PD-CNN和Xception模型推测时间对比[34]
Table 5. Comparison of inference time of PD-CNN with that of Xception[34]
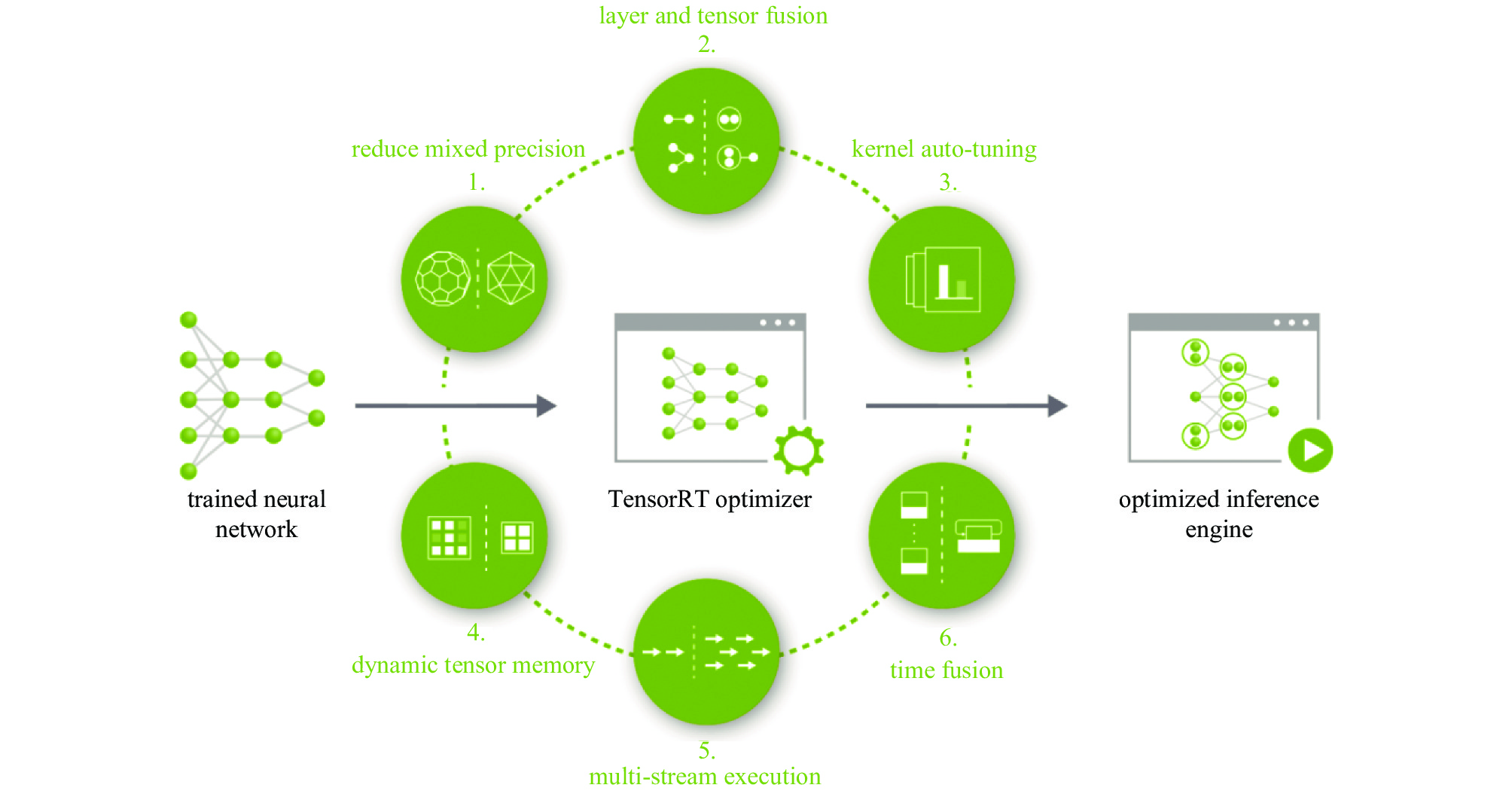
network focal model/ms defocused model/ms PD model/ms PD-CNN 2.2495 2.2989 2.5591 Xception 10.469 10.1108 10.469 表 6 经TensorRT优化前后的推测时间对比[34]
Table 6. Comparison of inference time with and without optimization by TensorRT[34]
model before acceleration/ms after acceleration/ms acceleration ratio focal model 2.2495 0.4678 4.8091 defocused model 2.2989 0.4406 5.2178 PD model 2.5591 0.4909 5.2135 表 7 WFSless AO仿真软件
Table 7. WFSless AO simulation software
AO simulation tool deep learning framework Soapy[21] PyTorch (www.pytorch.org) HCIPy[52] Keras (www.keras.io) OOMAO[54] TensorFlow (www.tensorflow.org) YAO[55] MATLAB + Deep Learning Toolbox DASP[56] Caffe (https://caffe.berkeleyvision.org/) Soapy:Simulation ‘OptiqueAdaptative’ with Python HCIPy:High Contrast Imaging for Python
OOMAO:Object-Oriented MATLAB Adaptive Optics Toolbox YAO:Yorick Adaptive Optics
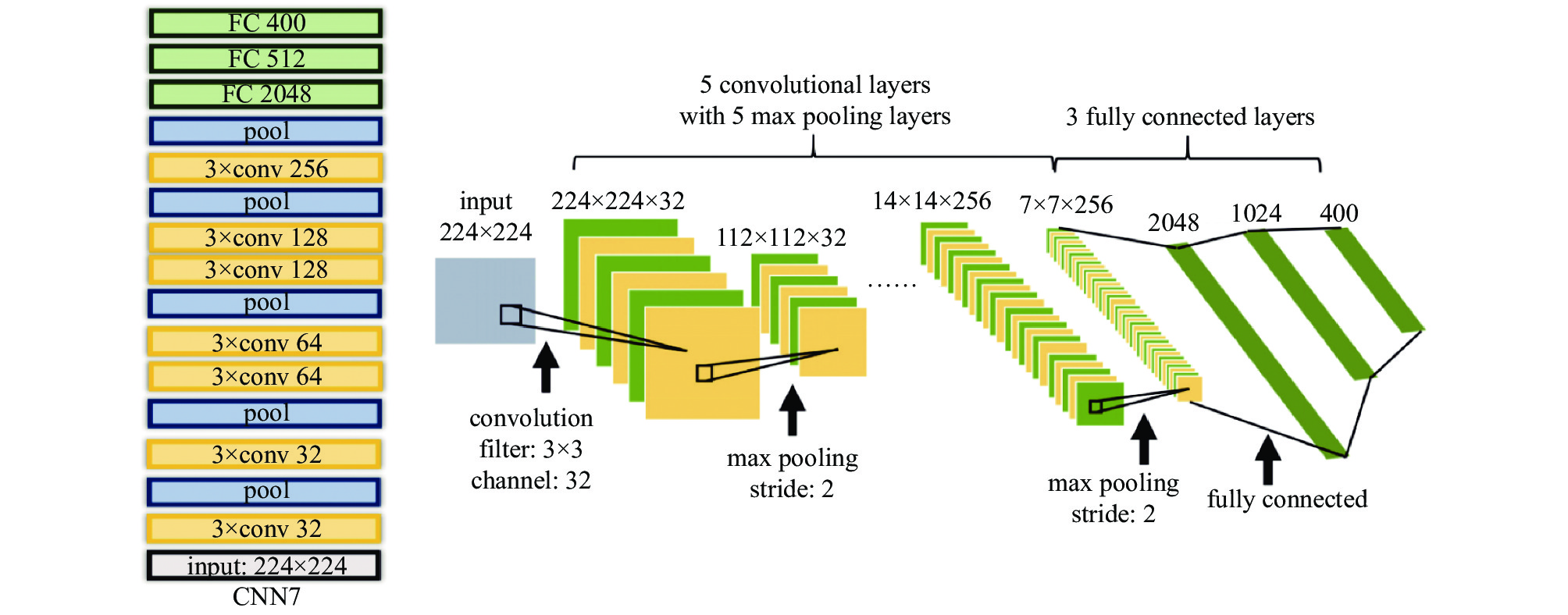
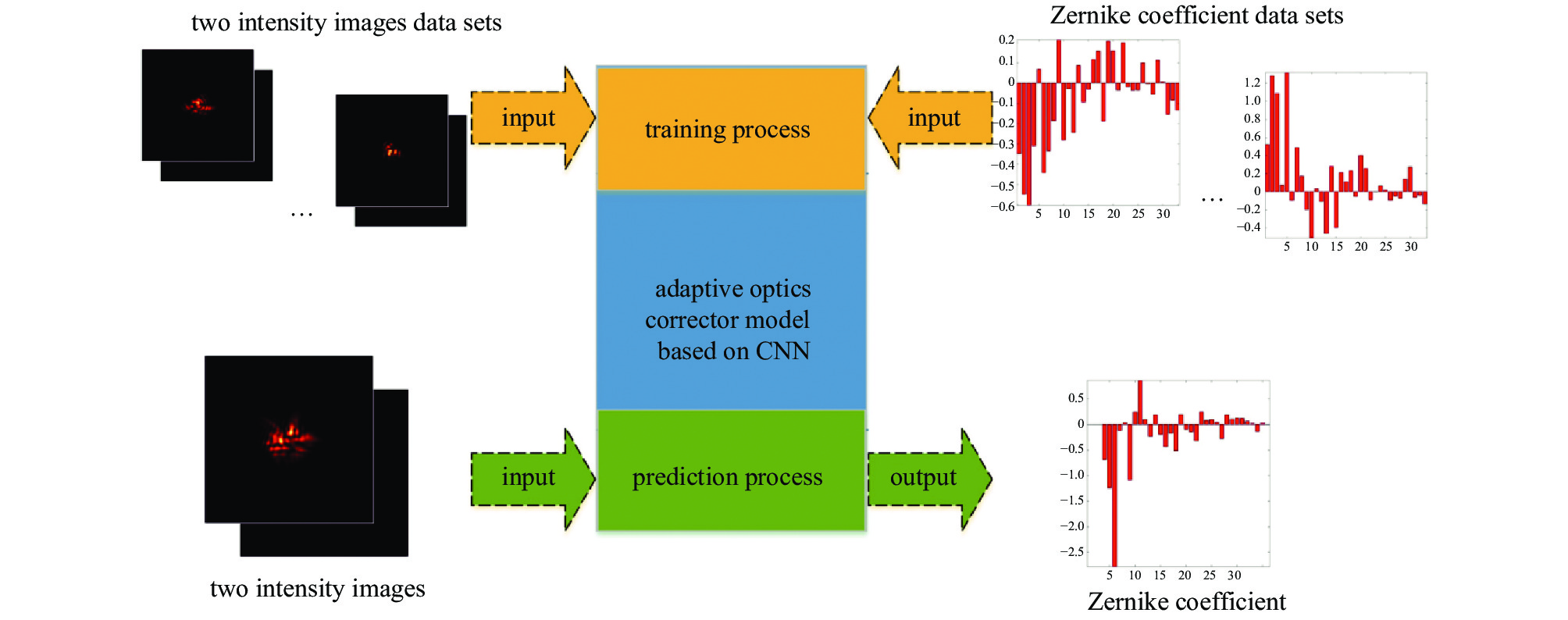
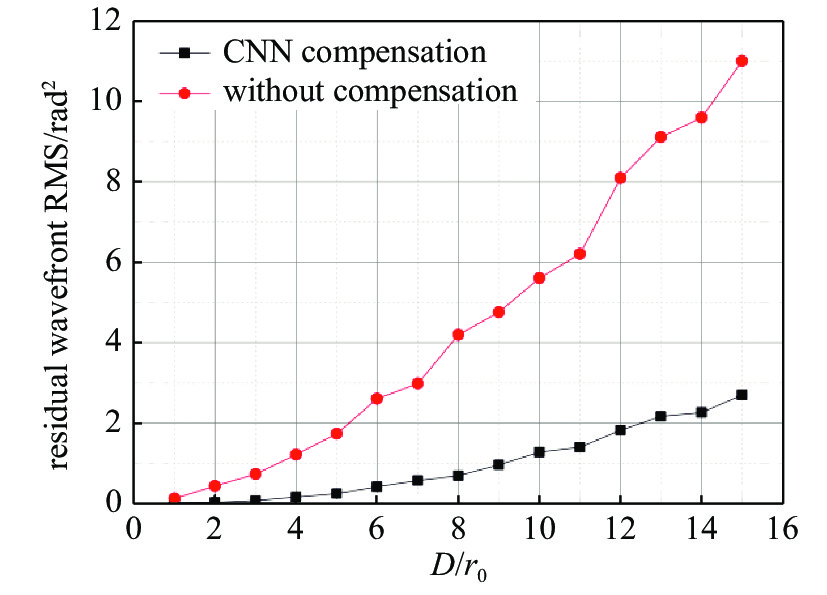
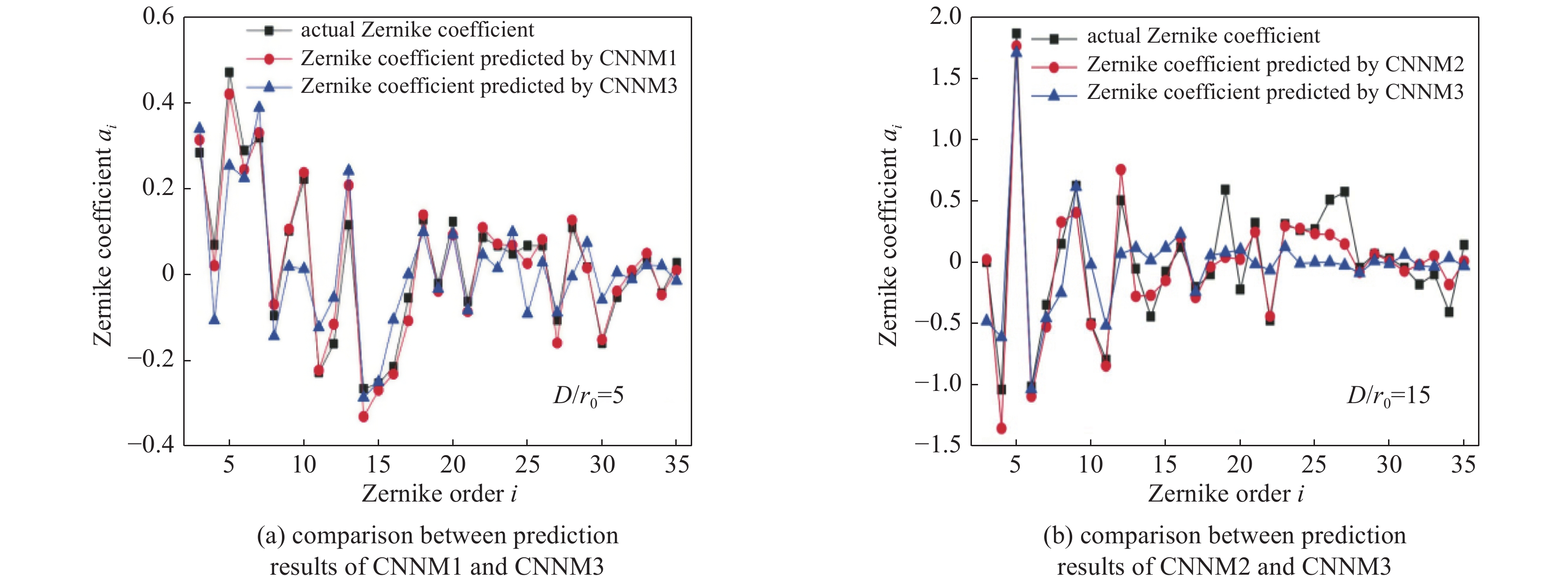
DASP: Durham Adaptive Optics Simulation Platform -
[1] Shorter R S. Principles of adaptive optics, 3rd edn., by Robert K. Tyson[J]. Contemporary Physics, 2011, 52(5): 501-502. [2] 冯麓, 张玉佩, 宋菲君, 等. 夜天文中的自适应光学[J]. 物理, 2018, 47(6):355-366. (Feng Lu, Zhang Yupei, Song Feijun, et al. Adaptive optics for night astronomy[J]. Physics, 2018, 47(6): 355-366 doi: 10.7693/wl20180602 [3] Yazdani R, Hajimahmoodzadeh M, Fallah H R. Adaptive phase aberration correction based on imperialist competitive algorithm[J]. Applied Optics, 2014, 53(1): 132-140. doi: 10.1364/AO.53.000132 [4] 杨慧珍, 陈波, 李新阳, 等. 自适应光学系统随机并行梯度下降控制算法实验研究[J]. 光学学报, 2008, 28(2):205-210. (Yang Huizhen, Chen Bo, Li Xinyang, et al. Experimental demonstration of stochastic parallel gradient descent control algorithm for adaptive optics system[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2008, 28(2): 205-210 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2239.2008.02.001 [5] Facomprez A, Beaurepaire E, Débarre D. Accuracy of correction in modal sensorless adaptive optics[J]. Optics Express, 2012, 20(3): 2598-2612. doi: 10.1364/OE.20.002598 [6] Huang Linhai, Rao Changhui. Wavefront sensorless adaptive optics: a general model-based approach[J]. Optics Express, 2011, 19(1): 371-379. doi: 10.1364/OE.19.000371 [7] 方舟, 徐项项, 李鑫, 等. 自适应增益的SPGD算法[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2020, 49:20200274. (Fang Zhou, Xu Xiangxiang, Li Xin, et al. SPGD algorithm with adaptive gain[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2020, 49: 20200274 [8] Zommer S, Ribak E N, Lipson S G, et al. Simulated annealing in ocular adaptive optics[J]. Optics Letters, 2006, 31(7): 939-941. doi: 10.1364/OL.31.000939 [9] 杨平, 许冰, 姜文汉, 等. 遗传算法在自适应光学系统中的应用[J]. 光学学报, 2007, 27(9):1628-1632. (Yang Ping, Xu Bing, Jiang Wenhan, et al. Study of a genetic algorithm used in an adaptive optical system[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2007, 27(9): 1628-1632 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2239.2007.09.017 [10] Yang Huizhen, Li Xinyang. Comparison of several stochastic parallel optimization algorithms for adaptive optics system without a wavefront sensor[J]. Optics & Laser Technology, 2011, 43(3): 630-635. [11] Booth M J. Wavefront sensorless adaptive optics for large aberrations[J]. Optics Letters, 2007, 32(1): 5-7. doi: 10.1364/OL.32.000005 [12] 杨慧珍, 吴健, 龚成龙. 基于模型的无波前探测自适应光学系统[J]. 光学学报, 2014, 34:0801002. (Yang Huizhen, Wu Jian, Gong Chenglong. Model-based sensorless adaptive optics system[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2014, 34: 0801002 doi: 10.3788/AOS201434.0801002 [13] Wen Lianghua, Yang Ping, Wang Shuai, et al. A high speed model-based approach for wavefront sensorless adaptive optics systems[J]. Optics & Laser Technology, 2018, 99: 124-132. [14] Huang Linhai. Coherent beam combination using a general model-based method[J]. Chinese Physics Letters, 2014, 31: 094205. doi: 10.1088/0256-307X/31/9/094205 [15] Wen Lianghua, Yang Ping, Yang Kangjian, et al. Synchronous model-based approach for wavefront sensorless adaptive optics system[J]. Optics Express, 2017, 25(17): 20584-20597. doi: 10.1364/OE.25.020584 [16] Song Hong, Fraanje R, Schitter G, et al. Model-based aberration correction in a closed-loop wavefront-sensor-less adaptive optics system[J]. Optics Express, 2010, 18(23): 24070-24084. doi: 10.1364/OE.18.024070 [17] Angel J R P, Wizinowich P, Lloyd-Hart M, et al. Adaptive optics for array telescopes using neural-network techniques[J]. Nature, 1990, 348(6298): 221-224. doi: 10.1038/348221a0 [18] Sandler D G, Barrett T K, Palmer D A, et al. Use of a neural network to control an adaptive optics system for an astronomical telescope[J]. Nature, 1991, 351(6324): 300-302. doi: 10.1038/351300a0 [19] Barrett T K, Sandler D G. Artificial neural network for the determination of Hubble Space Telescope aberration from stellar images[J]. Applied Optics, 1993, 32(10): 1720-1727. doi: 10.1364/AO.32.001720 [20] Paine S W, Fienup J R. Machine learning for improved image-based wavefront sensing[J]. Optics Letters, 2018, 43(6): 1235-1238. doi: 10.1364/OL.43.001235 [21] Szegedy C, Vanhoucke V, Ioffe S, et al. Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2016: 2818-2826. [22] Byrd R H, Lu Peihuang, Nocedal J, et al. A limited memory algorithm for bound constrained optimization[J]. SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing, 1995, 16(5): 1190-1208. doi: 10.1137/0916069 [23] Nishizaki Y, Valdivia M, Horisaki R, et al. Deep learning wavefront sensing[J]. Optics Express, 2019, 27(1): 240-251. doi: 10.1364/OE.27.000240 [24] Chollet F. Xception: Deep learning with depthwise separable convolutions[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2017: 1251-1258. [25] Kingma D, Ba J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization[DB/OL]. arXiv preprint, arXiv: 1412.6980, 2014. [26] Tian Qinghua, Lu Chenda, Liu Bo, et al. DNN-based aberration correction in a wavefront sensorless adaptive optics system[J]. Optics Express, 2019, 27(8): 10765-10776. doi: 10.1364/OE.27.010765 [27] Polo A, Haber A, Pereira S F, et al. An innovative and efficient method to control the shape of push-pull membrane deformable mirror[J]. Optics Express, 2012, 20(25): 27922-27932. doi: 10.1364/OE.20.027922 [28] Gonsalves R A. Phase retrieval and diversity in adaptive optics[J]. Optical Engineering, 1982, 21: 215829. [29] Ma Huimin, Liu Haiqiu, Qiao Yan, et al. Numerical study of adaptive optics compensation based on convolutional neural networks[J]. Optics Communications, 2019, 433: 283-289. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2018.10.036 [30] Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton G E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[C]//Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. 2012: 1097-1105. [31] 马慧敏, 焦俊, 乔焰, 等. 一种基于光强图像深度学习的波前复原方法[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2020, 57:081103. (Ma Huimin, Jiao Jun, Qiao Yan, et al. Wavefront restoration method based on light intensity image deep learning[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2020, 57: 081103 [32] Simonyan K, Zisserman A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[DB/OL]. arXiv preprint, arXiv: 1409.1556, 2014. [33] Guo Hongyang, Xu Yangjie, Li Qing, et al. Improved machine learning approach for wavefront sensing[J]. Sensors, 2019, 19(16): 3533. doi: 10.3390/s19163533 [34] Wu Yu, Guo Youming, Bao Hua, et al. Sub-millisecond phase retrieval for phase-diversity wavefront sensor[J]. Sensors, 2020, 20(17): 4877. doi: 10.3390/s20174877 [35] Nvidia Tensor RT[EB/OL]. (2021-07-09). https://developer.nvidia.com/tensorrt. [36] Vera E, Guzmán F, Weinberger C. Boosting the deep learning wavefront sensor for real-time applications [Invited][J]. Applied Optics, 2021, 60(10): B119-B124. doi: 10.1364/AO.417574 [37] Weinberger C, Guzmán F, Vera E. Improved training for the deep learning wavefront sensor[C]//Proceedings Volume 11448, Adaptive Optics Systems VII. 2020, 11448: 114484G. [38] Wang Kaiqiang, Zhang Mengmeng, Tang Ju, et al. Deep learning wavefront sensing and aberration correction in atmospheric turbulence[J]. PhotoniX, 2021, 2: 8. doi: 10.1186/s43074-021-00030-4 [39] He Kaiming, Zhang Xiangyu, Ren Shaoqing, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2016: 770-778. [40] Hochreiter S, Schmidhuber J. Long short-term memory[J]. Neural Computation, 1997, 9(8): 1735-1780. doi: 10.1162/neco.1997.9.8.1735 [41] Xin Qi, Ju Guohao, Zhang Chunyue, et al. Object-independent image-based wavefront sensing approach using phase diversity images and deep learning[J]. Optics Express, 2019, 27(18): 26102-26119. doi: 10.1364/OE.27.026102 [42] Liu Xuewen, Morris T, Saunter C. Using long short-term memory for wavefront prediction in adaptive optics[C]//Proceeding of the 28th International Conference on Artificial Neural Networks. Munich: Springer, 2019: 537-542. [43] Chen Ying. LSTM recurrent neural network prediction algorithm based on Zernike modal coefficients[J]. Optik, 2020, 203: 163796. doi: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2019.163796 [44] Swanson R, Lamb M, Correia C, et al. Wavefront reconstruction and prediction with convolutional neural networks[C]//Proceedings Volume 10703, Adaptive Optics Systems VI. 2018, 10703: 107031F. [45] Mnih V, Kavukcuoglu K, Silver D, et al. Human-level control through deep reinforcement learning[J]. Nature, 2015, 518(7540): 529-533. doi: 10.1038/nature14236 [46] Hu Ke, Xu Bing, Xu Zhenxing, et al. Self-learning control for wavefront sensorless adaptive optics system through deep reinforcement learning[J]. Optik, 2019, 178: 785-793. doi: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2018.09.160 [47] Hu Ke, Xu Zhenxing, Yang Wei, et al. Build the structure of WFSless AO system through deep reinforcement learning[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2018, 30(23): 2033-2036. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2018.2874998 [48] Konda V R, Tsitsiklis J N. Actor-critic algorithms[C]//Proceedings of Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. 2000: 1008-1014. [49] Nousiainen J, Rajani C, Kasper M, et al. Adaptive optics control using model-based reinforcement learning[J]. Optics Express, 2021, 29(10): 15327-15344. doi: 10.1364/OE.420270 [50] Cantalloube F, Farley O, Milli J, et al. Wind-driven halo in high-contrast images. I. Analysis of the focal-plane images of SPHERE[J]. Astronomy and Astrophysics, 2020, 638: A98. doi: 10.1051/0004-6361/201937397 [51] Landman R, Haffert S Y, Radhakrishnan V M, et al. Self-optimizing adaptive optics control with reinforcement learning[C]//Proceedings Volume 11448, Adaptive Optics Systems VII. 2020, 11448: 1144849. [52] Por E H, Haffert S Y, Radhakrishnan V M, et al. High Contrast Imaging for Python (HCIPy): an open-source adaptive optics and coronagraph simulator[C]//Proceedings Volume 10703, Adaptive Optics Systems VI. 2018, 10703: 1070342. [53] Gendron E, Léna P. Astronomical adaptive optics. II. Experimental results of an optimized modal control[J]. Astronomy and Astrophysics Supplement Series, 1995, 111: 153-167. [54] Conan R, Correia C. Object-oriented Matlab adaptive optics toolbox[C]//Proceedings Volume 9148, Adaptive Optics Systems IV. 2014, 9148: 91486C. [55] Rigaut F, Van Dam M. Simulating astronomical adaptive optics systems using YAO[C]//Third AO4ELT Conference - Adaptive Optics for Extremely Large Telescopes. 2013. [56] Basden A G, Bharmal N A, Jenkins D, et al. The Durham Adaptive Optics Simulation Platform (DASP): Current status[J]. SoftwareX, 2018, 7: 63-69. doi: 10.1016/j.softx.2018.02.005 [57] Zhu Licheng, Wen Lianghua, Yang Ping, et al. Aberration correction based on wavefront sensorless adaptive optics in membrane diffractive optical telescope[J]. Optics Communications, 2019, 451: 220-225. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2019.06.063 [58] Marx V. Microscopy: hello, adaptive optics[J]. Nature Methods, 2017, 14(12): 1133-1136. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.4508 [59] Booth M J. Adaptive optical microscopy: the ongoing quest for a perfect image[J]. Light: Science & Applications, 2014, 3: e165. [60] Hussain S A, Kubo T, Hall N, et al. Wavefront-sensorless adaptive optics with a laser-free spinning disk confocal microscope[J]. Journal of Microscopy, 2020. [61] 刘立新, 张美玲, 吴兆青, 等. 自适应光学在荧光显微镜中的应用[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2020, 57:120001. (Liu Lixin, Zhang Meiling, Wu Zhaoqing, et al. Application of adaptive optics in fluorescence microscope[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2020, 57: 120001 [62] Qin Zhongya, He Sicong, Yang Chao, et al. Adaptive optics two-photon microscopy enables near-diffraction-limited and functional retinal imaging in vivo[J]. Light: Science & Applications, 2020, 9: 79. [63] Jian Yifan, Lee Sujin, Ju M J, et al. Lens-based wavefront sensorless adaptive optics swept source OCT[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 27620. doi: 10.1038/srep27620 [64] 牛超君, 于诗杰, 韩香娥. 无波前探测自适应光学对光通信性能影响分析[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2015, 52:080102. (Niu Chaojun, Yu Shijie, Han Xiang’e. Analysis about effect of wavefront sensorless adaptive optics on optical communication[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2015, 52: 080102 [65] 徐晓帆, 陆洲. 星地激光通信可靠性保障技术研究现状[J]. 中国电子科学研究院学报, 2018, 13(6):650-657. (Xu Xiaofan, Lu Zhou. Research status of mitigation techniques to assure the reliability of satellite-to-ground laser communications[J]. Journal of CAEIT, 2018, 13(6): 650-657 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5692.2018.06.005 -




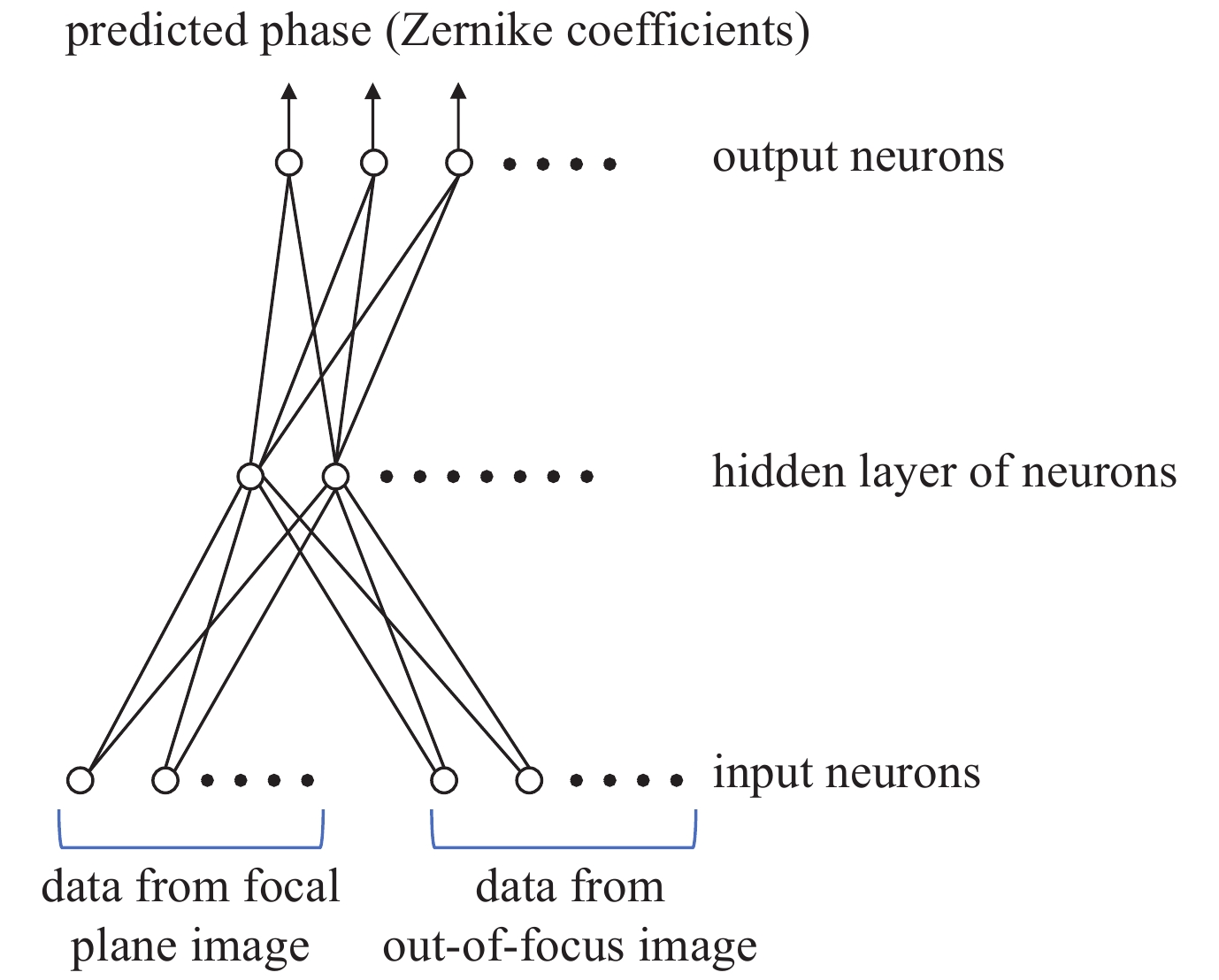
 下载:
下载: