Accelerator beam orbit prediction based on multi-stage cascaded BP neural networks
-
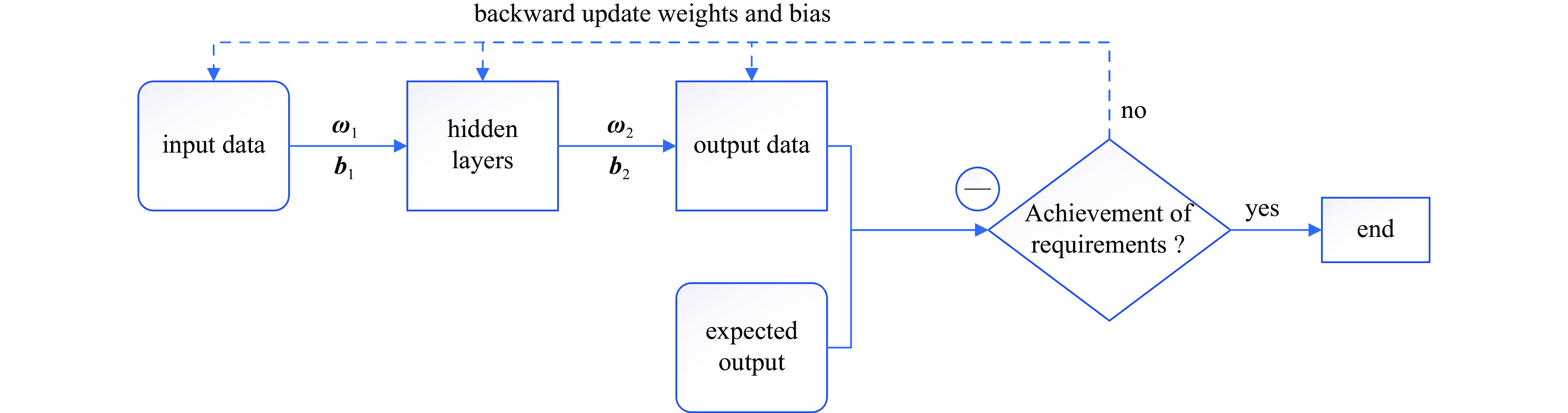
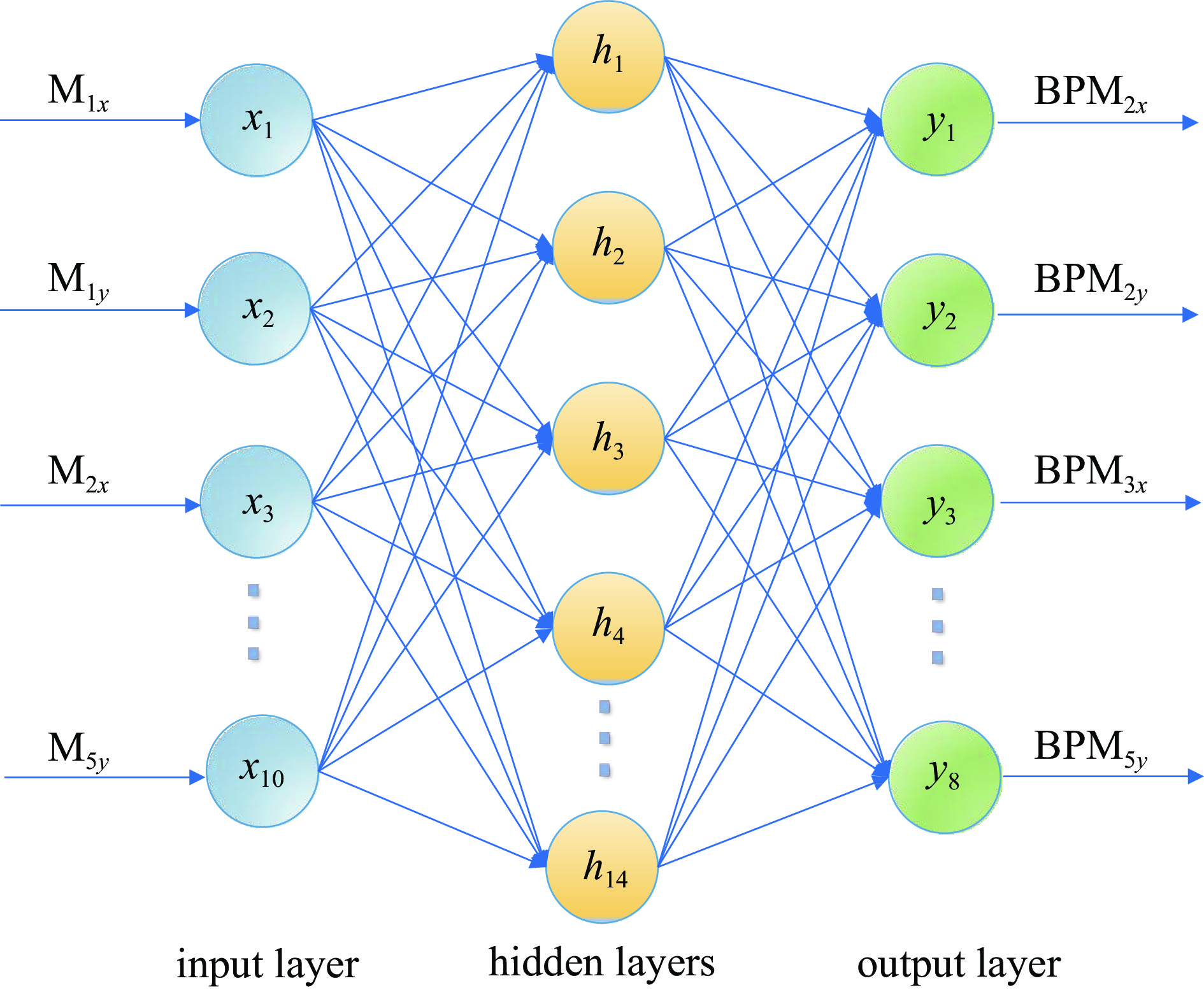
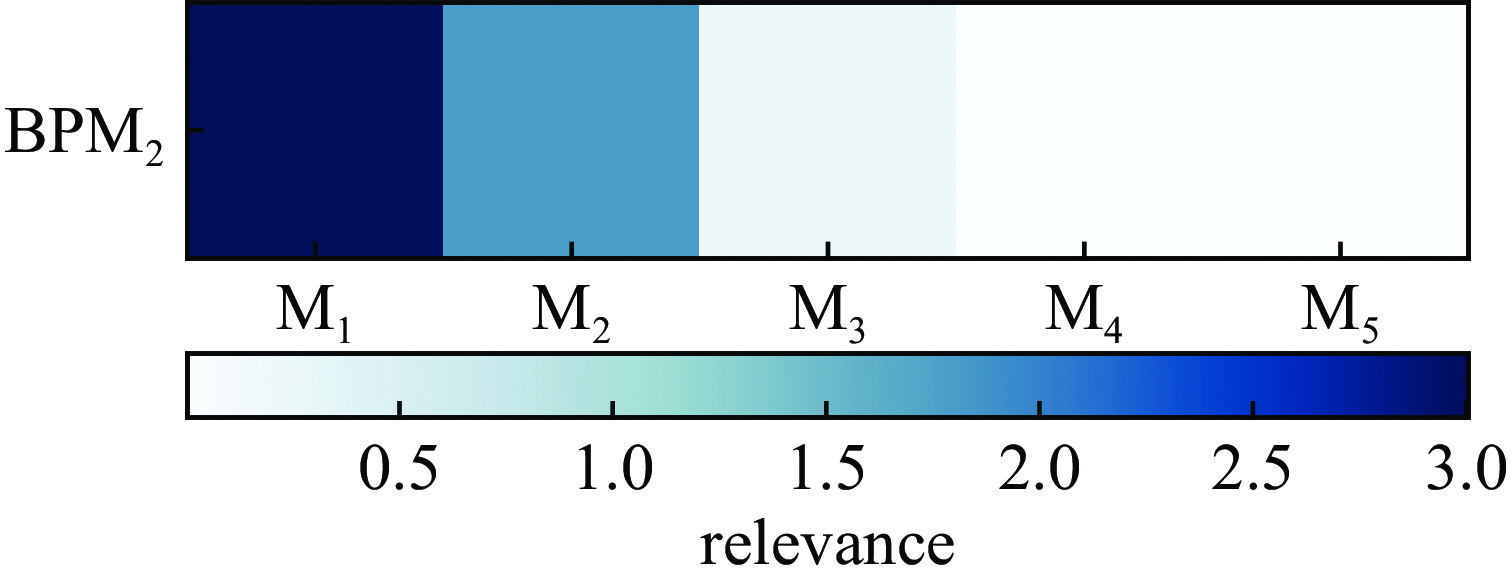
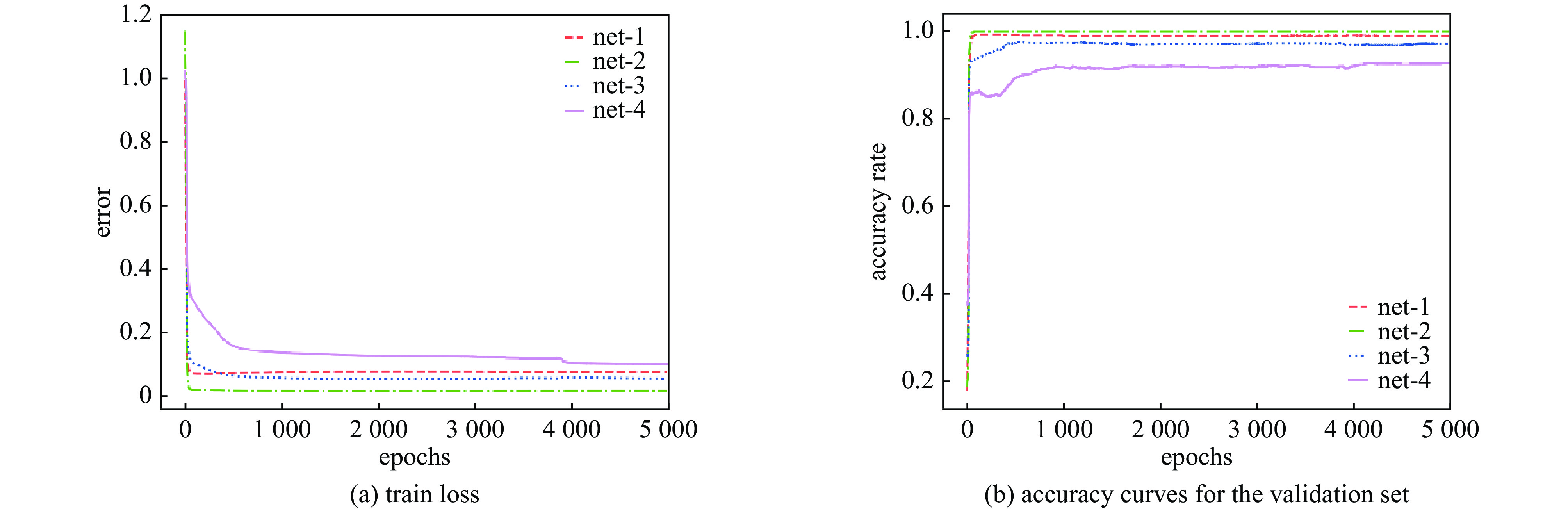
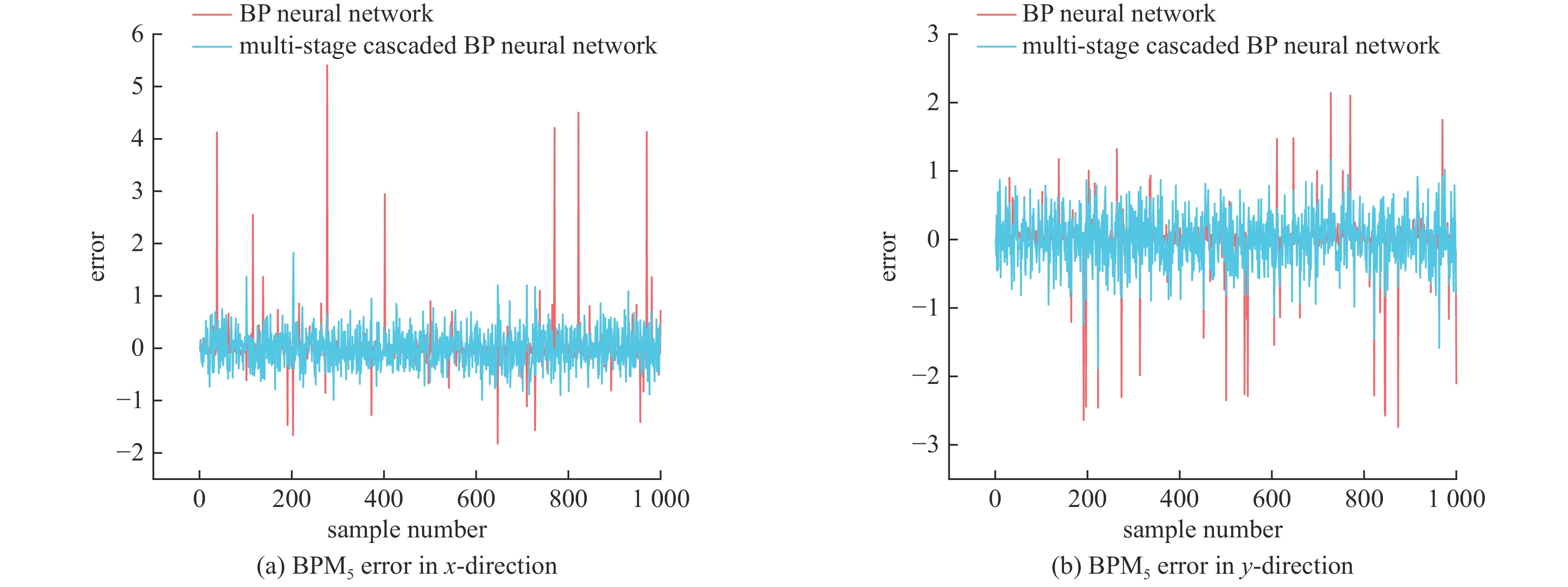
摘要: 加速器束流轨道校正对于加速器稳定运行具有非常重要的作用,精确预测加速器束流轨道的变化对于实现束流自动化校准也具有重要意义。通过对束流轨道变化的准确预测,可以为调整加速器控制参数提供可靠的信息,从而实现对束流的精确控制和调节。通过研究束流在直线加速器中等能量传输段的传输过程,利用模拟加速器数据,基于多级级联的反向传播(BP)神经网络搭建了加速器束流轨道预测模型,能够实现对束流轨道参数的预测。结果表明,与采用传统单隐层BP神经网络建立的预测模型相比,多级级联BP神经网络能够实现更高的预测精度与可靠性,为直线加速器中等能量传输段的优化设计和束流轨道自动化校准提供了一种有效的方法。
-
关键词:
- 加速器驱动次临界系统 /
- 中等能量传输段 /
- 级联网络 /
- 反向传播神经网络 /
- 束流轨道预测
Abstract: Since accelerator beam orbit correction is crucial for stable operation of accelerators, accurate prediction of the changes of the accelerator beam orbit is also essential for automated beam calibration. Precise predictions of beam orbit changes can provide reliable information for adjusting accelerator control parameters to achieve precise control and regulation of beam orbit. In this paper, based on a multi-stage cascaded back propagation (BP) neural network and simulated accelerator data, the beam transport process in the medium energy transfer section of a linear accelerator is studied and an accelerator beam orbit prediction model is constructed to predict beam orbit parameters. The results show that the proposed multi-stage cascaded BP neural network achieves higher prediction accuracy and reliability than the prediction model built using a traditional single hidden layer BP neural network. This provides an effective method for optimally designing the medium energy transfer section of the linear accelerator and automating the calibration of the beam orbit. -
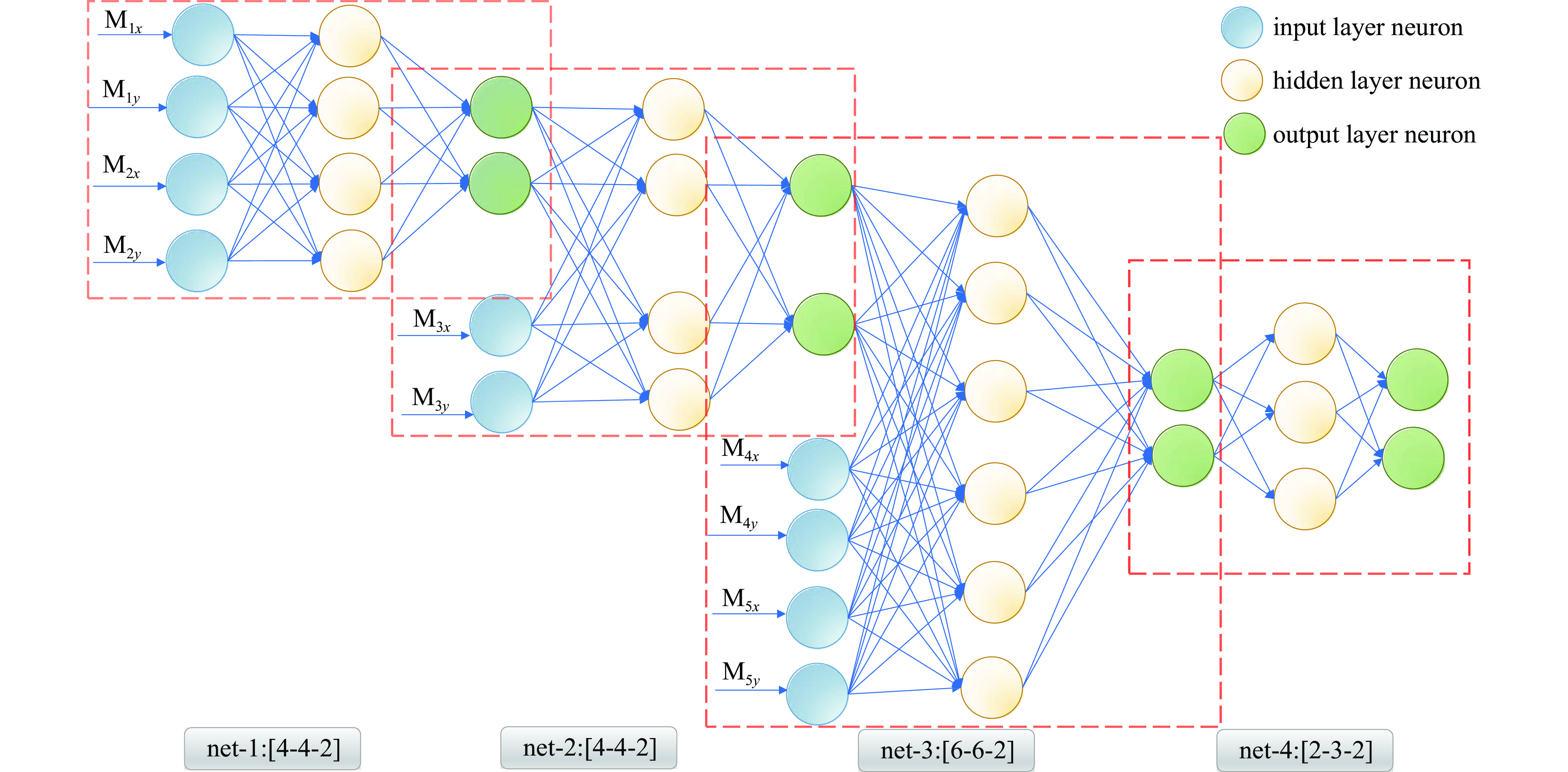
表 1 级联模型中各级BP神经网络结构
Table 1. BP neural network structure at all levels in the cascade model
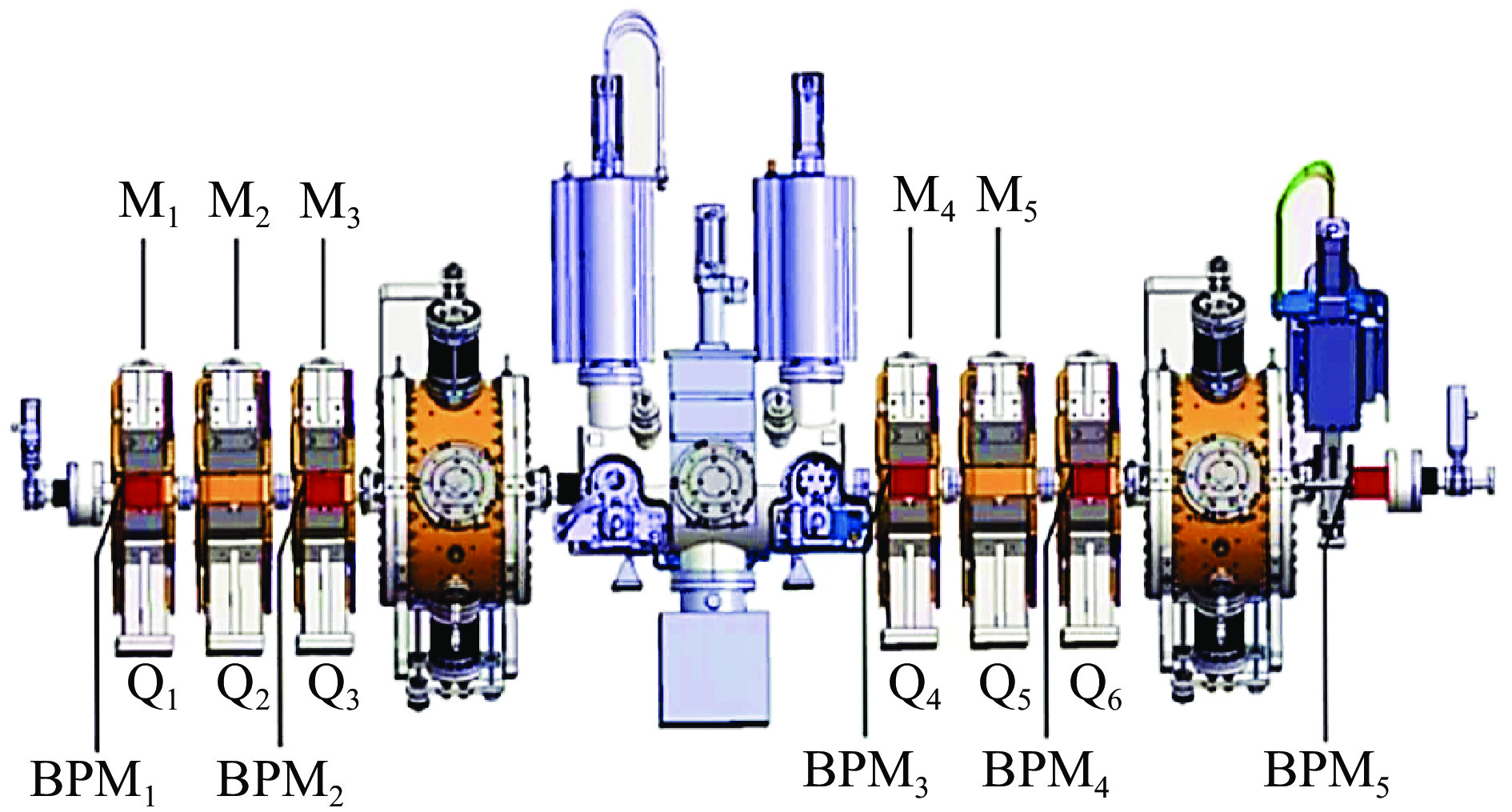
net input number of neurons in hidden layer output 1 M1, M2 4 BPM2 2 BPM2, M3 4 BPM3 3 BPM3, M4, M5 6 BPM4 4 BPM4 3 BPM5 算法1:多级级联BP神经网络算法 输入:Data的训练集和验证集;学习率η;迭代次数Epochs;批次大小Batch Size 1. 在(0,1)范围内随机初始化网络中的连接权和偏置; 2. 构建第一个网络的训练集Data-1:[(M1,M2), BPM2]; 3. for Epochs 4. for all [(M1, M2), BPM2]∈ Data-1 do: 5. 训练第一个网络: 6. 前向传播,根据公式(3)、(4)得到输出${\text{BPM}}_2'$;根据公式(4)计算误差L-1; 7. 定义一个类似指针的变量:start_idx,根据Batch Size标记抽取样本的位置; 8. 取Batch Size个样本的BPM3信息,构建第二个网络的输入[(${\text{BPM}}_2'$, M3),BPM3]; 9. 训练第二个网络:(得到输出$ {\text{BPM}}_3' $;误差L-2) 10. 重复步骤5-8,依次构建并训练第三个和第四个网络; 11. 所有网络完成一个批次训练后,反向传播误差,更新连接权和偏置; 12. end for 13. 每轮训练完成后,利用验证集检验; 14. until 达到停止条件 输出:连接权和偏置确定的4个BP神经网络 表 2 学习率及迭代次数选择
Table 2. Learning rate and epochs selection
No. learning rate epochs batch size number of neurons in hidden layer passing rate/% prediction accuracy/mm training time/s 1 0.01 1000 64 14 97.2 0.038 286.42 2 0.005 1000 64 14 97.9 0.032 298.74 3 0.001 1000 64 14 95.8 0.047 293.56 表 3 隐藏层神经元个数及训练批次大小选择
Table 3. Number of hidden layer neurons and training batch size selection
No. learning rate epochs batch size number of neurons in
hidden layerpassing rate/% prediction
accuracy/mmtraining time/s 1 0.005 1000 64 9 97.3 0.036 296.42 2 0.005 1000 128 9 96.9 0.040 267.58 3 0.005 1000 256 9 95.7 0.048 251.24 4 0.005 1000 64 14 97.9 0.032 298.74 5 0.005 1000 128 14 97.2 0.036 263.51 6 0.005 1000 256 14 96.3 0.047 247.14 表 4 网络模型的预测能力及可靠性
Table 4. Comparison of the predictive power and reliability of network models
net name learning rate epochs batch size prediction accuracy of
BPM5/mmstandard deviation
of sampleresponse
time/sBP neural network 0.005 5000 64 0.151 0.389 0.002 multi-stage cascaded BP neural network 0.005 5000 64 0.135 0.368 0.001 -
[1] 肖国青, 徐瑚珊, 王思成. HIAF及CiADS项目进展与展望[J]. 原子核物理评论, 2017, 34(3):275-283Xiao Guoqing, Xu Hushan, Wang Sicheng. HIAF and CiADS national research facilities: progress and prospect[J]. Nuclear Physics Review, 2017, 34(3): 275-283 [2] 骆鹏, 王思成, 胡正国, 等. 加速器驱动次临界系统——先进核燃料循环的选择[J]. 物理, 2016, 45(9):569-577Luo Peng, Wang Sicheng, Hu Zhengguo, et al. Accelerator driven sub-critical systems——a promising solution for cycling nuclear fuel[J]. Physics, 2016, 45(9): 569-577 [3] 汪柏帆, 袁辰彰, 蔡汉杰, 等. CAFe DUMP前刮束器的设计研制[J]. 原子核物理评论, 2022, 39(3):326-333Wang Baifan, Yuan Chenzhang, Cai Hanjie, et al. Design and development of the collimator in front of the CAFe DUMP[J]. Nuclear Physics Review, 2022, 39(3): 326-333 [4] 陈伟龙. 基于束流损失控制的LEBT设计[D]. 兰州: 中国科学院研究生院(近代物理研究所), 2016: 53-55Chen Weilong. LEBT design based on beam loss control[D]. Lanzhou: Institute of Modern Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2016: 53-55 [5] 万金宇, 孙正, 张相, 等. 机器学习在大型粒子加速器中的应用回顾与展望[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2021, 33:094001 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202133.210199Wan Jinyu, Sun Zheng, Zhang Xiang, et al. Machine learning applications in large particle accelerator facilities: review and prospects[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2021, 33: 094001 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202133.210199 [6] Yang Xuhui, Zhou Qingguo, Wang Jinqiang, et al. Predictive control modeling of ADS’s MEBT using BPNN to reduce the impact of noise on the control system[J]. Annals of Nuclear Energy, 2019, 132: 576-583. doi: 10.1016/j.anucene.2019.06.034 [7] Bozoki E, Friedman A. Neural networks and orbit control in accelerators[R]. Washington: Brookhaven National Lab. , 1994. [8] Meier E, Morgan M J, Biedron S, et al. Electron beam energy stabilization using a neural network hybrid controller at the Australian Synchrotron Linac[C]//Particle Accelerator Conference. 2009: 1201-1203. [9] 李超, 张智磊, 齐新, 等. TOPOPIC对强流束流在周期FODO结构中的传输研究[J]. 原子核物理评论, 2015, 32(2):191-195Li Chao, Zhang Zhilei, Qi Xin, et al. High intensity beam transport study with TOPOPIC in FODO structure[J]. Nuclear Physics Review, 2015, 32(2): 191-195 [10] Sosa A G, Baron R, Danared H, et al. Status of testing and commissioning of the medium energy beam transport line of the ESS normal conducting LINAC[C]//Proceedings of the 31st Linear Accelerator Conference. 2022: 376-379. [11] 周浩. 加速器束流诊断中数字BPM系统研究[D]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学, 2009: 1-2Zhou Hao. Research on DBPM system in accelerator beam diagnosis[D]. Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China, 2009: 1-2 [12] 袁任贤, 叶恺容. 束流位置探头的理论设计[J]. 核技术, 2003, 26(4):261-265Yuan Renxian, Ye Kairong. Design of beam position monitor[J]. Nuclear Techniques, 2003, 26(4): 261-265 [13] Chen Xiaolong, Jia Yongzhi, Qi Xin, et al. Orbit correction based on improved reinforcement learning algorithm[J]. Physical Review Accelerators and Beams, 2023, 26: 044601. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevAccelBeams.26.044601 [14] 魏源源, 秦庆. 响应矩阵分析方法在BEPC储存环上的应用[J]. 高能物理与核物理, 2006, 30(s1):43-45Wei Yuanyuan, Qin Qing. Application of response matrix at the BEPC storage ring[J]. High Energy Physics and Nuclear Physics, 2006, 30(s1): 43-45 [15] 李京纬, 刘祖平, 王筠华. 合肥光源电子储存环束流闭轨的局部校正[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 1998, 10(2):291-295Li Jingwei, Liu Zuping, Wang Yunhua. Local correction of electron beam closed orbit in HLS storage ring[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 1998, 10(2): 291-295 [16] 张峡, 黄团华, 赵晓岩. 基于遗传算法进行加速器自动调束[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2004, 16(9):1222-1224Zhang Xia, Huang Tuanhua, Zhao Xiaoyan. Automatic beam tuning in accelerator based on genetic algorithms[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2004, 16(9): 1222-1224 [17] Rumelhart D E, Hinton G E, Williams R J. Learning representations by back-propagating errors[J]. Nature, 1986, 323(6088): 533-536. doi: 10.1038/323533a0 [18] 鲁智勇, 张权, 张希, 等. 等效分组级联BP网络模型及其应用[J]. 电子学报, 2010, 38(6):1349-1354Lu Zhiyong, Zhang Quan, Zhang Xi, et al. Equivalent grouping-cascaded BP network model and its applications[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2010, 38(6): 1349-1354 [19] Heaton J. Introduction to neural networks with Java[M]. 2nd ed. St Louis: Heaton Research, 2008: 159. -




 下载:
下载: