Reactive force field molecular dynamics simulation of structure and mechanical property of Si-doped glow discharge polymer
-
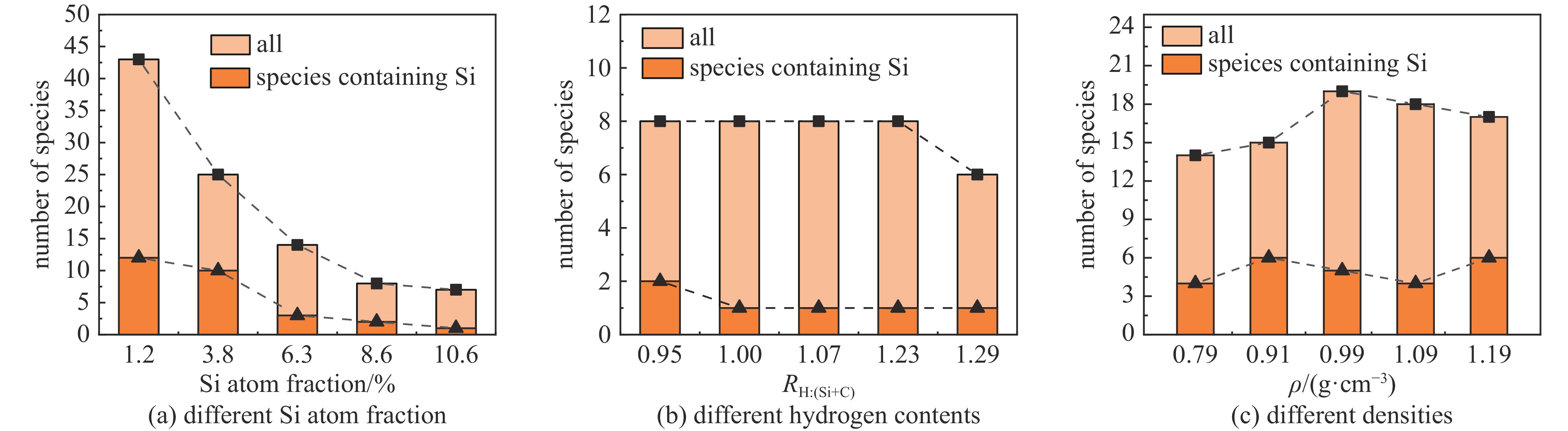
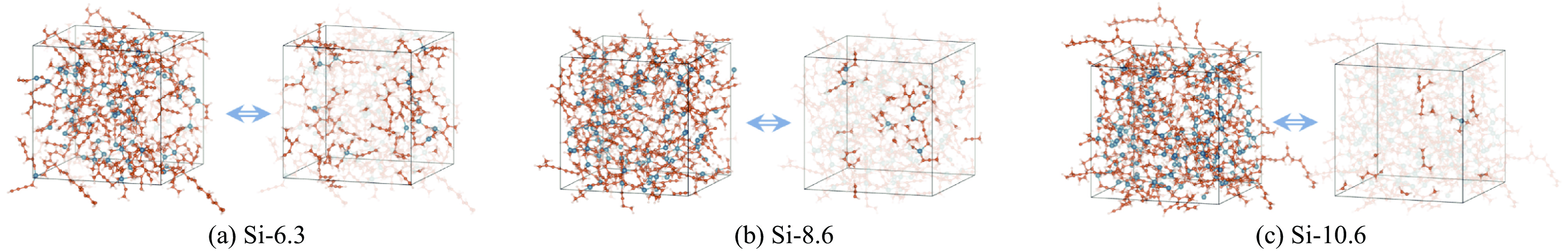
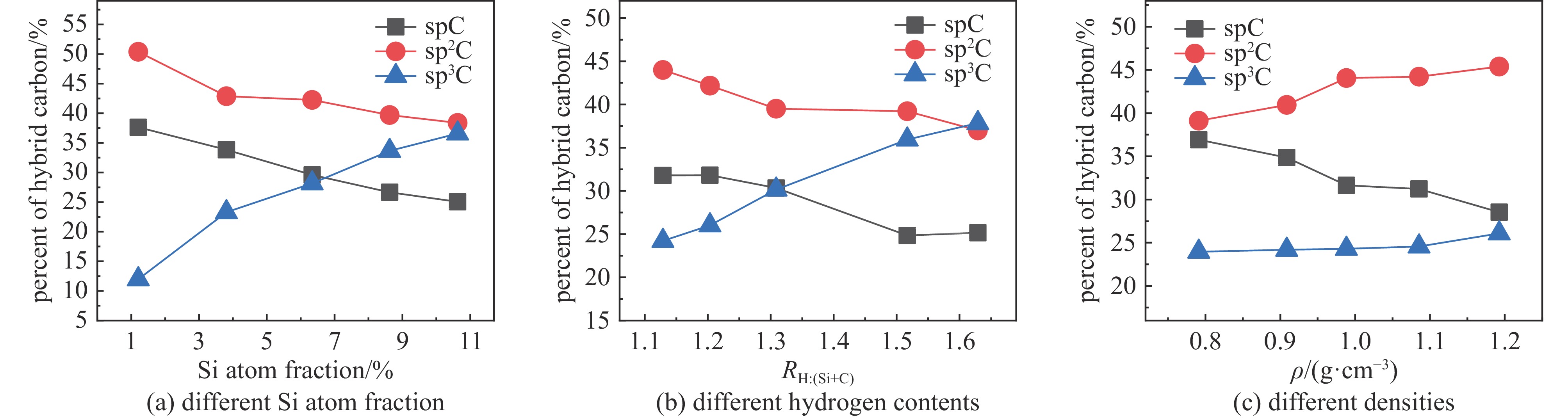
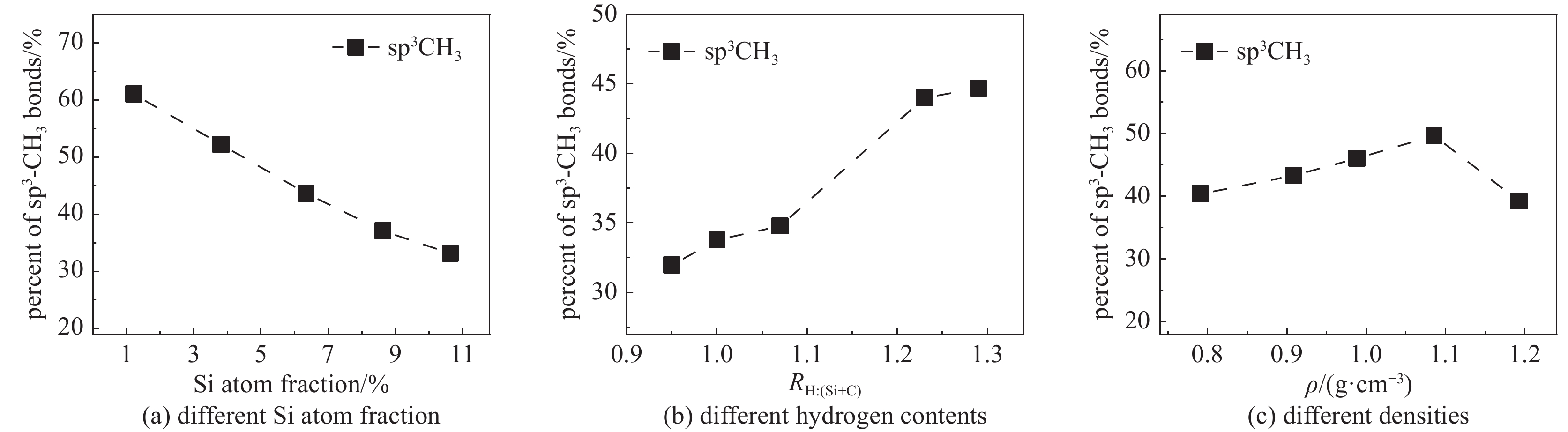
摘要: 构建了硅掺杂辉光放电聚合物(Si-GDP)模型,采用反应力场分子动力学模拟(ReaxFF MD)探讨了硅含量、碳氢比及密度对其杂化碳键合与力学性能的影响。研究结果表明:随着硅含量增加,聚合物中sp3C含量增加,趋向于形成一个大分子,同时小分子种类和数目减少,促进了碳硅原子成键并抑制端基CH3生成,进而提高材料力学性能;随着氢含量的增加,sp3C和端基CH3比例增加,生成的端基CH3降低了分子间交联程度,进而降低了材料力学性能,而分子基团数目变化不明显;随着密度的提升,聚合物中sp2C比例提升明显,sp3C比例有少量提升,分子基团数目变化不大,密度主要通过提升sp2C比例提升材料力学性能。研究结果为评估和理解硅掺杂辉光放电聚合物的结构和力学性能提供了新的视角和方法。Abstract: The structural models of Si-doped glow discharge polymer (Si-GDP) were established using reactive force field molecular dynamics simulation (ReaxFF MD), and the effects of silicon content, hydrogen content, and density on its hybrid carbon bonding and mechanical properties were investigated. The results show that with the silicon content increasing, the molecules tend to form a silicon-containing macromolecule, and the types and number of small molecules decrease, the silicon content improves the mechanical properties by promoting the binding of carbon and silicon atoms and inhibiting the formation of end-group sp3CH3. Besides, species such as ·C2H3, ·C3H5 and ·Si(CH3)3 were found during the formation of Si-GDP, which were in good agreement with the thin film deposition experiment of glow discharge polymer. The hydrogen content is measured as the atomic ratio of hydrogen to carbon and silicon, as the ratio grows, the number of model molecules did not change significantly, the ratio of sp3C and sp3CH3 increased, and the hydrogen content decreased the mechanical properties mainly by promoting the formation of sp3CH3. With the density increasing, the number of molecular species in the model did not change much, and the proportion of sp2C in the model was significantly increased, while the proportion of sp3C was slightly increased, the mechanical properties of Si-doped hydrogenated amorphous carbon were mainly improved by increasing the proportion of sp2C. This study provides an example for constructing Si-GDP by ReaxFF MD, and may provide a new method and reference for evaluating the structure and mechanical properties of Si-GDP.
-
表 1 Si-GDP模型参数
Table 1. Model parameters of Si-GDP
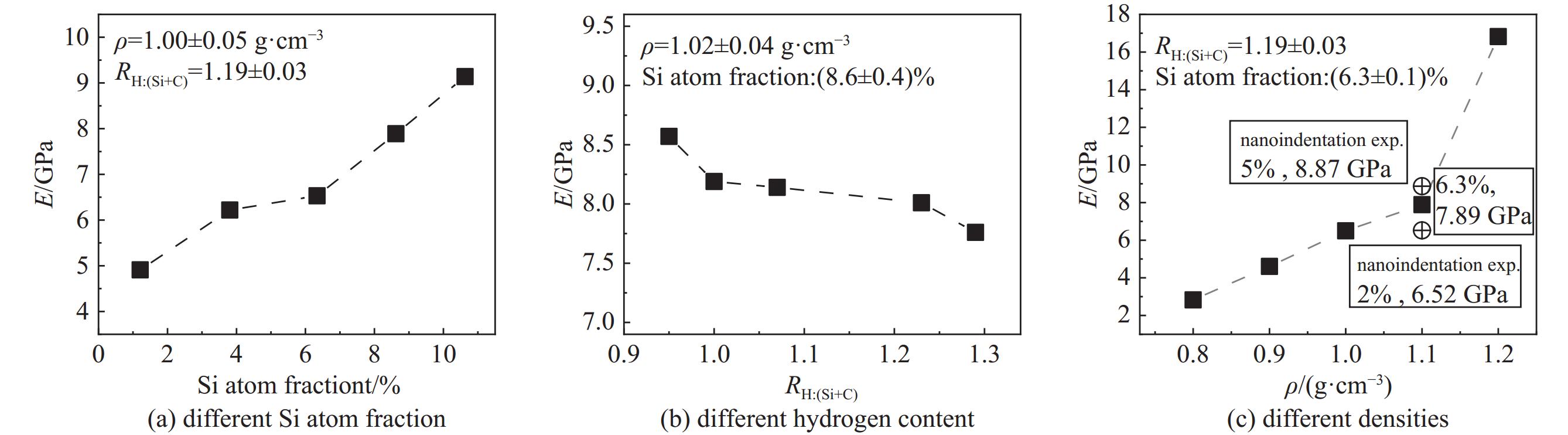
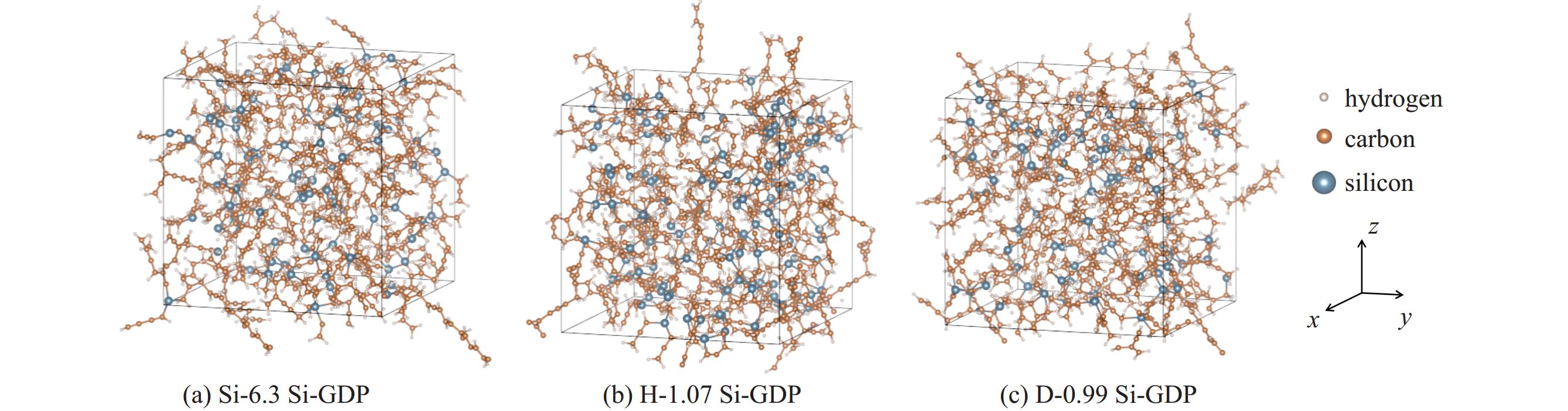
model name number of atoms Si atom fraction/% RH:(Si+C) density/(g·cm−3) all C H Si Si-1.2 1488 645 825 18 1.2 1.19 ± 0.03 0.95 Si-3.8 1418 597 767 54 3.8 1.19 ± 0.03 0.95 Si-6.3 1420 567 763 90 6.3 1.19 ± 0.03 0.98 Si-8.6 1461 548 787 126 8.6 1.19 ± 0.03 1.03 Si-10.6 1524 525 837 162 10.6 1.19 ± 0.03 1.07 H-0.95 1419 613 692 114 8.6 ± 0.4 0.95 1.08 H-1.00 1396 580 698 118 8.6 ± 0.4 1.00 1.04 H-1.07 1402 554 725 123 8.6 ± 0.4 1.07 1.02 H-1.23 1471 534 810 127 8.6 ± 0.4 1.23 1.01 H-1.29 1436 496 808 132 8.6 ± 0.4 1.29 0.97 D-0.79 1108 463 573 72 6.3 ± 0.1 1.10 ± 0.02 0.79 D-0.91 1306 533 693 80 6.3 ± 0.1 1.10 ± 0.02 0.91 D-0.99 1401 580 733 88 6.3 ± 0.1 1.10 ± 0.02 0.99 D-1.09 1538 638 804 96 6.3 ± 0.1 1.10 ± 0.02 1.09 D-1.19 1693 703 886 104 6.3 ± 0.1 1.10 ± 0.02 1.19 -
[1] Robertson J. Diamond-like amorphous carbon[J]. Materials Science and Engineering:R:Reports, 2002, 37(4/6): 129-281. [2] 阳志林, 何智兵, 宋之敏, 等. 反式二丁烯和氢气流量比对辉光放电聚合物热稳定性能的影响[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2010, 22(5):1044-1048 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20102205.1044Yang Zhilin, He Zhibing, Song Zhimin, et al. Influence of T2B/H2 flow ratio on thermal stability of glow discharge polymer prepared by low-pressure plasma chemical vapor deposition[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2010, 22(5): 1044-1048 doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20102205.1044 [3] 李蕊, 何智兵, 何小珊, 等. 射频功率对辉光放电H2/C4H8等离子状态的影响[J]. 物理学报, 2012, 61:215203 doi: 10.7498/aps.61.215203Li Rui, He Zhibing, He Xiaoshan, et al. Influence of radio-frequency power on the state of H2/C4H8 glowing discharge plasma[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2012, 61: 215203 doi: 10.7498/aps.61.215203 [4] 李蕊, 何智兵, 杨向东, 等. 工作压强对射频辉光放电H2/C4H8等离子状态的影响[J]. 物理学报, 2013, 62:058104 doi: 10.7498/aps.62.058104Li Rui, He Zhibing, Yang Xiangdong, et al. Influence of working pressure on the state of H2/C4H8 glowing discharge plasma[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2013, 62: 058104 doi: 10.7498/aps.62.058104 [5] Frolov V D, Zavedeev E V, Pimenov S M, et al. Nanocones on (a-C: H): Si composite films: thermal stability, growth dynamics and electrical properties[J]. Diamond and Related Materials, 2007, 16(4/7): 1218-1221. [6] Li Longqiu, Xu Ming, Song Wenping, et al. The effect of empirical potential functions on modeling of amorphous carbon using molecular dynamics method[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2013, 286: 287-297. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2013.09.073 [7] 张洪亮, 吴卫东, 何智兵, 等. Fe掺杂氢化非晶碳薄膜制备及其热稳定性能[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2008, 20(4):621-624Zhang Hongliang, Wu Weidong, He Zhibing, et al. Preparation and thermal stability of Fe-doped hydrogenated amorphous carbon films[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2008, 20(4): 621-624 [8] Ernst K H, Oral B. On the chemistry at the Si, Ti-doped a-C: H/TiC interface[J]. Thin Solid Films, 2004, 446(1): 72-77. doi: 10.1016/S0040-6090(03)01324-5 [9] Mangolini F, Hilbert J, McClimon J B, et al. Thermally induced structural evolution of silicon- and oxygen-containing hydrogenated amorphous carbon: a combined spectroscopic and molecular dynamics simulation investigation[J]. Langmuir, 2018, 34(9): 2989-2995. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.7b04266 [10] Erdemir A, Donnet C. Tribology of diamond-like carbon films: recent progress and future prospects[J]. Journal of Physics D:Applied Physics, 2006, 39(18): R311-R327. doi: 10.1088/0022-3727/39/18/R01 [11] Ray S C, Bao C W, Tsai H M, et al. Electronic structure and bonding properties of Si-doped hydrogenated amorphous carbon films[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2004, 85(18): 4022-4024. doi: 10.1063/1.1812594 [12] Hoppe M L. Large glass shells from GDP shells[J]. Fusion Technology, 2000, 38(1): 42-45. doi: 10.13182/FST00-A36113 [13] 张颖, 何智兵, 李萍, 等. 硅掺杂辉光放电聚合物薄膜的热稳定性研究[J]. 物理学报, 2011, 60:126501 doi: 10.7498/aps.60.126501Zhang Ying, He Zhibing, Li Ping, et al. Thermal stability of Si-doped glow discharge polymer films[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2011, 60: 126501 doi: 10.7498/aps.60.126501 [14] 张颖, 何智兵, 闫建成, 等. 工作压强对硅掺杂辉光放电聚合物结构和性能的影响[J]. 物理学报, 2011, 60:066803 doi: 10.7498/aps.60.066803Zhang Ying, He Zhibing, Yan Jiancheng, et al. Influence of pressure on structure and properties of Si-doped glow discharge polymer film[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2011, 60: 066803 doi: 10.7498/aps.60.066803 [15] Chouquet C, Gerbaud G, Bardet M, et al. Structural and mechanical properties of a-C: H and Si doped a-C: H thin films grown by LF-PECVD[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2010, 204(9/10): 1339-1346. [16] 何智兵, 阳志林, 闫建成, 等. 辉光放电聚合物结构及力学性质研究[J]. 物理学报, 2011, 60:086803 doi: 10.7498/aps.60.086803He Zhibing, Yang Zhilin, Yan Jiancheng, et al. Structure and mechanical property of glow discharge polymer[J]. Acta physica Sinica, 2011, 60: 086803 doi: 10.7498/aps.60.086803 [17] Bilek M M M, McKenzie D R, McCulloch D G, et al. Ab initio simulation of structure in amorphous hydrogenated carbon[J]. Physical Review B, 2000, 62(5): 3071-3077. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.62.3071 [18] Hamel S, Benedict L X, Celliers P M, et al. Equation of state of CH1.36: first-principles molecular dynamics simulations and shock-and-release wave speed measurements[J]. Physical Review B, 2012, 86: 094113. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.86.094113 [19] De Tomas C, Suarez-Martinez I, Marks N A. Graphitization of amorphous carbons: a comparative study of interatomic potentials[J]. Carbon, 2016, 109: 681-693. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2016.08.024 [20] Hilbert J, Mangolini F, McClimon J B, et al. Si doping enhances the thermal stability of diamond-like carbon through reductions in carbon-carbon bond length disorder[J]. Carbon, 2018, 131: 72-78. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2018.01.081 [21] Chenoweth K, van Duin A C T, Goddard W A. ReaxFF reactive force field for molecular dynamics simulations of hydrocarbon oxidation[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 2008, 112(5): 1040-1053. doi: 10.1021/jp709896w [22] van Duin A C T, Dasgupta S, Lorant F, et al. ReaxFF: a reactive force field for hydrocarbons[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 2001, 105(41): 9396-9409. doi: 10.1021/jp004368u [23] Senftle T P, Hong S, Islam M M, et al. The ReaxFF reactive force-field: development, applications and future directions[J]. npj Computational Materials, 2016, 2: 15011. doi: 10.1038/npjcompumats.2015.11 [24] Liu Qingkang, Ssong Wenping, Huang Qitao, et al. ReaxFF reactive molecular dynamics simulation of the oxidation of silicon-doped amorphous carbon film in heat-assisted magnetic recording[J]. Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica, 2017, 33(12): 2472-2479. [25] 唐钰杰, 郑默, 任春醒, 等. ReaxFF MD局部区域反应追踪与物理性质可视化分析[J]. 物理化学学报, 2021, 37:2003037Tang Yujie, Zheng Mo, Ren Chunxing, et al. Visualized reaction tracking and physical property analysis for a picked 3D area in a reactive molecular dynamics simulation system[J]. Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica, 2021, 37: 2003037 [26] Thompson A P, Aktulga H M, Berger R, et al. LAMMPS - a flexible simulation tool for particle-based materials modeling at the atomic, meso, and continuum scales[J]. Computer Physics Communications, 2022, 271: 108171. doi: 10.1016/j.cpc.2021.108171 [27] Aktulga H M, Fogarty J C, Pandit S A, et al. Parallel reactive molecular dynamics: numerical methods and algorithmic techniques[J]. Parallel Computing, 2012, 38(4/5): 245-259. [28] Newsome D A, Sengupta D, Foroutan H, et al. Oxidation of silicon carbide by O2 and H2O: a ReaxFF reactive molecular dynamics study, part I[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2012, 116(30): 16111-16121. doi: 10.1021/jp306391p [29] 高巍, 朱嘉琦, 牛丽, 等. 非晶碳结构建模和电子结构的第一性原理研究[J]. 物理学报, 2008, 57(1):398-404 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3290.2008.01.062Gao Wei, Zhu Jiaqi, Niu Li, et al. et al. Ab initio structural simulation and electronic structure of amorphous carbon[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2008, 57(1): 398-404 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3290.2008.01.062 [30] Martínez L, Andrade R, Birgin E G, et al. PACKMOL: a package for building initial configurations for molecular dynamics simulations[J]. Journal of Computational Chemistry, 2009, 30(13): 2157-2164. doi: 10.1002/jcc.21224 [31] Suter U W, Eichinger B E. Estimating elastic constants by averaging over simulated structures[J]. Polymer, 2002, 43(2): 575-582. doi: 10.1016/S1089-3156(01)00007-1 [32] Ai Xing, Chen Guo, Zhang Ling, et al. The radial distribution of ions and electrons in RF inductively coupled H2/T2B plasmas[J]. Plasma Chemistry and Plasma Processing, 2018, 38(1): 281-292. doi: 10.1007/s11090-017-9858-y -




 下载:
下载: