High voltage damped oscillator based on interstage self-triggering Marx circuit
-
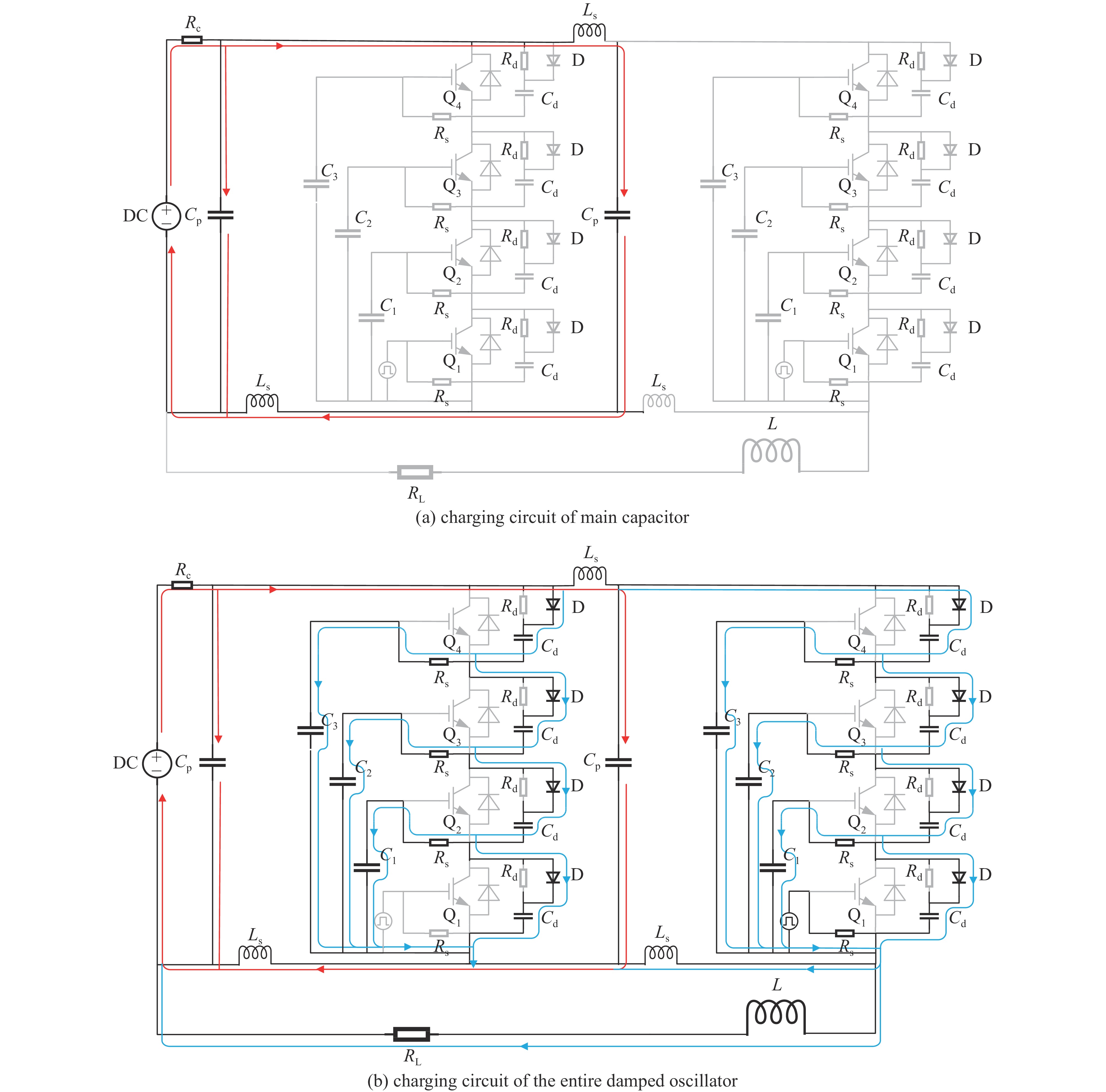
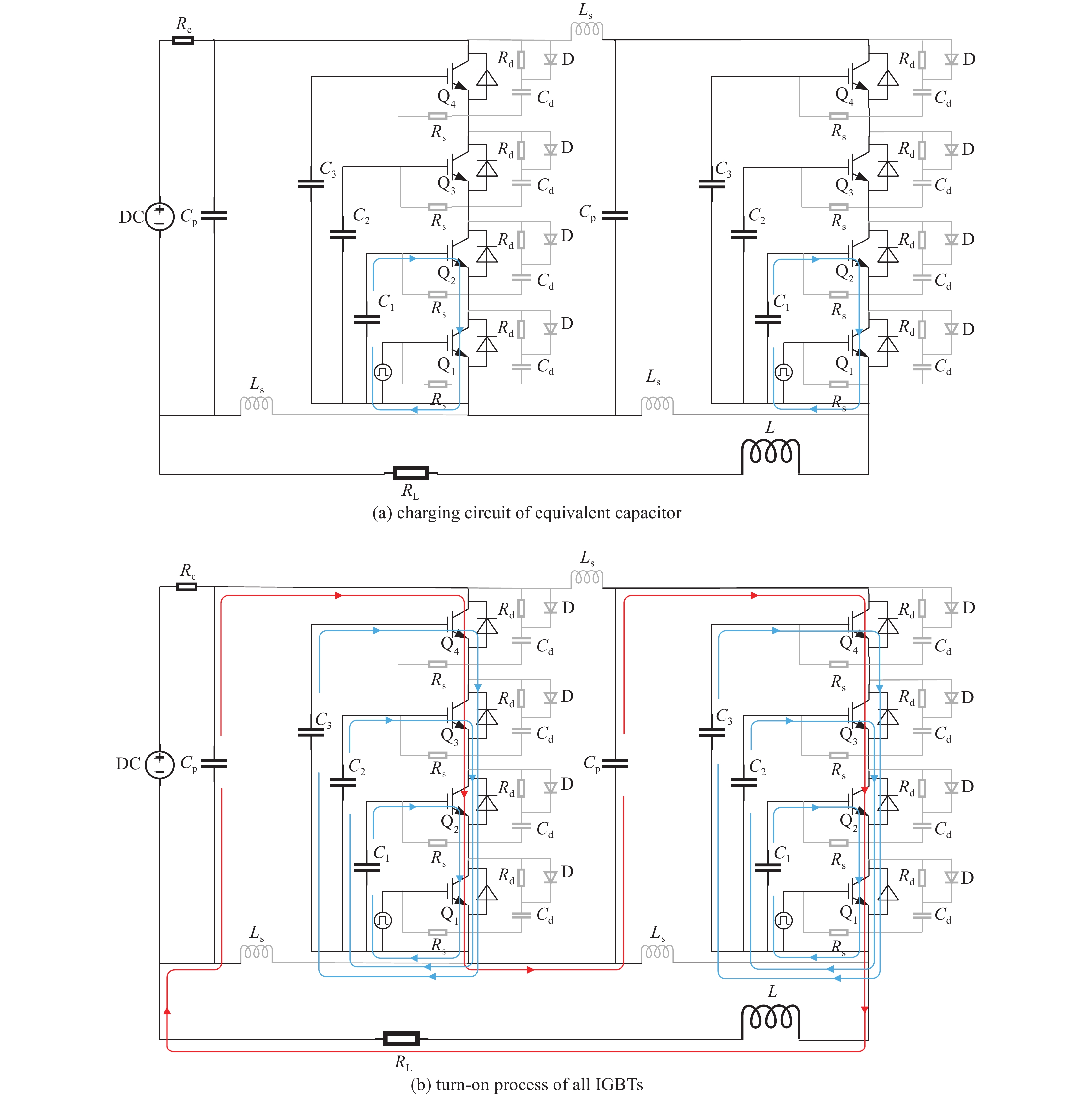
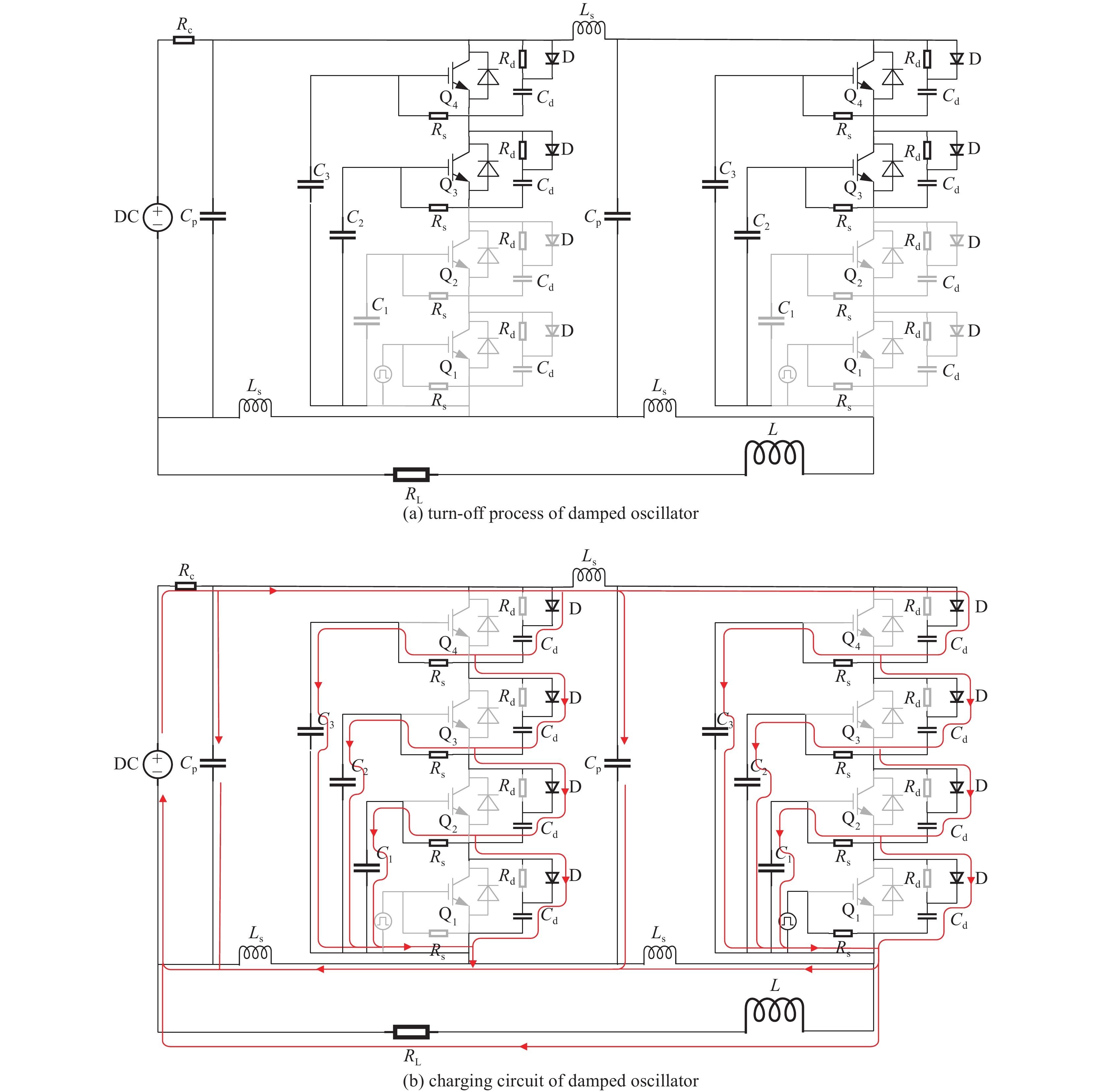
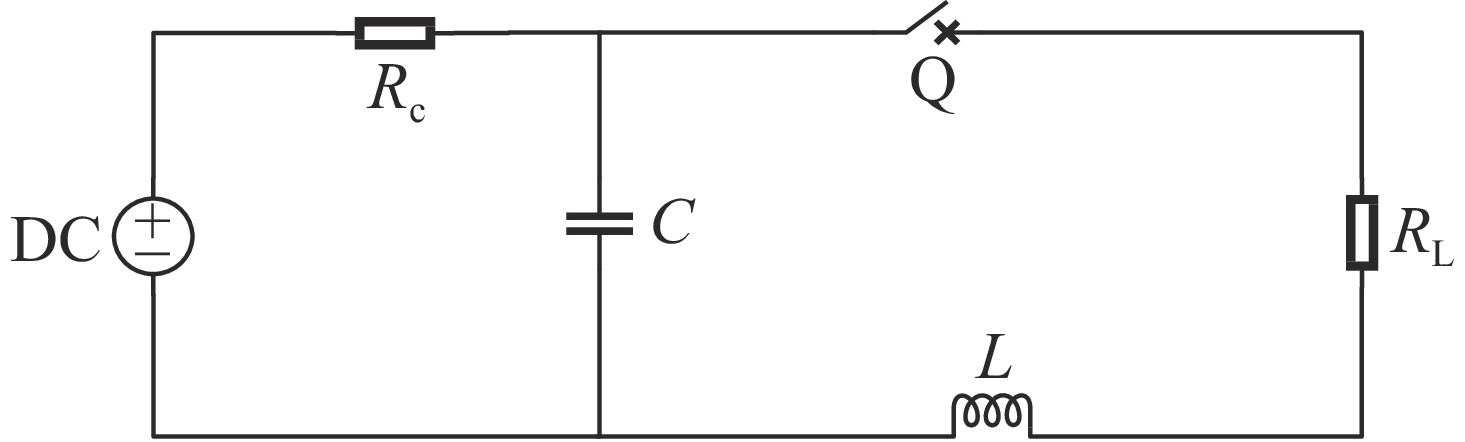
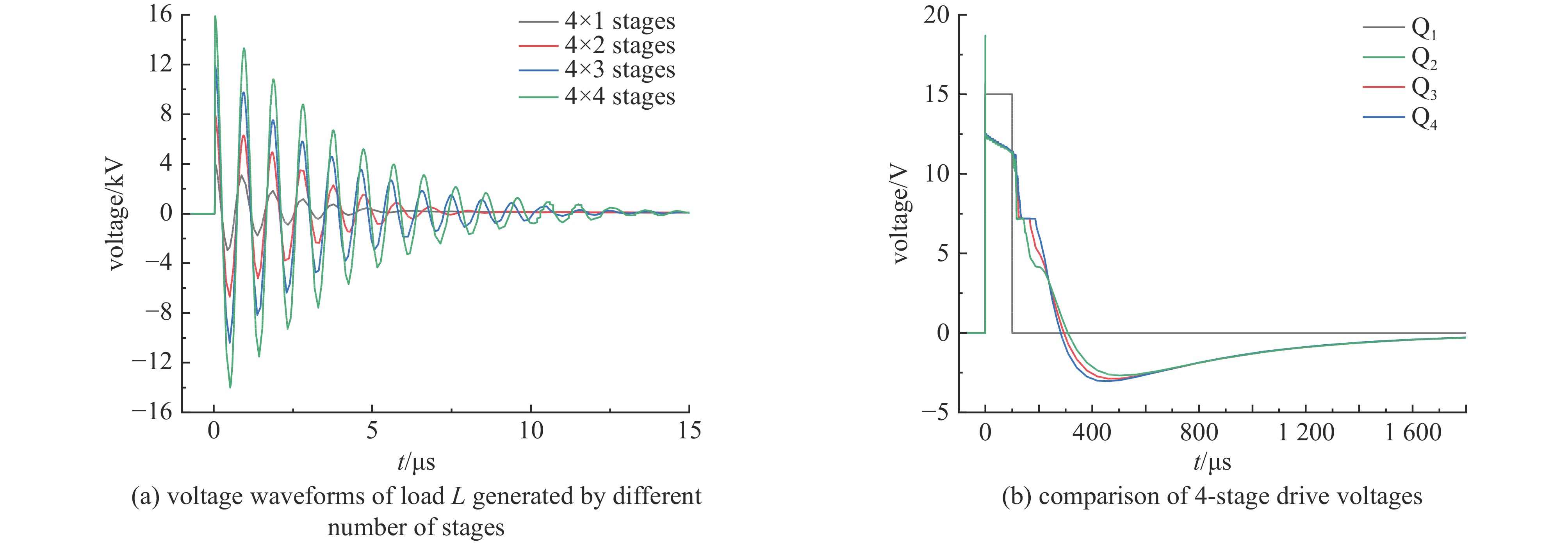
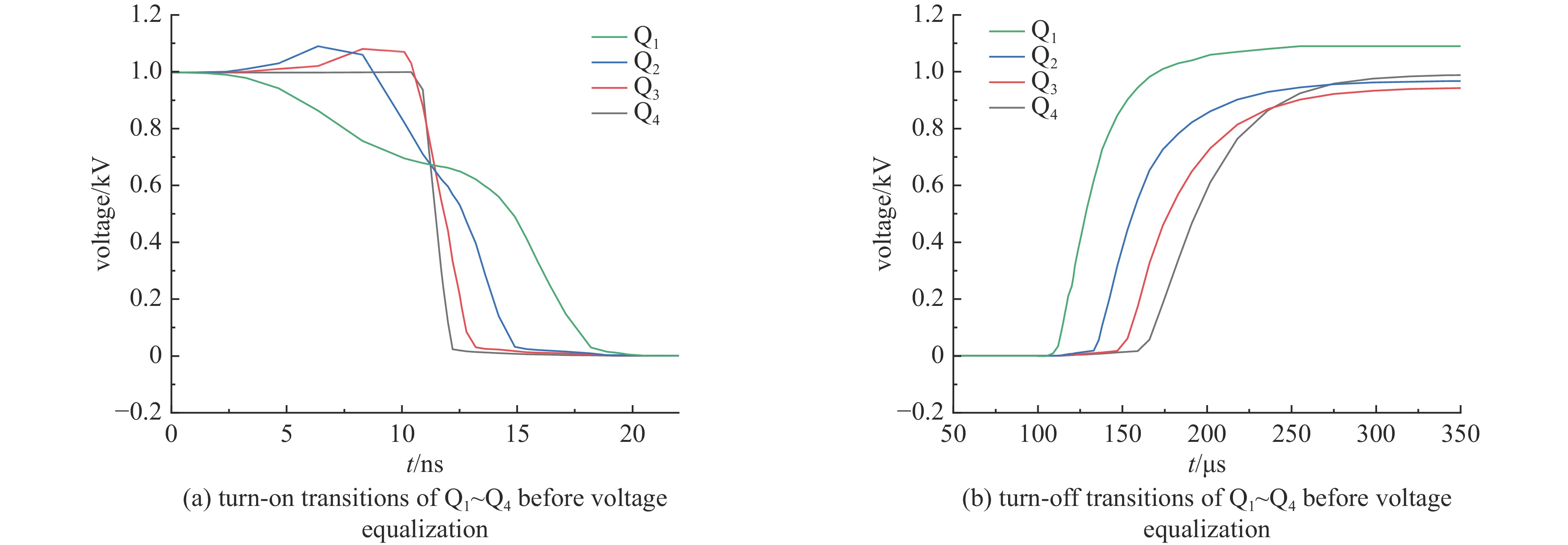
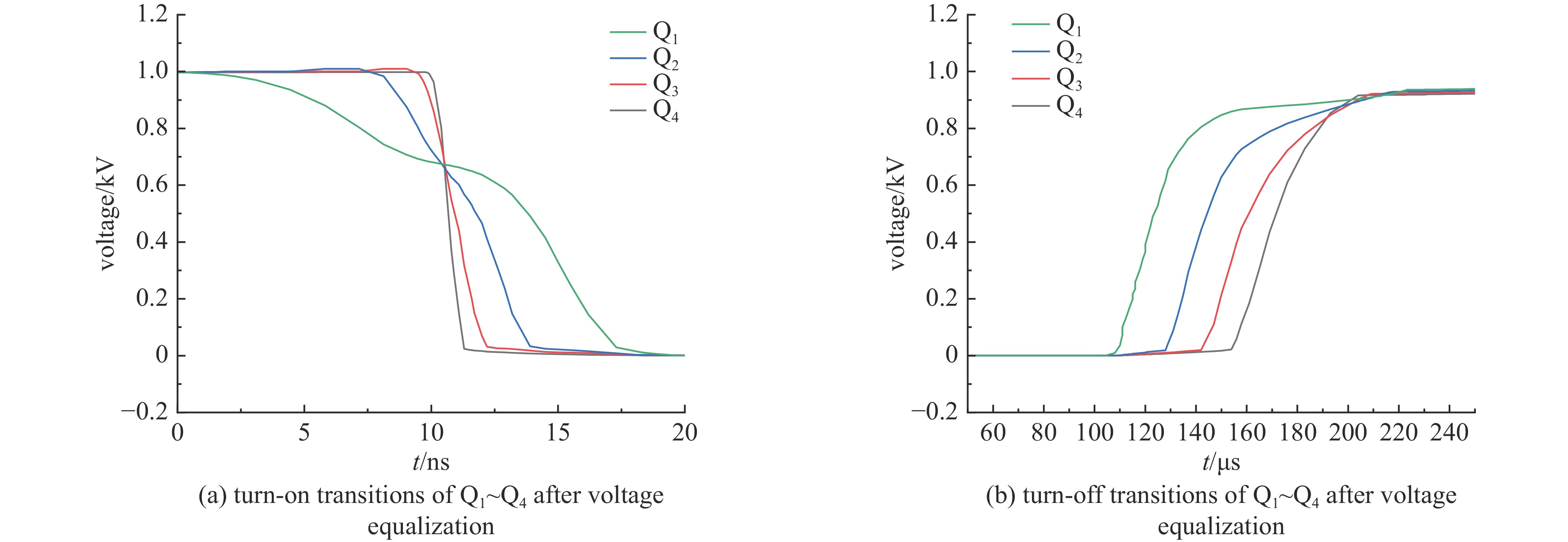
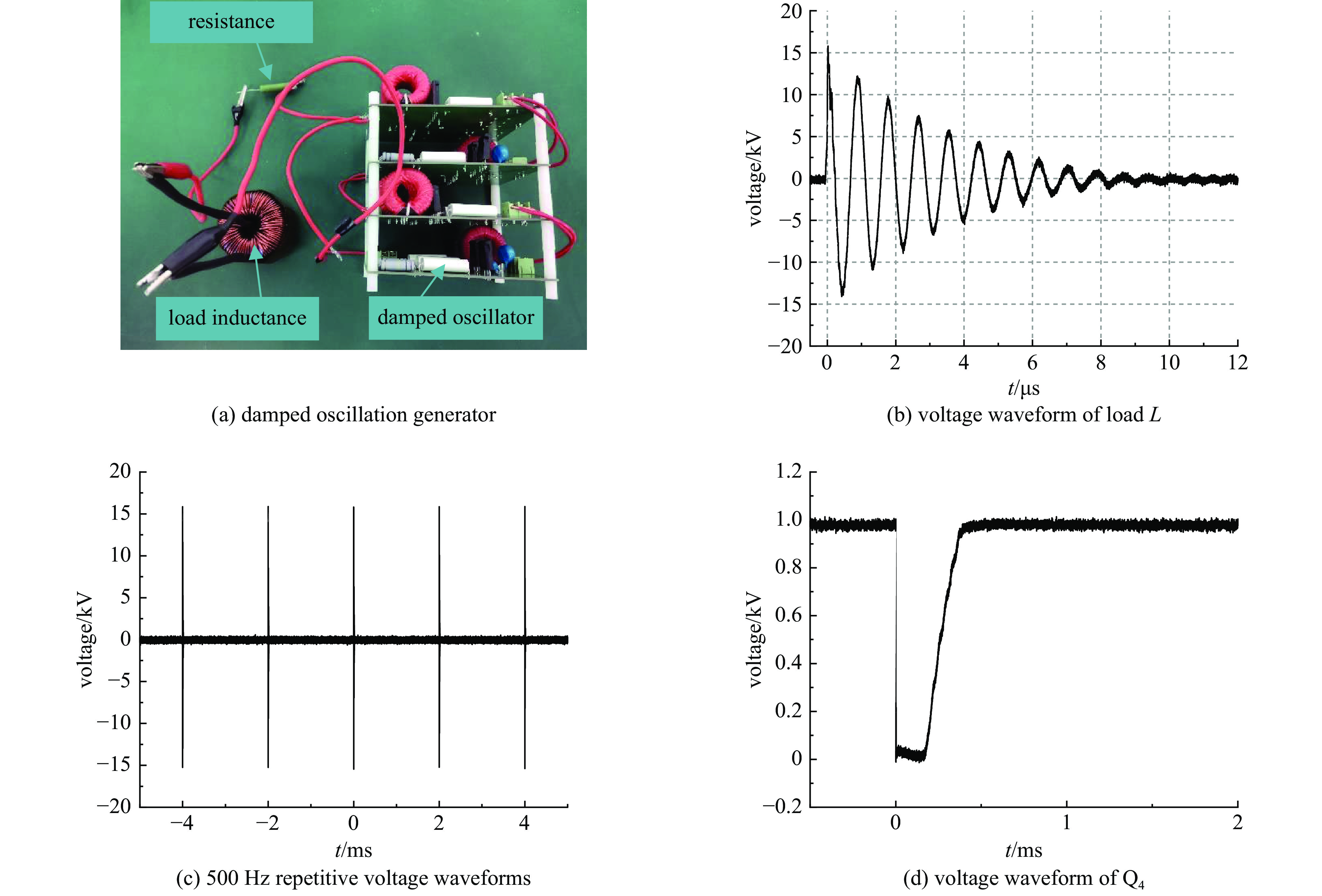
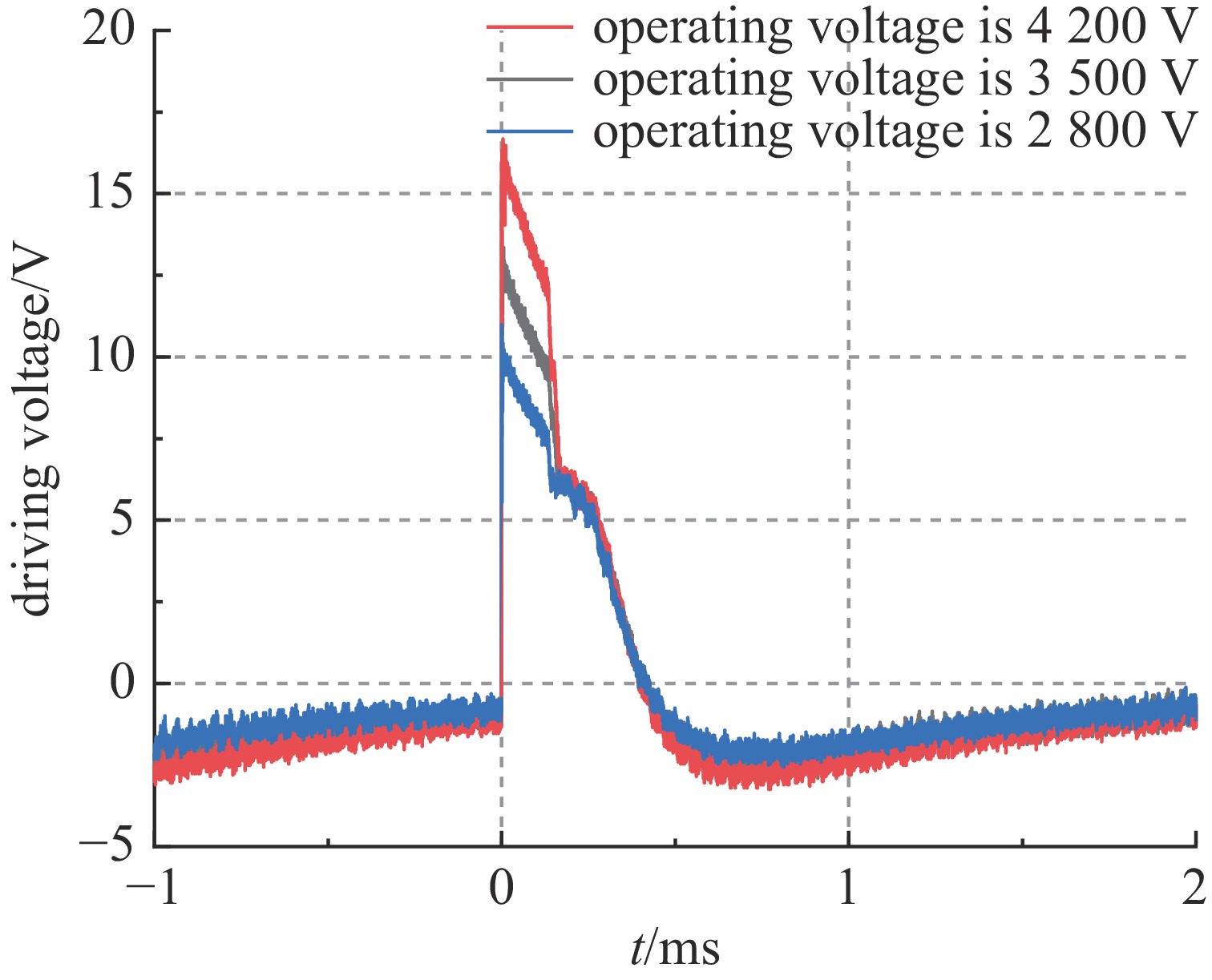
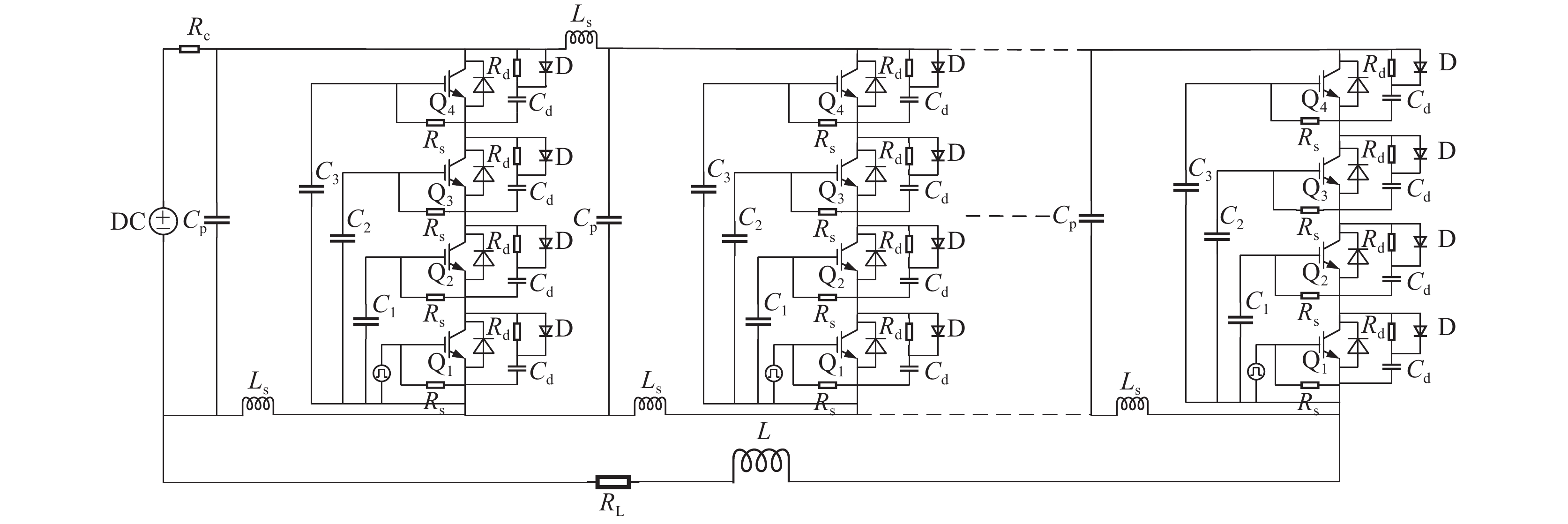
摘要: 为了增大输出电压的同时减小高压阻尼振荡发生器的体积和降低其成本,建立了一种4×4级间自触发Marx结构的阻尼振荡发生器模型。该模型每级的主开关采用基于电容触发方式的串联IGBT模块,只需提供一路隔离信号控制一级放电开关管的导通和关断,通过级间电容实现对相邻级放电管的栅极自动充电和放电,使其导通和关断。该模型提高了Marx单级的工作电压和简化了每级的驱动电路,并且通过加入缓冲电路,解决开关管动态、静态均压问题。基于这种拓扑结构搭建了一台高压阻尼振荡发生器样机,在电感负载上输出16 kV、振荡频率1 MHz的阻尼振荡波形,波形上升时间约为75 ns,重复频率500 Hz。样机体积小巧、工作稳定,验证了该方案的可行性。Abstract: To increase the output voltage and reduce the volume and cost of the high voltage damped oscillator, a 4×4 stage self-triggering Marx structure damped oscillator model is established in this paper. In this model, the main switch of each stage adopts series IGBTs module based on capacitor trigger mode. Only one isolated signal is provided to control the turn-on and turn-off of the primary discharge switch tube. The grid of the adjacent discharge tube is automatically charged and discharged through the interstage capacitance to make it turn-on and turn-off. The model improves the working voltage of Marx single stage and simplifies the driving circuit of each stage, and solves the problem of dynamic and static voltage equalization of switching tube by adding buffer circuit. Based on this topology, a prototype of a high-voltage damped oscillator is built, which outputs 16 kV damped oscillation waveform with a frequency of 1 MHz on an inductive load. The rise time of the waveform is about 75 ns, and the repetition frequency is 500 Hz. The prototype is small in size and stable in operation, which verifies the feasibility of the scheme.
-
Key words:
- self-triggering /
- series IGBT /
- Marx circuit /
- damped oscillation generator /
- high voltage
-
表 1 电路参数
Table 1. Circuit parameters
input DC
voltage/Vsignal
width/μsstorage capacitance
of Cp/nFgate parallel
resisitance Rs/kΩisolation
inductance Ls/μHequalizing
resistance Rd/kΩbuffer capacitance
Cd/μFresistance
of load/Ωinductance
of load/μH4200 100 1.5 10 100 100 0.1 20 60 -
[1] 陈连明. 基于阻尼振荡电压的直流电缆典型缺陷局部放电检测[D]. 北京: 华北电力大学, 2021: 4-10Chen Lianming. Partial discharge detection of typical defects for DC cables based on damped AC voltage[D]. Beijing: North China Electric Power University, 2021: 4-10 [2] Takahashi T, Takahashi T, Okamoto T. Insulation diagnosis for XLPE cables using damping oscillating high voltage[C]//2008 Annual Report Conference on Electrical Insulation and Dielectric Phenomena. 2008: 471-474. [3] GB/T 17626.18-2016, 电磁兼容 试验和测量技术 阻尼振荡波抗扰度试验[S]GB/T 17626.18-2016, Electromagnetic compatibility—Testing and measurement techniques—Damped oscillatory wave immunity test[S] [4] 陆征军, 李超群, 李燕, 等. 就地安装的智能电子设备的电磁兼容问题[J]. 高压电器, 2013, 49(7):92-95Lu Zhengjun, Li Chaoqun, Li Yan, et al. EMC issues of IEDs installed locally[J]. High Voltage Electrical Apparatus, 2013, 49(7): 92-95 [5] 李祥超, 周中山, 陈璞阳, 等. 雷电阻尼振荡波发生器的设计方法[J]. 电瓷避雷器, 2015(2):99-104Li Xiangchao, Zhou Zhongshan, Chen Puyang, et al. Design method of lightning damped oscillatory wave generator[J]. Insulators and Surge Arresters, 2015(2): 99-104 [6] 嵇建飞, 袁宇波, 庞福滨. 智能变电站就地智能设备电磁兼容抗扰度实验分析[J]. 电工技术学报, 2014, 29(S1):454-462Ji Jianfei, Yuan Yubo, Pang Fubin. Experimental analysis of EMC immunity for field installed intelligent equipment of intelligent substation[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2014, 29(S1): 454-462 [7] 李振华, 胡蔚中, 闫苏红, 等. 隔离开关开合下电子式互感器传导干扰分析及抗干扰方法[J]. 高电压技术, 2016, 42(1):233-240Li Zhenhua, Hu Weizhong, Yan Suhong, et al. Conductive interference analysis and anti-interference methods of electronic transformers in disconnector switching test[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2016, 42(1): 233-240 [8] 胡逸帆. 配电开关柜开关操作对二次设备电磁骚扰的研究[D]. 北京: 华北电力大学, 2019: 21-27Hu Yifan. Study of the electromagnetic disturbance caused by the switching operation of the distribution switchgear on the secondary equipment(s)[D]. Beijing: North China Electric Power University, 2019: 21-27 [9] 张志华, 宋光达, 甄建辉, 等. 配电网一二次融合开关传导电磁干扰试验方法研究[J]. 高压电器, 2021, 57(8):69-77Zhang Zhihua, Song Guangda, Zhen Jianhui, et al. Study on conduction electromagnetic interference test method for primary and secondary fusion switch in distribution network[J]. High Voltage Apparatus, 2021, 57(8): 69-77 [10] Kando M. A high voltage damped oscillating wave generator[C]//2004 IEEE Region 10 Conference TENCON 2004. 2004: 124-127. [11] Liang Jianfeng, Zhang Liang, Li Junhao, et al. Study on oscillating switching impulse voltage generation for power transformer onsite test[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery, 2014, 29(5): 2223-2230. doi: 10.1109/TPWRD.2014.2308542 [12] 陈鹏, 陶智. 间接雷电效应测试用快速衰减振荡波发生器研制[J]. 高电压技术, 2017, 43(5):1425-1431Chen Peng, Tao Zhi. Development of fast damped oscillatory wave generators for indirect lighting effects test[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2017, 43(5): 1425-1431 [13] 李婧, 黄晨曦, 郭金明, 等. 30kV阻尼交流振荡波测试系统用新型电力电子开关的研制[J]. 电气技术, 2015(12):42-46Li Jing, Huang Chenxi, Guo Jinming, et al. Development of a novel 30kV semiconductor switch for damped oscillating voltage testing system[J]. Electrical Engineering, 2015(12): 42-46 [14] Zeng Weirong, Yao Chenguo, Dong Shoulong, et al. Self-triggering high-frequency nanosecond pulse generator[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2020, 35(8): 8002-8012. doi: 10.1109/TPEL.2020.2967183 [15] Pang Lei, Long Tianjun, He Kun, et al. A compact series-connected SiC MOSFETs module and its application in high voltage nanosecond pulse generator[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2019, 66(12): 9238-9247. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2019.2891441 -




 下载:
下载: