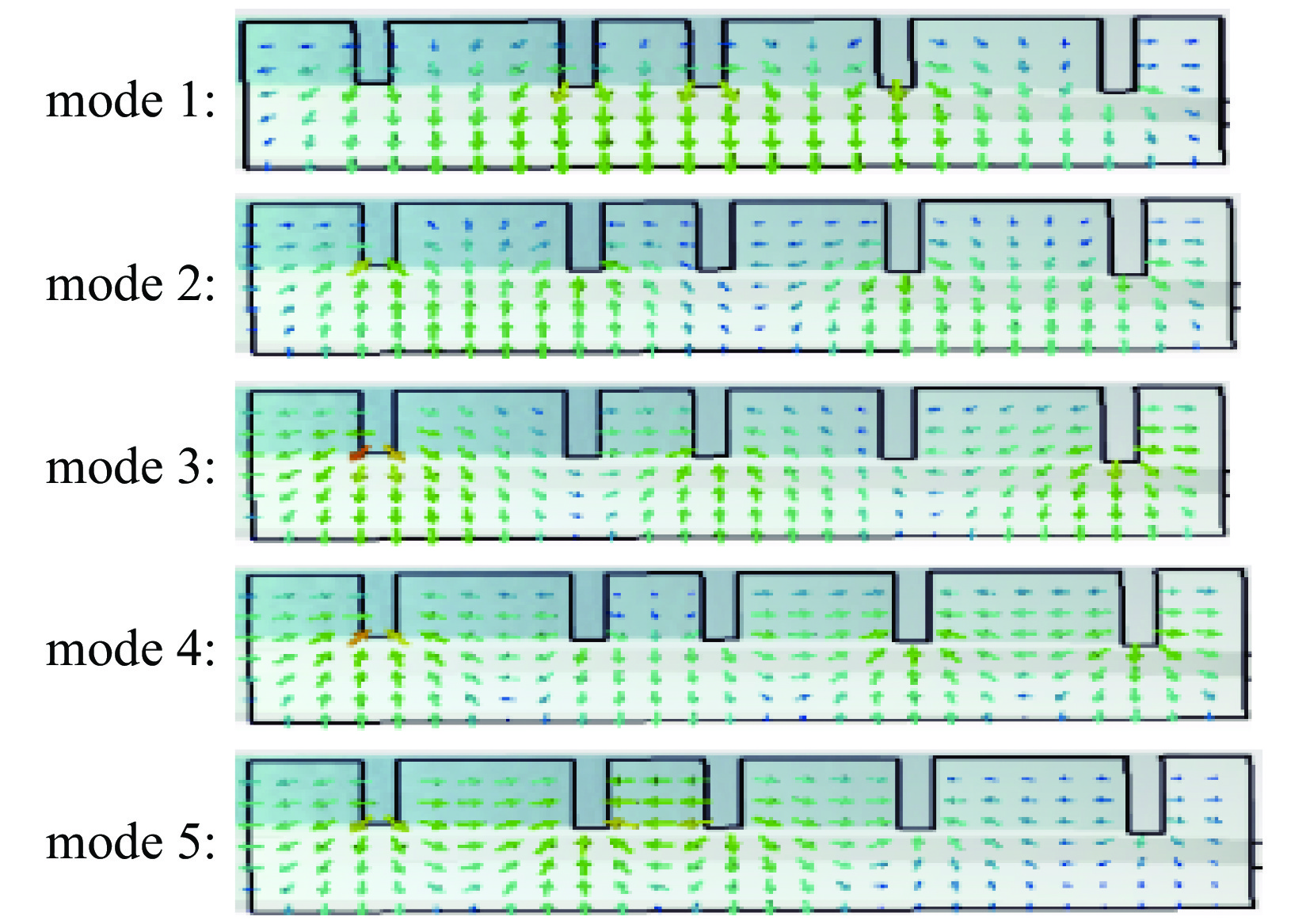
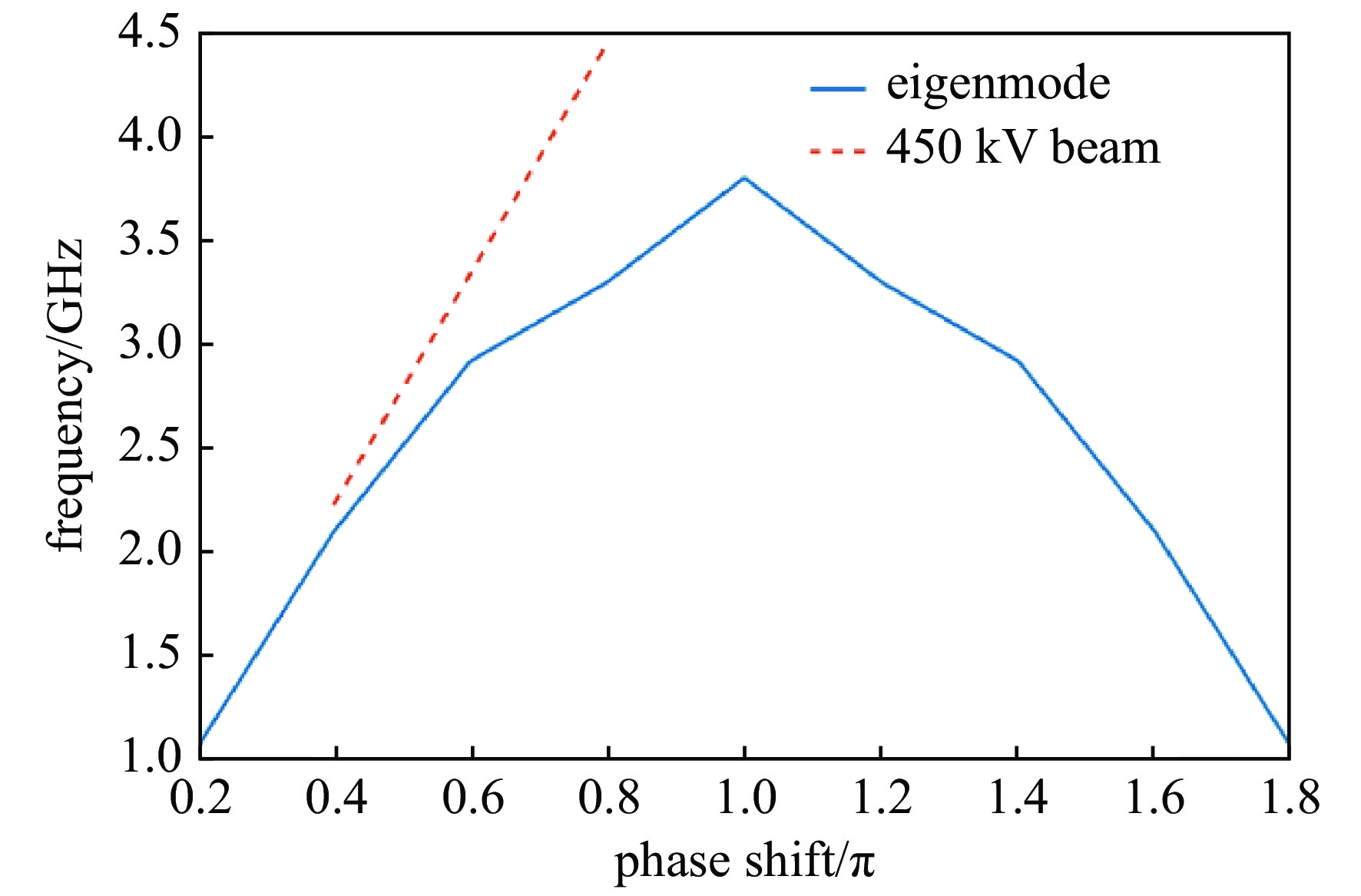
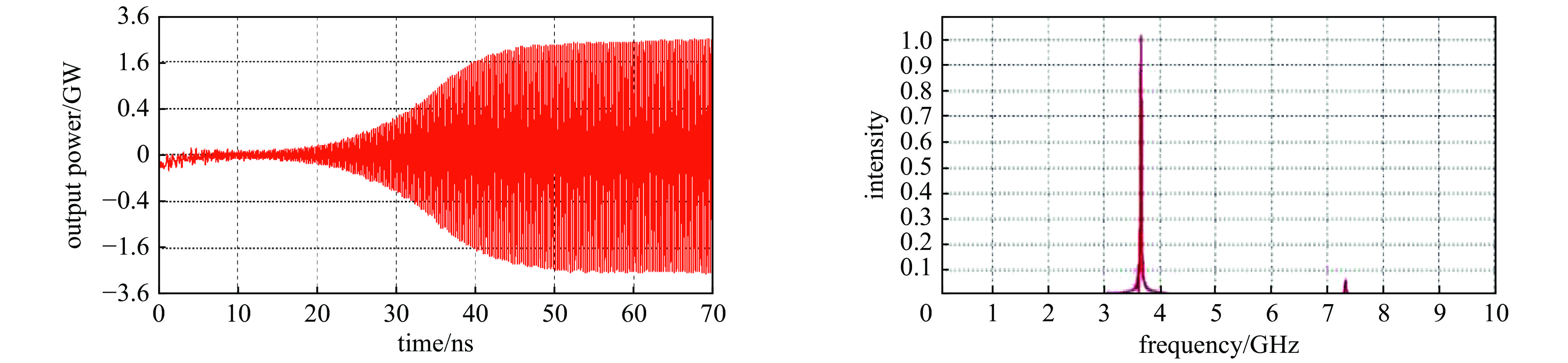
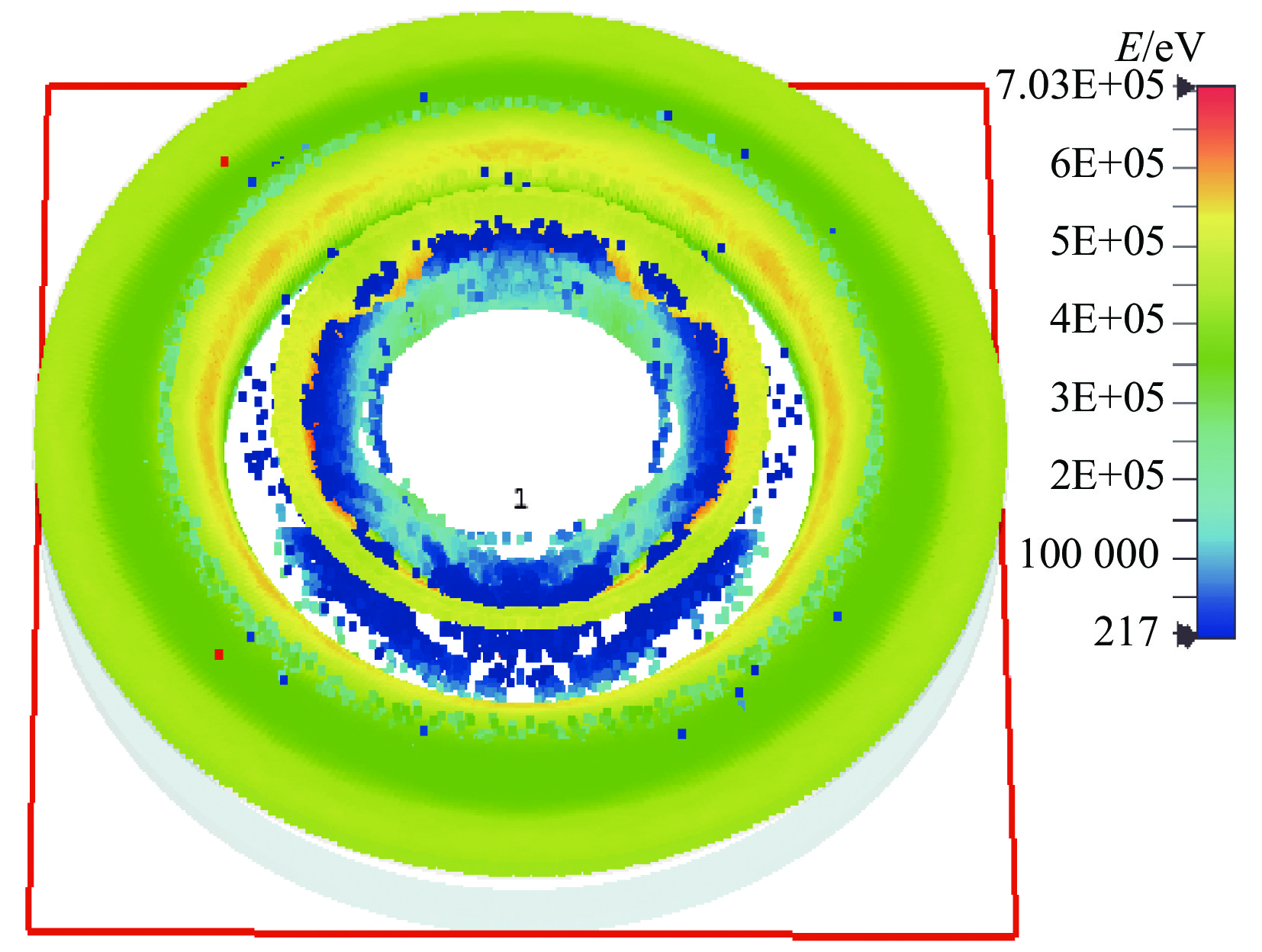
-
摘要:
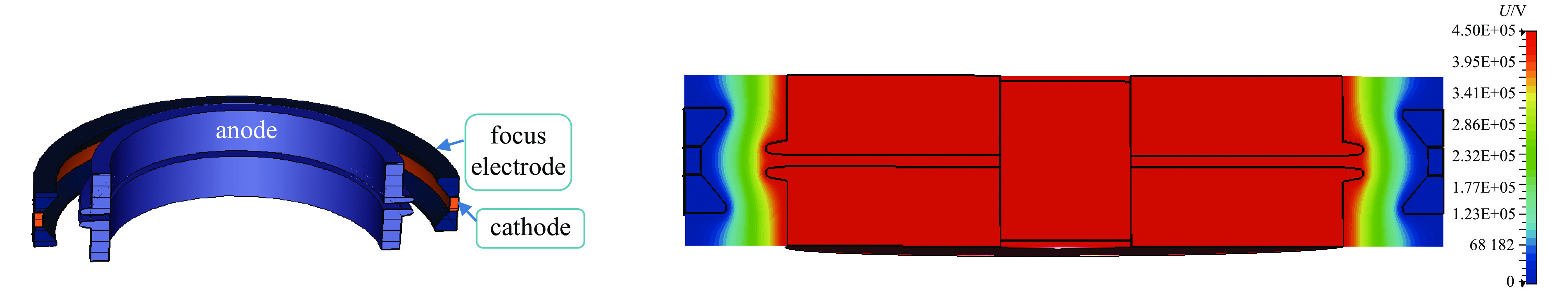
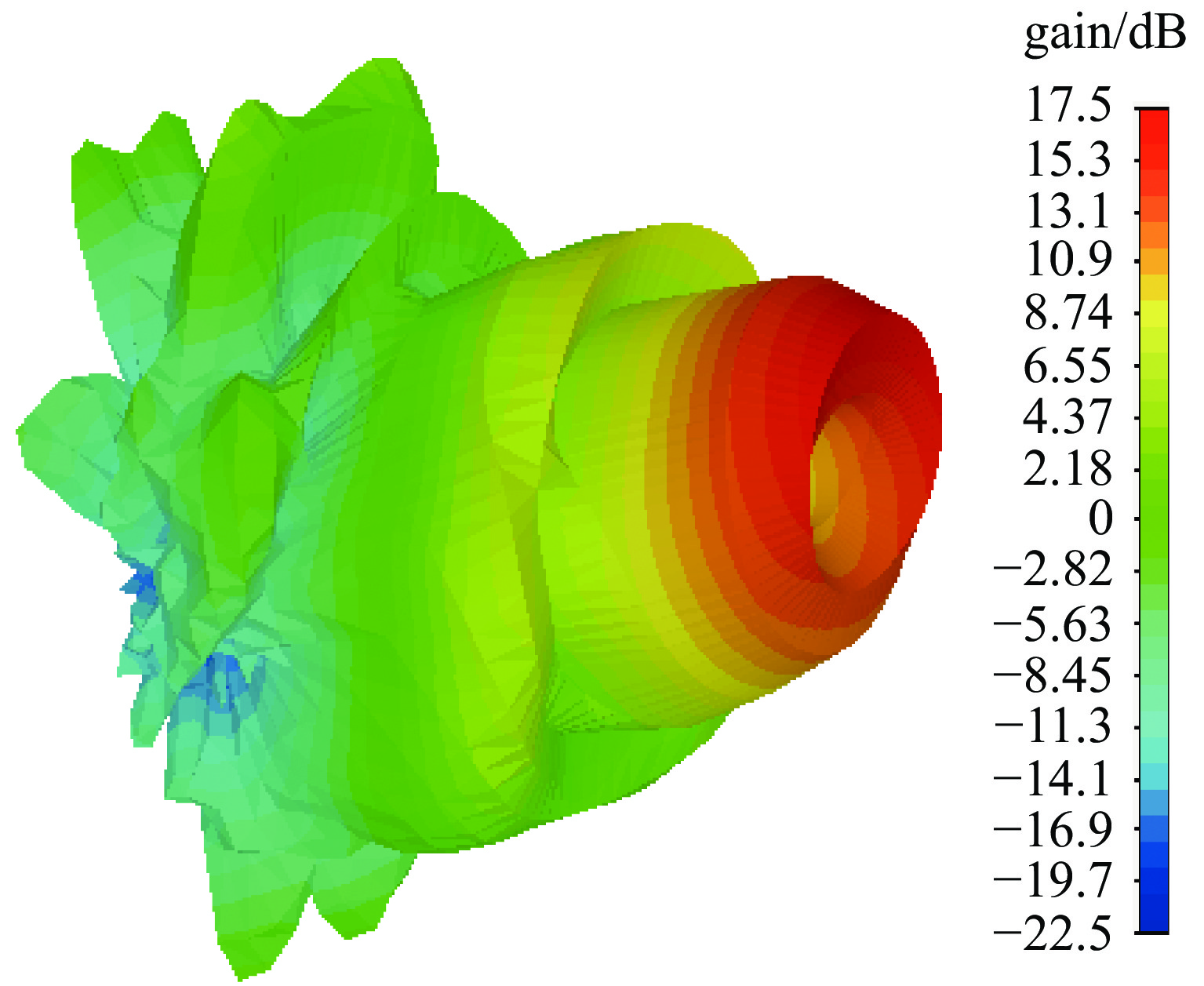
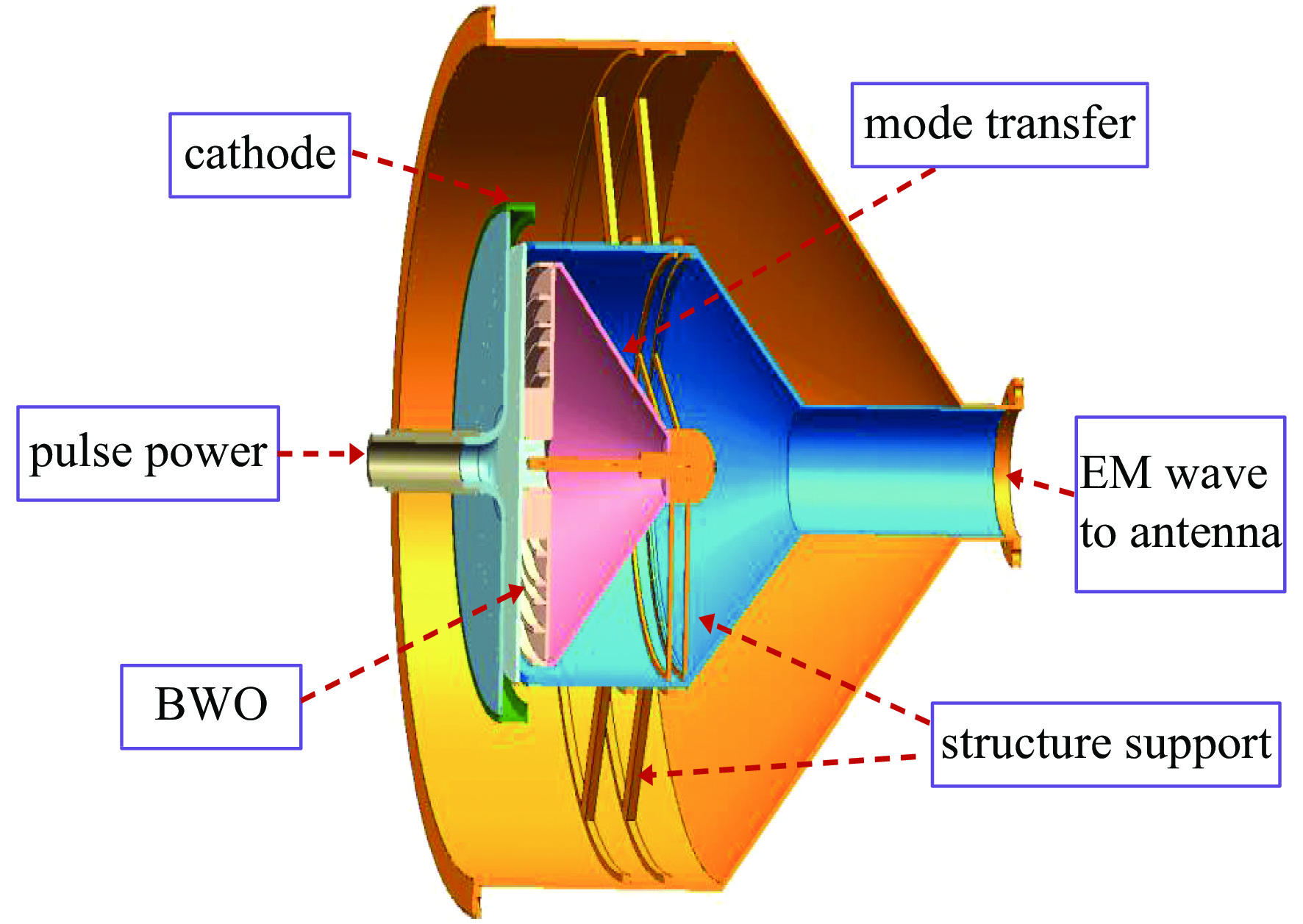
高功率微波器件在雷达、电子对抗等方面具有重要的应用潜力,因此得到广泛的关注。然而,庞大的体积和重量,以及较低的效率和较短的寿命,严重限制了高功率微波的应用范围。提出了一种径向电子注驱动的同轴槽振荡器,该振荡器无需聚焦系统,从而能够大幅度减少体积和耗能。采用由外向内的径向电子注,阴极电流密度低,可以采用热阴极替代爆炸发射阴极,从而提高器件寿命。PIC仿真中,采用460 kV,6 kA径向电子注能够在3.8 GHz产生1.2 GW的输出,对应效率43.5%。
Abstract:High power microwave devices are investigated extensively, because of their potential applications, such as advanced radars, electromagnetic warfare systems. However, low efficiency, enormous volume, huge weight and short lifetime limit their applications. In this paper, a coaxial grating slow wave structure backward wave oscillator (BWO) driven by radial beam is proposed. The focusing system is eliminated in the particle in cell simulation, which can reduce the volume and the power loss in practice. The lifetime of the BWO can also be improved with the thermionic radial beam cathode instead of the explosive emission cathode. After optimization, the BWO driven by 460 kV, 6 kA radial beam can produce 1.2 GW at frequency 3.8 GHz, with the efficiency of 43.5%.
-
Key words:
- radial electron beam /
- back wave oscillator /
- high power microwave
-
Table 1. Parameters for the PIC simulation
voltage of
the sheet
beam,
U/kVcurrent of
the sheet
beam,
I/kAthickness
of the
beam,
Sbeam/mmmagnetic
field,
B/Tthickness
of the
BWO, H/mmouter radius
of the
BWO, Rout/mminner radius
of the
BWO,
Rin/mmradius of
the first
grating, R1/mmradius of
the second
grating, R2/mmradius of
the third
grating, R3/mmradius of
the fourth
grating, R4/mmradius of
the fifth
grating, R5/mmdepth of
the
grating,
D/mm460 6 5 0 30 180 60 166 140 115 100 75 12.5 Table 2. Parameters of the radial beam gun
voltage of the cathode, Uc/kV voltage of the focus, Uf/kV voltage of the anode, Ua/V thickness of the cathode, Tc/mm radius of the cathode, Rc/mm thickness of the focus, Tf/mm inner radius of the focus, Rf/mm radius of the anode, Ra/mm −460 −460 0 17 209 23 197 180 Table 3. Parameters of the Vlasov antenna
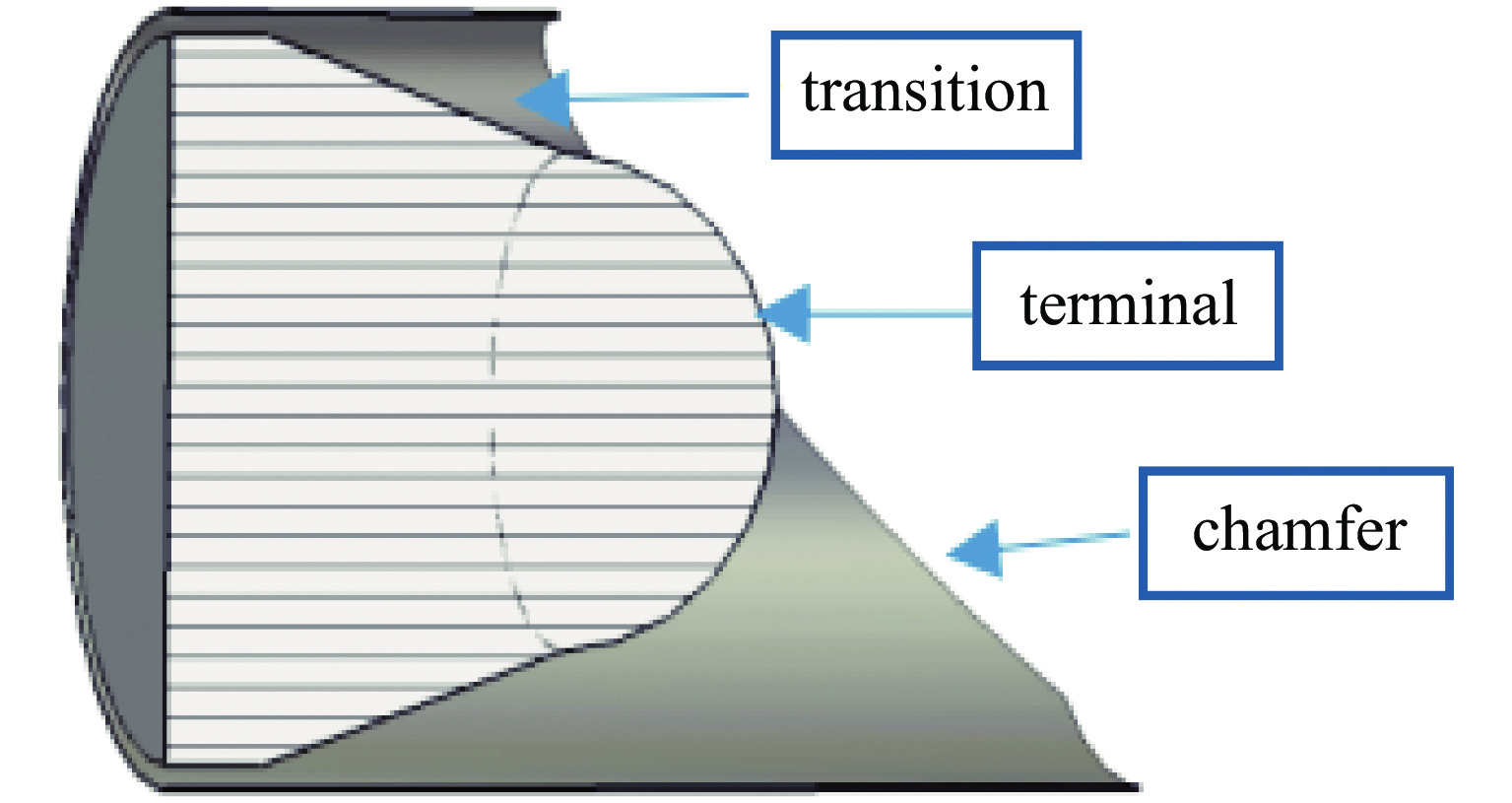
length of the transition, Zt/mm radius of the terminal, Rt/mm length of the antenna, La/mm corner cut of the antenna Cc/(°) −150 110 450 45 -
[1] Zhou Chuanming, Liu Guozhi, Liu Yonggui, et al. High-power microwave sources[M]. Beijing: Atomic Energy Press, 2007. [2] Booske J H, Dobbs R J, Joye C D, et al. Vacuum electronic high power terahertz sources[J]. IEEE Trans Terahertz Sci Technol, 2011, 1(1): 54-75. doi: 10.1109/TTHZ.2011.2151610 [3] Wang Zhanliang, Gong Yubin, Wei Yanyu, et al. High-power millimeter-wave BWO driven by sheet electron beam[J]. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 2013, 60(1): 471-477. doi: 10.1109/TED.2012.2226587 [4] Zhang Yabin, Gong Yubin, Wang Zhanliang, et al. Study of high-power Ka-band rectangular double-grating sheet beam BWO[J]. IEEE Trans Plasma Sci, 2014, 42(6): 1502-1508. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2014.2301719 [5] Liu Zhenbang, Huang Hua, Jin Xiao, et al. Investigation of an X-band pulse high-power high-gain coaxial multibeam relativistic klystron amplifier[J]. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 2019, 66(1): 722-728. doi: 10.1109/TED.2018.2879193 [6] Xiao Renzhen, Chen Changhua, Sun Jun, et al. A High-power high-efficiency klystronlike relativistic backward wave oscillator with a dual-cavity extractor[J]. Appl Phys Lett, 2011, 98: 101502. doi: 10.1063/1.3562612 [7] Wang Zhanliang, Xu Xiong, Gong Yubin, et al. Simulation on W-band sheet beam rectangular waveguide grating backward-wave oscillator[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2015, 27: 083005. doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201527.083005 [8] Zhang Jiande, Ge Xingjun, Zhang Jun, et al. Research activities on high-power microwave sources in national university of defense technology of China[C]//IEEE Pulsed Power Conference. 2015: 1-20. [9] Klimov A I, Kurkan I K, Polevin S D, et al. A multigigawatt X-Band relativistic backward wave oscillator with a modulating resonant reflector[J]. Tech Phys Lett, 2008, 34(3): 235-237. doi: 10.1134/S1063785008030176 [10] Hahn K, Schamiloglu E. Long-pulse relativistic backward wave oscillator operation utilizing a disk cathode[C]//28th IEEE International Conference on Plasma Science and 13th IEEE International Pulsed Power Conference. 2001: 1618-1621. [11] Hegeler F, Schamiloglu E, Korovin S D, et al. Recent advances in the study of a long pulse relativistic backward wave oscillator[C]//Proceedings of the 12th IEEE International Pulsed Power Conference. 1999: 825-828. [12] Agee F J. Evolution of pulse shortening research in narrow band, high power microwave sources[J]. IEEE Trans Plasma Sci, 1998, 26(3): 235-245. doi: 10.1109/27.700749 [13] Gunin A V, Landl V F, Korovin S D, et al. Experimental studies of long-lifetime cold cathodes for high-power microwave oscillators[J]. IEEE Trans Plasma Sci, 2000, 28(3): 537-541. doi: 10.1109/27.887668 [14] Liu Zhenbang, Huang Hua, Jin Xiao, et al. High power operation of an X-band coaxial multi-beam relativistic klystron amplifier[J]. Phys Plasmas, 2013, 20: 113101. doi: 10.1063/1.4825357 [15] Jiang Peijie, Li Zhenghong, Wu Yang. Operating characteristics of an S-band relativistic backward wave oscillator with low magnetic field[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2019, 31: 033001. doi: doi:10.11884/HPLPB201931.190010 [16] Konoplev I V, McGrane P, He W, et al. Experimental study of coaxial free-electron maser based on two-dimensional distributed feedback[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 2006, 96: 035002. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.96.035002 [17] Gan Yanqing, Huang Hua, Lei Lurong, et al. Experimental investigation on an S-band relativistic klystron oscillator[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2008, 20(5): 815-818. [18] Parson J M, Mankowski J J, Dickens J C, et al. Imaging of explosive emission cathode and anode plasma in a vacuum-sealed vircator high-power microwave source at 250 A/cm2[J]. IEEE Trans Plasma Sci, 2014, 42(10): 2592-2593. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2014.2331688 [19] Ma Qiaosheng. A novel efficient vircator[J]. High Power Laser Part Beams, 2015, 27: 053005. doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20152705.53005 [20] Qin Fen, Wang Dong, Chen Daibing, et al. Rigorous analysis of high-frequency characteristics of higher-order depressed MILO slow wave structure[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2013, 25(s): 119-123. doi: 10.3788/HPLPB2013250s.0119 [21] Dang Fangchao, Zhang Xiaoping, Zhong Huihuang, et al. A small-signal theory for the radial-line relativistic klystron amplifier[J]. J Appl Phys, 2017, 121: 083302. doi: 10.1063/1.4977065 [22] Dang Fangchao, Zhang Xiaoping, Zhang Jun, et al. Experimental demonstration of a Ku-band radial-line relativistic klystron oscillator based on transition radiation[J]. J Appl Phys, 2017, 121: 123305. doi: 10.1063/1.4979309 [23] Konoplev I V, Fisher L, Cross A W, et al. Surface wave Cherenkov maser based on a periodic lattice[J]. Appl Phys Lett, 2010, 96: 261101. doi: 10.1063/1.3456618 [24] Hofmann I. Stability of anisotropic beams with space charge[J]. Phys Rev E, 1998, 57(4): 4713-4724. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.57.4713 [25] Humphries S, Russell S, Carlsten B, et al. Focusing of high-perveance planar electron beams in a miniature wiggler magnet array[J]. IEEE Trans Plasma Sci, 2005, 33(2): 882-891. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2005.845088 -




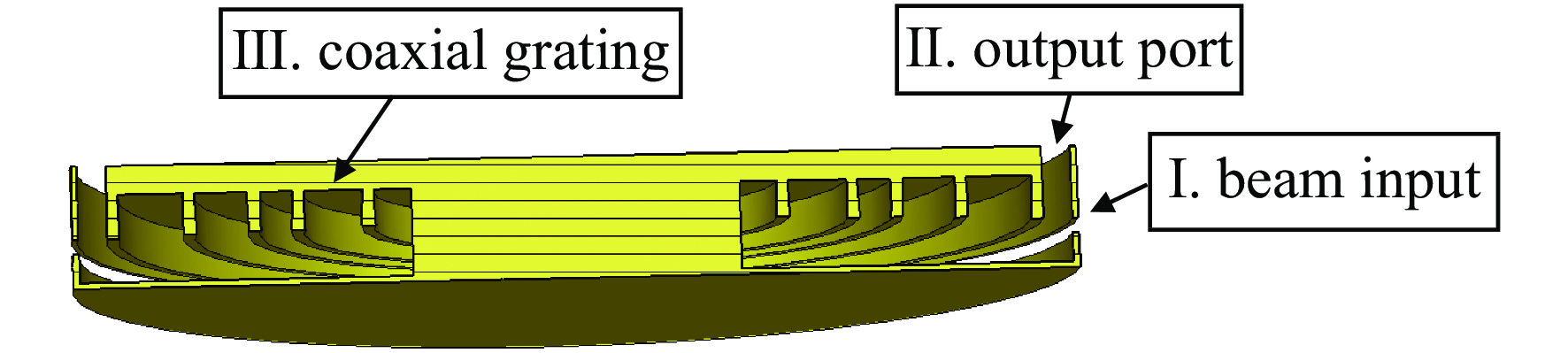
 下载:
下载: