Design of 648 MHz superconducting cavity tuner forChina Spallation Neutron Source phase II
-
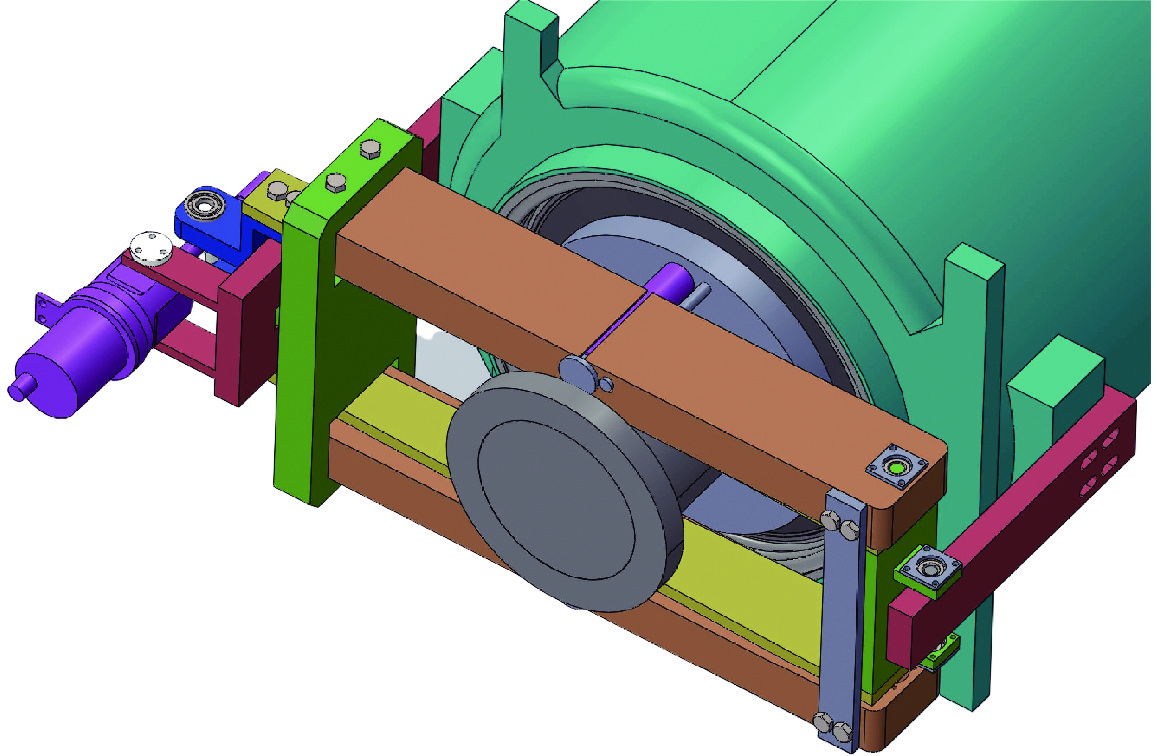
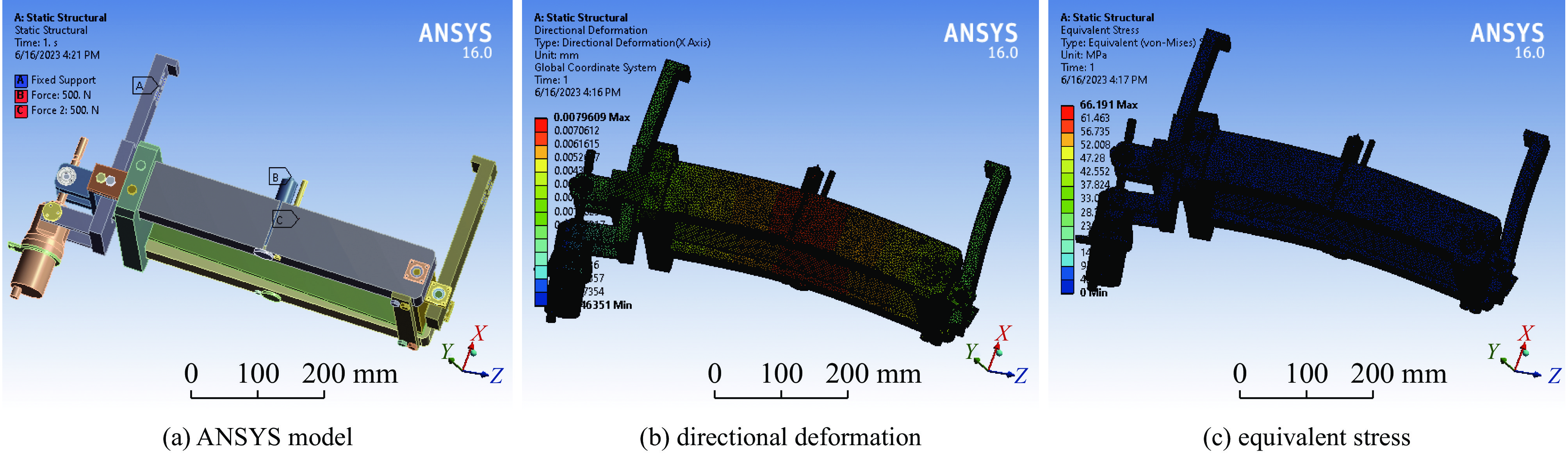
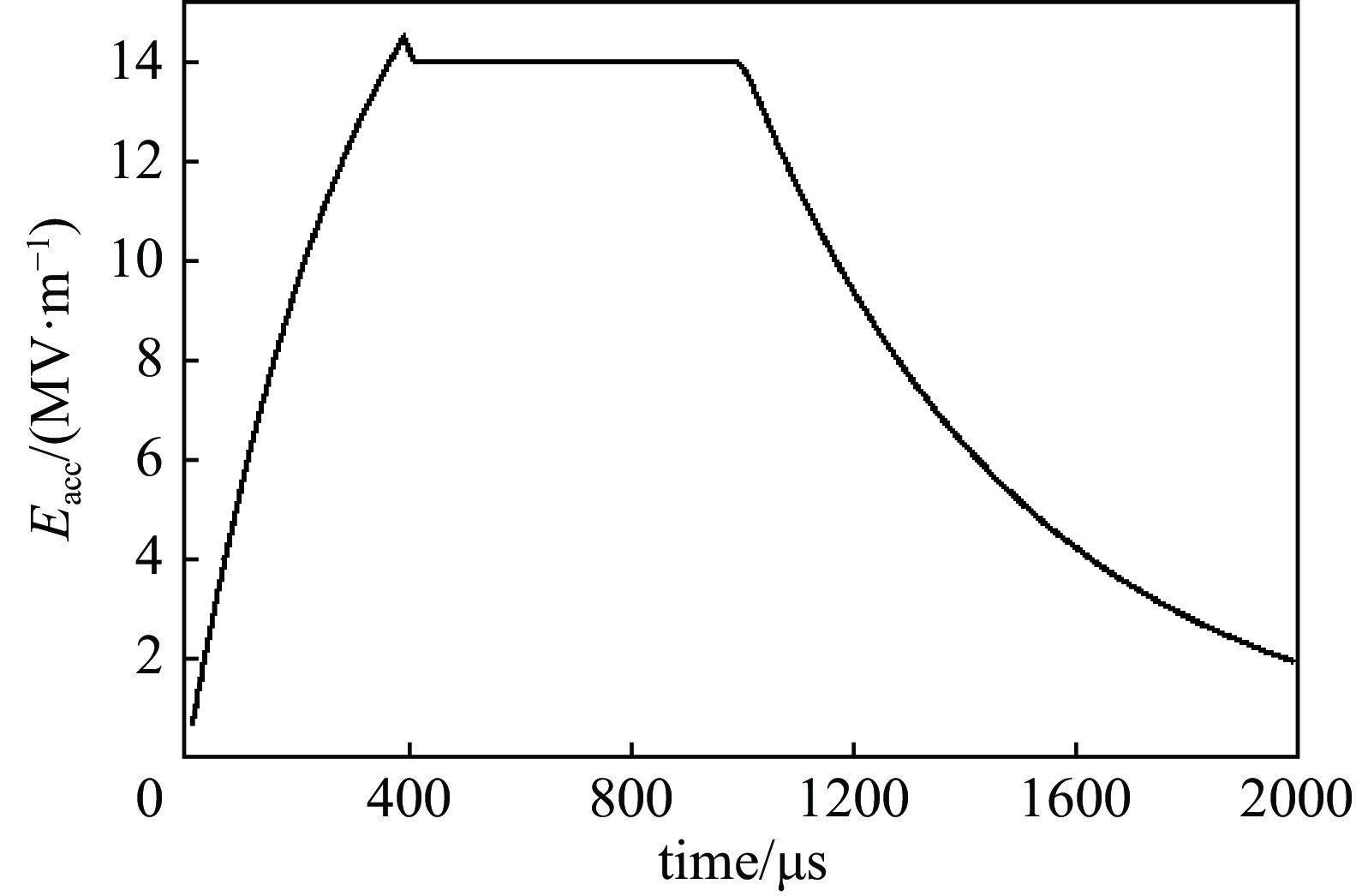
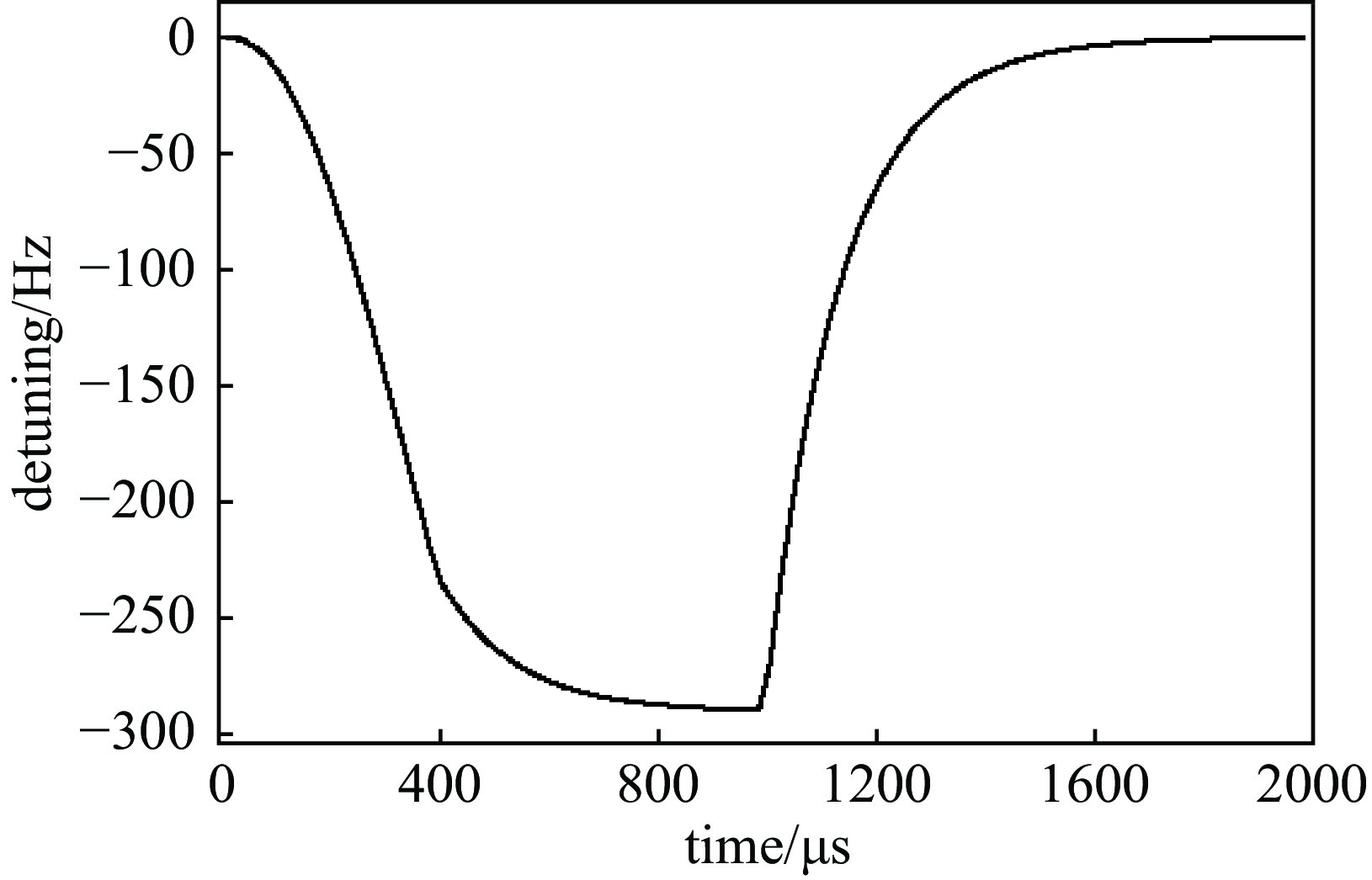
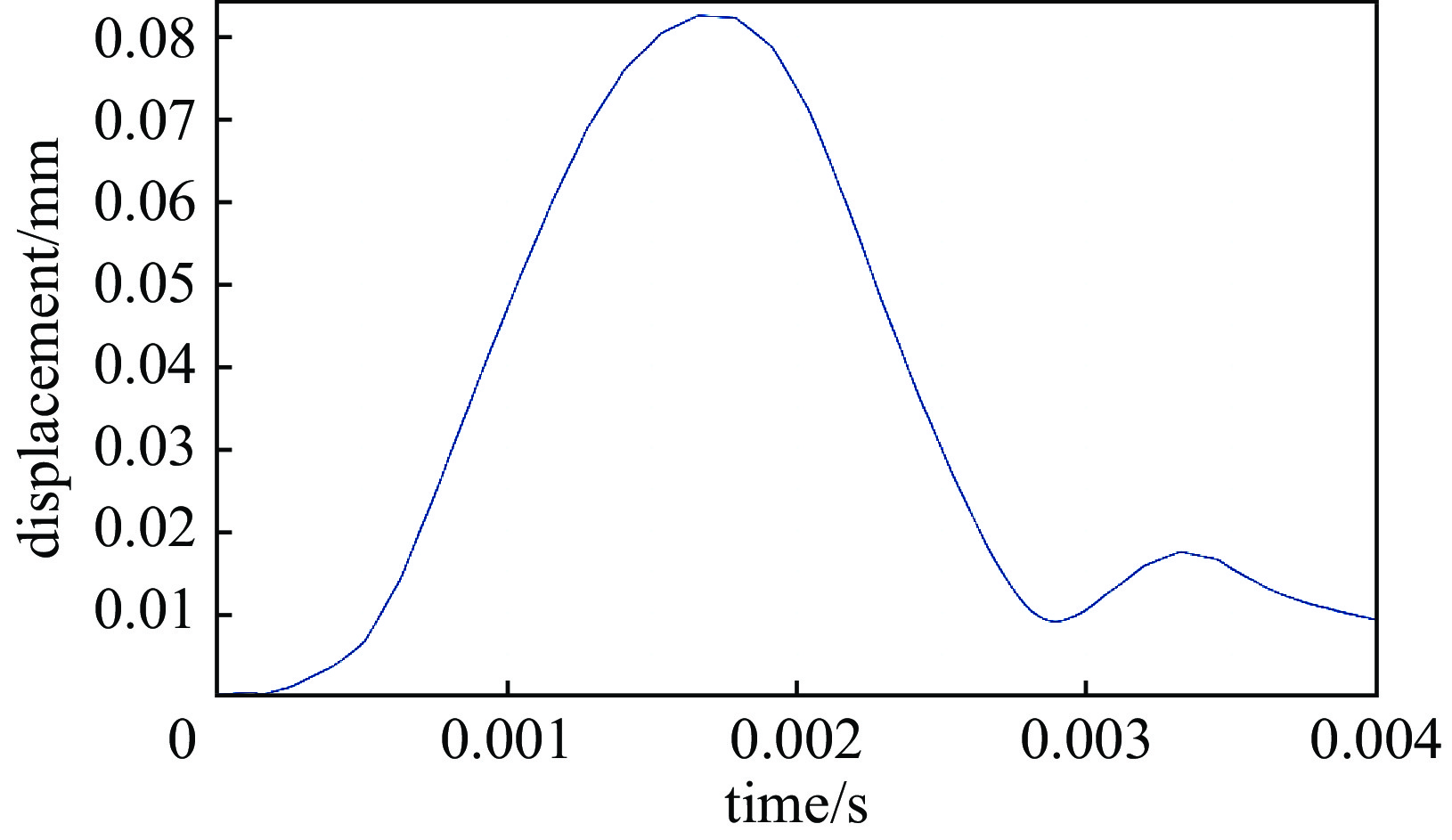
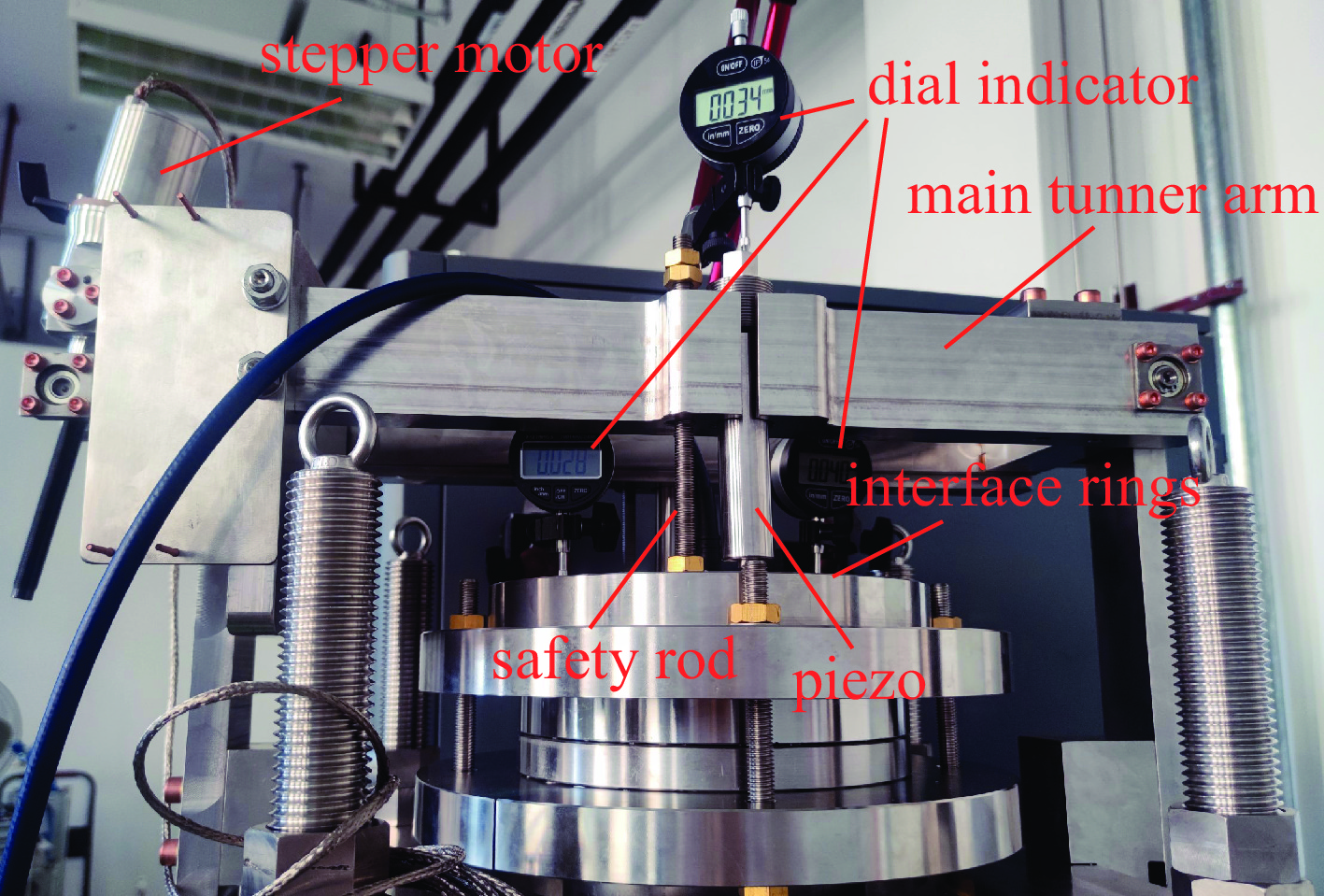
摘要: 中国散裂中子源二期升级采用超导腔技术方案,其中在165~300 MeV能量段采用648 MHz 6-cell 超导腔模组,每个模组中集成3只6-cell超导腔。超导腔工作在脉冲模式,为了保证超导腔2 K下的频率满足运行要求,每只超导腔需要一套低温调谐器对其频率进行精确调节控制。针对648 MHz 6-cell超导腔的结构和运行特点进行了低温调谐器的设计,采用快慢组合机构补偿超导腔的频率偏移,对调谐器的基本性能和超导腔脉冲模式运行下的动态洛伦兹失谐进行了分析。Abstract: The China Spallation Neutron Source phase II (CNSS-II) is upgraded with superconducting cavity technology, which uses 648 MHz 6-cell superconducting cavity module in the energy range of 165−300 MeV. Three 6-cell superconducting cavities are integrated in each module. The superconducting cavity works in pulse mode. To ensure that the frequency of the superconducting cavity meets the operation requirements at 2 K, each superconducting cavity needs a set of low-temperature tuner to precisely adjust and control its frequency. According to the structure and operation characteristics of the 648 MHz 6-cell superconducting cavity, a low-temperature tuner is designed. The frequency offset of the superconducting cavity is compensated by a fast-slow combination mechanism. The basic performance of the tuner and the dynamic Lorentz detuning of the superconducting cavity in pulse mode are analyzed.
-
Key words:
- superconducting cavity /
- tuner /
- dynamic Lorentz detuning /
- piezoelectric ceramics
-
表 1 超导腔运行主要参数
Table 1. Superconducting cavity operating parameters
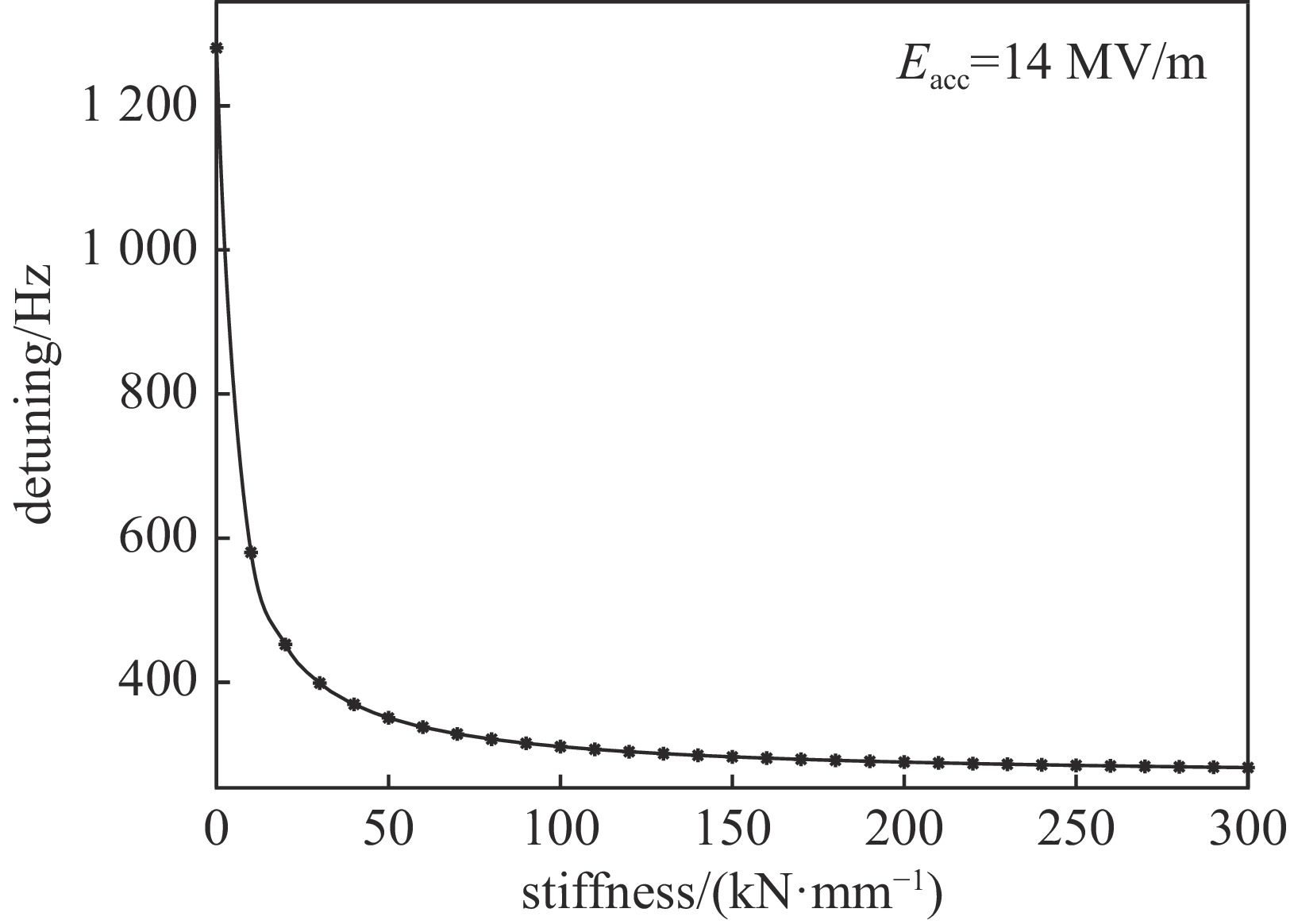
working frequency/MHz bandwidth of cavity/Hz operation mode pulse frequency/Hz operating gradient/(MV·m−1) 648 668 pulse 25 14 KL/(Hz·m2·MV−2) pressure sensitivity/(Hz·Pa−1) field flatness (R/Q)/Ω beam current/mA 1.5 0.15 > 90% 310 40 operation temperture/K operation pressure/Pa maximum allowable working pressure/MPa cavity axial stiffness/(N·mm−1) tuning sensitivity/(kHz·mm−1) 2 3100 0.2(room temperaturer), 0.4(2 K) 2225 171 表 2 调谐器系统需求参数
Table 2. Tuner system requirement parameters
tuner system stiffness/(kN·mm−1) slow tuner frequency range/kHz stepper motor resolution/Hz piezo tuner frequency range/kHz piezo tuner resolution/Hz > 100 > 100 10 1 4 表 3 648 MHz超导腔机械特性
Table 3. Mechanical properties of 648 MHz superconducting cavity
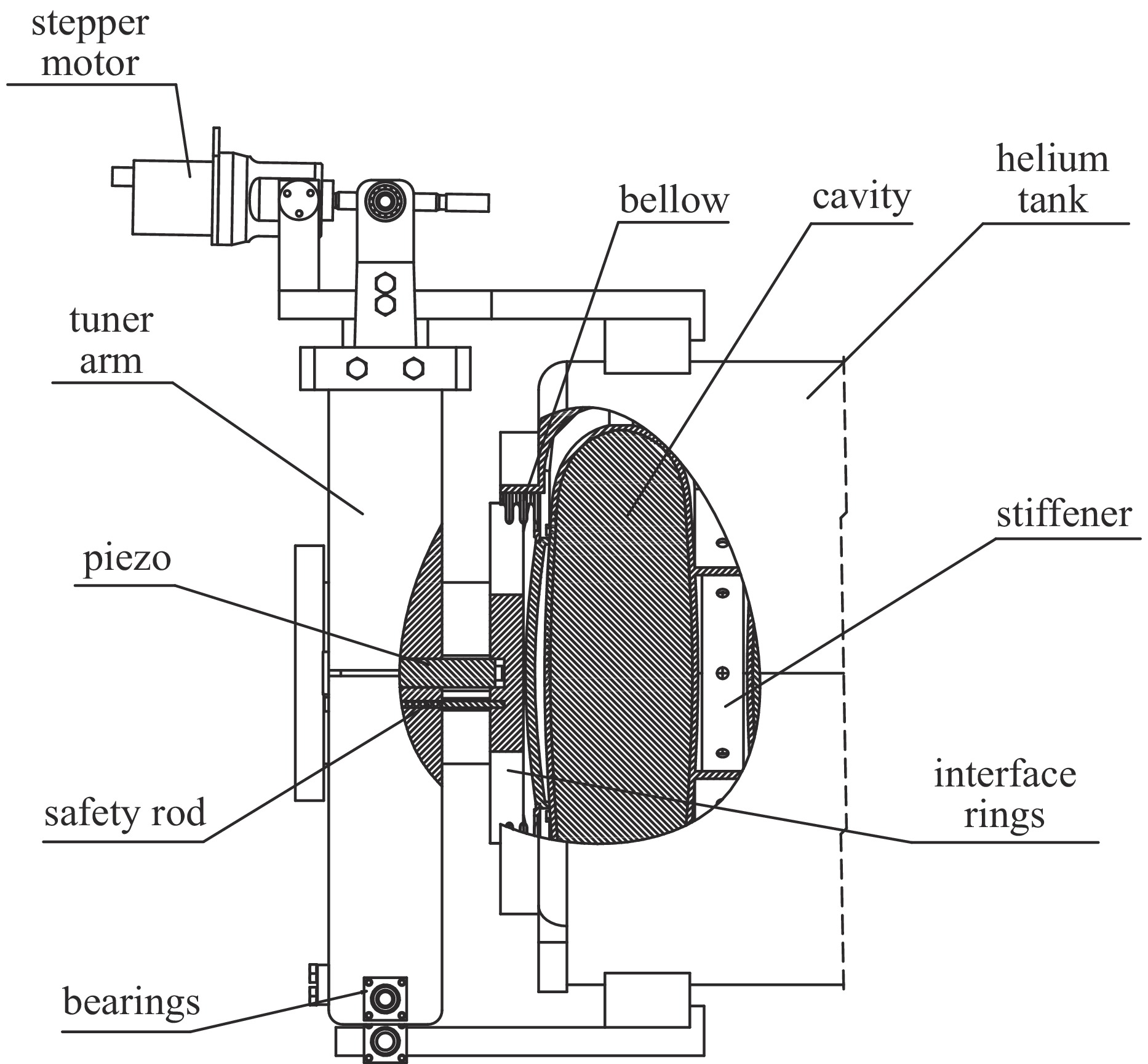
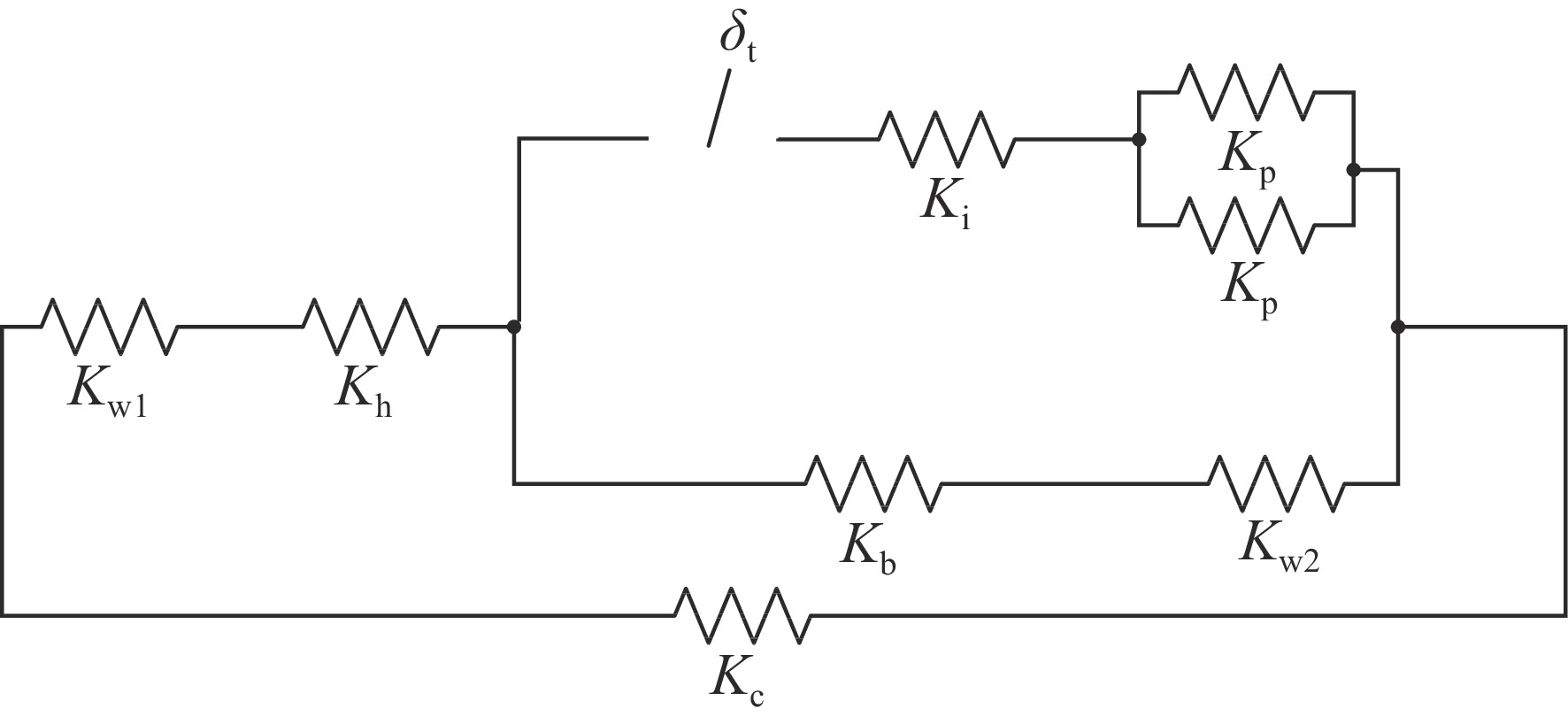
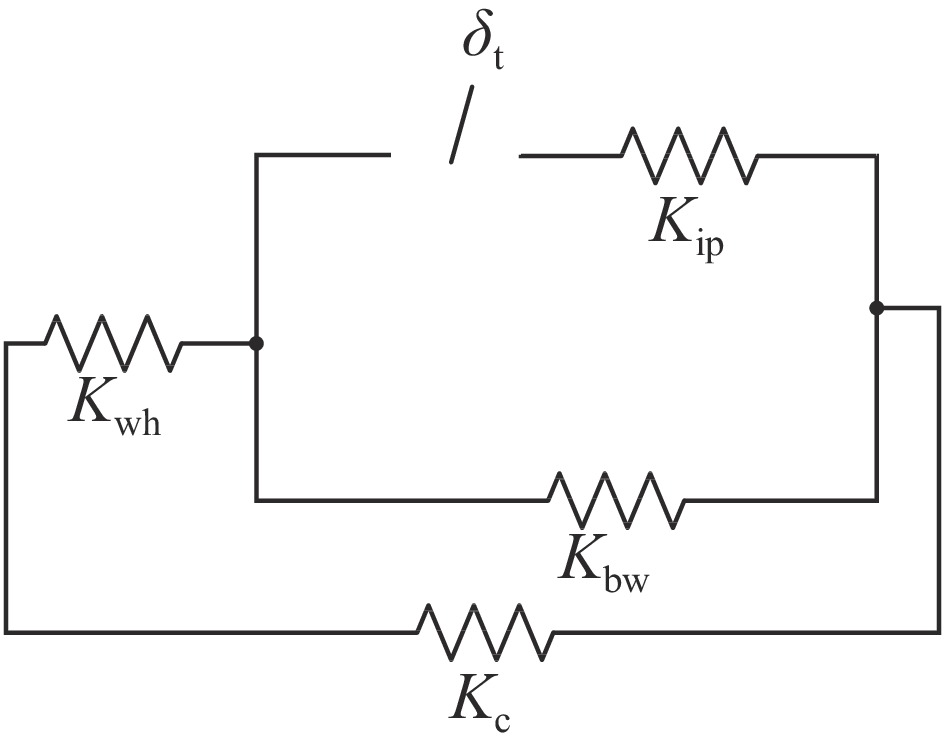
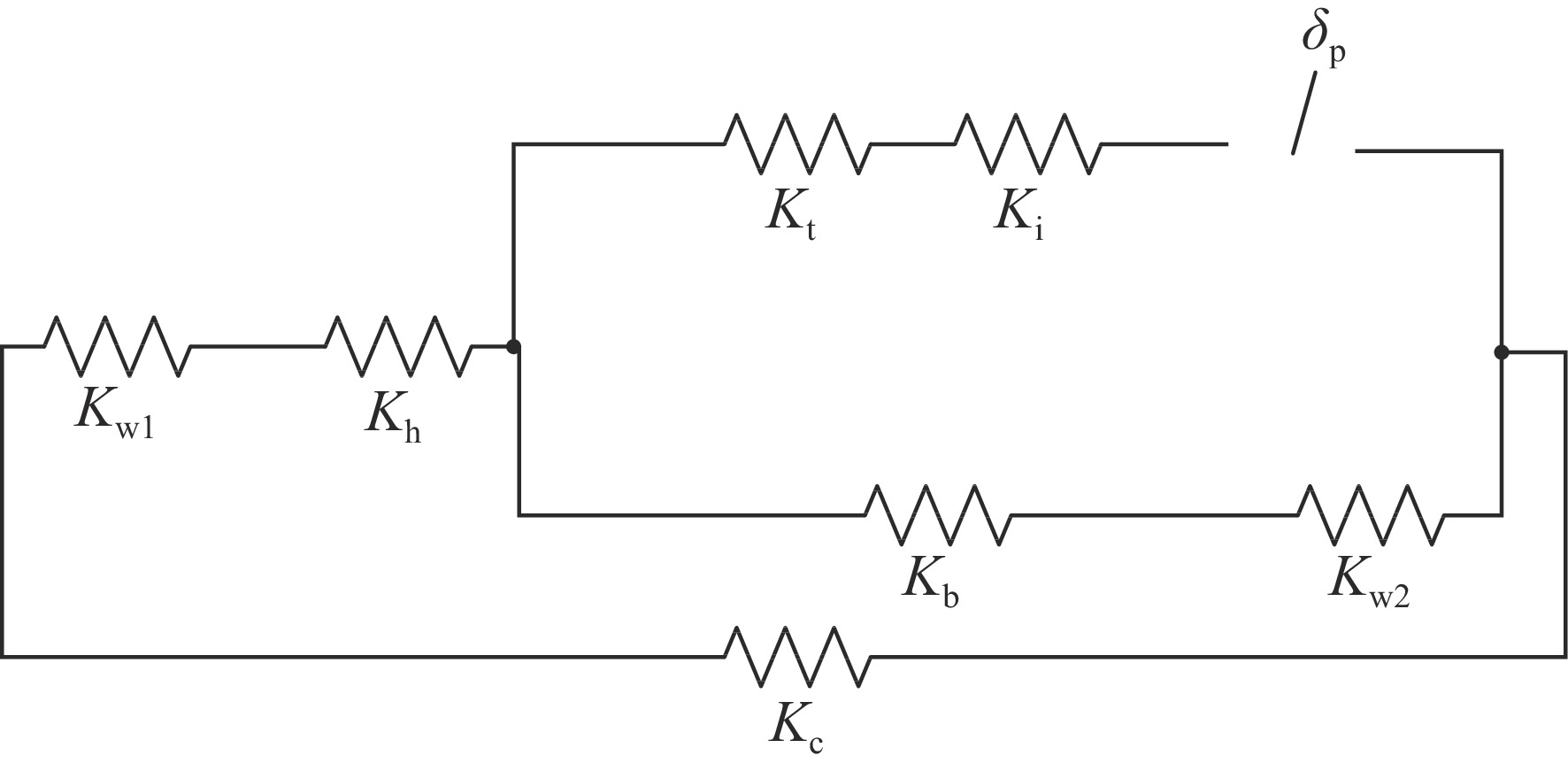
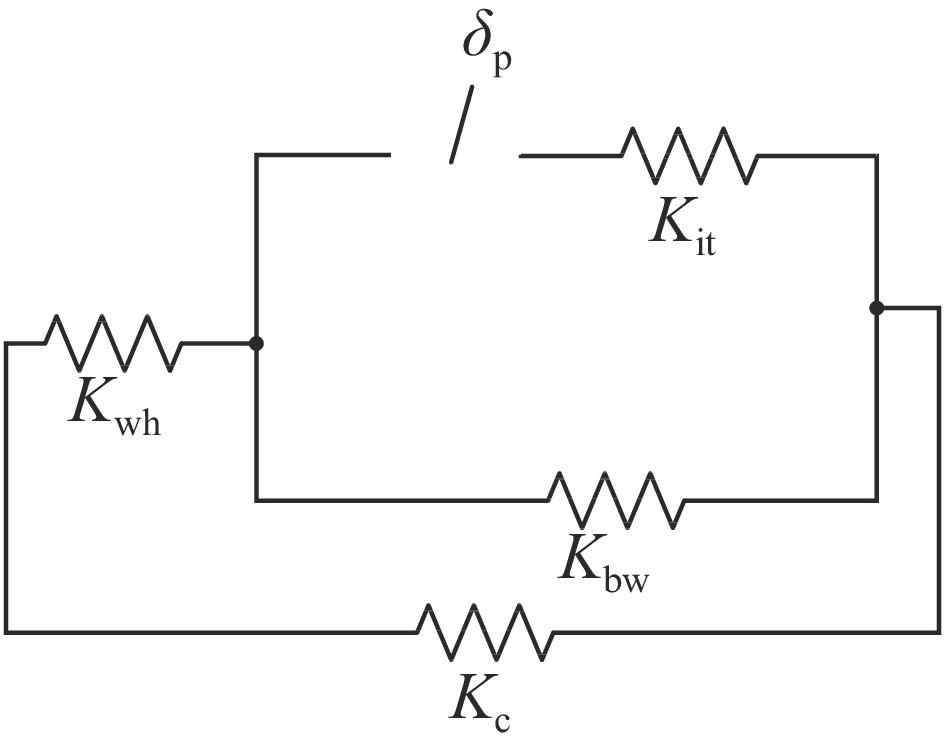
parts material axial flexibility/(mm·kN−1) axial rigidity/(kN·mm−1) cavity Nb 0.4494 2.225(Kc) front washer disk Nb55Ti 0.0339 29.52($ {K}_{\mathrm{w}1} $) end washer disk Nb55Ti 0.01914 52.24($ {K}_{\mathrm{w}2} $) helium tank Ti 0.008996 111.16($ {K}_{\mathrm{h}} $) tuner bellow Ti 32.327 0.031($ {K}_{\mathrm{b}} $) tuner 316L 0.00796 125.61($ {K}_{\mathrm{t}} $) interface rings Ti 0.00196 509.68($ {K}_{\mathrm{i}} $) piezo actuator HP 0.0125 80($ {K}_{\mathrm{p}} $) 表 4 机械调谐器产生
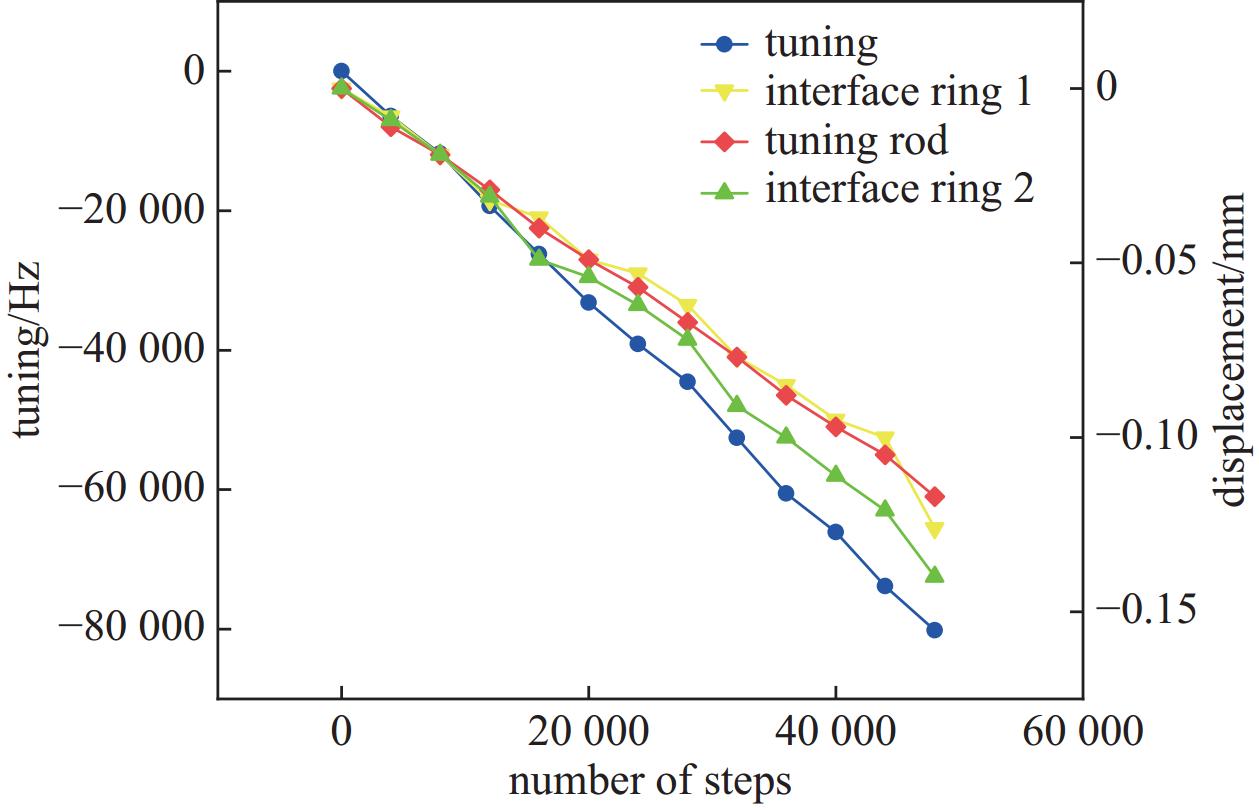
$ 1\;{\text{μ}}{\rm{m}}$ 位移时各部件受力及位移状态表Table 4. Force and displacement status of each component, when the mechanical tuner produces a displacement of
$ 1\;{\text{μ}}{\rm{m}} $ parts force/N displacement/${\text{μ}}\mathrm{m} $ piezo actuator/interface rings −2.03 −0.017 tuner bellow/end dishes −0.03 −0.980 helium tank/Front dishes −2.00 −0.086 cavity 2.00 0.898 表 5 压电陶瓷调谐器产生
$ 1\;{\text{μ}}{\rm{m}} $ 位移时各部件受力及位移状态表Table 5. Force and displacement status of each component, when the piezoelectric ceramics produces a displacement of
$ 1\;{\text{μ}}{\rm{m}} $ parts force/N displacement/$ {\text{μ}}{\rm{m}} $ tuner/interface rings −2.02 −0.020 tuner bellow/end dishes −0.03 −0.980 helium tank/front dishes −1.99 −0.085 cavity 1.99 0.895 表 6 安装调谐器前后洛伦兹力失谐参数表
Table 6. Lorentz force detuning parameters before and after installing the tuner
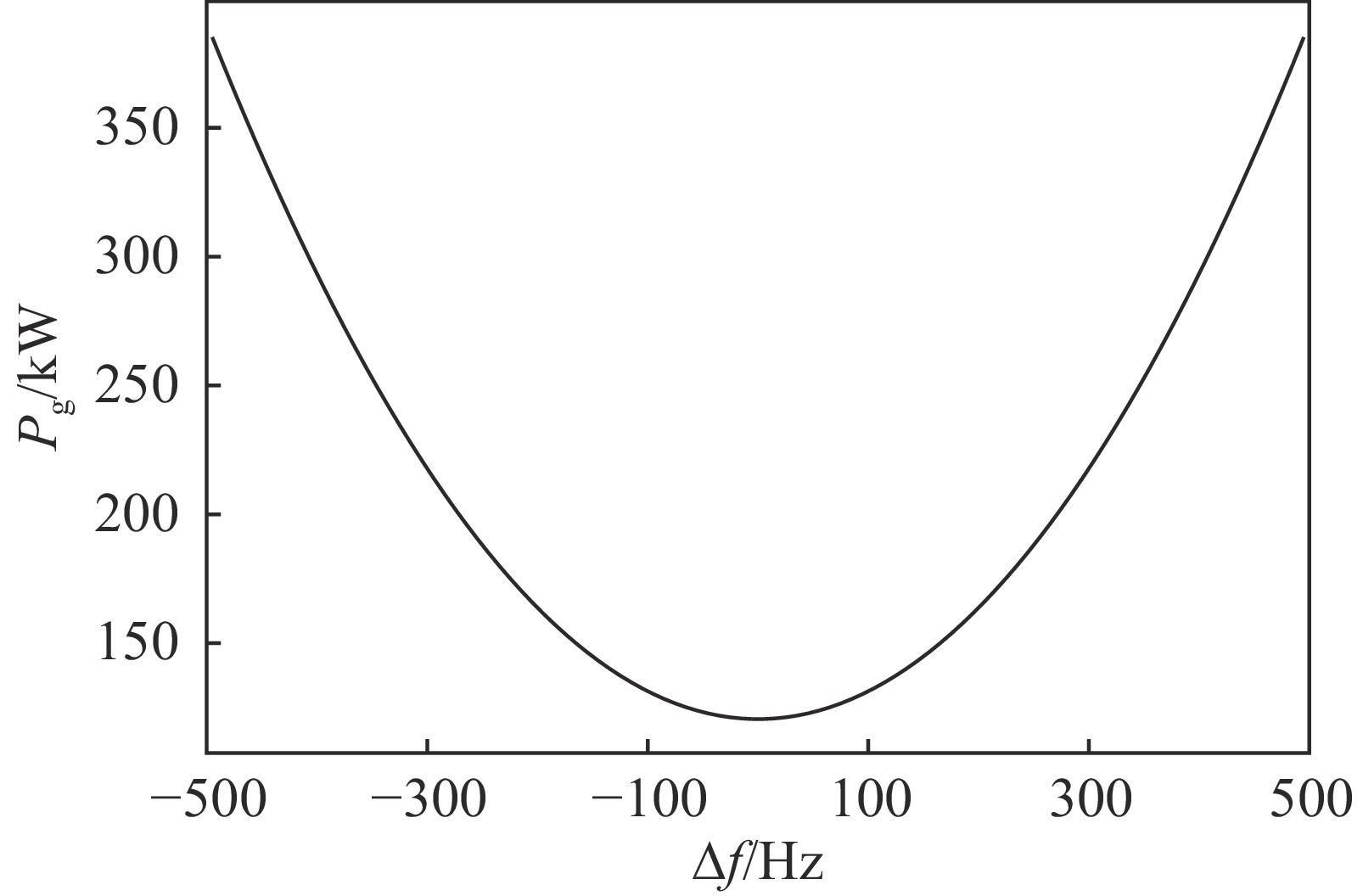
state LFD factor/
(Hz·m2·MV−2)maximum
detuning/Hzwithout tuner 9.32 1827 with tuner 1.48 290 -
[1] 周文中, 潘卫民, 葛锐, 等. 中国散裂中子源二期双spoke超导腔设计[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2023, 35:034004 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202335.220266Zhou Wenzhong, Pan Weimin, Ge Rui, et al. Design of the China Spallation Neutron Source phase II double spoke resonator[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2023, 35: 034004 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB202335.220266 [2] Delayen J R. Ponderomotive instabilities and microphonics—a tutorial[J]. Physica C:Superconductivity, 2006, 441(1/2): 1-6. [3] 倪柏初, 戴建枰, 张娟, 等. Spoke012超导腔低温调谐器的研制[J]. 核电子学与探测技术, 2015, 35(4):403-407 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-0934.2015.04.021Ni Baichu, Dai Jianping, Zhang Juan, et al. Development of a cryogenic tuner for the Spoke012 superconducting cavity[J]. Nuclear Electronics & Detection Technology, 2015, 35(4): 403-407 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-0934.2015.04.021 [4] Mitchell R, Matsumoto K, Ciovati G, et al. Lorentz force detuning analysis of the Spallation Neutron Source (SNS) accelerating cavities[R]. Los Alamos: Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator Facility, 2001. [5] Rathore M, Jain V K, Atulkar A, et al. Study of Lorentz force detuning and its compensation in superconducting radiofrequency cavity: a review[J]. Materials Today:Proceedings, 2021, 44: 1369-1374. doi: 10.1016/j.matpr.2020.11.506 [6] Schmidt C, Branlard J, Bousonville M, et al. Operational experience with the European XFEL SRF linac[C]//Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Radio-Frequency Superconductivity. 2023. [7] Kern R S, Svanberg C, Fransson K, et al. Completion of testing series double-spoke cavity cryomodules for ESS[C]//Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Radio-Frequency Superconductivity. 2023. [8] Pischalnikov Y, Contreras-Martinez C. Review of the application piezoelectric actuators for SRF cavity tuners[C]//Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference & Exhibition. 2023. [9] Belomestnykh S, Posen S, Bafia D, et al. Key directions for research and development of superconducting radio frequency cavities[DB/OL]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2204.01178, 2022. [10] Borissov E, Gonin I, Khabiboulline T, et al. Design of a compact lever slow/fast tuner for 650 MHz cavities for project X[C]//Proceedings of LINAC2014. 2014: 957-959. [11] Contreras-Martinez C. Electromagnetic and mechanical properties of medium β SRF elliptical cavities[D]. East Lansing: Michigan State University, 2021. [12] 米正辉. 超导腔调谐器设计研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院高能物理研究所, 2015Mi Zhenghui. Design and research of tuner for superconducting cavity[D]. Beijing: Institute of High Energy Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2015 [13] Pagani C, Bosotti A, Michelato P, et al. Report on fast piezo blade tuner (UMI tuner) for SCRF resonators design and fabrication[R]. CARE-Note-05-021-SRF, 2005. [14] Cano-Pleite E, Amorim A, Swieszek J S, et al. Numerical evaluation of the tuning, pressure sensitivity and Lorentz force detuning of RF superconducting crab cavities[C]//Excerpt from the Proceedings of the 2018 COMSOL Conference in Lausanne. 2018. [15] Ayvazyan V, Simrock S N. Dynamic Lorentz force detuning studies in TESLA cavities[C]//Proceedings of the EPAC 2004. 2004. [16] Gassot H M. Etudes de la stabilité mécanique des cavités supraconductrices et de la méthode de rigidification par projection thermique de cuivre[R]. IPNO-T-2002-01, 2001. -




 下载:
下载: