Atmospheric breakdown delay and ionization rate of repetitive microwave pulses
-
摘要: 针对高功率微波在大气传输中可能出现的击穿现象,研究了脉冲序列中首次脉冲击穿延时和后续脉冲击穿延时,研究结果发现首次脉冲击穿延时在脉宽范围内大致均匀分布,后续脉冲击穿延时波动性较小。根据击穿延时数据对电离率进行了分析,指出在重复频率条件下,初始电子密度较高,电子密度分布不适用指数分布,无法用延时数据标准差对电离率进行估计。提出了一种用重复频率脉冲击穿延时数据计算电离率的方法,并将计算结果与仿真结果进行了对比,结果显示,二者有较好的对应关系。Abstract: Aiming at the possible breakdown phenomenon of high power microwave in atmospheric transmission, this paper focuses on the study of the first pulse burst delay and subsequent pulse burst delay in pulse sequences. It is found that the first pulse burst delay is approximately uniformly distributed within the pulse width range, and the subsequent pulse burst delay has a small jitter. The ionization rate is analyzed based on the breakdown delay data, and it is pointed out that under the repeated frequency condition, the initial electron density is high, and the electron density distribution is not suitable for exponential distribution, which makes it impossible to estimate the ionization rate using the standard deviation of the delay data. At the end, the paper proposes a method for calculating ionization rate using repeated frequency pulse burst delay data, and compares the calculated results with the simulation results, which have a good correspondence.
-
Key words:
- repetition frequency /
- microwave breakdown /
- ionization rate /
- pulse delay /
- estimate
-
表 1 实验结果
Table 1. Results of experiments
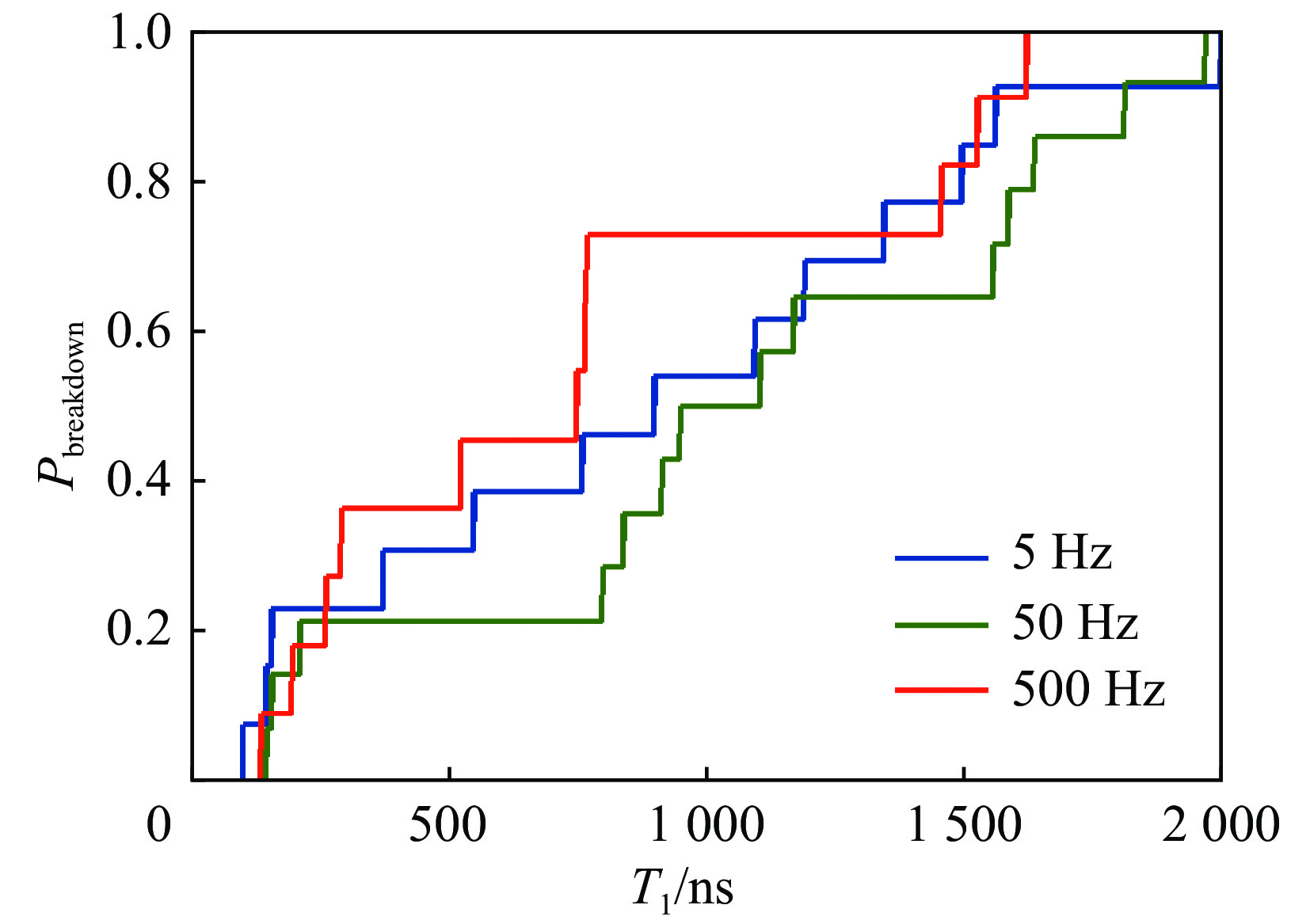
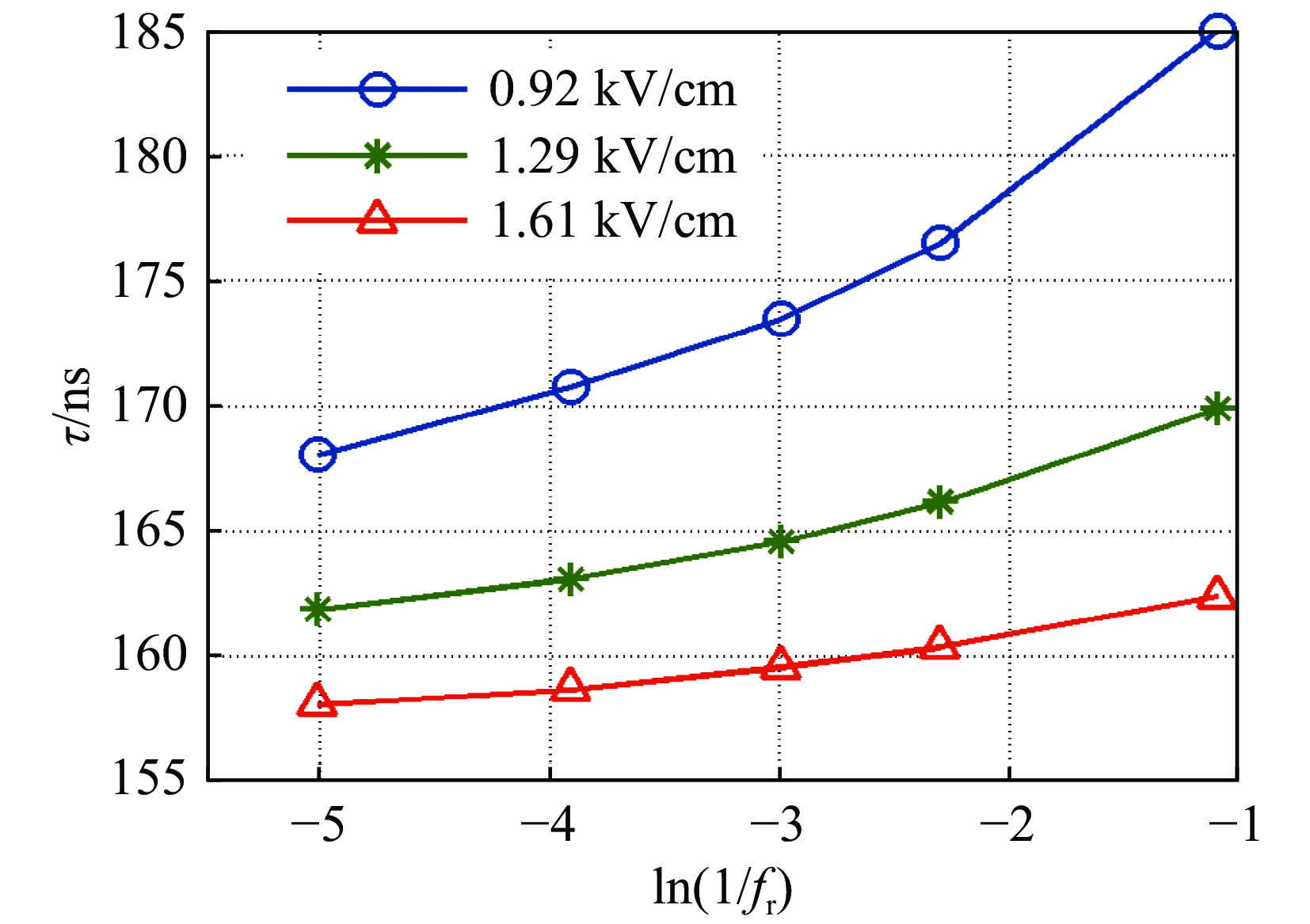
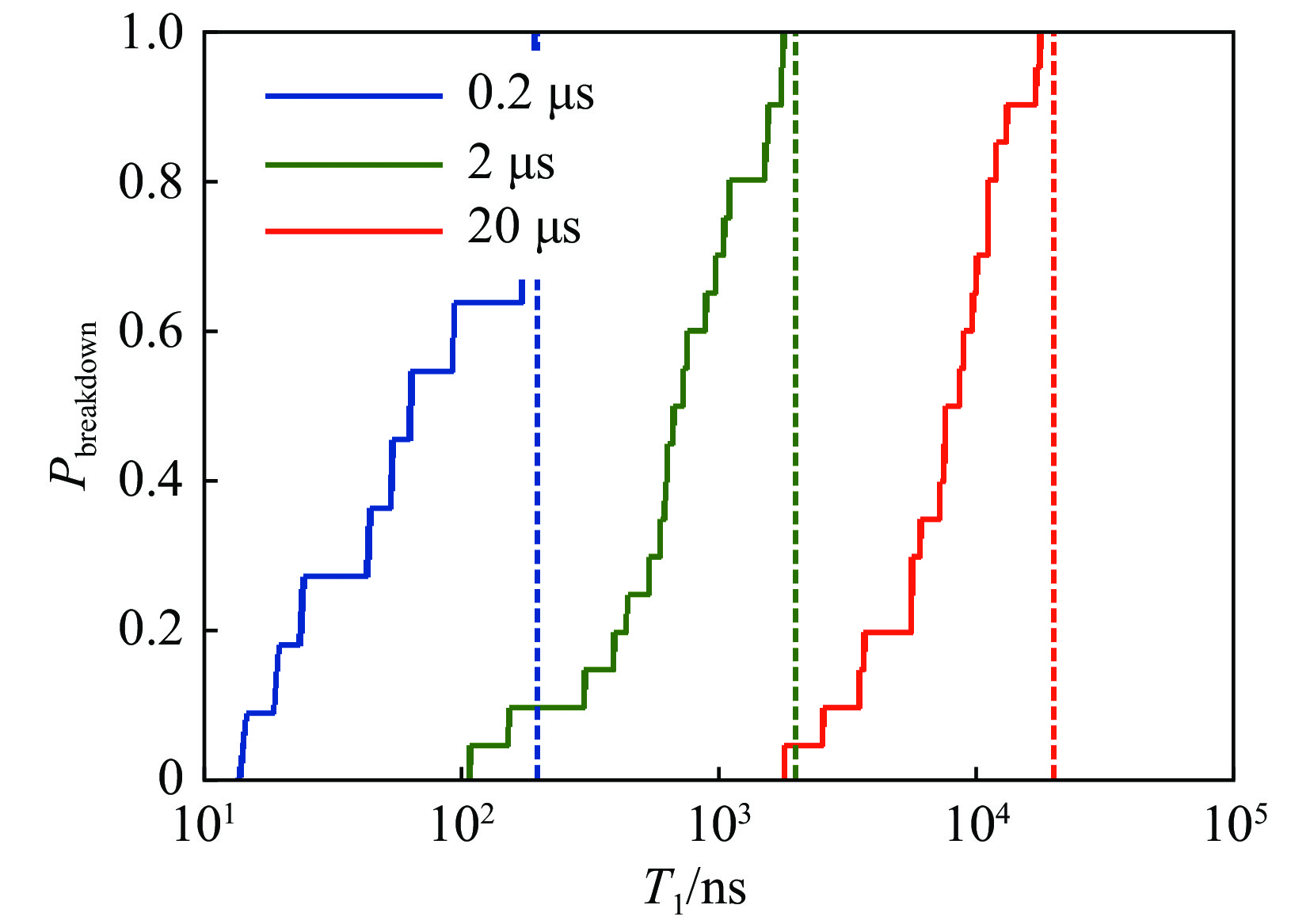
No. pressure/Pa electric intensity/(kV·cm−1) repetitive frequency/Hz pulse width /ns Tavg/ns A1 1000 0.92 20 20000 45 A2 1000 1.29 20 20000 22.5 B1 300 0.92 5 2000 35 B2 300 0.92 50 2000 25 B3 300 0.92 500 2000 15 C1 300 1.29 50 20 10 C2 300 1.29 50 200 10 C3 300 1.29 50 2000 10 C4 300 1.29 50 20000 10 表 2 击穿延时数据
Table 2. Breakdown delay data
electric field/
(kV·cm−1)breakdown delay time/ns fr=3 Hz fr=10 Hz fr=20 Hz fr=50 Hz fr=150 Hz 0.92 185.0 176.5 173.5 170.8 168.1 1.29 169.9 166.2 164.6 163.1 161.9 1.61 162.4 160.4 159.6 158.7 158.1 -
[1] Barker R J, Schamiloglu E. 高功率微波源与技术[M]. 刘国治, 周传明, 译. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2005Barker R J, Schamiloglu E. High-power microwave sources and technologies[M]. Liu Guozhi, Zhou Chuanming, trans. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2005: 154-158 [2] 杨浩, 闫二艳, 郑强林, 等. 临近空间高功率微波辐照放电试验技术[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2019, 31:103216 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201931.190151Yang Hao, Yan Eryan, Zheng Qianglin, et al. Examination research of high power microwave irradiation discharge in near space[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2019, 31: 103216 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201931.190151 [3] Sprangle P, Hafizi B, Milchberg H, et al. Active remote detection of radioactivity based on electromagnetic signatures[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2014, 21: 013103. doi: 10.1063/1.4861633 [4] Isaacs J, Miao C L, Sprangle P. Remote monostatic detection of radioactive material by laser-induced breakdown[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2016, 23: 033507. doi: 10.1063/1.4943404 [5] Nusinovich G S, Pu R F, Antonsen T M, et al. Development of THz-range gyrotrons for detection of concealed radioactive materials[J]. Journal of Infrared, Millimeter, and Terahertz Waves, 2011, 32(3): 380-402. doi: 10.1007/s10762-010-9708-y [6] Nusinovich G S, Sprangle P, Semenov V E, et al. On the sensitivity of terahertz gyrotron based systems for remote detection of concealed radioactive materials[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2012, 111: 124912. doi: 10.1063/1.4730959 [7] Dorozhkina D, Semenov V, Olsson T, et al. Investigations of time delays in microwave breakdown initiation[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2006, 13: 013506. doi: 10.1063/1.2158696 [8] Foster J, Krompholz H, Neuber A. Investigation of the delay time distribution of high power microwave surface flashover[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2011, 18: 013502. doi: 10.1063/1.3534823 [9] Kim D, Yu D, Sawant A, et al. Remote detection of radioactive material using high-power pulsed electromagnetic radiation[J]. Nature Communications, 2017, 8: 15394. doi: 10.1038/ncomms15394 [10] 魏进进, 周东方, 余道杰, 等. 高功率微波作用下O−离子解吸附产生种子电子过程[J]. 物理学报, 2016, 65:055202 doi: 10.7498/aps.65.055202Wei Jinjin, Zhou Dongfang, Yu Daojie, et al. Seed electron production from O− detachment in high power microwave air breakdown[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2016, 65: 055202 doi: 10.7498/aps.65.055202 [11] 杨浩, 闫二艳, 郑强林, 等. 一种准光反射聚焦微波放电大气等离子体装置[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2019, 31:053002 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201931.180350Yang Hao, Yan Eryan, Zheng Qianglin, et al. A microwave plasma system with quasi optical focusing reflector[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2019, 31: 053002 doi: 10.11884/HPLPB201931.180350 [12] SIGLO database[OL]. [2013-06-04]. http://www.lxcat.laplace.univ-tlse.fr. [13] Lawton S A, Phelps A V. Excitation of the b1Σ+ g state of O2 by low energy electrons[J]. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 1978, 69(3): 1055-1068. doi: 10.1063/1.436700 -




 下载:
下载: