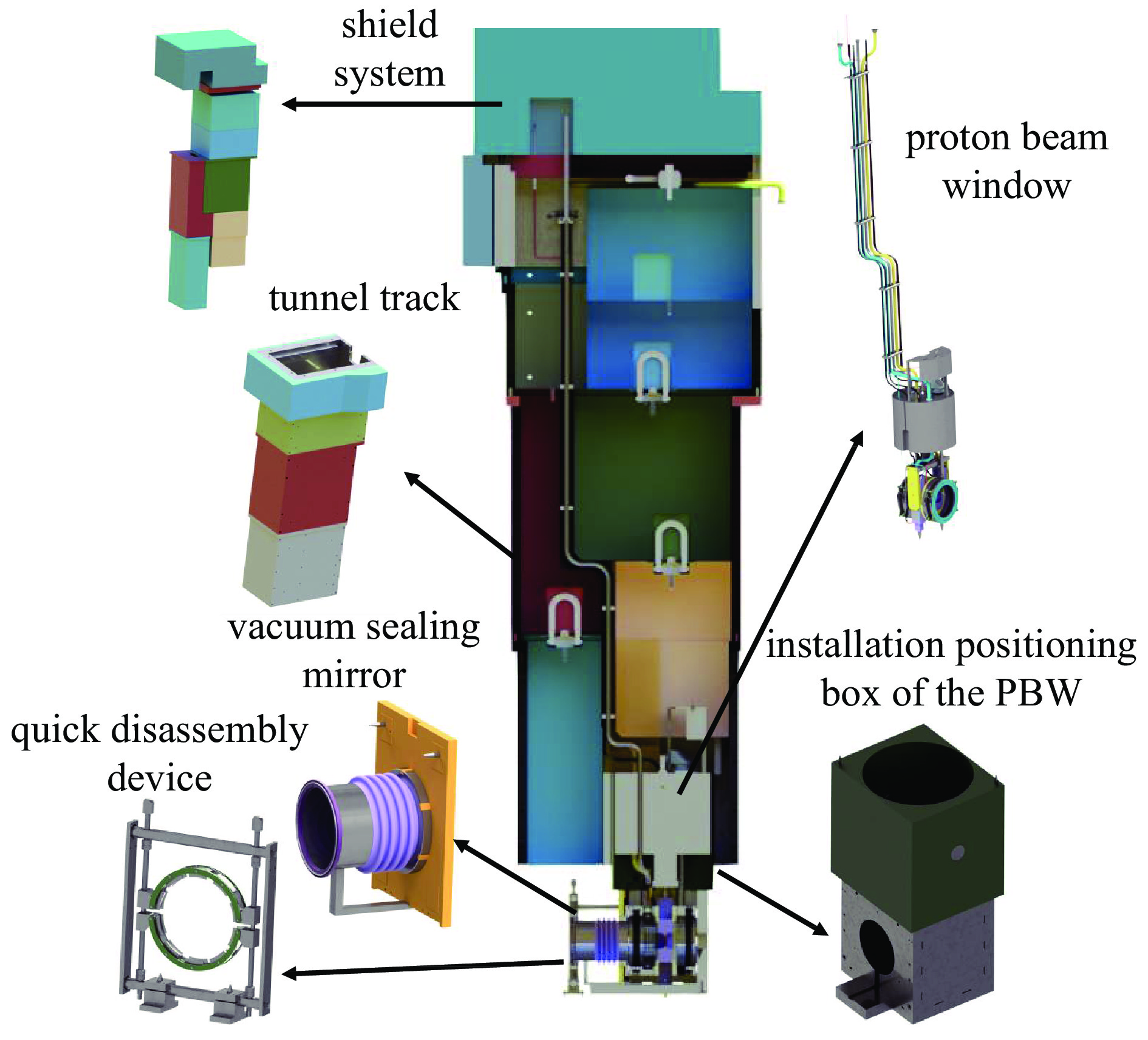
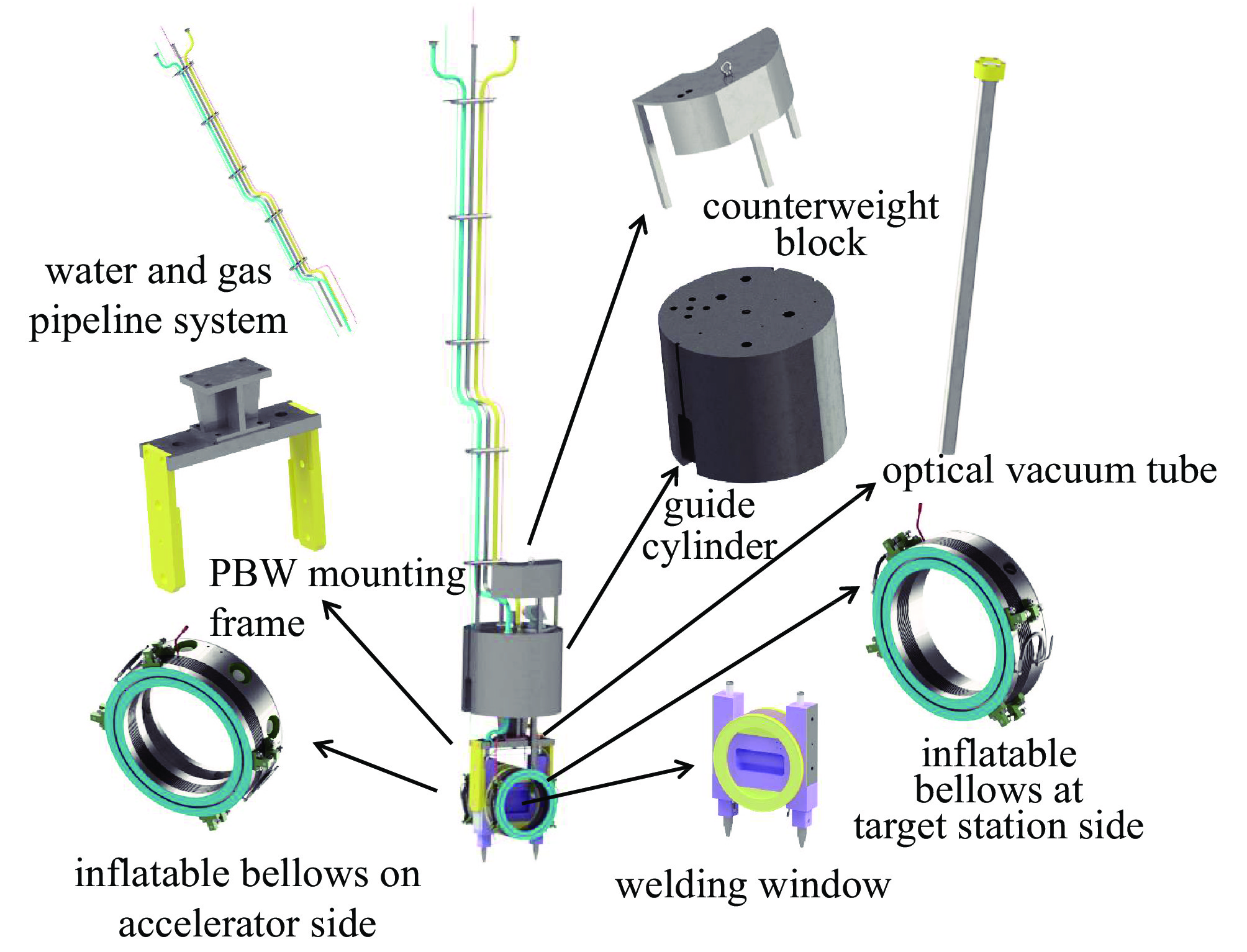
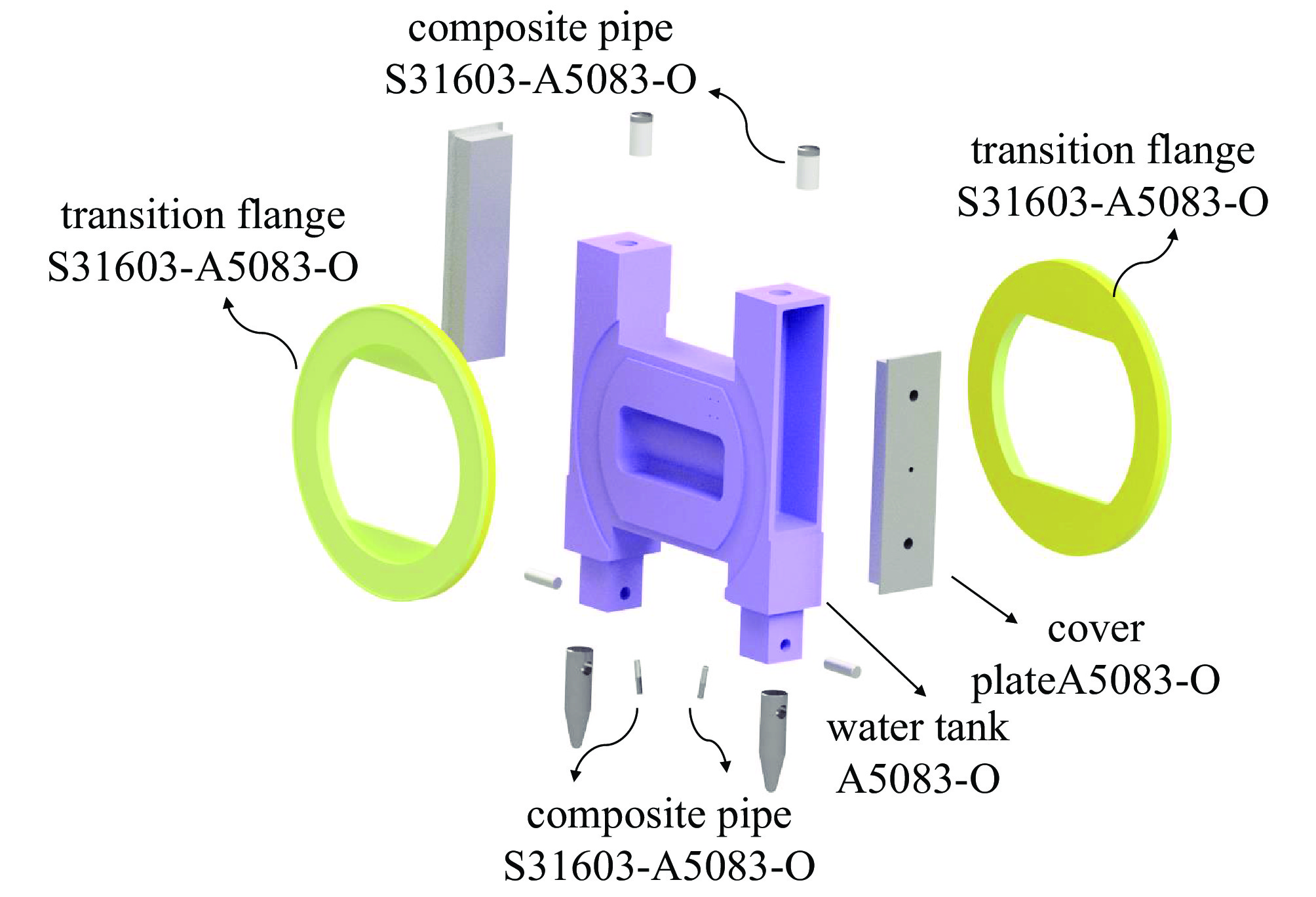
Structure design and optimization analysis of proton beam window in target station for CSNS-II
-
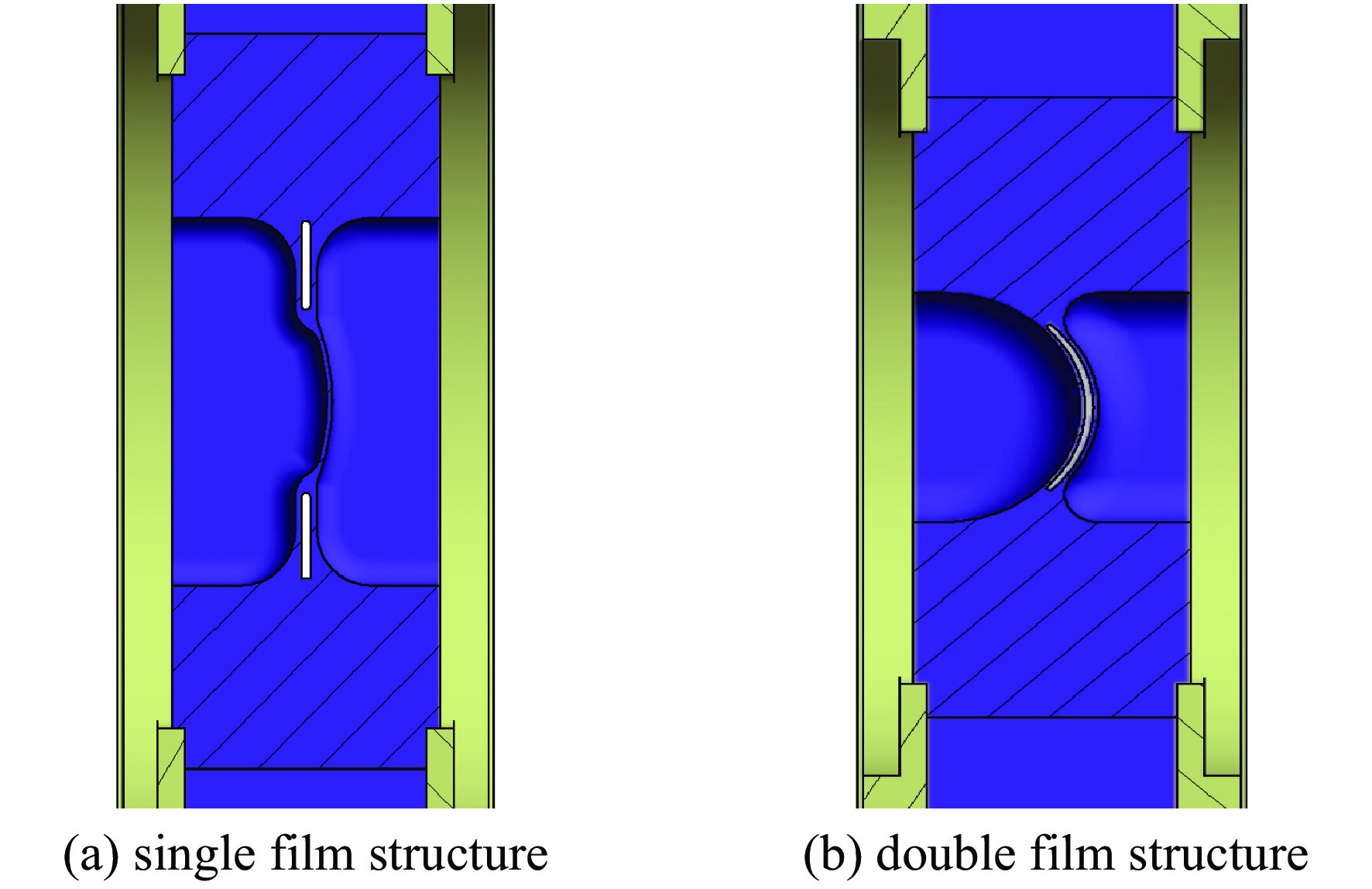
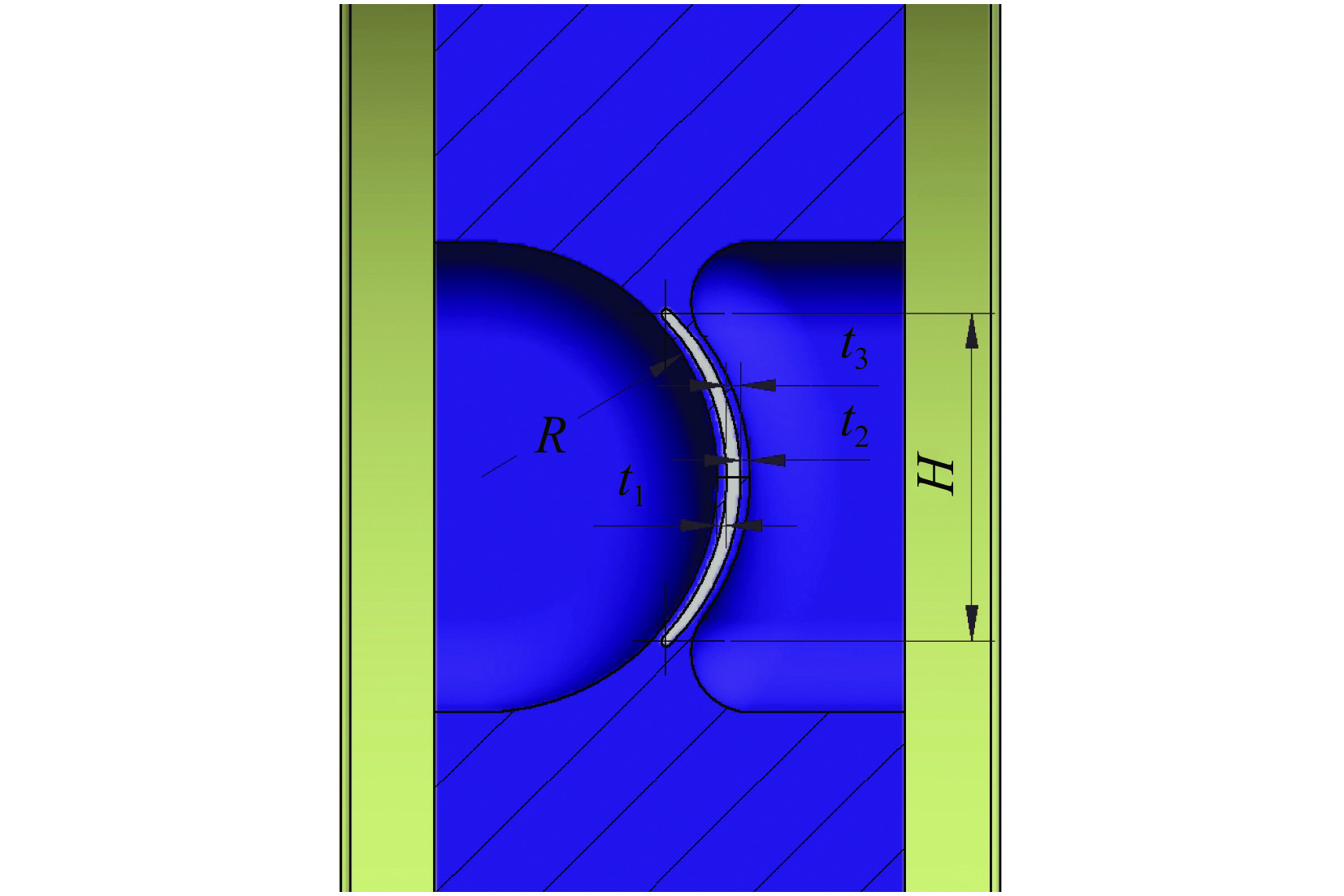
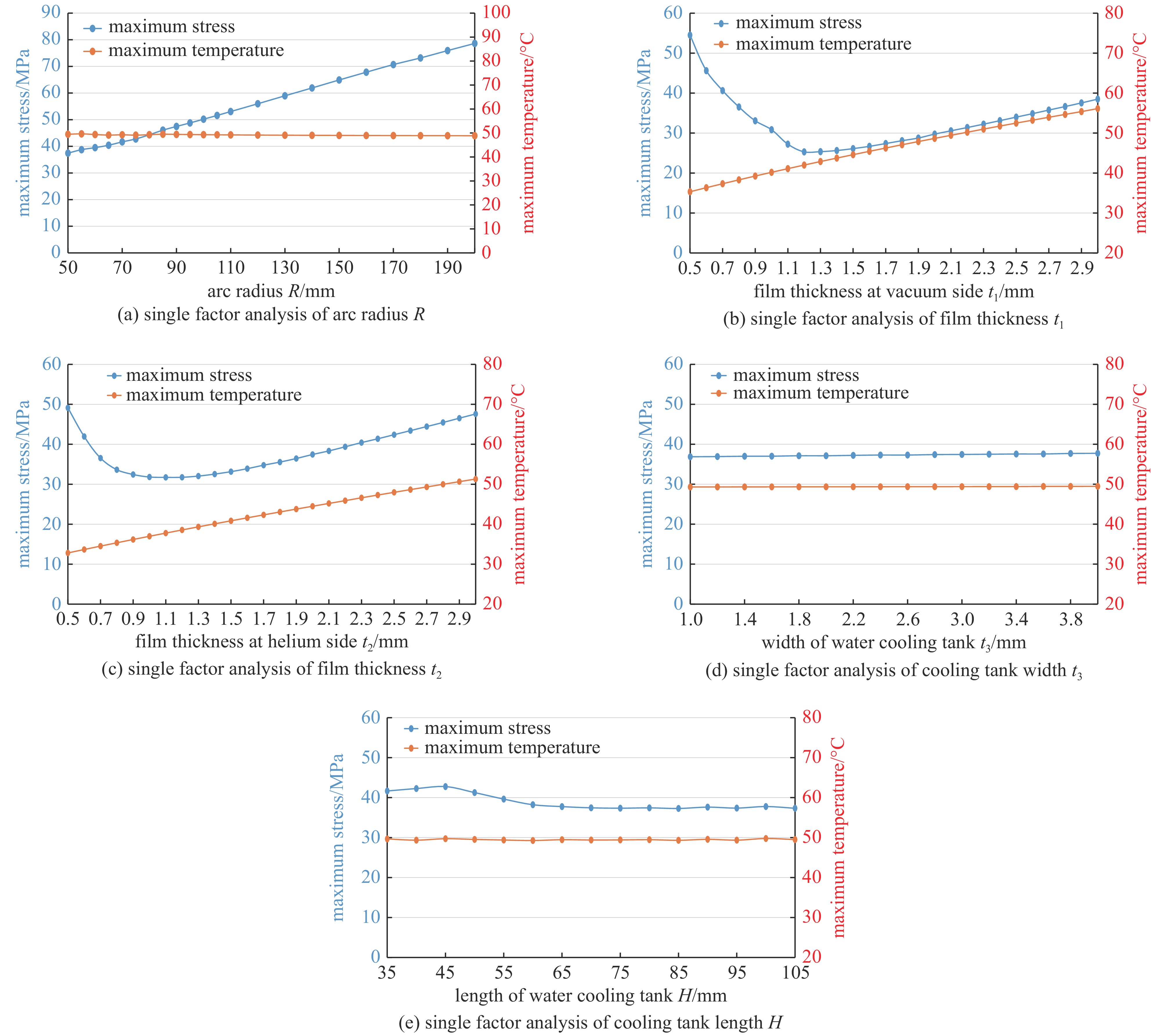
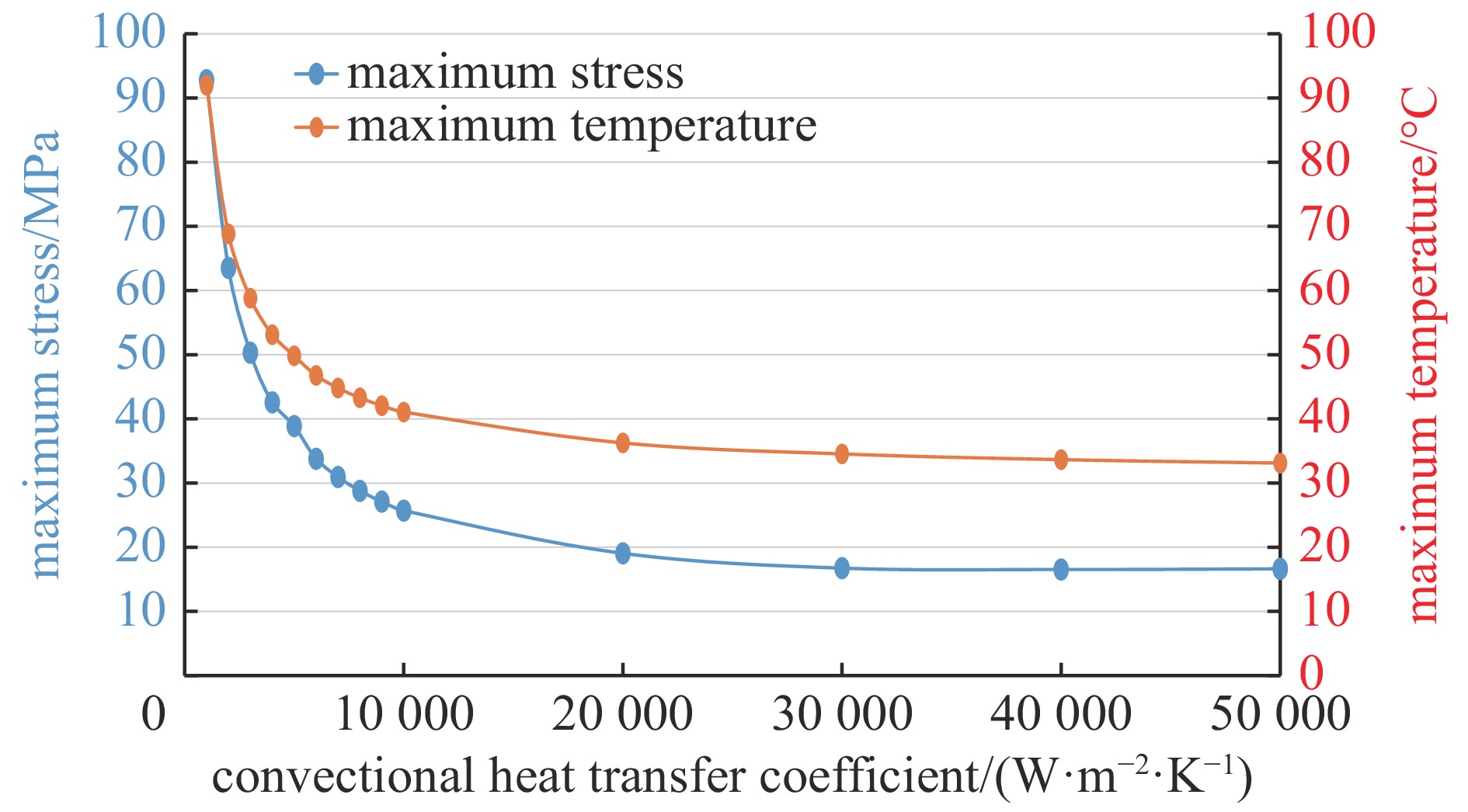
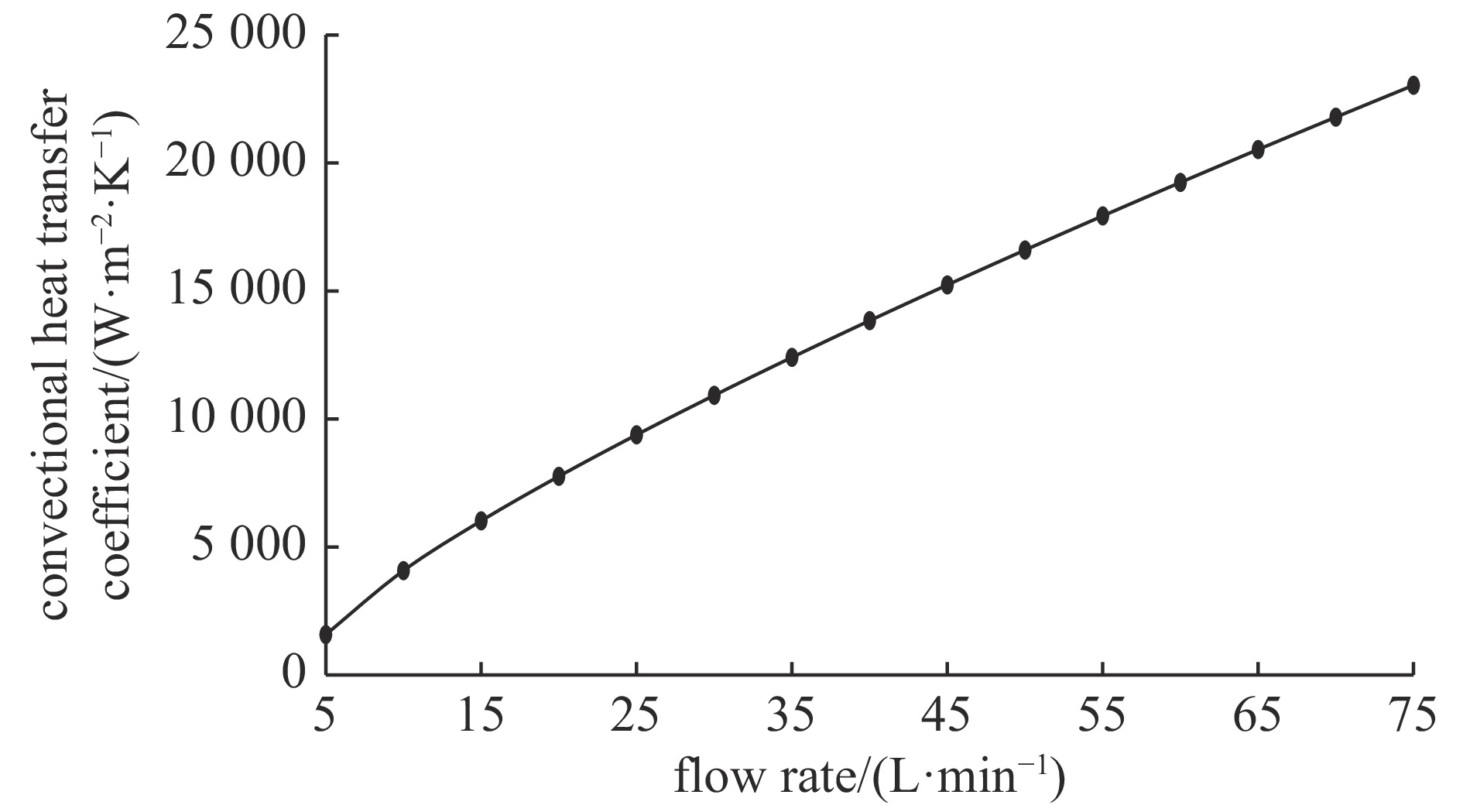
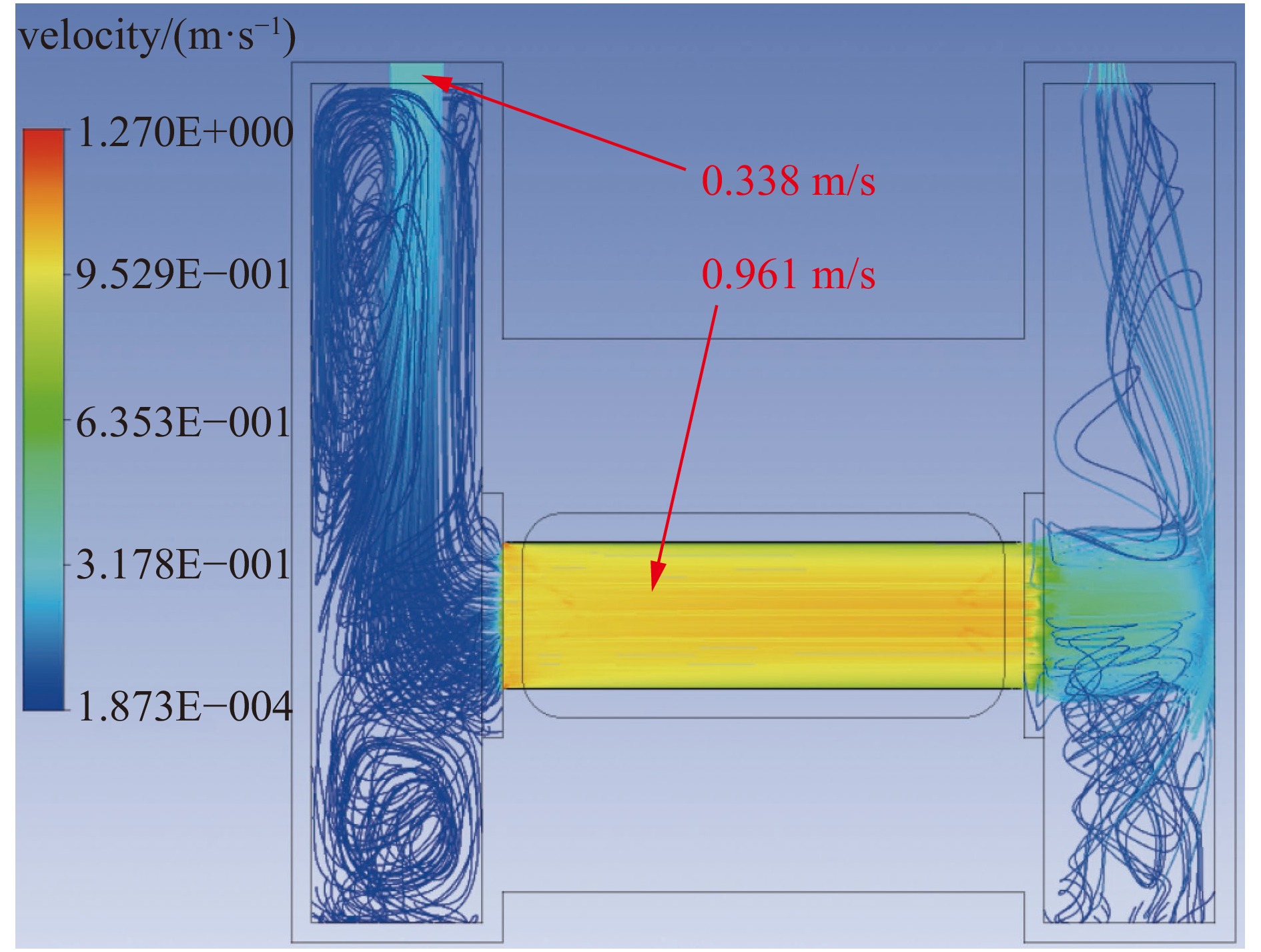
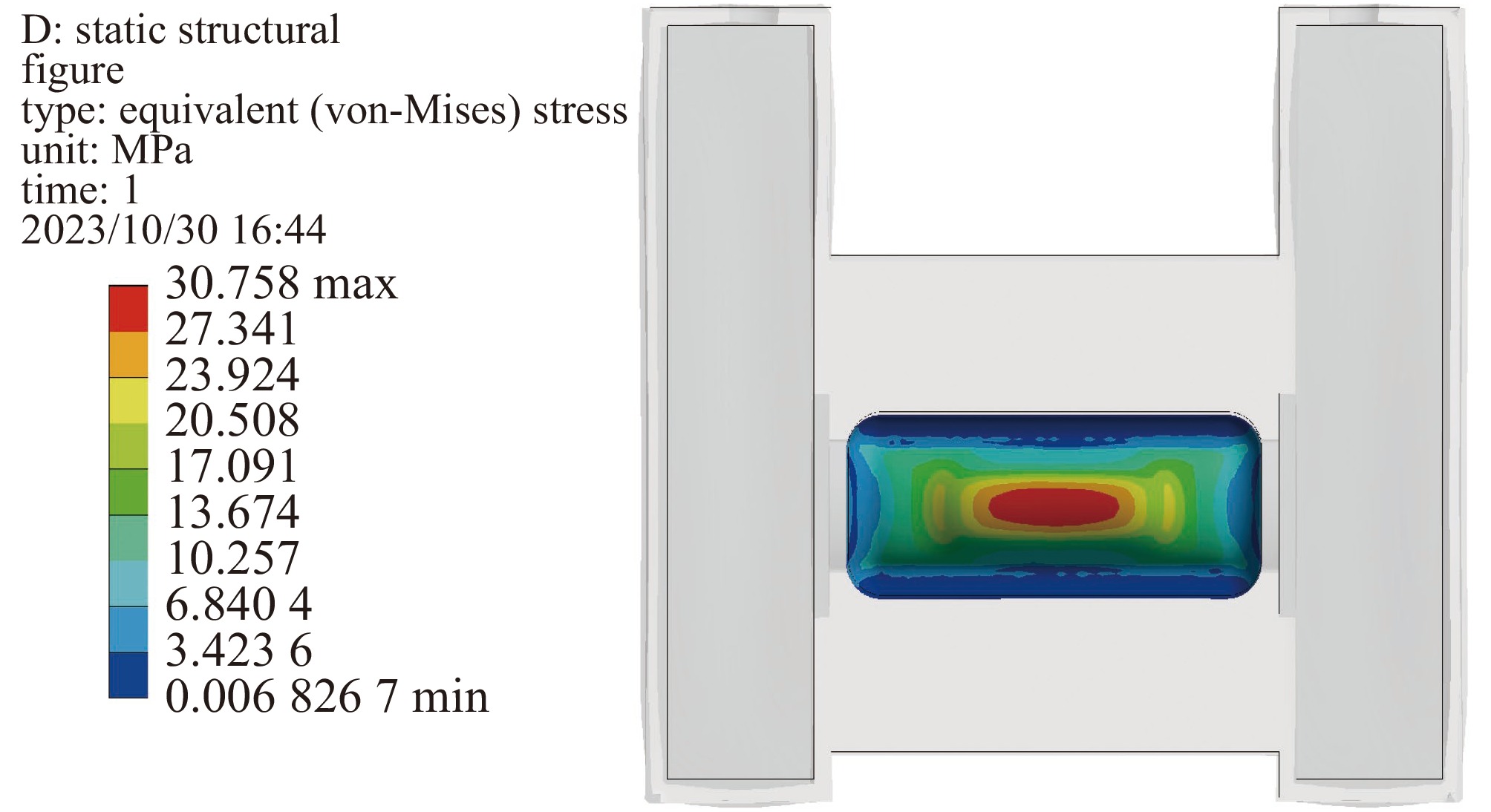
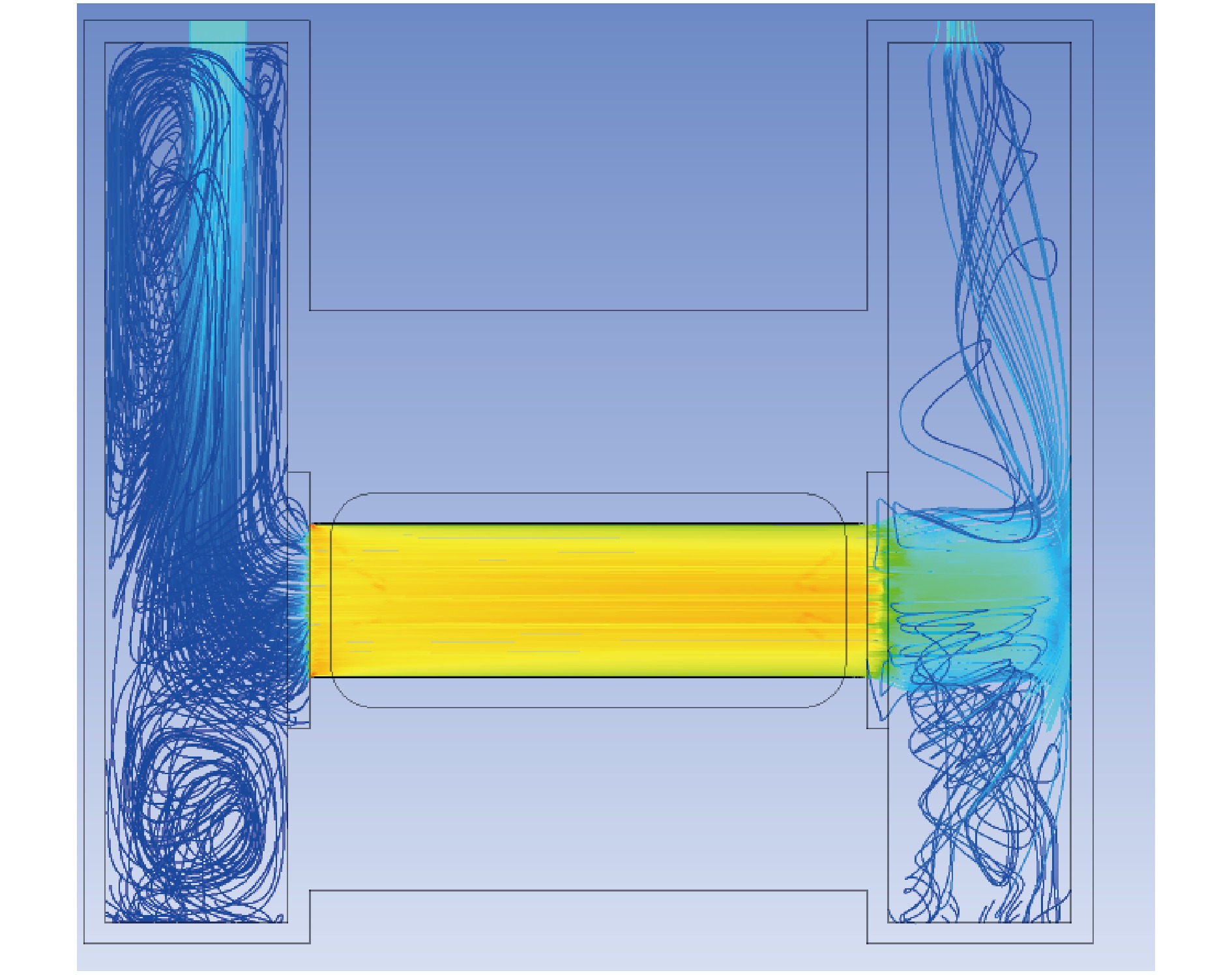
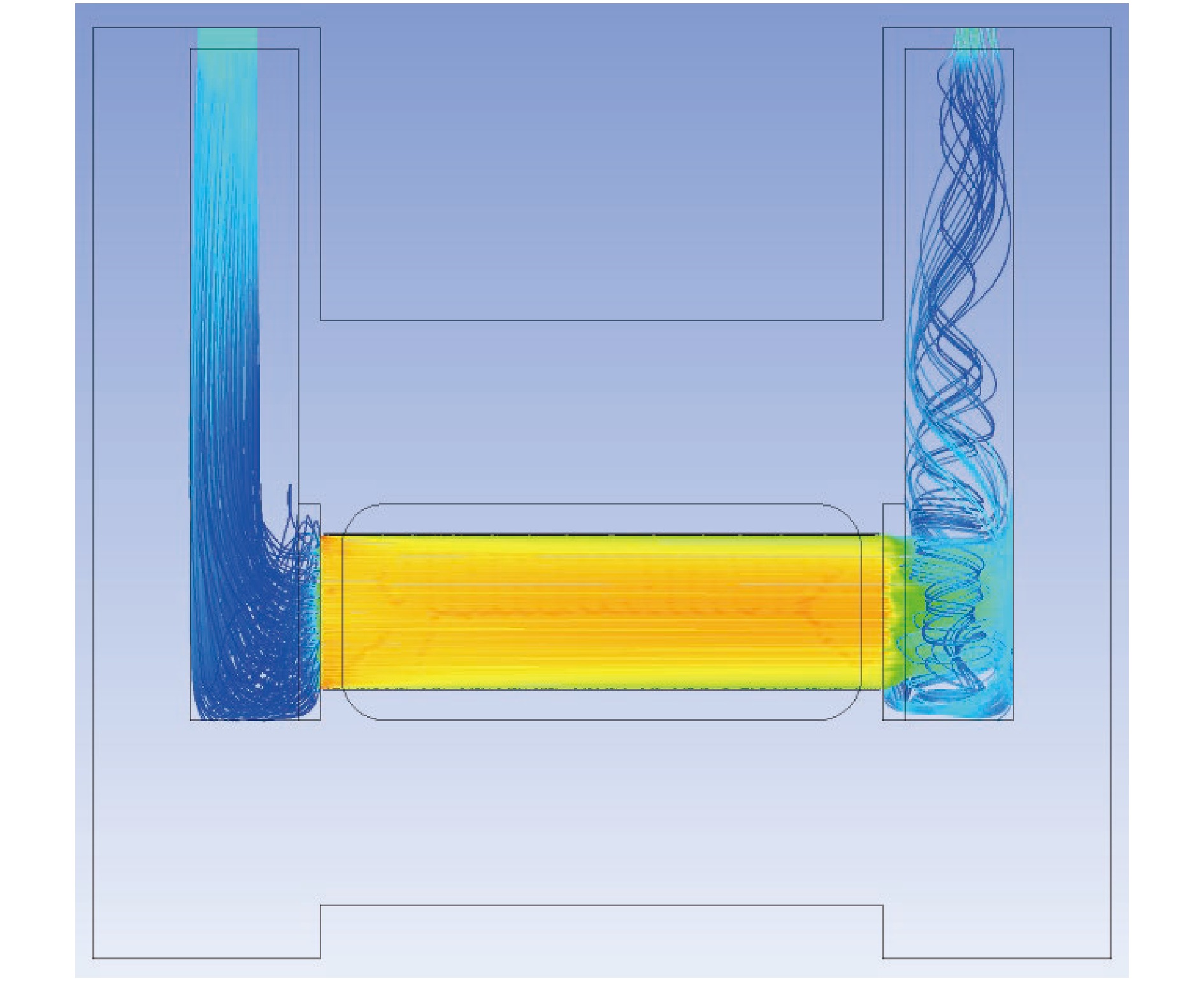
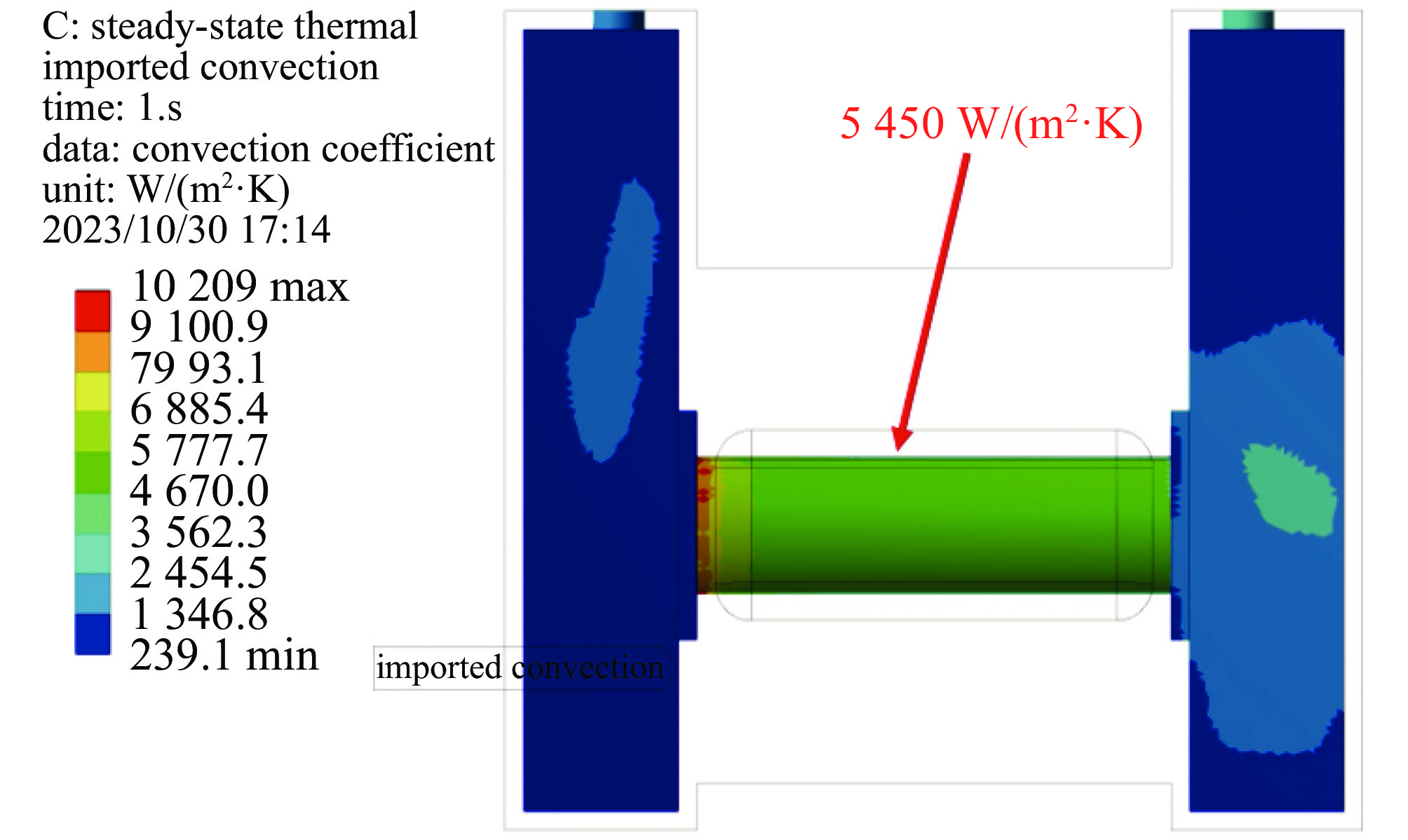
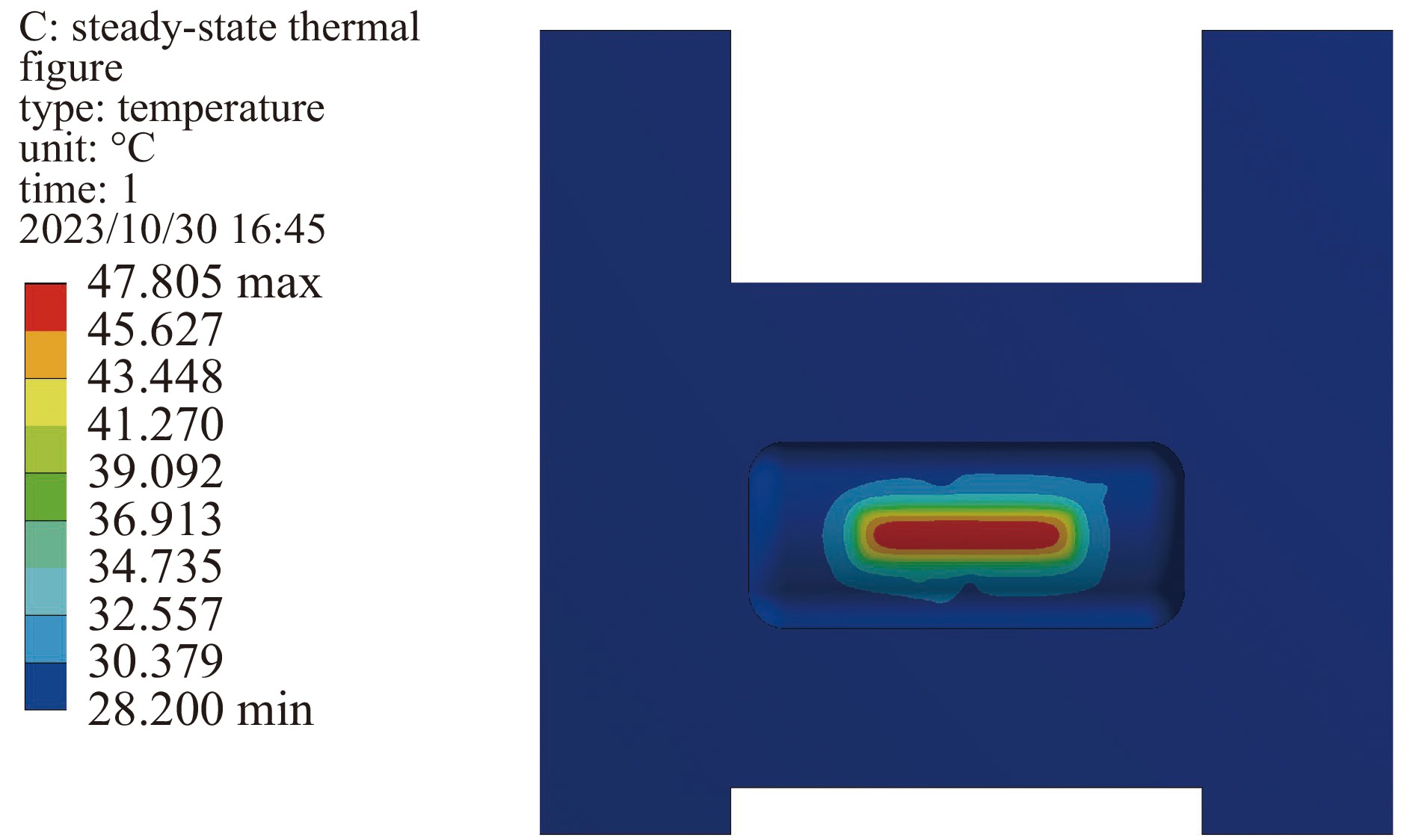
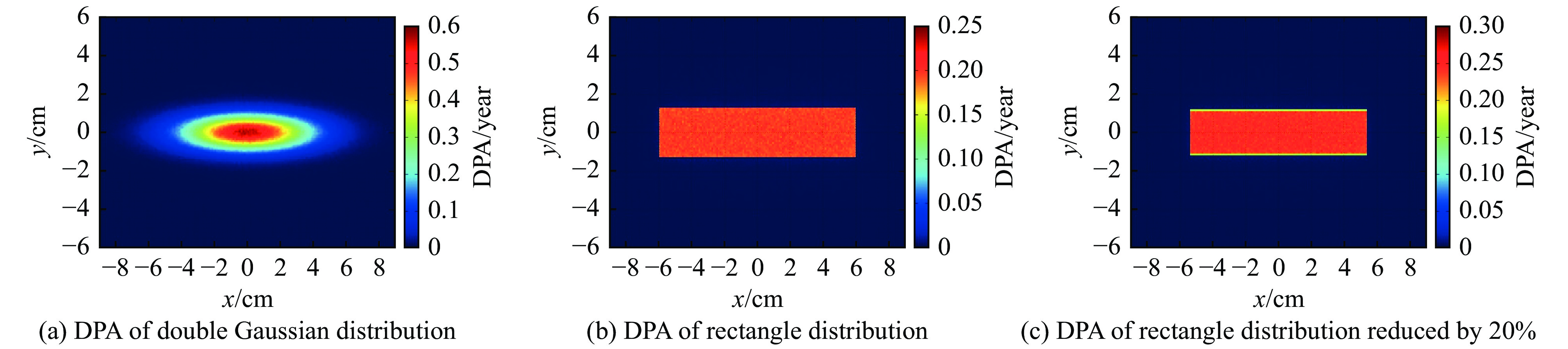
摘要: 中国散裂中子源(CSNS)靶站质子束窗位于环到靶站输运线(RTBT)与靶站交接面,起到隔离加速器高真空和靶站氦气环境的作用。随着束流功率提高,目前质子束窗单层膜结构形式已无法满足CSNS-II 500 kW的高功率需求,因此开展CSNS-II质子束窗研制,设计出双层膜中间通水的冷却结构,完成质子束窗双层膜的薄膜半径、薄膜厚度、水冷槽长度与宽度、对流换热系数等各参数对质子束窗温升与热应力的影响分析。通过冷却水需求分析得出,冷却水流速需大于15 L/min。通过质子束窗主体的流固耦合分析,消除箱体内部死水区域。最终优化后质子束窗薄膜位置最高温度47.8 ℃,薄膜位置最高热应力30.758 MPa。通过FLUKA软件对质子束窗材料的辐照损伤性能进行分析,在每年5000 h工作时长、500 kW高功率束流的辐照下,辐照损伤DPA计算值为1.285 DPA,质子束窗的安全使用寿命在7年以上。Abstract: The proton beam window of the CSNS target station is located at the interface between the Ring to Target Beam Transport (RTBT) line and the target station, which can isolate the high vacuum of the accelerator and the helium environment of the target station. With the increase of the beam power of CSNS-II, the single-layer film structure of the proton beam window can no longer meet the high power of 500 kW, so the upgrading and development of the CSNS-II proton beam window are carried out. The structure design of the CSNS-II proton beam window is emphasized, and the cooling structure with water in the middle of the double-layer membrane is designed. The influence of the parameters of proton beam window, such as film radius, film thickness, length and width of water cooling tank, and convection heat transfer coefficient, on the temperature rise and thermal stress of the proton beam window was analyzed. Analysis on cooling water demand shows that the cooling water flow rate should be greater than 15 L/min. Through the fluid structure coupling analysis of the main body of the proton beam window, the dead water area inside the box is eliminated. The maximum temperature of the optimized proton beam window film is 47.8 ℃. The maximum thermal stress at the film position is 30.758 MPa. The radiation damage performance of proton beam window material is analyzed by FLUKA software. Under the irradiation of 5000 h of operation per year and 500 kW high power beam current, the calculated value of DPA of radiation damage per year is 1.285 DPA, and the life of proton beam window is more than 7 years.
-
表 1 不同功率束窗的功率损失及热应力
Table 1. Power loss and thermal stress of PBWs under different beam power
beam power/kW lost power/W maximum temperature/℃ maximum stress/MPa 100 67.5 61.7 58.9 170 114.0 83.8 80.1 200 135.0 93.4 93.4 240 162.0 106.1 110.4 300 202.0 125.0 136.0 500 337.5 195.1 230.6 -
[1] Wei Jie, Chen Hesheng, Chen Yanwei, et al. China Spallation Neutron Source: design, R&D, and outlook[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 2009, 600(1): 10-13. [2] Wei Jie, Fu Shinian, Tang Jingyu, et al. China Spallation Neutron Source—an overview of application prospects[J]. Chinese Physics C, 2009, 33(11): 1033-1042. doi: 10.1088/1674-1137/33/11/021 [3] Wang Sheng, Fang Shouxian, Fu Shinian, et al. Introduction to the overall physics design of CSNS accelerators[J]. Chinese Physics C, 2009, 33(S2): 1-3. doi: 10.1088/1674-1137/33/S2/001 [4] Chen Hesheng, Wang Xunli. China's first pulsed neutron source[J]. Nature Materials, 2016, 15(7): 689-691. doi: 10.1038/nmat4655 [5] Liu Huachang, Peng Jun, Gong Keyun, et al. The design and construction of CSNS drift tube linac[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 2018, 911: 131-137. [6] Wang Haijing, Liu Weibin, Qu Huamin, et al. Thermal analysis and optimization of proton beam window for the CSNS[J]. Chinese Physics C, 2013, 37: 077001. doi: 10.1088/1674-1137/37/7/077001 [7] 王梓豪, 屈化民, 朱东辉, 等. 环-靶站输运线末端准直器的研究[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2015, 27:055104 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20152705.55104Wang Zihao, Qu Huamin, Zhu Donghui, et al. Collimator at end of ring to target beam transport[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2015, 27: 055104 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20152705.55104 [8] Wang Haijing, Zhu Donghui, Qu Huamin, et al. Material test of proton beam window for CSNS[C]//Proceedings of the 6th International Particle Accelerator Conference. 2015: 2927-2930. [9] 朱道义, 孙红, 吴洪特. 套管换热器的强化效果试验研究[J]. 长江大学学报(自然科学版), 2010, 7(3):197-199Zhu Daoyi, Sun Hong, Wu Hongte. Experimental study on the effect of enhanced heat transfer in tube-in-tube heat exchanger[J]. Journal of Yangtze University (Natural Science Edition), 2010, 7(3): 197-199 [10] 解元玉. 基于ANSYS Workbench的流固耦合计算研究及工程应用[D]. 太原: 大原理工大学, 2011Xie Yuanyu. FSI calculation of research based on ANSYS Workbench and engineering applications[D]. Taiyuan: Taiyuan University of Technology, 2011 [11] 王福军. 计算流体动力学分析——CFD软件原理与应用[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2004Wang Fujun. Computational fluid dynamics analysis—principles and applications of CFD software[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2004 [12] 于全芝, 殷雯, 梁天骄. 中国散裂中子源靶站重要部件的辐照损伤计算与分析[J]. 物理学报, 2011, 60:052501 doi: 10.7498/aps.60.052501Yu Quanzhi, Yin Wen, Liang Tianjiao. Calculation and analysis of DPA in the main components of CSNS target station[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2011, 60: 052501 doi: 10.7498/aps.60.052501 [13] Korkut T, Korkut H. FLUKA simulations of DPA in 6h–SiC reactor blanket material induced by different radiation fields frequently mentioned in literature[J]. Journal of Fusion Energy, 2013, 32(1): 66-70. doi: 10.1007/s10894-012-9525-5 [14] Harada M, Watanabe N, Konno C, et al. DPA calculation for Japanese spallation neutron source[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2005, 343(1/3): 197-204. [15] Meigo S I, Ooi M, Harada M, et al. Radiation damage and lifetime estimation of the proton beam window at the Japan Spallation Neutron Source[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2014, 450(1/3): 141-146. -





 下载:
下载: